Vegetated graded soil bund [Этиоп]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
Yeafer Erken (Amharic)
technologies_1601 - Этиоп
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Water and Land Resource Centre Project (WLRC)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
12/05/2014
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Community Organizations and Mobilization for Soil and Water … [Этиоп]
Community mobilization for soil and water conservation work in a watershed planning unit is an approach for collective action by organizing all active labor forces living in the kebele/peasant association into development group of 20-30 members and further divide into 1:5 work force to implement construction of soil and water …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Gizaw Desta Gessesse

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [Этиоп]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
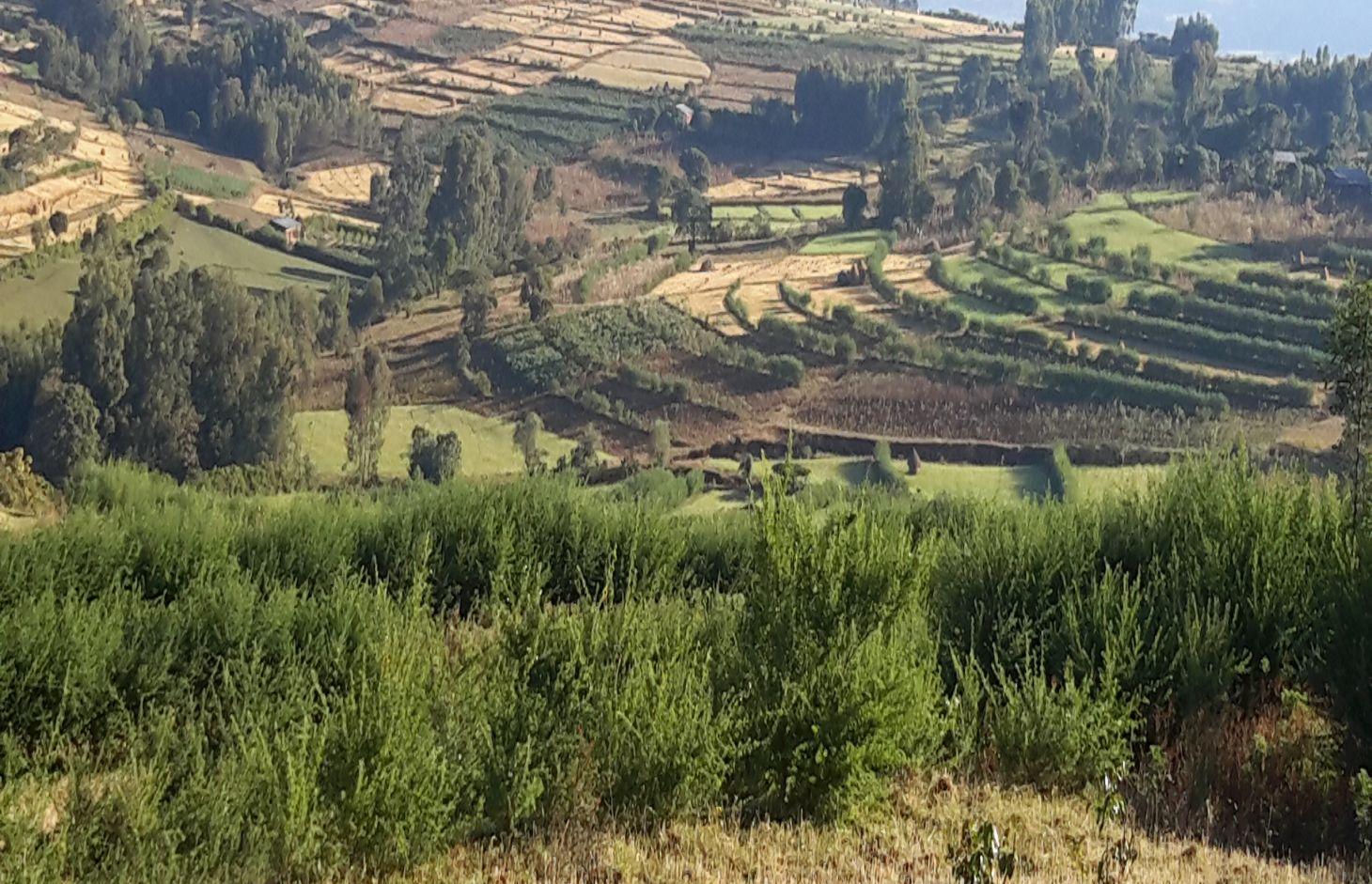
Vegetated graded soil bund is a soil conservation practice meant for cultivated lands and constructed by excavating graded channel on upper side and develop embankment on lower side which is planted with grass or shrub species in order to control soil erosion and drain excess runoff implemented through community mobilization.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Vegetated graded soil bund is a practice or soil conservation technology for cultivated lands and constructed by excavating graded channel and form embankment. It is practiced in areas where there is excess runoff to be disposed and where there is no stones available for construction. The design specifications (ditch gradient, width and height) and layout (spacing/vertical interval) vary on the amount of excess runoff and slope of the land. Soil bund construction begins from top of the catchment. Cut off drains are constructed on top of the catchment and where needed to drain excess runoff to well stabilized natural or man-made waterways. this helps to reduce runoff impact on gullies. The bund ditch/channel should be sufficient enough to drain excess runoff safely without causing channel erosion and creating downstream damages. At same time the embankment should be stable to withstand overflows and damage due to free grazing. One technique to stabilize bunds is to plant the embankment with grass and shrub species of multiple economic value in order to compensate production area lost by bund construction. Often, the species are preferably used for livestock feed. Thus, free grazing has to be controlled. To protect damage of channels and embankments by extreme runoff and floods, frequent supervision and maintenance is required.
The purposes are:
1) Reduce nutrient loss and soil erosion by shortening the slope length,
2) Safely drain excess runoff from upstream of gully into protected waterways,
4) Produce biomass of fodder and cash values.
Vegetated graded bunds are established by doing surveying using hand level to determine the layout of the technology along the slope. During the surveying, the position of bunds (spacing) and cutoff drains and connection to waterways are determined. Bunds are laid following 0.05% gradient and up to 80 m maximum length. The specifications of the structure are: height of bund is a minimum of 60 cm after compaction; depending on the soil, base width range between 1.0 and 1.5m; top width is between 30 and 50 cm. The construction is made across different parcels owned by different land users. If there is no natural waterways and where it is appropriate, paved waterways are constructed at every 80 m or less bund length to dispose drainage water. At the beginning of the rainy season, the embankments are covered with grass and/or shrubs either by direct sowing of seeds or planting the seedlings raised in the nurseries. Monitoring of damages due to flooding and animals, maintenance of the structure as well as replanting of dead seedlings on bunds is required to sustain the soil conservation technology.
The technology is appropriately applied in high rainfall and sub-humid areas of the sub-tropics, particularly where the soil is moderately deep and poorly drained. It is constructed on cultivated lands having slopes in the range of 3-15%. The practice can be constructed by land users. It also requires collective decision and actions to drain excess runoff through waterways. The living condition depends on subsistence crop-livestock mixed farming. On average households have 5-6 family size. Crop production is meant for home consumption with small surplus for local market. The services related to water supply, energy supply, and infrastructure are low. Besides it is an asset, animals often used to cope shocks during drought periods.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Этиоп
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Amhara National Regional State (ANRS)
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Mecha, Bahirdar Zuria and Yilmana Densa
2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The soil bunds are introduced before 30-40 years, however the integration of structural and combination of vegetative measures are applied in three years period in the WLRC learning watersheds.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation due to sheet erosion, rills and gullies, soil nutrient depletion, overgrazing, shortage of fuel wood, excessive removal of crop residuals, loss of vegetation and deforestation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, soil nutrient depletion, shortage of pasture
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- бүрэн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June-December; Second longest growing period in days: 180, Second longest growing period from month to month: June-November
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 m2.
The technology is applied on specific conditions within the watersheds or area of adoption
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт
- S3: Шаталсан суваг, шуудуу, голдирол
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

усны доройтол
- Hs: Гадаргын усны хэмжээ багасах
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (High tillage frequency on annual basis and steep slope cultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The cropping system is cereal based that induce erosion), overgrazing (Livestock graze on crop residues after harvesting of crops), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Extreme rainfall cause for high erosion), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep slopes or rugged topography), population pressure (Result in expansion of crop lands to steeper slopes)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation of scattered trees in the farm and forests upstream of crop lands), land tenure (Insecure tenure play role not to invest on long term), poverty / wealth (Poor can not afford to invest on soil conservation on his parcel), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
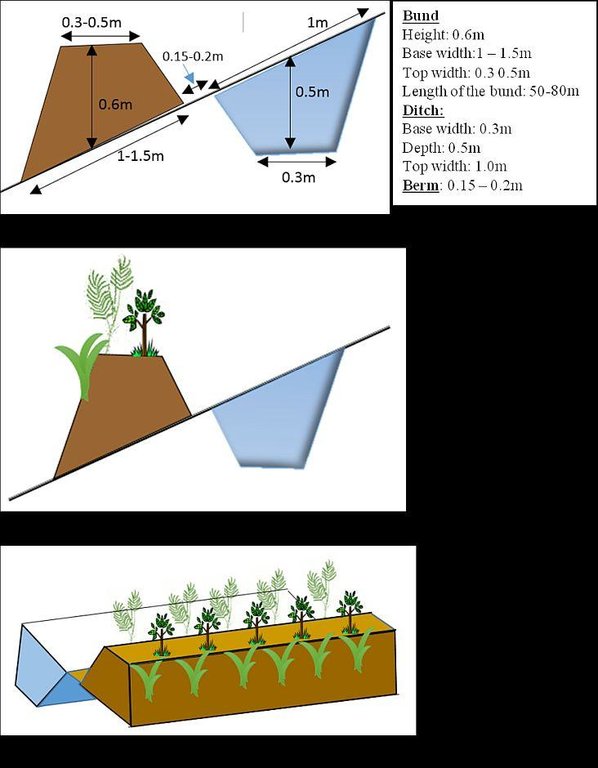
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
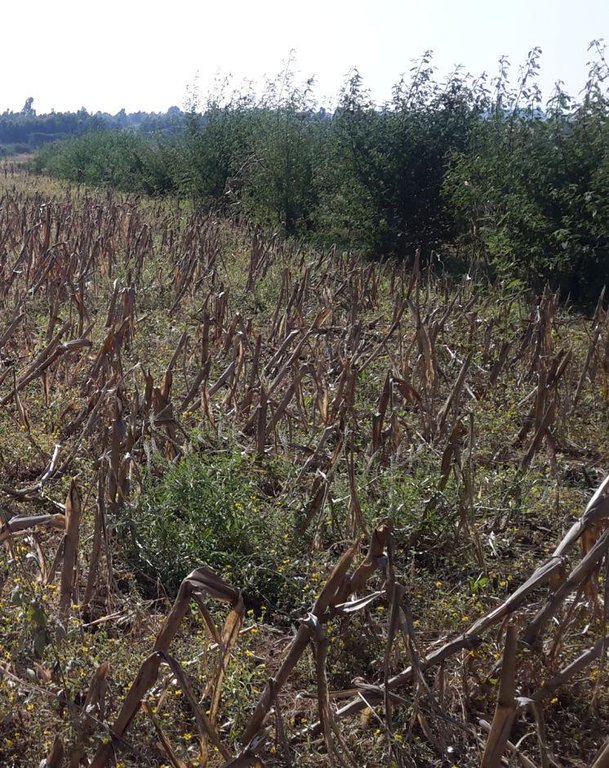
Vegetated graded soil bund showing the excavated ditch or channel and the embankment planted with grass and shrubs
Location: Amhara Region. Mecha, Yilmana Densa, Bahir Dar Zuria and Dessie Z
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Layout and design specification of soil bunds and cutoff drains vary on soil types, slopes, and rainfall conditions. Experts thus should acquire knowledge on specific hydrologic conditions)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Land users need skill to layout and construct bunds, monitor structures before the occurrence of excessive damage, and do regular maintenance)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): T=5333, C=160, G=1600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10-20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): T=0.3, C=5, G=0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia Africana, Polycantha, Sesbania Susban, Pigeon pea, Treelucer
Perennial crops species: Rhamnus
Grass species: Napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-15%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.05%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2-2.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-250
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.0
Bund/ bank: graded
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 10-20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-80
Construction material (earth): in-situ excavated soil
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-15%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.05%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
ETH BIRR
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
20.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.50
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparing planting materials | Ургамлын | January-May |
| 2. | Preparation of planting materials | Ургамлын | January-May |
| 3. | Transportation of grass splits/cuttings | Ургамлын | Start of rainy season/July |
| 4. | Transporting tree seedlings | Ургамлын | Start of rain season/July |
| 5. | Planting grass splits/cuttings | Ургамлын | Start of rainy season/July |
| 6. | Sowing seeds on bunds | Ургамлын | Start of rainy season/July |
| 7. | Planting tree seedlings on bunds | Ургамлын | Starting of rainy season/July |
| 8. | Surveying (layout of structures) | Барилга байгууламжийн | After crop harvest and before first tillage operation |
| 9. | Construction of cutoff drains | Барилга байгууламжийн | January-April |
| 10. | Construction of bunds (ditch and embankment) | Барилга байгууламжийн | January-April |
| 11. | Construction of waterways | Барилга байгууламжийн | January - April |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 1107.0 | 1107.0 | 79.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.6 | 300.6 | 50.0 |
| таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | stone | ha | 1.0 | 1300.0 | 1300.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | wood | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | earth | ha | 1.0 | 25.2 | 25.2 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 2889.8 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of planting materials | Ургамлын | January - May |
| 2. | Transportation of seedlings | Ургамлын | July |
| 3. | Re-plantation of seedlings and grass splits | Ургамлын | July |
| 4. | Maintenance of bunds, cutoff drain and waterways | Барилга байгууламжийн | January-April |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 279.0 | 279.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 299.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Cart, plastic tubes, spade, pickaxe, hand level, graduated ranging pole, spade, pickaxe, crowbar, hammer
The costs are calculated based on the labour, seedling/seed, grass splits required per hectare
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The cost variation in implementing vegetated soil bund is dependent upon availability of stones, workability of the soil, cost of seeds or seedlings for plantation, and distance for transporting seedlings.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Monsoon, 5-6 months rain and 6-7 dry months
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics. he lowest temperature is above 5oc but below 18oc etween November to January
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are involved in the construction of bunds with role of collecting stones, stabilize/compact the embankments and sometimes help men in excavating the earth
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users often do not have access to off-farm income unless those who are young and own small size of land go for seasonal labor to towns during the slack period
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Crop yield increase on sedimentation area of bunds
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Introduction of fodder crops on bunds
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Introduction of high value forage crops
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The area used for ditch construction can be taken as a loss of land
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In slope classes where spacing is narrow farm operation will be hindered
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increase in income due to yield increase and fodder production
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Watershed users committee established to regulate the development
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Field staffs and land users aware of erosion and soil conservation
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The technology aim to reduce the soil loss and improving the soil moisture to produce crops. On the other hand, the fodder production on bunds increase livestock productivity. Through improving crop and livestock productivity the livelihood of the watershed people is improved in long terms.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Overall effect of bunds show increase in surface water downstreams
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
reduction of concentrated runoff
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increase the rate of infiltration
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Soil loss is reduced by breaking the slope length
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In good drainage soils it increases infiltrated water and interflows
голын адагт үерлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Since it helps to reduce concentration of runoff it contributes to reduce flooding
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The main function of bunds is to reduce soil loss
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
All fields are treated with integrated bund, cutoff drain and waterways
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Тайлбар:
The technology has sufficient drainage ditch to tolerate excess runoff occurred during heavy rainfall events. However, it is sensitive to floods unless flood management measures such as strong cutoff drains and waterways are implemented
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The short term economic benefits of the technology includes increase in fodder production and slightly crop productivity due to improved soil moisture. Whereas the long term benefit can be obtained as a result of increased yield on areas where sediment accumulation occurs as well as production of fodder on soil bunds for livestock feed
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
The technology is implemented using community mobilization approach which involves all land users. All land users, who cultivate land in areas where bunds are suitable, implemented the technology. All parcels are covered with the technology/bunds except homesteads and degraded hillsides and gullies which are treated with different SLM technologies
Since the approach encourages collective action (through community organizations) to integrate different SLM technologies in the watershed level, there is no attempt by individual land users. However, there are motivations and implementation of land users on adjacent watersheds to implement the technology.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The trend is at increasing rate although land users need material support such as multipurpose seedlings to stabilize bunds. There is shortage of supply of fodder seeds. Community nurseries are inadequate and not well supported to raise seedlings to meet community demands.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increase in fodder production for livestock feed |
| Reduce conflict among adjacent land users (i.e., upstream and downstream land users) that arise due to concentrated runoff |
| Reduce soil erosion |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The technology reduces soil loss and associated nutrient loss significantly in the first 3 to 4 years and further reduce siltation of reservoirs and land degradation |
| Increase the soil moisture in the landscape/watershed |
| Improves the greenness, soil carbon and micro-climate |
| Increase level of awareness of land users to produce fodder and diversify production and income |
| Reduce the concentration of runoff and safely drain without causing damage |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Hinder farm operations like turning oxen become difficult while ploughing | It can be sustained through proper layout and allow space for human and animal paths |
| Plantation on bunds harbor birds | This can be avoided by harvesting the mature branches of the shrubs for livestock feed on seasonal basis. |
| Appearance of new weeds species along the drainage ditches | Regular weed monitoring and manual control |
| Hinders livestock to graze on crop residues | Try to use cut and carry grazing system (both crop residues and fodders) and develop forage development strategies in every possible niches |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| High labor requirement to establish and maintain the technology | Increase the awareness level of land users and strength collective actions and local organizational setups |
| Small land loss for construction | Introduce production options (like fodder production) on bunds to compensate the lost land |
| It requires some years to accumulate sediment on bund area and form bench | It can be improved by modifying the design of drainage ditchs |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Vegetated Graded Soil Bund: A Technique to Reduce Runoff Impact and Increase Soil Moisture Storage and Fodder Biomass, WLRC Brief No. 4
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
WWW.wlrc-eth.org
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Community Organizations and Mobilization for Soil and Water … [Этиоп]
Community mobilization for soil and water conservation work in a watershed planning unit is an approach for collective action by organizing all active labor forces living in the kebele/peasant association into development group of 20-30 members and further divide into 1:5 work force to implement construction of soil and water …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Gizaw Desta Gessesse

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [Этиоп]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- Эмхэтгэгч: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна