Use of household ponds for garden irrigation and fish production. [Камбодж]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christoph Kaufmann
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
ការប្រើប្រាស់ស្រះគ្រួសារសំរាប់ស្រោចស្រពច្បារដំណំានឹងការចឹញ្ចឹមត្រី (Khmer)
technologies_1627 - Камбодж
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Khun Lean Hak
kleanghak@yahoo.com / sofdec@camintel.com
SOFDEC/LAREC
Камбодж
1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
07/07/2014
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
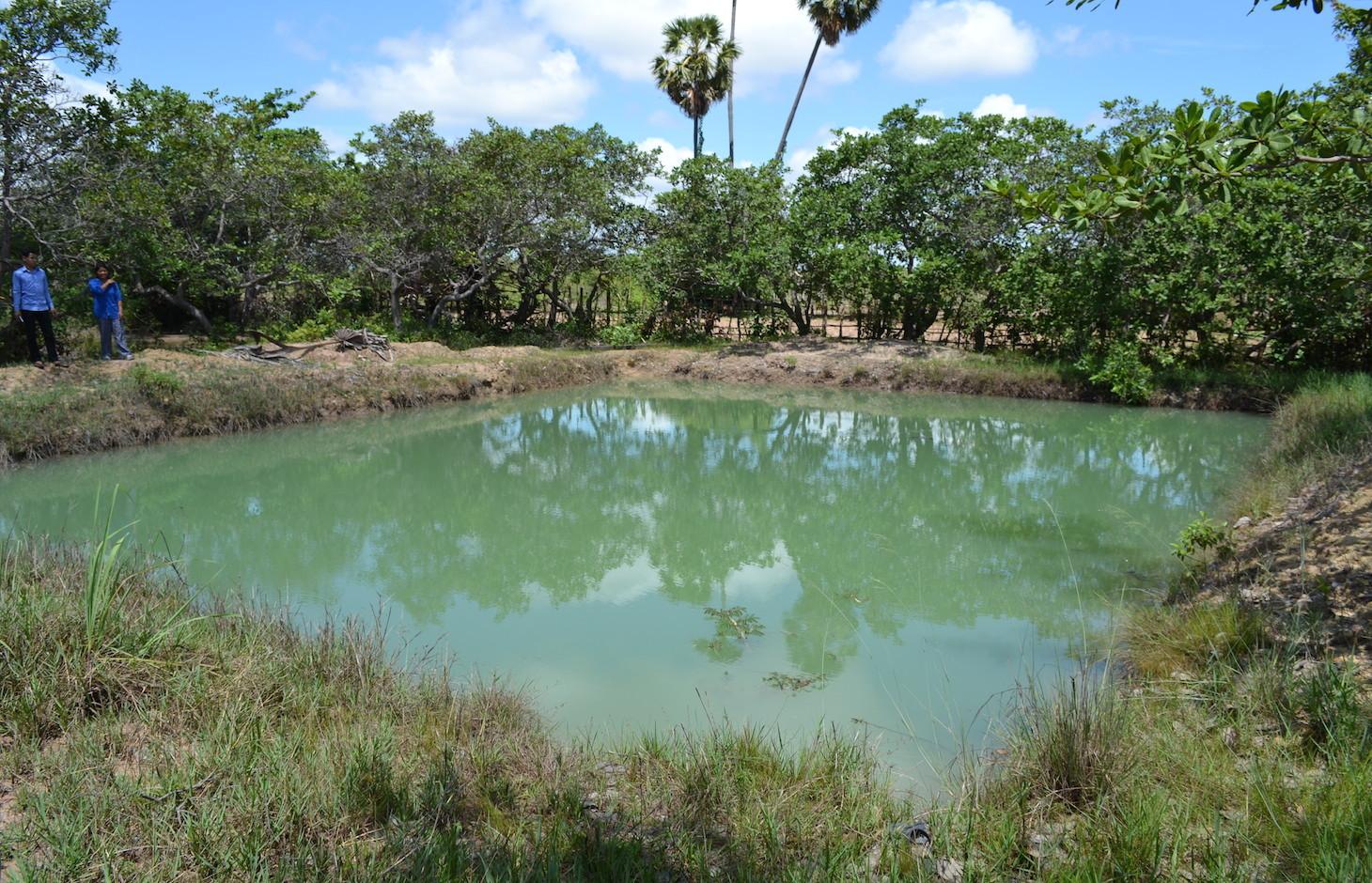
Ponds are used at household level to raise fish as well as to irrigate vegetable gardens and rice seedlings
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Wet-season rice is the predominantly grown crop in the area, but some land users also grow other crops (e.g. sweet potatoes, pumpkins, or peanuts). However, if droughts occur or if the rainfall patterns are erratic, the production can be harmed. Furthermore, due to the lack of water, the land users usually leave their fields bare during the dry season. This results in an increase of wind erosion and in negative impacts on the soil biota due to its exposure to the sun.
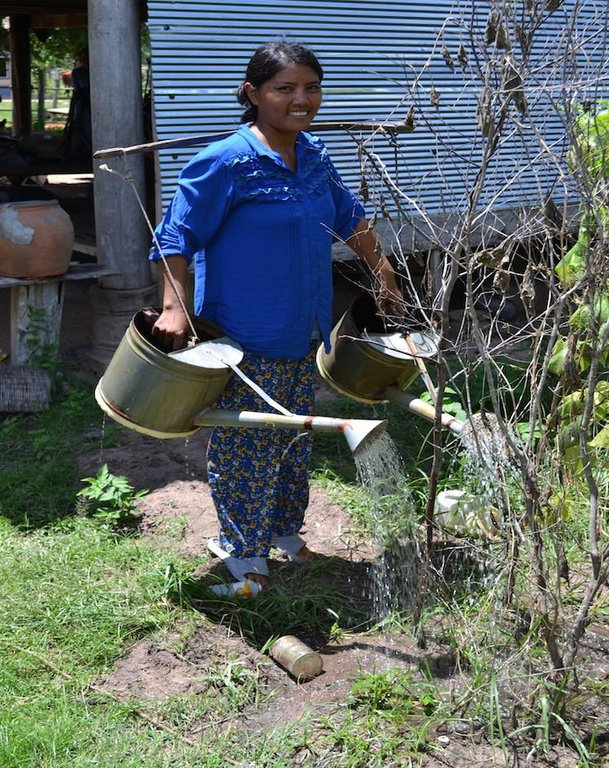
In order to tackle these challenges, ponds of 4 m depth (1 m deeper than the groundwater table during the dry season) are used at household level. By building ponds, some fields can be irrigated during the dry season, thus crops can be grown the whole year round. In this case study, sweet potatoes are the main cash crop grown on the irrigated fields during the dry season. The vines can be transplanted to the fields during the beginning of the rainy season, resulting in a better productivity of the crop. Peanuts and cucumbers are other cash crops grown on the irrigated fields.
Additionally, fish are introduced to the pond. These fish, which are caught during fishing for consumption in the flooded rice fields or nearby streams, increase the resilience of the land users: On one hand, they generate additional income and on the other hand, they allow the land users to eat fish the whole year round.
To build the ponds, the land users of this case study benefited from the road construction. The constructer needed soil, and offered to dig a pond for free if they could use the soil. They only dug 2 of the total 4 meters depth of the pond. The land users had to hire someone to dig deeper, as the groundwater level drops below 3 meters soil level during the dry season. The additional benefits from the pond, the fish are introduced as fingerlings when they are caught with the bigger fish. They are fed with termites (around 5 kg of termite nest each day) and with rice bran (1 kg every 3 days). As the pond is only 2 years old, the maintenance activities like digging out the mud did not have to be done yet.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter, the pH is sinking, the area has been deforested a long time ago and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season). and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge that different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Камбодж
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kampong Chhnang
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Roloer pha-er/Bantheay Preal/Tob Srauv (Village)
2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The pond was built in 2012 by the land user.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low soil fertility, lack of water during the dry season, more recurrent droughts due to climate change, leaving the fields bare after the rice is harvested which results in higher erosion and in the loss of soil biota, predominance of rice monocultures, low technical knowledge of the land users about land conservation measures.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Droughts, especially in the early rainy season. Rice seedlings need a reliable source of water.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June to December
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Усжуулалтын менежмент (усан хангамж, ус зайлуулалт зэрэг.)
- гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг, гол, нуур, тэнгис гэх мэт)
- Зөгийн аж ахуй, загасны аж ахуй, тахиа үржүүлэг, туулай үржүүлэг, торгоны хүүхэлдэйн аж ахуй г.м
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- < 0.1 км2 (10 га)
Тайлбар:
There are 4 ponds in the village. They are used to irrigate the rice seedlings if the rainy season starts with delay, or if there is a drought after the seeding. In the dry season they are used to irrigate vegetables. Total area of the irrigated fields is around 1 ha.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S4: Тэгшилсэн ба шаталсан шуудуу, нүх
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

биологийн доройтол
- Bq: биомасс буурах

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Mainly annuals with high water demand are planted.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing of soil, lack of water retention.), change in temperature (More hot days, drying up the soil.), change of seasonal rainfall (Beginning of rain season is unpredictable.), droughts (.Especially detrimental in the beginning of the monsoon.), education, access to knowledge and support services (A lot of agricultural knowledge was lost during the Khmer Rouge Regime.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
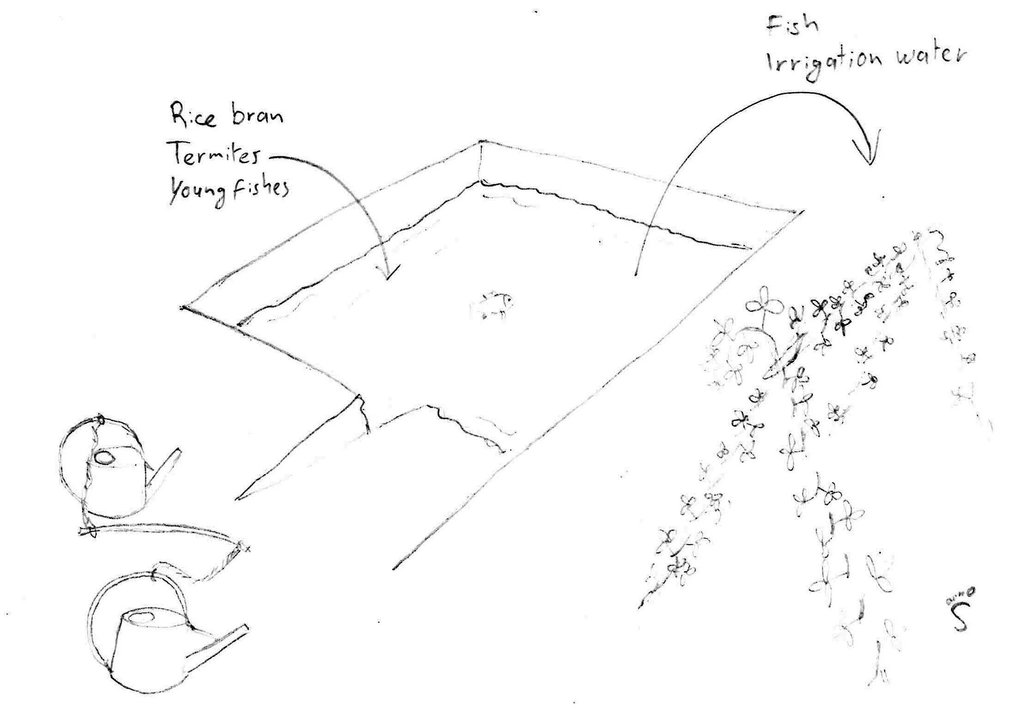
Pond used for irrigation as well as for fish production. In this case two watering cans are used, with a stick between them to transfer the weight to the shoulders.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No field staff was involved.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 12
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 18
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 800m3
Catchment area: ground waterm2
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
5.00
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig the first 2 m | Барилга байгууламжийн | Dry season |
| 2. | Dig the last 2 m | Барилга байгууламжийн | Dry season |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 50.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 100.0 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Catch and select fingerlings in the rice fields and canals. | Барилга байгууламжийн | Every year during wet season |
| 2. | Select fingerlings from catch in local streams to add in pond. | Барилга байгууламжийн | Every year during dry season. |
| 3. | Dig out the pond. Not yet done, as the pond is still new. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 4. | Feed the fish with termites and rice bran. | Барилга байгууламжийн | Regularly. |
| 5. | Fertilize the pond | Барилга байгууламжийн | Yearly in the beginning of the wet season |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | 1.0 | 134.5 | 134.5 | 100.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 134.5 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Fishing traps. 1 costs around 1.2 US$. Fishing net, around 6.5 US$. They had them anyway to catch fish for consumption.
The costs were calculated for one pond, as the area is not relevant.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The most expensive factor is the availability of an excavator to dig the pond.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
1486.45 mm (2013) in Kampong Chhnang
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27-35°C
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: during dry season
Availability of surface water: during dry season
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Handicraft, remittances, factory work
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Тайлбар:
Land users have a title that is not recognized by the state.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Fish
бүтээмж буурах эрсдэл
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Ponds allow the land user to grow crops the whole year round. Furthermore, there are fish in the pond which provide a reliable source of food.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны хэмжээ
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 50 -иас их %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The farmer from this case study got a kind of subsidy: For the construction of the nearby road, the builders needed soil. They offered to dig a pond if they could get the soil. They only dug 2 of the 4 meters of the pond debt, the farmer had to hire somebody to dig out the rest. The other land users who have implemented the ponds also collaborated with construction workers to dig the pond. The lack of money hinders most of the farmers to implement the technology.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Water available in the dry season for cash crops. The rice fields can be used in the dry season instead of being left bare. |
| The rice seedlings can be irrigated during the early wet season in case of drought or erratic rainfall. |
| Diversification of diet and income: fish is available the whole year round. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| As parts of the rice fields are irrigated and planted during the dry season, there is less wind erosion and the soil is improving. |
| The fish feed (rice bran and termites) consists of local resources. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| If flooded the fish can go away. | Nets need to be put around the pond in the wet season. This farmer already does this. |
| Fingerlings are difficult to find. | Find a fish breeder, or breed fish by themselves. Creating niches in the ponds for the offspring, where the bigger fish do not eat it, could do the breeding. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Fingerlings of different sizes and species are put into the pond. The bigger eat the smaller. | Fence off areas for bigger fish, and move the big fish there so they cannot catch the smaller. Or build structures where the smaller fish can hide. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Konhel Pith, Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre LAREC in Kampong Chhnang; khonhel@gmail.com
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна