Radical Terraces [Руанда]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Desire Kagabo
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Amaterasi y'indinganire
technologies_1553 - Руанда
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ИталиТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Rwanda Agriculture Board (Rwanda Agriculture Board) - Руанда1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
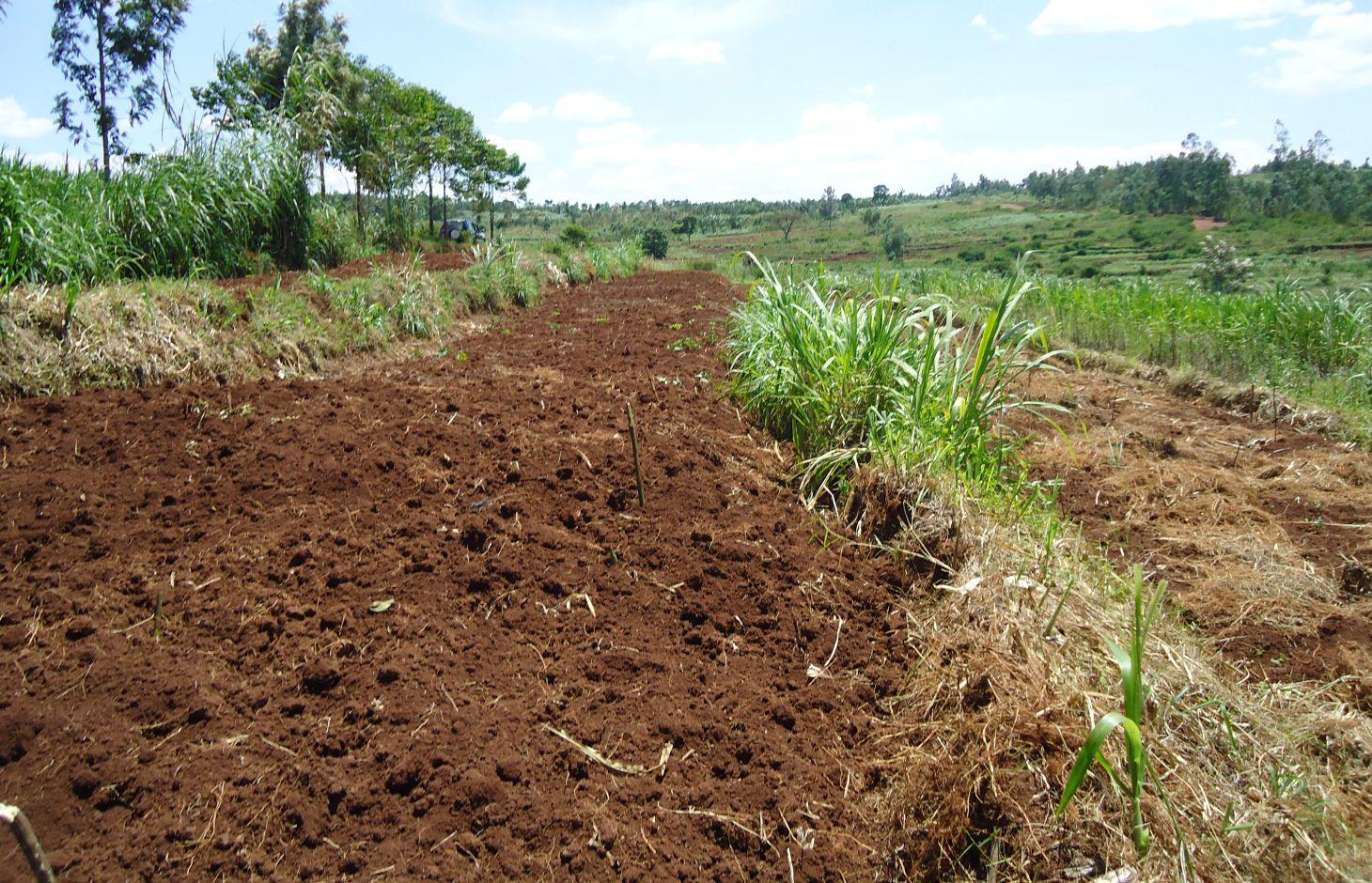
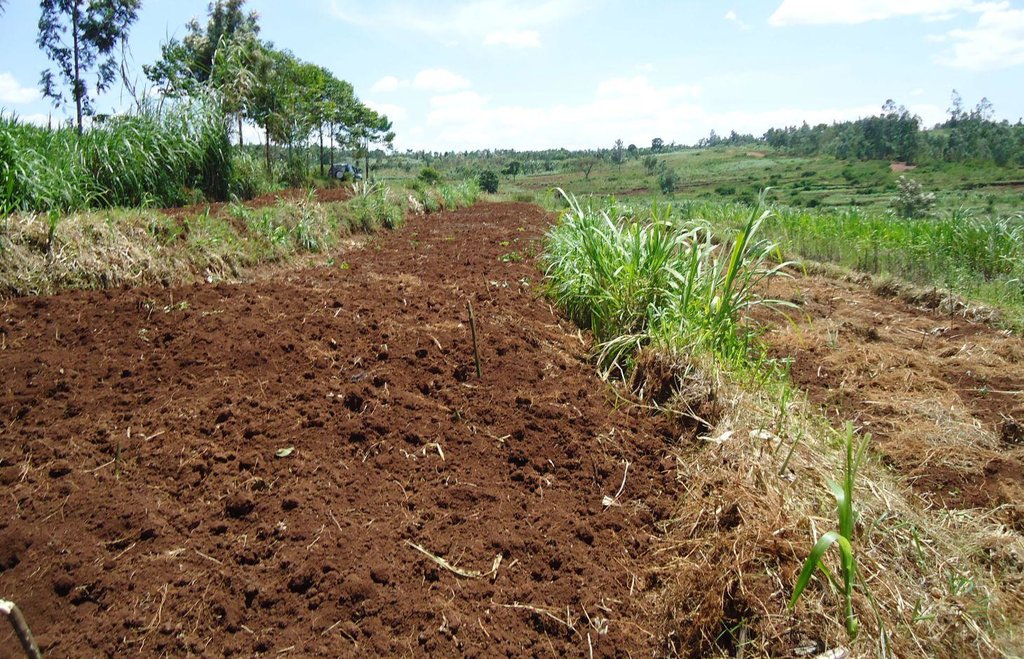
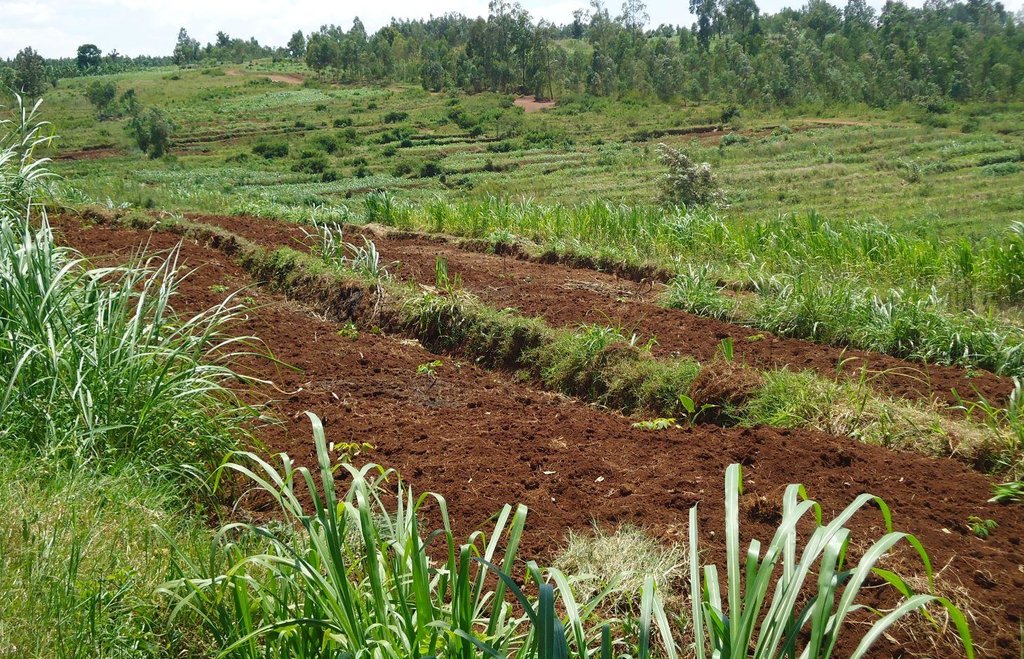
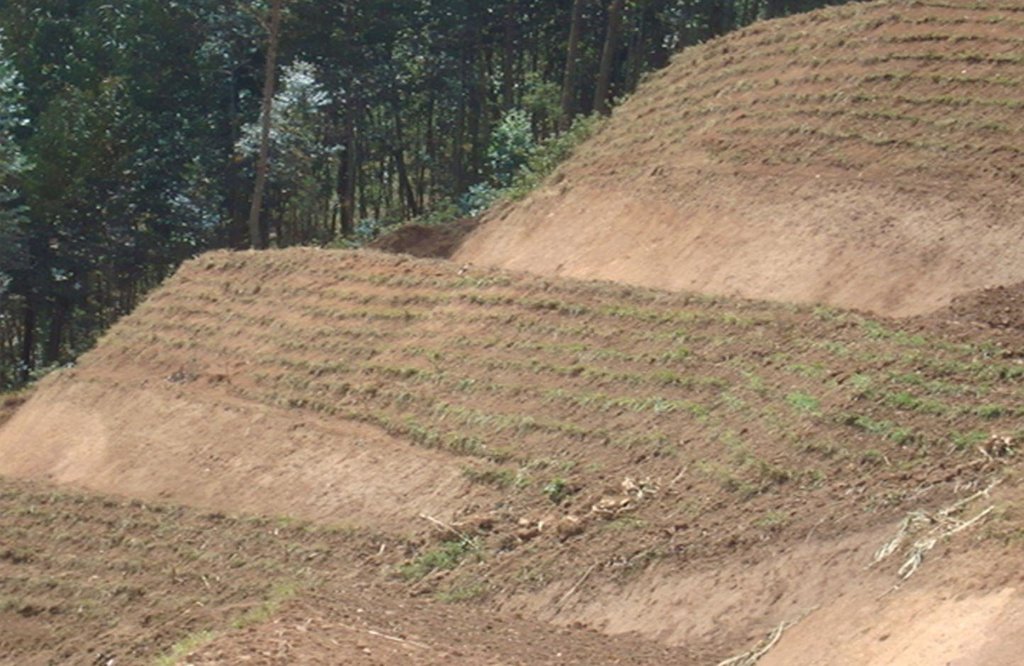
Locally referred to as ‘radical terracing’, the method involves earth moving operations that create reverse-slope bench terraces which have properly shaped risers stabilized with grass or trees on embankment to avoid collapse.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
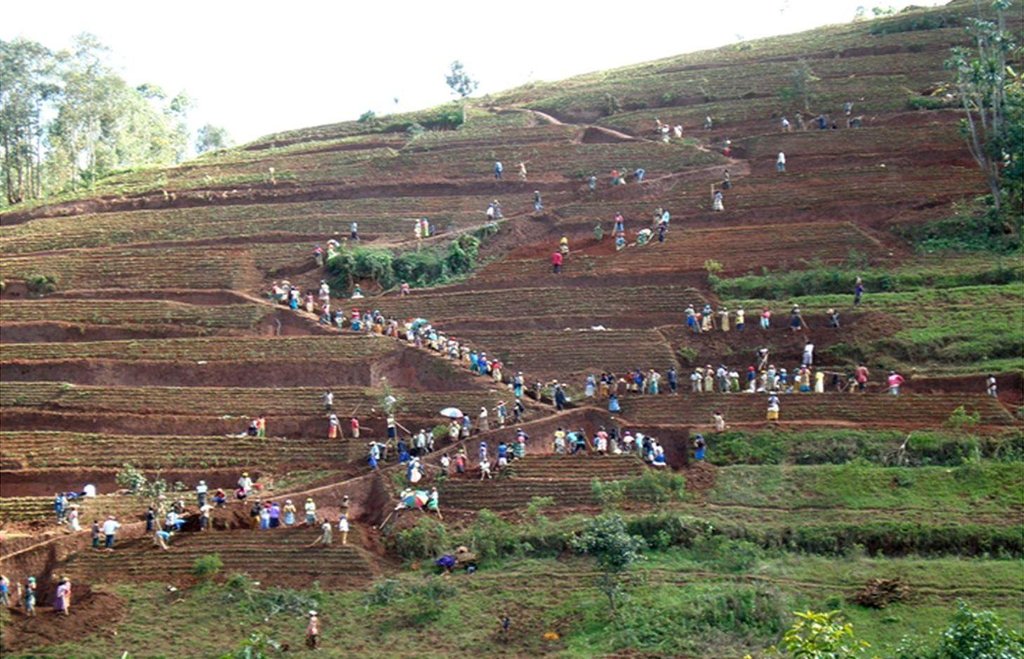
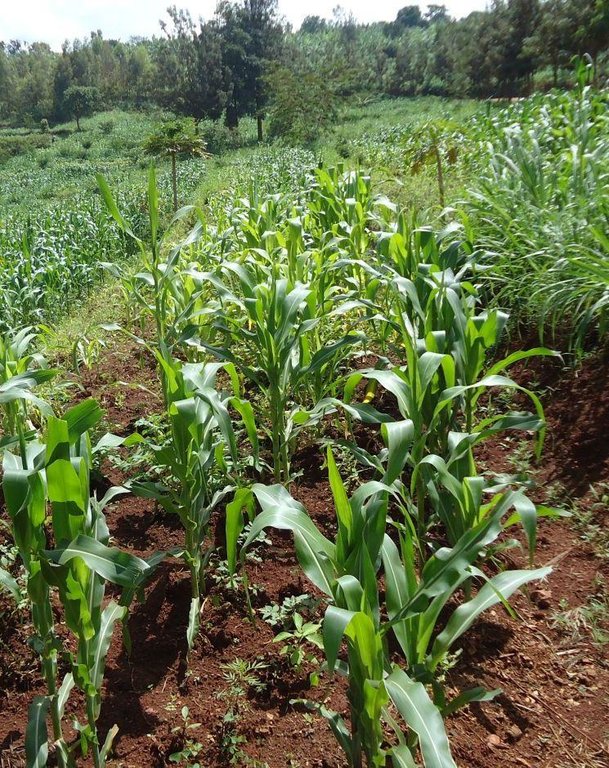
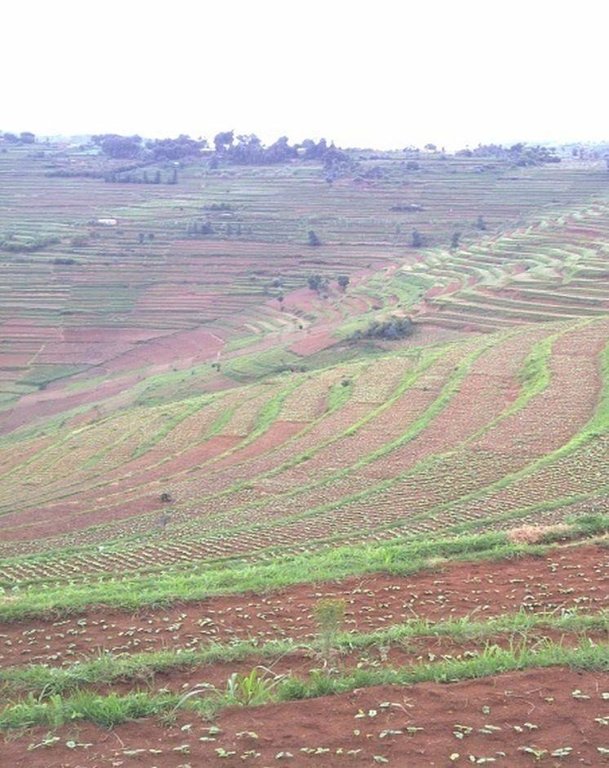
In Rwanda, a unique method of back-slope terracing originally introduced by missionaries growing wheat in the Northern Province in the 1970s, has been widely adopted by smallholder farmers in many parts of the country. The farmers are careful to isolate the topsoil, then they re-work the subsoil to create the required reverse-slope bench, after which the topsoil is spread over the surface. The riser is planted with short runner grass for stabilization, all within the same day. Radical terracing is usually done manually with hoes and shovels, mostly by communal group-work involving hundreds of farmers (see left photo). Thus, a hillside can be terraced in one day. Where radical terraces have been constructed, the effects have been dramatic, achieving optimum water and soil conservation on slopes exceeding 50%, while adoption rates have been quite extensive. This high adoption of radical terracing is related to the existing policies and programs such as land consolidation, land management and crop intensification programs. These policies/programs boost the use of radical terraces by providing farmers more opportunities to easily access inputs such as improved seeds and manure for increasing the productivity of constructed radical terraces. Recent studies (e.g. Fleskens, 2007, Bizoza and de Graaff 2012 and Kagabo et al. 2013) assert that radical terraces in the highlands of Rwanda are only financially viable when the opportunity cost of labour and manure are below the local market price levels and when agriculture area on these radical terraces can be substantially intensified. Ten to 30 metric tons of manure (organic) are required to restore the soil fertility of newly established radical terraces.
Purpose of the Technology: In Rwanda, radical terraces are principally designed (1) to reduce soil losses through enhanced retention and infiltration of runoff, (2) to promote permanent agriculture on steep slopes and (3) to promote land consolidation and intensive land use.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Newly established radical terraces should be protected at their risers and outlets, especially in the first or second year of the establishment. After establishing a terrace, a riser is shaped and grasses or shrubs/trees are planted soon after. Napier grass is commonly planted and is used as forage for livestock. Risers on radical terraces are seen as a new production niche of forage as a result of land shortage and a strict zero grazing policy.
Natural / human environment: Radical terraces have the potential of improving farmers’ livelihoods and increasing the resilience of a degraded environment.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Руанда
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Rwanda
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kayonza District (Eastern province)
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
- Government
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The Government introduced it through local leaders and agronomist. It was established in 2004
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
major cash crop: Sweet potato and pineapple
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to high runoff on the steep slopes, deforestation, intensive cultivation and lack of suitable land management methods.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low crop production, soil erosion and lack of fodder
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September- January; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March - June
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 10.3 km2.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (Grazing and fodder), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Extreme topography: steep slopes in many cases over 50%), population pressure (High density (in rural area over 400 inhabitant per ha))
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Use of cooking energy (fire wood)), poverty / wealth (Farmers have low income and have less access to off farm income or remittances), education, access to knowledge and support services (High rate of irriteracy)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
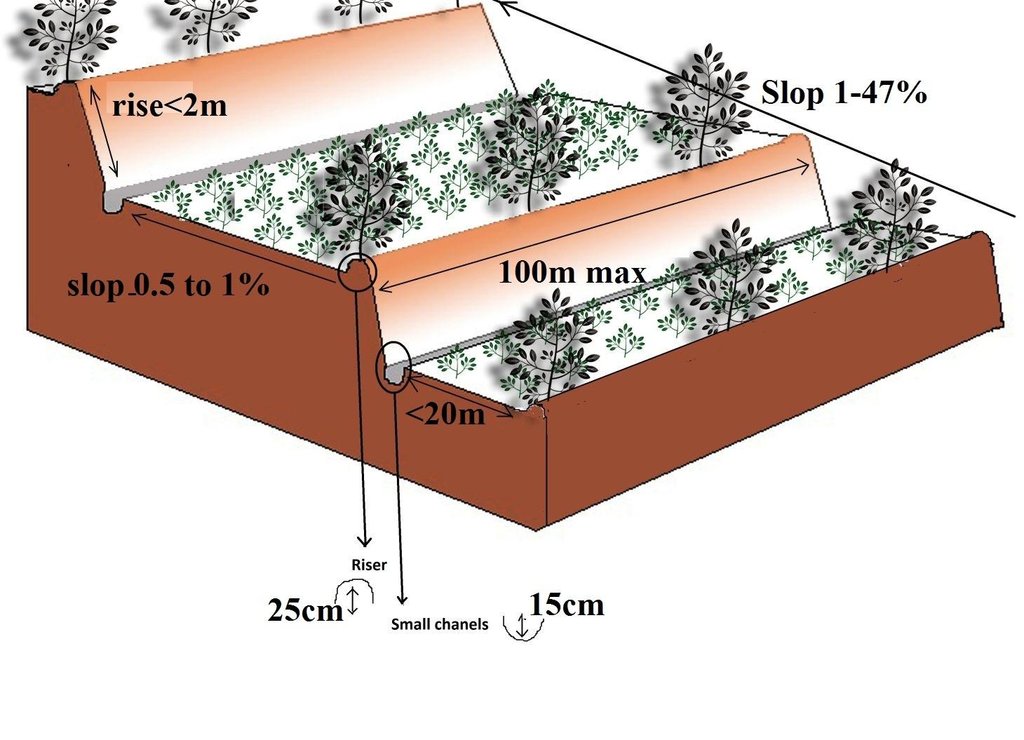
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
The farmers are careful to isolate the topsoil, then they re-work the subsoil to create the required reverse-slope bench, after which the topsoil is spread over the surface. The riser is planted with short runner grass for stabilization, all within the same period.
Location: Nyamirama. Kayonza/West/Rwanda
Date: 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Special training should be provided to field staff to be able to make an adequate design)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Land users are required to only implement the technology under the supervision of field staff)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Grass species: Pennisetum
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 35%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 4
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 20-50%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Rwandan francs
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
640.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
1000
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cuttings of grasses | Ургамлын | Rain season |
| 2. | Transport of grass cuttings | Ургамлын | Rain season |
| 3. | Planting of grass cuttings | Ургамлын | Rain season |
| 4. | Land surveying (slope determination, soil structure and texture analysis) | Барилга байгууламжийн | any time |
| 5. | Construction of bunds (risers) with soil from upper and lower sides | Барилга байгууламжийн | dry season |
| 6. | Level terraces bed (surface soil moved from upper to lower part of terraces) | Барилга байгууламжийн | dry season |
| 7. | cutting subsurface soil, leveling and refilling surface soil | Барилга байгууламжийн | dry season |
| 8. | Make lips on edges of terraces | Барилга байгууламжийн | dry season |
| 9. | Compact risers | Барилга байгууламжийн | dry season |
| 10. | Plant grasses including agro-forestery trees. | Барилга байгууламжийн | rainy season |
| 11. | Input/ application of farmyard manure and liming | Барилга байгууламжийн | rainy season |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Cuttings of grasses | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 1000.0 | 2000.0 | 60.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Transport of grass cuttings | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 10000.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Planting of grass cuttings | persons/day/ha | 20.0 | 1000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Land surveying (slope determination, soil structure and texture | persons/day/ha | 6.0 | 20000.0 | 120000.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Lime | kg/ha | 2500.0 | 40.0 | 100000.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Famyard manure | kg/ha | 30000.0 | 5.0 | 150000.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Mineral fertilizers | kg/ha | 300.0 | 500.0 | 150000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Construction of bunds | persons/day/ha | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Level terraces bed | persons/day/ha | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 250000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Cutting subsurface soil | persons/day/ha | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 250000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Make lips on edges of terraces | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 10000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Compact risers | persons/day/ha | 50.0 | 1000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| Бусад | Labour: Plant grasses including agro-forestery trees | persons/day/ha | 50.0 | 1000.0 | 50000.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1262000.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Ургамлын | Before crop planting/each cropping season |
| 2. | Manure application | Ургамлын | Before crop planting/annually |
| 3. | Grass streaming | Ургамлын | Throughout the year |
| 4. | Cleaning of channels and drains | Барилга байгууламжийн | through out the year |
| 5. | Regular repair of destroyed risers | Барилга байгууламжийн | through the year |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Weeding | persons/day/ha | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Manure application | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Grass streaming | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 1000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Cleaning of channels and drains | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Labour: Regular repair of destroyed risers | persons/day/ha | 6.0 | 333.3333 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 22000.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Small hoes and machete, Hoes, machete, spade, A.fram, macako and meters.
The cost is calculated using the rate of US dollars at present time and were estimated according to the cost of construction of one radical terrace. At present the labor is 1.6$ per day. This was calculated on 25/07/2011.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Factors that affect the cost are labor, soil structure and slope
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
1000-1500 mm: September - December
1500-2000 mm: February - June
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months are above 18 degree C.
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water available but very far to fetch.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
75% of the land users are poor and own 60% of the land.
25% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduce crop area
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Require high quantity of FYM and mineral fertilizers
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The technology is newly established and the soil need enough farmyard manure and inputs to re-stabilize and regain its fertility
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
гадаргын урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрс алдагдах
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
циклон, бороо, шуурганы нөлөө
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
disturbance of fertile top soil
biodiversity
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | мэдэхгүй |
| land slides | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 50 -иас их %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
150 households covering 75 percent of stated area
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
140 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The real advantages of the technology are observed after 5 to 6 years with good maintenance of structures
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
It reduces soil runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good maintenance of structures |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
It controls soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? There is a need to plant grasses or trees on risers to stabilize terraces |
|
It increases soil water holding capacity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Organic manure should be added to the terrace to effectively increase the soil water holding capacity. |
|
It increases fodder availability as new niches for fodder production are created. How can they be sustained / enhanced? High value nutritive fodder should be planted (napier grass, calliadra, tripsucum, etc.) on risers |
|
It increases crop productivity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Terraces should be well maintained by providing more inputs and regular maintenance of bench struactures |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| It reduces the cropped land | Farmers should be supported in accessing high value crops and inputs to maximize crop yield. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The establishment of radical terraces is expensive | The construction of radical terraces should be subsided by the government. |
| The initial soil structure is disturbed (lost of soil organic matter) | Heavy investments are needed to replenish the soil fertility, especially by adding organic manure. |
| The establishment of radical terraces decreases cropped land. | Grow high value crops and use adequate quantity of inputs. |
| With poor maintenance or poor design of radical terraces, landslides may occur. | To be much more rigorous in the design and implementation/development of terraces by making sure that professionals are involved in the whole process of establishing terraces. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Kagera TAMp project website
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна