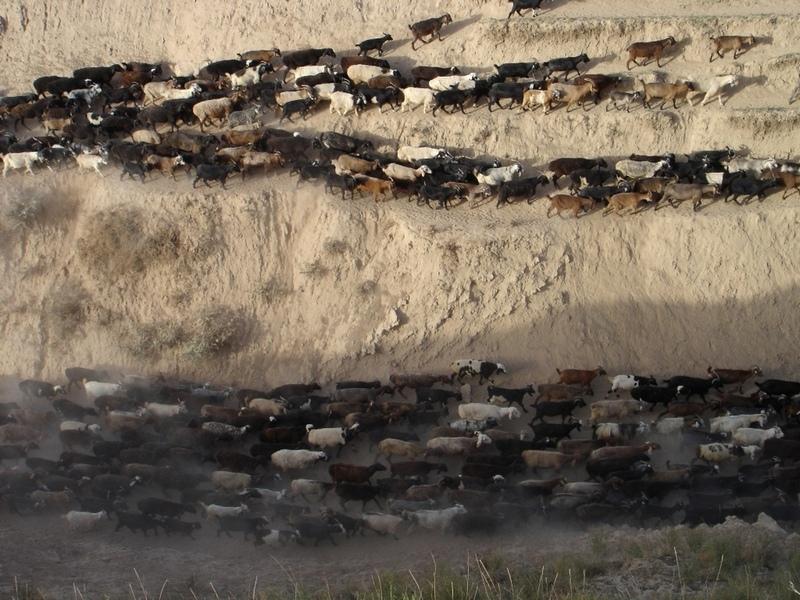
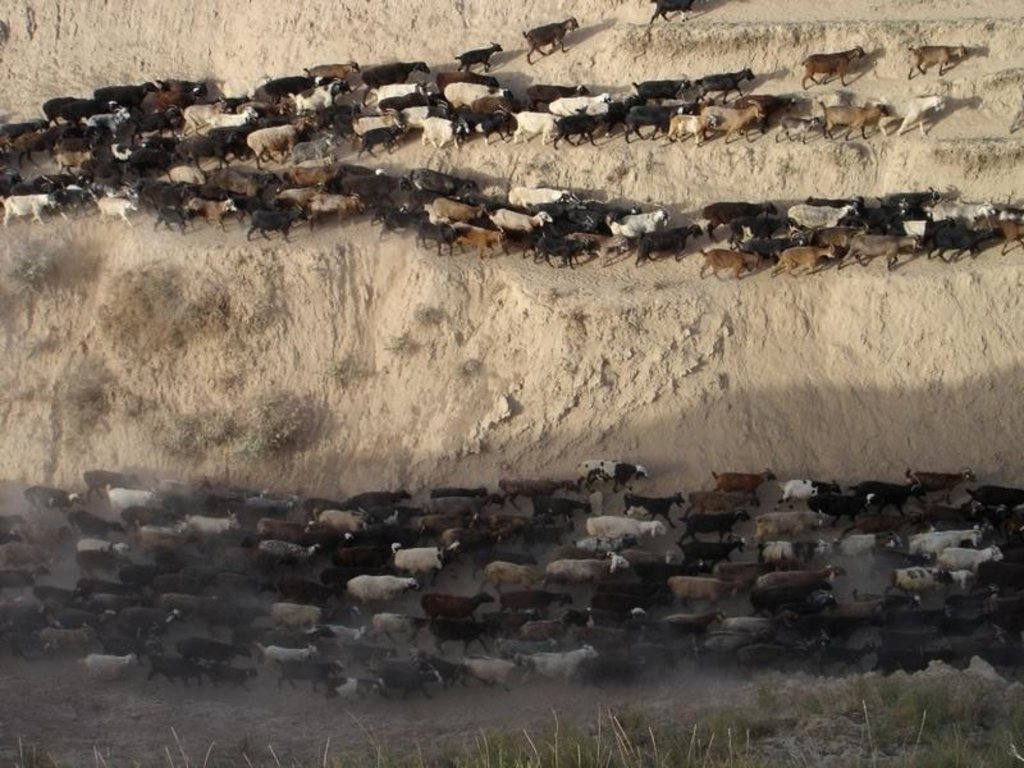
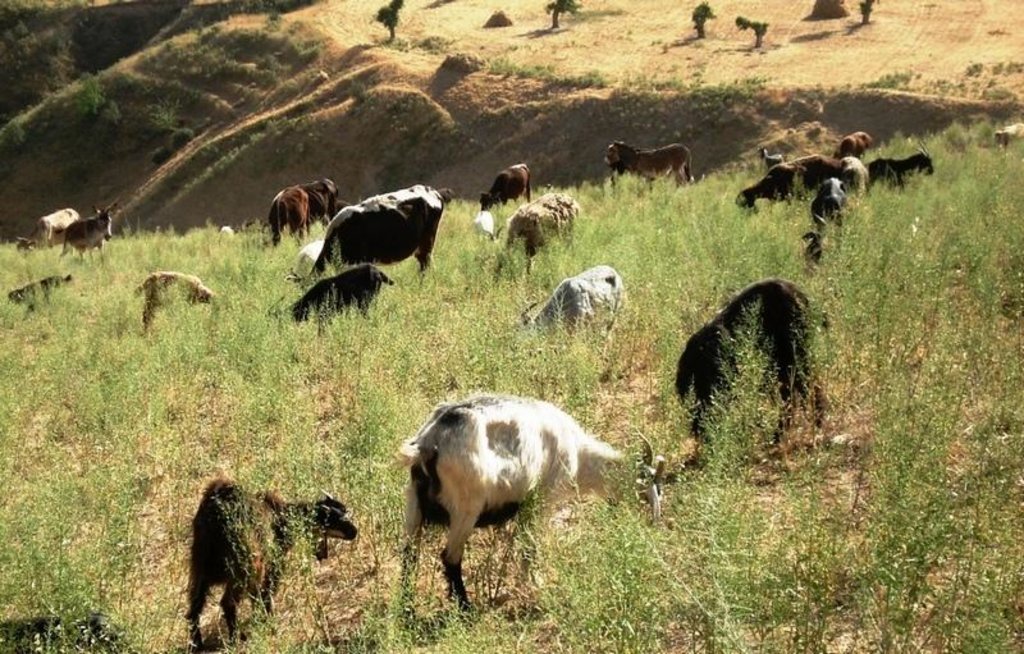
Daily grazing of village-herds [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Charogo bistumi (pasture for everyone)
technologies_1408 - Тажикистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Киргизстан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/08/2008
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл
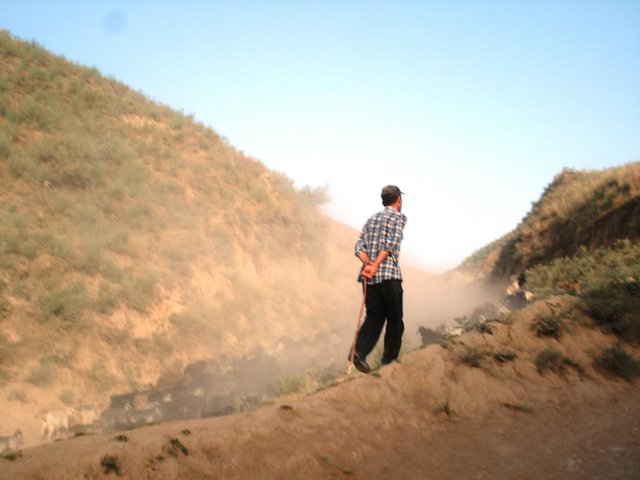

Common village herding [Тажикистан]
Village herding system with daily alternation of the herders including each household in a monthly turnus.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Rotational grazing on village pastures with heavy pressure with daily to weekly change of grazing places.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
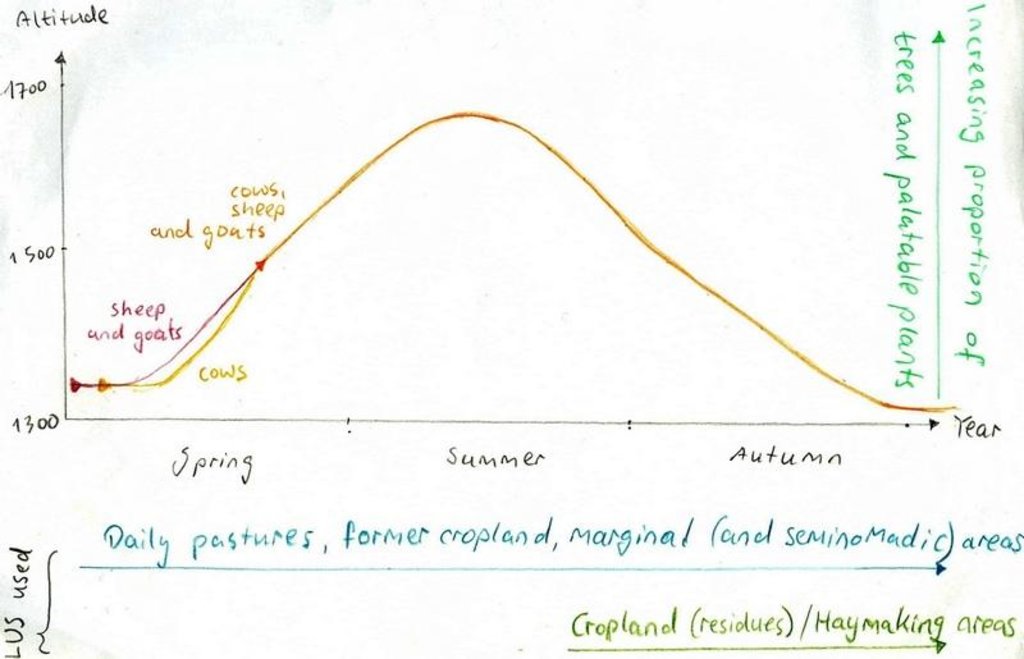
The herding season is from the beginnning of March to the End of Octobre or even beginning of Decembre. Total area is between 10-20 km2, depending on how strictly the borders are understood. Cows, sheep, goats and donkeys compose the herds. Grazing begins when soil moisture begins to decreaset, first with the little animals, that are supposed to better cope with slippery conditions. After two weeks the cows are led to the pastures and in some cases they will be grazed alone, because sheep and goats disturb them. The grazing zone is situated between 1400 and 1700 m. Rotation begins on the lower pastures, at the beginning of summer the higher pastures are used and towards autumn the animals graze near the villages again, sometimes on cropland, feeding on crop residues. The herders are advised to change place after 2-3 days, but often stay in one place for a longer time. The animals are gathered on the way out of the village a little after dawn, than brought to the pastures. At noon-time they will be lead to a shady place close to a stream, if possible. The same places are visited three or more times per season.
Purpose of the Technology: The animals should be nourished and the cows should give milk. A land user kept his cow at home towards the end of summer, because it stopped giving milk, from the sparse and dry vegetation on the pastures.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The costs for this form of herding are lost days at school for the children. It largely works without external inputs (such as fertilisers). Other inputs such as salt for the animals are covered by the landowner.
Natural / human environment: These pasture-areas are heaviliy suffering from overuse on one hand and from droughts on the other side. They are in a generally well-conserved state. Fractional vegetation cover is low, especially tree cover, and the proportion non-palatable species relatively high. Erosion by water, including gullies, and crusting, are common phenomena, especially in low cover areas.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Region of Republican Subordination
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Already before the USSR the villages used to have their hamlets and grazed them around the villages, but also in the formerly not very populated plains. By the settlement of people in the plains and population growth from the 1970ies onward livestock numbers and pressure on natural resources started to increase there. And through Soviet collective agriculture people were forced to keep livestock close to the villages, as a consequence of their employment. In addition, grazing on the territory of forest administration, founded in the 1960ies, was forbidden for the villagers.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуйн газар:
- Ранч
Голлох малын төрөл ба бүтээгдэхүүн:
sheep and goats / cows and donkeys.
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soils are heavily degraded in the sense of generally high levels of compaction and crusting and low organic matter contents. Vegetation is especially reduced in cover, not necessarily in biomass and, the fraction of good pasture species is low.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Many trees have been cut down during civil war and till today, leaving back a soil without protection. Animals grazing on these pastures are not fat, often sick and cows give little and sometimes (in summer) no milk. An often mentioned problem is the situation of drought in 2008 and animals staying in one place for longer periods, which leads to degradation of vegetation.
Ranching: sheep and goats / cows and donkeys.
Grazingland comments: In spring sheep and goats are herded before cows, then in a separate herd and toward the end of the season, together.
Type of grazing system comments: In spring sheep and goats are herded before cows, then in a separate herd and toward the end of the season, together.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jul
Малын нягт (шаардлагатай бол):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 10-100 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15 m2.
For some villages figures are available, for instance for Karsang: This village has alltogether 850 ha of common grazing land, for officially 212 cows and 775 little animals. For the whole Jamoat the figures are of around 2500 ha of pasture-land (not all in the study-area) for 2695 cows and 5950 little animals.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wm: Хөрсний нуралт, шилжилт

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Big livestock numbers on little surface.), poverty / wealth (People depend on livestock and on cheap pastures.)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Many people mention that rainfalls were much lower in 2007-2008 than normally.), population pressure (Especially from the 1970ies onward population increased rapidly.), land tenure (As long as no-one is really responsible for the are, conservation measures are difficult to implement.), war and conflicts (Civil war was detrimental to the (little) economic, non-agricultural sector (textiles, car-parts) and to the institutions, so that many people had to return to agricultural activities.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Rotation of the village herds.
Location: Karsang and other villages. Faizabad
Date: 20.08.09
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The practiced rotation follows the humour of the herders (often children) and is not complicated.)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of biomass (quantity)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: The begin of grazing and the rotation is fixed by a village committee. Animals should not stay at one place for longer than 3 days.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Somoni
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
3.42
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Villagers buy animals, usually 6-10 goats and / or sheep, 1-2 cows and / or donkeys. | Менежментийн | Constantly size is regulated. |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Бусад | buy the animals | per year | 1.0 | 1170.0 | 1170.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1170.0 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Per capita fee taxes | Менежментийн | Once per year. |
| 2. | Buying concentrated feed, depending on the financial resources of the land user. | Менежментийн | Bought once per year, for winter period. |
| 3. | Haymaking and / or buying, depending on labour, financial resources and livestock numbers. | Менежментийн | June-July, respectively later, if bought. |
| 4. | Medecine and salt for animals | Менежментийн | Irregularly, resp. daily to weekly. |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Бусад | Per capita fee taxes | per year | 12.0 | 1.0 | 12.0 | |
| Бусад | Buying concentrated feed | kg | 425.0 | 0.53 | 225.25 | |
| Бусад | Medecine and salt for the animals | for all animals | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 282.25 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The calculated costs apply to each land user's cost for this herding system.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The most important cost factor is buying livestock. Recurrent costs are low, but rent fees for pastures are percieved as being high.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altidudinal zone: Most pastures are close to the villages, on around 1300-1500 m, but some pastures reach altitudes of 1600-1700 m.
Landforms: The pasture-areas usually follow N-S-ridges and most pastures are in slope-areas.
Slopes on average: Also hilly
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture (topsoil): Loess soils
Soil fertility low: In most places high proportions of non-graminoids and leguminous species.
Topsoil organic matter: High proportion of hot-spots and degrading areas according to Wolfgramm's (2007) hot-brightspot-map.
Soil drainage / infiltration poor: Most soils are crusted and compacted.
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: Often no groundwater, because too hilly
Availability of surface water: Most areas far from open water bodies
Water quality (untreated): No pesticides, but water is contaminated by animal dung.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
In comparison with other areas.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Many children are working as herders, because of labour shortage (young men in Russia).
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are rich (People who have a house made of concrete or with a ribbed roof instead of one made of cement asbesto).
70% of the land users are average wealthy (Compared to the rest of society: People have enough food, children go to school, they have a mud-hou).
Off-farm income specification: Nearly all people have family members (mostly sons) in Russia, who send remittances.
Market orientation of production system subsistence (self-supply): Animals are mainly used for own consumption (meat and milk).
Market orientation of production system commercial / market: Animals are sold, if the family needs money (for medecine or education).
So, it is still better from their perspective to have animals ("as a bank", according to many villagers), than not having this security. And it is comparatively cheap, even if a land user admits that he has to feed his cow with leaves of his muleberry trees, because pastures are so unproductive, that his cow does not give milk anymore (in August).
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology 2-5 ha: This corresponds to the average for the whole study-area, including haymaking areas.
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology 5-15 ha: Households having a farmer's association mostly have more than the average.
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology 15-50 ha: Some rich families even have more land that they rent to others.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
Pasture-use is theoretically regulated as described above, but additionally to the village herd there are other herders with private animals using the same pastures.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Compared with all other areas the proportion of forbs is very high.
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Compared with an efficient grazing rotation, returns (in terms of milk and meat) are very low.
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Very little trees are left because of goats eating them.
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
During war most people depended on cropland (wheat).
Орлого, зарлага
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
This system does not depend on professional herders, is thus economic, also in financial terms.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
It is better for land users to have communal pastures but worse than having a well-implemented rotational grazing system, but the family does not have to buy meat.
олон нийтийн институц
Livelihoods and human well-being
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially trampling paths of livestock are very vulnerable to water erosion
Хөрс
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The degree of compaction is higher than elsewhere.
хөрс нягтрах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The degree of compaction is higher than elsewhere.
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Organic matter is very low compared with all other areas. Biomass might be stonger reduced with animals grazing earlier in spring.
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Тайлбар:
Pasture areas, that remain the same since the USSR, could be changed every few years to permit their recovery and regrowth of trees, chopped during and after civil war. The very basic rotational schemes existing in all villages are little effective. It is not possible to recognise conservation effects due to the generally very critical state of resources.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Тайлбар:
The land users see the problem of reduced productivity when pastures are overexploited. They complain about having to sell animals, but mainly attribute this to droughts.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
NA
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 90-100 %
Тайлбар:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: No subsidies have been paid for buying livestock. But, as people highly depend on remittances, it can be assumed that these have also been invested into livestock.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Young families who do not yet have livestock are thinking of buying animals in the future. On the other hand herding in the upper areas still has potential and wealthy people might want to send their animals there with professional herders in the future.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Animal husbandry is an economic basis which permits development. How can they be sustained / enhanced? People should be allowed to keep as much animals as they want to. And the pasture-area should not become smaller. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
It is the most cheap form of self-sufficient meat-production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Pasture-quality needs to be preserved, otherwise the carrying-capacity of pastures will be reduced. |
|
Livestock with its semimonetary value is much more stable in value than money on the bank (increasing livestock prices). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Only if alternatives for animal husbandry emerge will the prices for livestock not fall. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Animals and pastures are less productive (reduced biomass) and pastures show more signs of erosion than those on forest department. There, pasture-areas are bigger and, by consequence, there is more space for herding. | If there were not always more people affording to rent land for orchards or haymaking the pressure on the remaining pastures would not increase. |
| The pastures very much depend on enough water: If there is little rain (like in 2008) animals return hungry from the pastures. | There is hope that the planned water pipe from Rogun (planned giant dam) will bring water for irrigation (of cropland, where animals graze in late summer and where forbs are collected as winter fodder). |
| Rent fees have to be paid, which are percieved as high by some land users. They fear additional per-capita animal taxes. | No more taxes should be introduced and herding should not be stronger regulated, because many people depend on animal husbandry. |
| This herding system is vulnerable to droughts and temperature increase, which are percieved as main degradation causes. Besides this, excessive livestock numbers are seen as a cause of cover reduction and compaction. Especially where animals graze the soil is naked and dry after 2-3 days. | It might be helpful to let the pastures recover for 3-5 years for trees (which bring moisture) to grow. But this might require administration through external institutions and people fear that they will not get back the pastures. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Degradation of soils and vegetation on these relatively small areas is high and the pastures cannot recuperate due to constant pressure. | The pastures need to have periods of recovery. |
| The soils are decreasing in fertility because animal dung is used as energy source. | A not too expensive alternative for hot water might be solar heaters or charcoal. And to counteract general fertility problems interchanging pasture- and haymaking areas would bring dung everywhere. But this would require fencing of the remaining trees in order not to further damage vegetation cover. |
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Common village herding [Тажикистан]
Village herding system with daily alternation of the herders including each household in a monthly turnus.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна