Improved terraces [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Madhav Dhakal
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
GARA SUDHAR- Nepali
technologies_1499 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Shreshta Bhubhan
977015525313
bhshreshta@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Nakarmi Gopal
977015525313
gnakarmi@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Merz Juerg
977015525313
jmerz@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Швейцар
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Shrestha Smriti
977015525313
smshrestha@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Adhikari Krishna.Raj
977015525313
mdhakal@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Shah P.B.
977015525313
pshah@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Bhuchar Sanjeev
977015525313
sbhuchar@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Singh Bijendra K
bijendra@hotmail.com
District Soil Conservation Office Dhulikhel
Kavrepalanchowk, Nepal
Непал
Газар ашиглагч:
Thapa Kalpana
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Непал
Газар ашиглагч:
Thapa Gore
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Непал
Газар ашиглагч:
Thapa Leela
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Непал
Газар ашиглагч:
Tamang Indra
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - Непал1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
07/02/2003
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
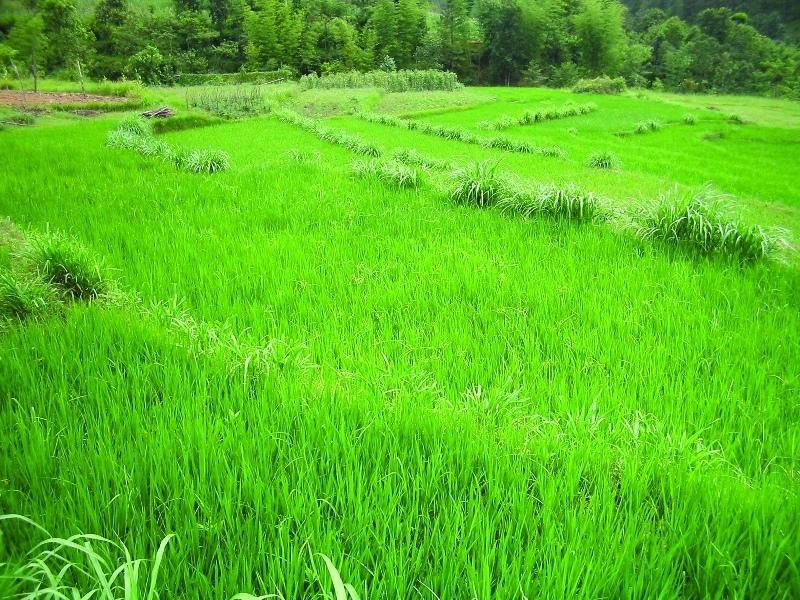
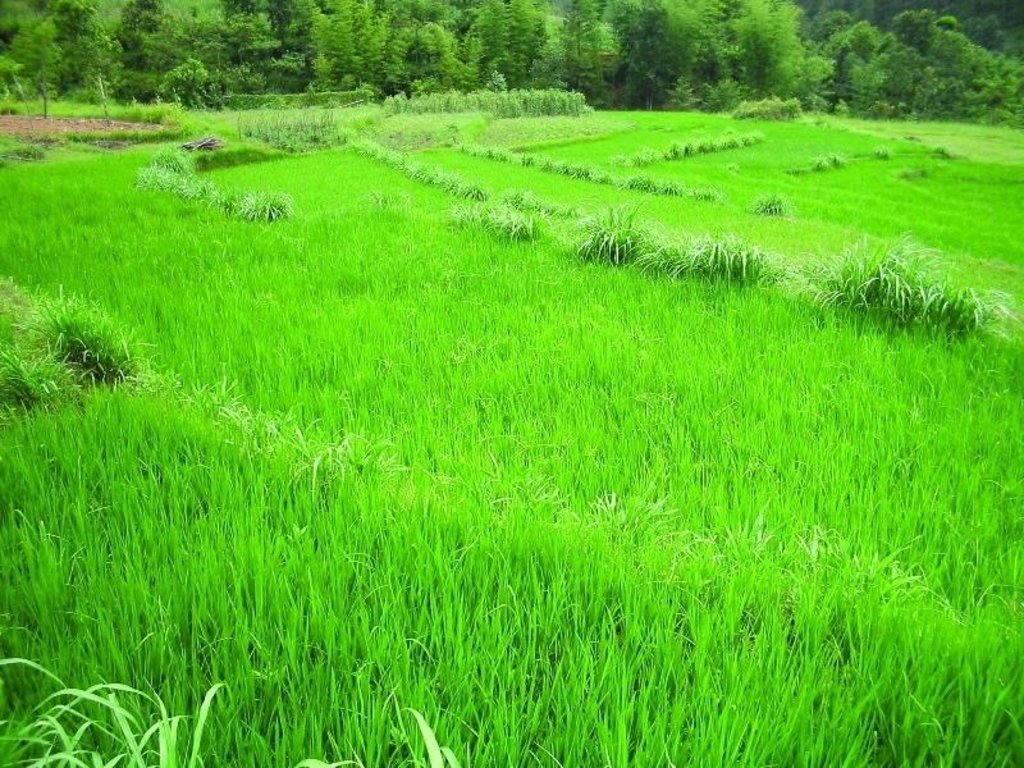
Hillside forward-sloping terracing and stabilisation using structural and vegetative measures
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
This technology addresses the soil erosion and water runoff problems associated with traditional outward-sloping terraces by reshaping the land into a series of level or gently sloping platforms across the slope. This technology is a variant of sloping land agricultural technology (SALT) or contour hedgerow technology. Nitrogen-fixing hedgerow species and quality fodder grass species, which bind the soil, are cultivated along terrace riser margins to improve terrace stability. This also enhances soil fertility and increases fodder availability. The plants are grown in either single or multiple layers. The practice is applied under rainfed conditions and is culturally acceptable and affordable. After establishment, the technology also addresses the problems of fodder scarcity making it easier and less time consuming for women and
girls to gather fodder.
The hedgerow and grass species are established between January and June. Complete establishment of this technology may take one year. The first step in creating the terraces is to build retaining walls using cement bags filled with soil which are then supported with bamboo cuttings along the contour (= future terrace risers). This divides the land into the planned terrace sections. The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the original field. Secondly, the soil is excavated from the upper part of the terraces and is used to build up the lower part above and behind the terrace riser wall to create a level bed. The fertile top soil must be kept aside and later spread over the newly terraced fields. The final step is to plant grass and hedgerow species on the outermost margins of the terrace above the risers.
Maintenance involves slicing the terrace risers once or twice a year with a spade, and smoothing off rills that appear on the surface of terraces after the premonsoon and monsoon periods. Hedgerows should be cut regularly but not more than twice a year, normally to a height of about 50 cm. Grasses should be cut about once to twice a month depending on their rate of growth.
The technology is applied under humid subtropical climate conditions (1300 mm annual rainfall with about 80% of it falling in the monsoon months of June - September). The case study area has hill slopes of 16-30% that are mostly highly erodible red soils (FAO classification: luvisols).
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Hokse VDC ward no2
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
It is a combination of traditional knowledge and practice along with new scientific research findings from within the region and elsewhere, e.g., N-fixing fodder species related information from Phillipines.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
major cash crop: Potato and tomato
major food crop: Maize and wheat
other: Beans and chilli
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem in the area documented is the small per capita cropping landholding size. The fields are mostly rainfed and have low soil fertility and acidity problems and are susceptible to erosion. The high intensity of rainfall leads to considerable soil loss (rill and gully erosion) at the beginning of rainy seasons.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The production of the cultivable land is declining. Management of slopes is inappropriate, the farmers experience serious constraints in terms of adopting better farming options, e.g., cash crops (due to fertility / erosion and soil moisture problems).
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Rice Premonsoon and monsoon( March- Novevember ) or Maize intercropped with Beans (April to August) ,Wheat and Potato ( September to January/ February) ,Tomato (January/February- April )
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 3
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
- Усны урсац зохицуулах болон салаалах
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- < 0.1 км2 (10 га)
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0126 km2.
The technology has been evaluated on the bases of village as a unit. Therefore the values calculated in terms of land use percentages is on the bases of village( Kubinde) data.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Soil erosion due to high intensity rainfall during rainy season and uneven distribution of rainfall during lean season.), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge - with regards to SWC measures)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - lack of improved farming options), poverty / wealth (lack of captial - realted to inmproved seeds, technologies etc.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
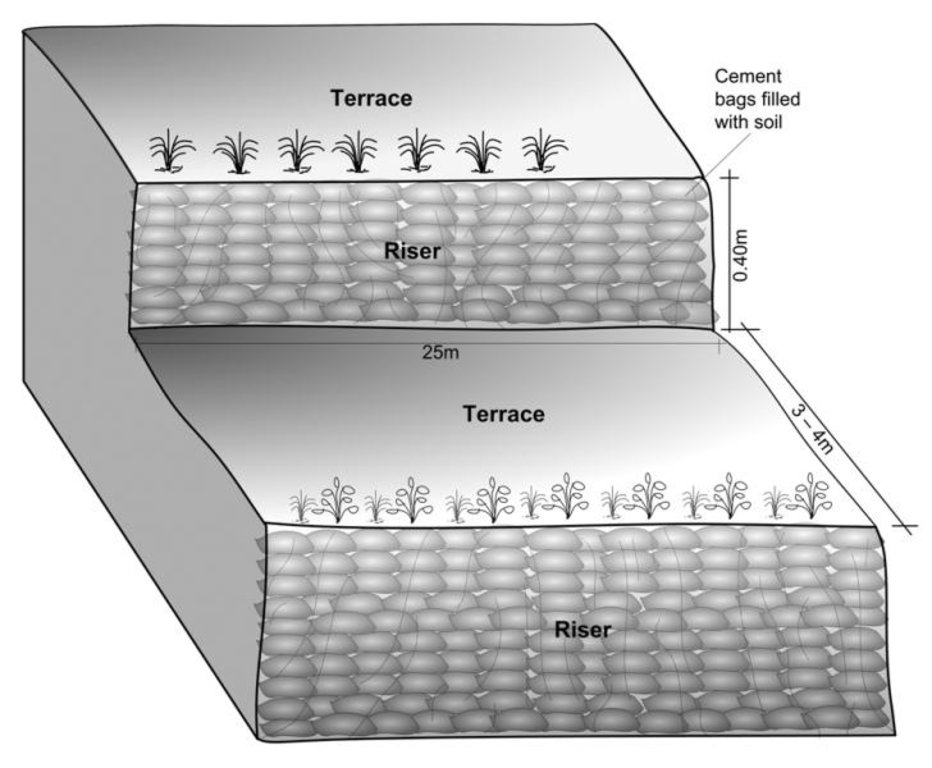
Schematric view after intervention
[terracing and vegetative measures]
Riser slope: 75 degree
Terrace slope: ~ 2 degree
Location: Kubinde
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: on risers
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3 to 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Sunhemp(Crotalaria juncea),Tephrosia (Tephrosia candida) and Flemingia (Flemingia microphylla)
Grass species: Napier(Pennisetum purpureum),Molasses (Melinis minutiflora) and Stylo(Stylosanthes guianensis)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 75.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3-4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10-15
Construction material (earth): Cement bag filled with soil, Bamboo nets were used to make risers.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
-1.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
1.40
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Area estimation ( for vegetative measures) | Ургамлын | before rainy seasonn/lean period (February) |
| 2. | Selection of fodder grass species | Ургамлын | Before rainy season (Feb) |
| 3. | Planting of grasses and hedgerow species on the outward margins | Ургамлын | During rainy season. |
| 4. | Establishment of riser, using cement bags (filled with soil) and bamboo culms for terrace stabilisation | Барилга байгууламжийн | Beginning of rainy season(May) |
| 5. | Terrace leveling:The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the field. Excavate soil from the upper part of the terrace field and use it to build up the lower part behind the terrace riser wallt creat a level plateform/bed. | Барилга байгууламжийн | Beginning of rainy season(May) |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 970.0 | 970.0 | 50.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Total costs | ha | 1.0 | 92.0 | 92.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | |
| таримал материал | Bamboo | culms | 80.0 | 1.0 | 80.0 | 50.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Cement bags | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 50.0 |
| Бусад | Supervision charge | ha | 1.0 | 10.5 | 10.5 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1287.5 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hedgerow/grass maintenance: Hedgerows are cut regularly but not | Ургамлын | Grass is cut once or twice a month. |
| 2. | (Re)plantation of hedge species if necessary | Ургамлын | Before monsoon /1*/year |
| 3. | Surface and riser maintenance: smooth the surface/rills on the | Барилга байгууламжийн | after pre monsoon and after monsoon/2 */ year ,Jun |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 310.0 | 310.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools total costs | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 342.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, Shovel, spade
All costs and amounts... are very roughly estimated by the technicians and authors.
Costs for structural measures are calculated considering the volume of excavated earth. 1 cubic meter excavated earth = 0.69 USD (labour cost). For vegetative measures it is normally based on daily wage = 1.4 USD as in 2006.
Labour cost is the major expenditure in the initial stage.
costs for tools for establishment are representative for the situation when tools for implementation of the SWC technology are not available (normally they are since the technology does not require very specific tools).
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
In case of projects interested in promoting this technology in the region, the labour cost is the major expenditure in the initial stage.The labour charges are decided by the district soil conservation office.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
1304.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture (topsoil): Clay loam
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good but when rigid surface, then low infiltration
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Availability of surface water: Sloping land , water available at downstream
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: natural spring
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
2% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
3% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (off farm employment).
95% of the land users are poor and own 75% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
Market orientation of production system: For subsistence there is: Rice, maize and wheat. Potato and tomato are for market or subsitence as well.
Level of mechanization: Land preparaion, planting,weeding and harvest is manual labour, but land preparation can also happen with animal traction.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Land fragmentation due to poulation growth, mostly of rainfed type
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
maize crop by 100%
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
households of neighbouring village benefitted.
тэжээлийн чанар
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
by >100% due to higher
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
terrace improvement group was formed
Livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Cropping pattern changed due to which, land users were able to produce more. Farm income and price of land increased.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
nearby hedgerows
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
along risers
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to levelled surface and hedgerow barrier
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Appearance of pests like rats due to introduction of planted
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Bigger area needs swc measures
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Fodder grass seed distribution
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
through farmer to farmer dissemination
Nutrients downstream
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to reduced nutrients leaching on-site
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The initial investment is high, but can be recovered within a short period
due to yield increment and cash crop production.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 50 -иас их %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
16 households in an area of 0.0126 sq km
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 50-90 %
Тайлбар:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The number of farmers applying the technology is increasing without further incentives being provided. Others have shown increasing interest in the technology without implementing it due to lack of incentives.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The price of land increased considerably from NRs 30,000 in 2001 (for 1 ropani – 508.5 sq. m) to between NRs 100, 000 and NRs 150,000 per ropani after the technology was established How can they be sustained / enhanced? The price would increase further if irrigation facilities were installed |
| Pedicels of Tephosia and Sunhemp can be used for firewood. |
| Instead of planting only maize a farmer started planting rice (primary crop) and cash crops like potato / tomato (secondary crops). |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The area of levelled terraces nearly doubled in Kubinde village from 2001 to 2003, which is an indicator of increased awareness of the benefi ts of soil and water conservation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing would help expand the area under improved terraces. |
|
Land productivity increased, maize, potato and bean production increased, vegetables and rice production started. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Irrigation facility could increase the production capacity of the terraces. |
|
Availability of grass/fodder (nitrogen fixing) increased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting horticultural fruits could increase farm incomes and so it should be promoted and more nitrogen fi xing species (preferably local) should be tried out |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| In the fi rst year of implementation, maize production was reduced due to soil amendment |
a phenomenon which is likely to occur with new terrace formation |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Presently the vegetative technology is confined to terrace margins | it should be extended to the risers also. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2002) Hydro-meteorological Year Book of Jhikhu Khola Watershed. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
ICIMOD
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Mathema, P.; Singh, B.K. (2003) Soil ErosionStudies in Nepal: Results and Implications. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Mathema, P. (2003) Watershed Managementin South Asia. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна