Polypit nursery [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Madhav Dhakal
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Plastic-Khalte nursery - Nepali
technologies_1498 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
15/11/2006
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
A simple, inexpensive and practical method for raising healthy plant seedlings
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
During the winter in Nepal’s middle mountains, the soil temperature generally remains at 5-10 degree celsius above the ambient air temperature. This principle was used to design a simple, inexpensive, and effective nursery technology for raising vegetable and horticulture seedlings in colder regions. The polypit technology allows seedlings to be raised by protecting them from the freezing temperatures that occur mostly
at night.
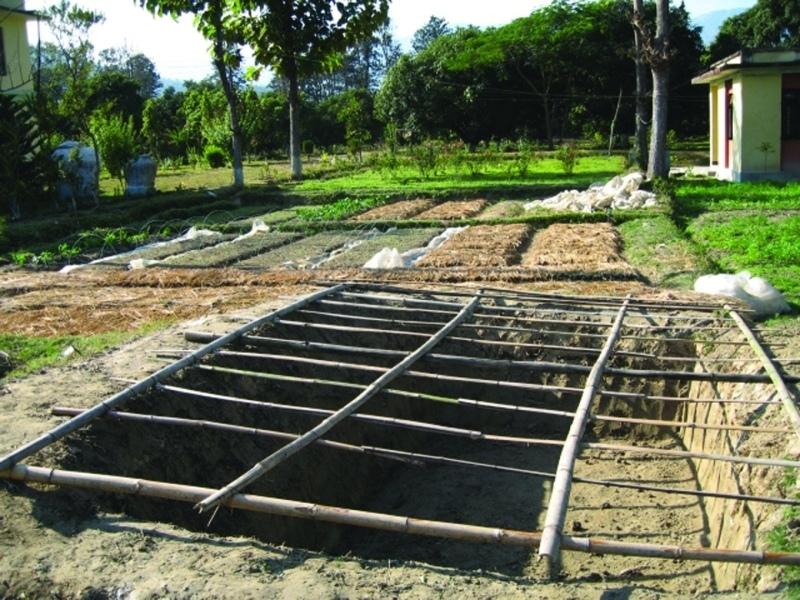
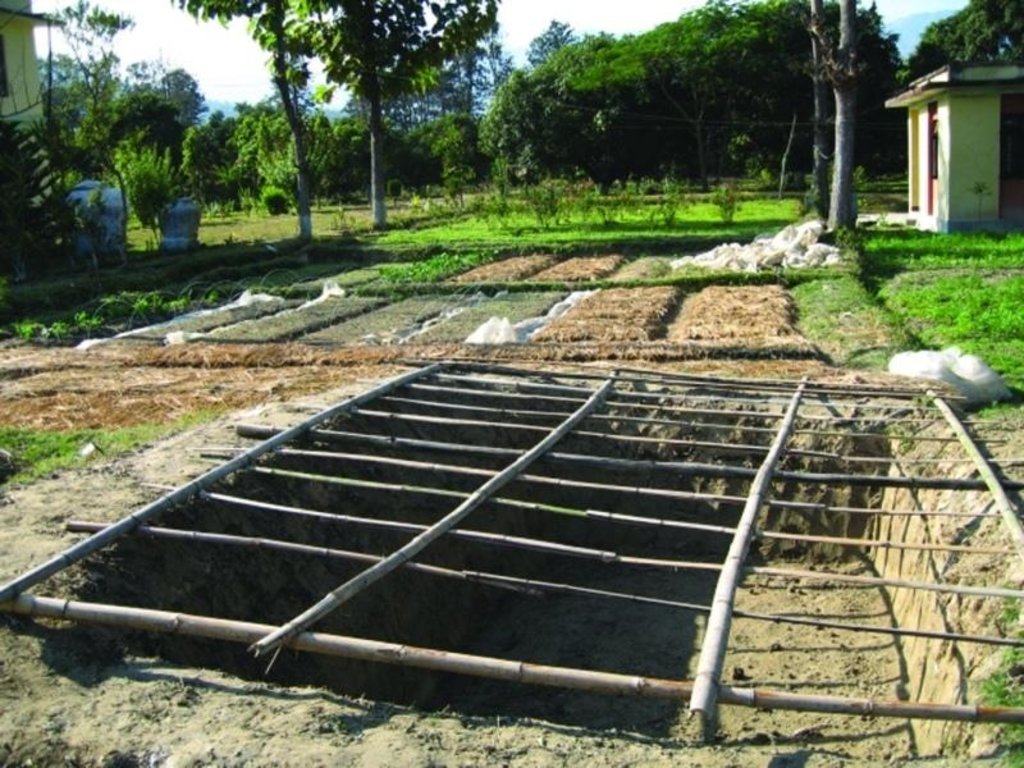
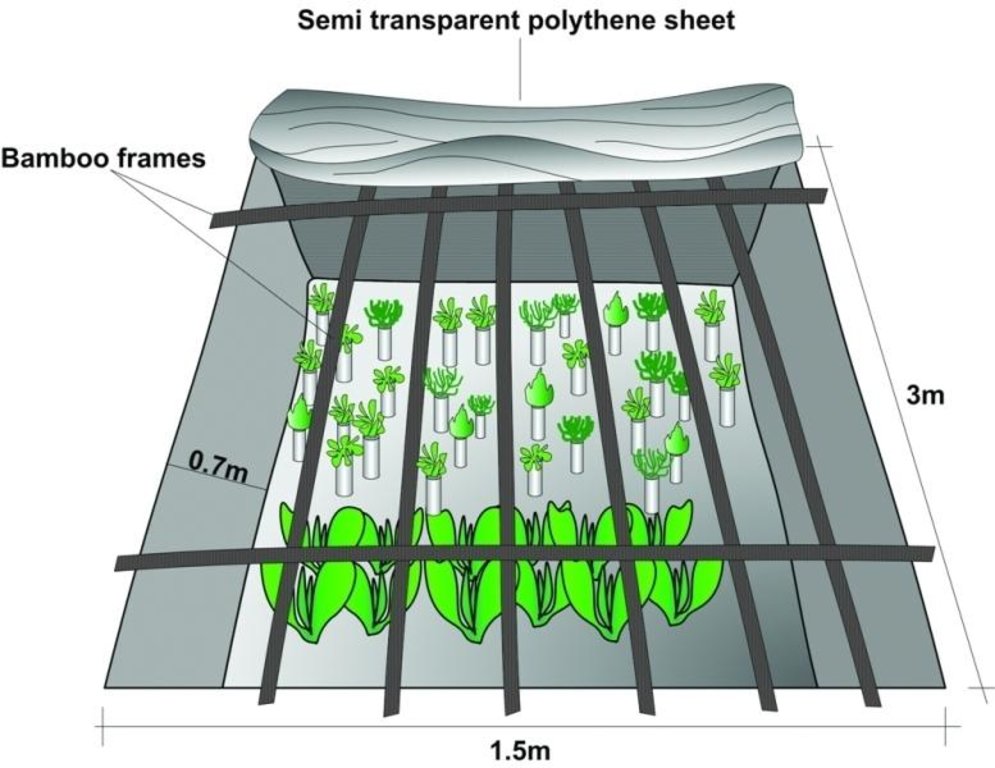
Polypits are about 1m deep pits dug into the ground and covered with semitransparent polythene sheets, preferably UV stabilised and supported on bamboo frames. A 30 cm high mud wall is built across the slope on the upper side of the pit. The polythene sheet is sealed on the upper side of the pit, leaving three sides unsealed but held down with stones that can be lifted to access the pit. The base and sides of the polypit are left as they are with no form of plastering.
The polythene sheet covering the pit reduces the photosynthetic photon flux (PPF) by around 30% inside the pit, still allowing sufficient sunlight to reach the plants inside. The polythene is usually removed during the day from 11 am to 4 pm to allow full sunlight to reach the plants except on rainy and very cold days. A modified version of these polypits - only 70 cm deep - were used in the Jhikhu Khola watershed to grow vegetable seedlings during the winter. The pits can be made of any reasonable size depending on the number of seedlings to be grown and the layout of the land. The Jhikhu Khola pits were about 3m long, 1.5m wide, and 0.7m deep.
Since the polypits are closed at night, the CO2 released by the plants and soil microbes accumulates and increases to well above levels outside the pit. In a completely sealed polypit, the CO2 concentration could reach up to 3000 ppm during the night which would be harmful for plants. Thus the polythene cover is only loosely sealed along the edges at night to regulate and maintain the concentration of CO2 at about two to four times the ambient concentration.
The warmer protected conditions and CO2 enrichment leads to extra growth and biomass gain for plants grown inside the pits during the winter. This technology is easy to maintain with the only maintenance costs being to repair damaged polythene sheets and frames.
The polypit technology is useful for mountain farmers where water scarcity and low temperatures limit the potential to raise quality seedlings. The technology is being promoted in the northwest Indian state of Uttarakhand, although only a few farmers have adopted it so far. It is a very promising technology and its use should be encouraged by hill farmers and research and development organisations engaged in raising seedlings. The technology needs more participatory action research to improve it and to encourage more farmers to adopt it spontaneously.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kavrepalanchowk district/Jhikhu Khola watershed
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The technology is developed by G.B Pant Institute of Himalayan Environment and Development (GBPIHED) in Almora (India) for raising healthy plant saplings, named as polypit (Palni et al. 1994).
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
major cash crop: Vegetables
major food crop: Rice , wheat and maize
other: Legume and oilseeds
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Production is limited due to insufficient water during winter and the pre-monsoon season (from Nov-May); insufficient
farm income due to small landholdings; increased inputs of chemical fertilisers
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Irrigation shortage during pre-monsoon and monsoon months.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize -vegetables/wheat-vegetables
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 3
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- full year planting
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Тайлбар:
The technology was tested in the farmers field at Lamdihi and Spice Crop Development Centre. atTamaghat.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S4: Тэгшилсэн ба шаталсан шуудуу, нүх
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Poly pit covered with semi transparent plastic sheet which is supported on a bamboo farme.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: protecting seedlings from frost, reduction of water loss, carbon dioxide enrichment
Structural measure: pit
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7m
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5 m
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3 m
Construction material (earth): a mud wall is made about 30 cm high from the ground, sloping on the two sides.
Construction material (wood): to place semi transparent plastic on a frame.
Construction material (other): plastic sheet: to cover the pit, rope, wire: frame preparation
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
Polypit nursery
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.10
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine the appropriate size (length, width and depth) of the pit | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 2. | Mark the area for soil excavation | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 3. | Excavate soil from the marked area | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 4. | Make a mud wall (~30 cm high) from the ground, sloping on two sides | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 5. | Make a bamboo fram of an appropriate size | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 6. | Lay the frame over the pit with one end resting on the mud wall | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 7. | Lay the plastic sheet over the frame | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 8. | Seal the polythene sheet on the higher side of the mud wall and leave three sides unsealed | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 9. | Lay the other three sides of the polythene sheet normally at ground level and weigh down with stones that can be removed to access the pit | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
| 10. | The base and sidesof the polypit do not need any form of plastering (even with mud) | Барилга байгууламжийн | beginning of the winter season |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Construction of polypit nursery | Persons/unit | 1.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Plastic | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Bamboo | unit | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Rope | unit | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 7.6 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 4 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The polythene cover is opened to acclimatized the plants to the outside environment | Барилга байгууламжийн | 11:00- 16:00/Every day |
| 2. | Cleaning the pit | Барилга байгууламжийн | After trasplanting the seedlings/ once or twice in |
| 3. | Replacing the frame and polythene sheet if it gets damaged. | Барилга байгууламжийн | before raising nursery/In case of damage |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintaining the pit | Persons/unit | 1.0 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 2.1 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: wooden/iron peg, spade, shovel ,knife, and saw
The cost was calculated only for unit technology , and it can not be extrapolated on hectare basis as in 2006.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The plastic sheet , but it is easily affordable by the land users.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
1200.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitudinal zone: 850 m a.s.l.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average: Variable
Soil texture: Fine/ heavy (clay) is red soil with high clay content but medium (loamy, silty) is non red soil
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water quality (untreated): Also good, but more in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: natural spring.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: About 50 percent of the product , especially vegetables are grown commercially.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour for planting, irrigation, harvesting; Animals are used for field preparation and in valley bottom machines can be used for field preparation
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
the pit interrupted land preparation
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
About the polypit and their advantages
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Inside the polypit high relative humidity is maintained.
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Protection of seedlings against frost
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Quality of seedlings
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
customers prefer to buy seedlings grown in polypits compared to those grown outside
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | сайн |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | мэдэхгүй |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The investment costs can be recouped within one season leading to positive results due to higher production.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
2 households
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There were not enough dissemination and awareness raising activities to inform farmers of the benefits of the technology and convince them to use it.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The survival rate for vegetable seedlings is higher and seedlings mature about two weeks earlier than if grown outside where they take about one month to be ready, leading to additional income for farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Polypits are a simple, inexpensive, practical and effective technique for raising and protecting plant seedlings from severe winter temperatures.They can be called ‘poor farmers greenhouses’ How can they be sustained / enhanced? More dissemination and awareness raising activities are needed to inform more farmers about the benefits of this technology |
|
The high relative humidity in polypits means that watering only needs to be carried out once or twice a month in comparison to fi ve to six times for open nursery beds, thus saving labour and water How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every aspect of the technology should be highlighted through experience sharing programmes |
|
The more physical conditions and CO2 enrichment in the pits during the winter months are refl ected in the extra growth and biomass gain of plants grown inside the pits How can they be sustained / enhanced? As above |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| In the demonstration, the bamboo frame to hold the sheet was too heavy making it diffi cult for the farmer to remove the frame and work inside. | Use a modifi ed frame with a space built in to allow a person to enter the pit easily without having to remove the frame. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| In completely sealed polypits, the CO2 concentration can become so high during the night that it harms the plants | Only loosely seal the sheet at night to regulate and maintain the CO2 concentration |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Bhuchar, S. (2004) Polypit: a Green-chamber for Poor Farmers, an article prepared for PARDYP Quarterly e-Newsletter-8, ICIMOD, Kathmandu
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICIMOD
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Palni, L.M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Kothyari, B.P. (1994) ‘A Simple Polypit can Greatly Reduce Nursery Time of Tree Seedlings”. In Journal of HIMA-PARYAVARAN, 6(2):10-11
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GBPIHED- Almora
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Vyas, P.; Bisht, M.S.; Bhuchar, S.; Sharma, S.; Palni, L.M.S. (1999) ‘Polypit: An Improved Technique for Raising Nursery Plants’. In Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 8(1): 43-59
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
GBPIHED- Almora
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна