Introducing tomato varieties using succession planting [Мали]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Dieter Nill
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
Introduction des variétés de tomates d’un cycle cultural échelonné (French)
technologies_1636 - Мали
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Dako Jean Parfait
parfaitdako@yahoo.fr
National Directorate of Agriculture
Мали
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Герман1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/07/2012
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Increasing the revenues of growers through the production of off-season tomatoes
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Tomato production in the off-season is restricted by the prevalence of insects and disease at that time. To mitigate these difficulties, it is important to find sustainable, non-polluting solutions that are accessible to producers. These solutions are: good tomato growing practices, the use of resilient and suitable tomato varieties, and biological control. Some varieties of off-season tomatoes have produced well and shown a certain resilience to diseases and other pests (nematodes and aphids). Growing tomatoes off season also means the market can be supplied when such produce is lacking.
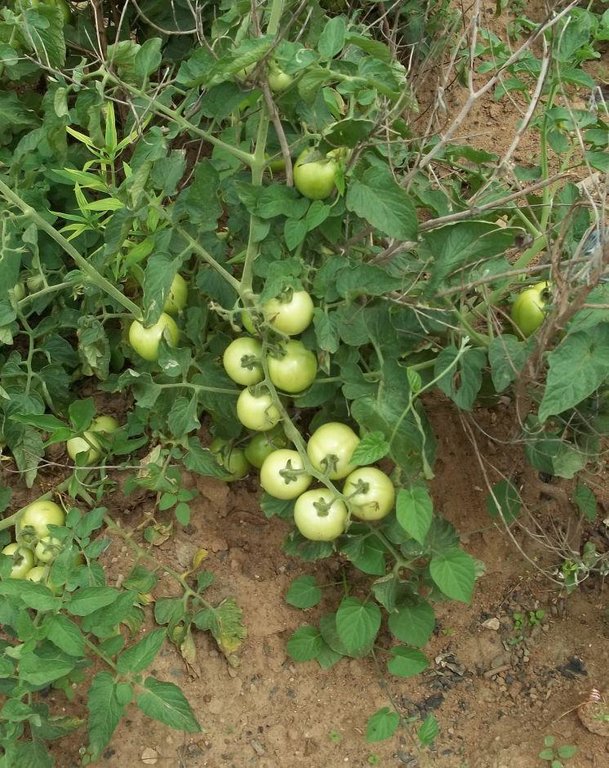
The specific objectives of growing off-season tomatoes are: promoting market garden production during the off-season; reducing the scarcity of tomatoes in the off-season; increasing the revenues of growers. The average yield obtained from each crop is around 15,500 kilograms per ha, with yields peaking at 35,500 kilograms per ha in some places.
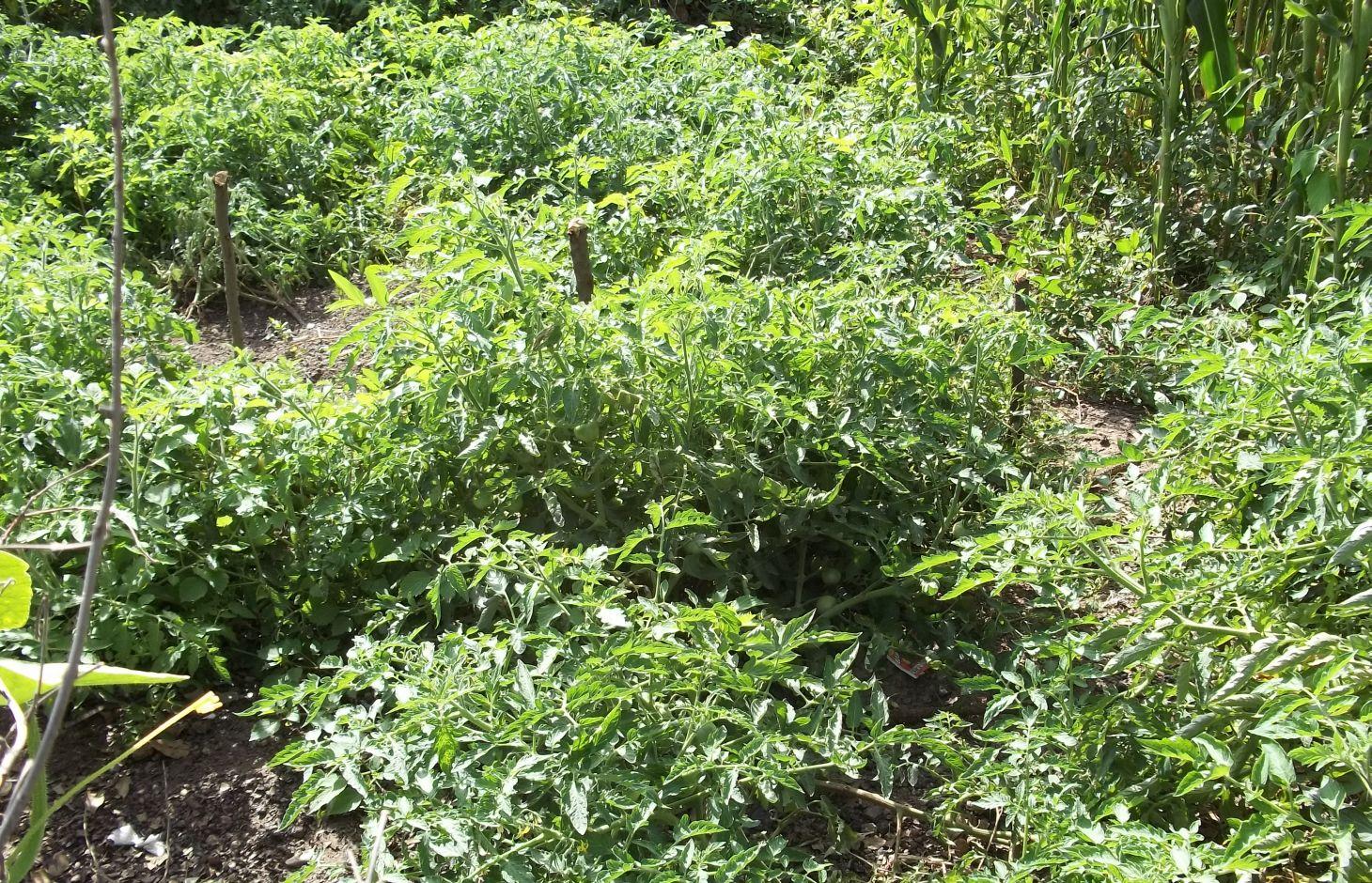
Implementation: 1) Select a site for the nursery that is near to a water source. Clean and turn the soil in the plot. The insects and weeds in the soil often pass on disease to young nursery plants. It is therefore necessary to disinfect the soil. Manure must be worked into the soil or compost prior to disinfection. In the week prior to treatment, the nursery soil must be kept sufficiently moist. Growers can disinfect their soil with fire, hot water, or chemical products. 2) The way a bed is prepared depends on the season. In the dry season, the nursery bed is sunk into the ground so that it holds water better. In the rainy season, the nursery bed is raised (mounded) to prevent waterlogging and promote good drainage once the rains have abated. 3) Seed requirement: Two to three grams for each 100-square-metre plot. Fresh market tomatoes: 300 grams per hectare. Industrial tomatoes: 400 grams per hectare. 4) Fertilisers are optional. During sowing, they can be applied in small quantities in soluble form. Alternatively, three kg of well-rotted manure can be applied per square metre. 5) Protecting plants: Combat leafminers and prevent damping off by applying authorised plant health products. Cover the nursery with a mosquito net until the seedlings are planted out. 6) Seedbeds are laid out in rows 15 to 20 centimetres apart. The seeds are sown along one-centimetre-deep furrows or simply scattered. Seed density should be 100 per linear metre, i.e. 500 per square metre. The seeds are then covered with earth or fine sand. The beds are covered with straw, which is removed as soon as the seedlings sprout. Duration of nursery stage: three to four weeks. 7) Healthy and strong plants with at least six proper leaves are planted out. The distance required between plants varies according to the season, growing conditions and varieties in question: 80 x 60 cm; 80 x 40 cm; 60 x 60 cm; 60 x 40 cm. When transplanting plants, compact the earth around the roots. Each plant must be carefully extracted along with the clump of earth its roots are embedded in. Dig a hole in the bed and insert the plant. Plants are planted in raised beds or mounds in the rainy season and in the beds or flat ploughed ground outside of the rainy season. Transplanting should be carried out at the end of the day, when it is cooler. Water plants immediately after planting them out. Whatever the growing season, it is best to cover young, freshly transplanted plants with a straw cover providing adequate shade. If some plants die, replace them with others held in the nursery. 8) How to prune tomato plants: Remove buds growing between the leaf and the stalk. Retain only one or two thick stalks with their leaves and their flowers. Pruning should be carried out once or twice a month. Prune tomato plants whose fruit will be used for industrial purposes or canned (determinate tomatoes may not be pruned). From time to time, remove suckers (a side shoot from an axillary bud) when weeding and hoeing. For fast-growing varieties, retain just one thick stalk. 9) The quantities of chemical fertiliser to apply vary as follows: 40 to 120 kilograms of nitrogen per ha, 30 to 90 kilograms of phosphate per ha, and 30 to 90 kilograms of potash per ha. Never spray fertilisers on young or wet plants as this will burn them. An alternative is 20 to 30 tonnes of organic fertiliser per ha 10) Plant care: Plants must be watered regularly (morning and evening), particularly during fruit formation. The water quantities are then reduced towards the end of the growing cycle. Weed and hoe regularly, especially in the early stages of planting. Stake the tomato cultivars before they begin forming fruit. This will stop the fruits touching the ground. Using mulch provides better quality fruit.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Мали
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Mali
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kayes, Koulikoro, Sikasso, Ségou, Mopti, Bamako
2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Ongoing for three years
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Tomato production in the off-season is restricted by the prevalence of insects and disease at that time, scarcity of tomatoes in the off-season
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August-November
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Хортон ба өвчний нэгдсэн менежмент (органик газар тариаланг хамруулна)
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.75 m2.
The succession planting programme for the 2010/11 and 2011/12 growing seasons covered a total of 40 circles in six regions (Kayes, Koulikoro, Sikasso, Ségou and Mopti and Bamako District). Farming advisors cascaded training to 1,200 producers who own succession-planted plots. Each succession plot is 400 square metres in size. In total, 75 hectares have been sown by producers.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
Тайлбар:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

биологийн доройтол
- Bp: Хортон шавьж/өвчлөл ихсэх, махчид цөөрөх
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (insects and diseases)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
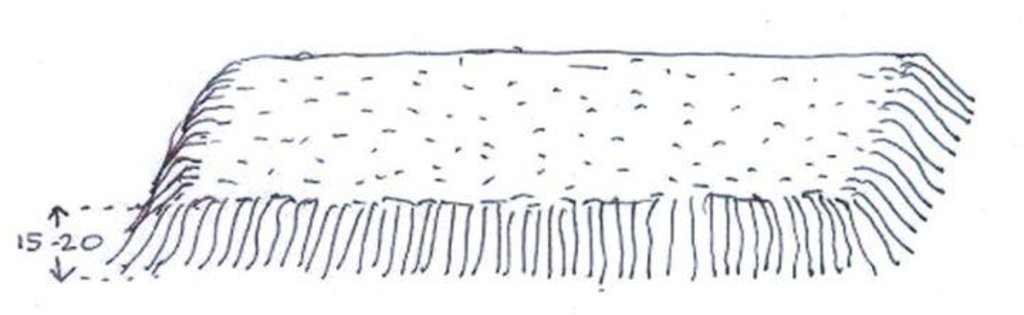
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Raised bed (15 to 20 centimetres high). In the rainy season, the nursery bed is raised (mounded) to prevent waterlogging and promote good drainage once the rains have abated. In the dry season, the nursery bed is sunk into the ground so that it holds water better.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), use of resilient and suitable tomato varieties
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a site for the nursery that is near to a water source | Ургамлын | |
| 2. | disinfect the soil | Ургамлын | |
| 3. | sowing of seeds | Ургамлын | |
| 4. | Fertilisers are optional. During sowing, they can be applied in small quantities in soluble form | Ургамлын | |
| 5. | Cover the nursery with a mosquito net until the seedlings are planted out | Ургамлын |
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Healthy and strong plants with at least six proper leaves are planted out | Ургамлын | |
| 2. | When transplanting plants, compact the earth around the roots. Each plant must be carefully extracted along with the clump of earth its roots are embedded in | Ургамлын | |
| 3. | Dig a hole in the bed and insert the plant. | Ургамлын | |
| 4. | Water plants immediately after planting them out | Ургамлын | |
| 5. | cover young, freshly transplanted plants with a straw cover providing adequate shade. | Ургамлын | |
| 6. | If some plants die, replace them with others held in the nursery | Ургамлын | |
| 7. | prune tomato plants | Ургамлын | |
| 8. | Plants must be watered regularly (morning and evening), particularly during fruit formation. | Ургамлын | |
| 9. | Weed and hoe regularly, especially in the early stages of planting. Stake the tomato cultivars before they begin forming fruit | Ургамлын |
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Economic analysis of off-season tomato production from 2012 to 2013:
Total area sown with off-season tomato: 175 hectares
Quantity of off-season tomatoes grown: 4,300 tonnes
Price of tomatoes grown in season: 170 to 200 CFA francs per kilogram
Price of tomatoes grown off season: 600 to 800 CFA francs per kilogram
Each grower produces an average 650 kilograms on a succession plot, with some producing up to 1,400 kilograms. Produce from the plots has earned growers between 300,000 and 630,000 CFA francs (gross) over the winter season, with 75% of production sold at 600 CFA francs per kilogram.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are very poor.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Тайлбар:
The irrigated land is allocated by the chief
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Some varieties of off-season tomatoes have produced well and shown a certain resilience to diseases and other pests (nematodes and aphids). Growing tomatoes off season also means the market can be supplied when such produce is lacking. The average yield obtained from each crop is around 15,500 kilograms per ha, with yields peaking at 35,500 kilograms per ha in some places.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | сайн |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| some varieties of off-season tomatoes have produced well and shown a certain resilience to diseases and other pests (nematodes and aphids). |
| reduction of the scarcity of tomatoes in the off-season |
| Growing tomatoes off season also means the market can be supplied when such produce is lacking |
| The possibility of selling tomatoes during the winter season is very useful for restarting and increasing production. Growers are very enthusiastic about the technology. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| availability of inputs and farming advisors for carrying out the practice |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
DNA (2012): Data sheet on growing off-season tomatoes
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
DNA (2013): Detailed report, West Africa Agricultural Productivity Program (WAAPP)
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна