Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd production [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Karela kheti ma thopa sinchai ko satha ma pasu mutra ko prayog (Nepali)
technologies_1751 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Director
+977 1 5520314
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Harihar Bhawan, Lalitpur
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Team Leader
+977 1 5543591
ssmp@helvetas.org.np
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
GPO Box 688, Kathmandu/Nepal
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
10/11/2008
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
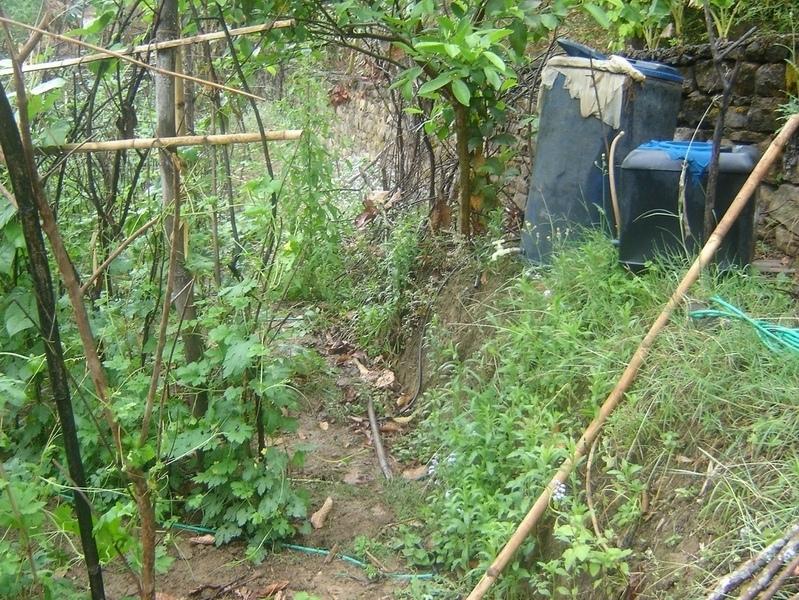
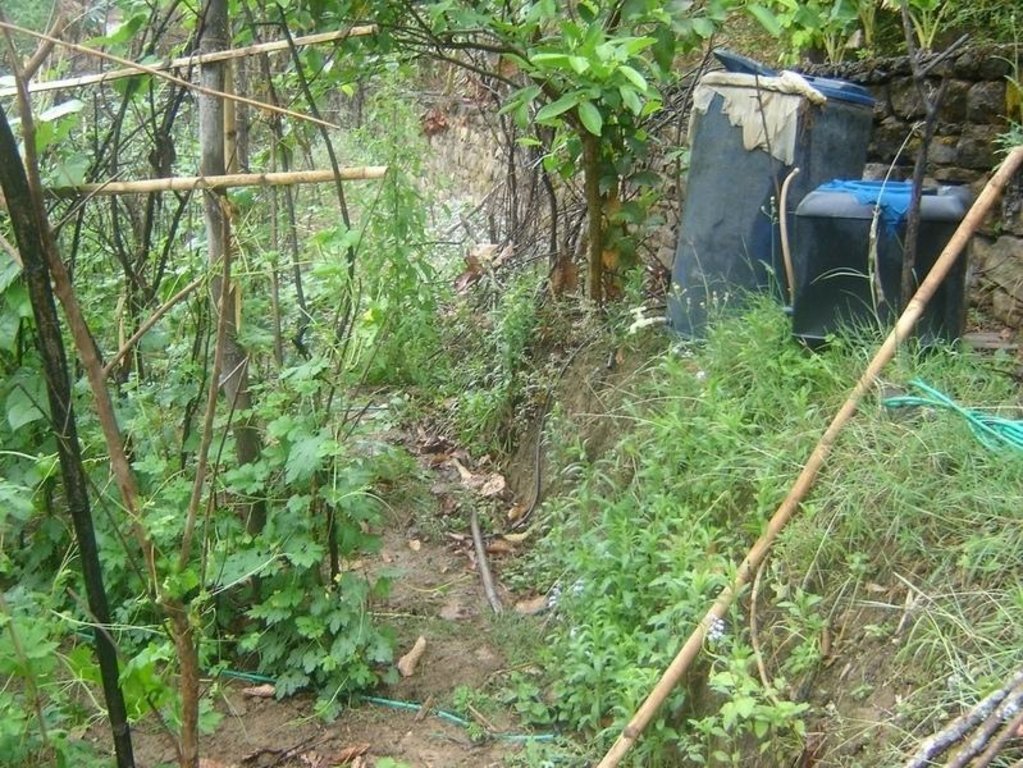
Bitter gourd vegetables fetch a high price in the off-season and respond well if grown with drip irrigation. This crop is planted in December/January and harvested from May through to July/August. The growing period mainly falls in the driest period of the year and therefore requires irrigation.
In addition to water, the plants need fertiliser to ensure healthy growth and good production. Nitrogen is the most important macronutrient for plants and high crop productivity can only be achieved if sufficient nitrogen is available. Nitrogen is also the most limiting nutrient in most areas of Nepal’s midhills. Traditionally farmers applied farmyard manure; but in many places this is being supplemented or entirely replaced by inorganic fertiliser, mainly urea. However, fertiliser prices have increased substantially in recent years and this type of fertiliser is often not available in
sufficient quantities in areas away from the roadheads. At the same time cultivation practices are intensifying with greater cropping intensities and more nutrient demanding crops as local varieties are replaced by hybrids and new crops are introduced. This can easily lead to nutrient mining and soil fertility decline unless there is an equivalent increase in inorganic or mineral fertilisation.
Cattle urine is a viable alternative to mineral fertiliser; it is nitrogen rich. The urine is collected in improved cattle sheds (fact sheet on urine collection QT NEP1). For constant fertiliser application and to reduce the water requirement, the collected urine can be added to the irrigation water in the drip irrigation tanks (fertigation). Farmers who have tried this say it has increased the yield of bitter gourd and other cash crops, in some cases by as much as 100%. Other crops that can be grown using drip irrigation with a water-urine mixture are cauliflower, cucumber, and other types of gourd.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Midhills districts of Nepal
Map
×3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil
fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through
excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams,
ponds, or groundwater. Also, irrigation water is in short supply during 6 to 8 months of the year. Fertigation allows about
20 to 30% of the irrigation water to be replaced by urine.
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Хөрсний үржил шимийн нэгдсэн менежмент
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
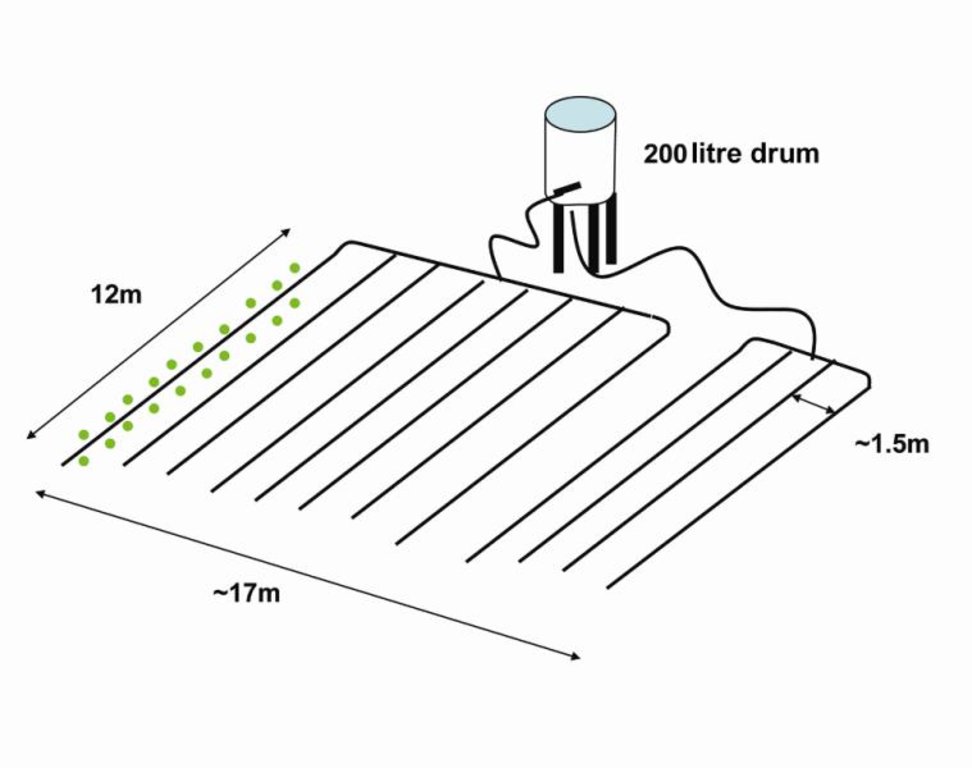
The following setup was used in Iman Singh Basnet’s fi eld:
- two drip irrigation sets: one set with
8 lines, one with 4 lines
- a 200 l plastic drum
- 20 bitter gourd plants per line with
1.5m spacing between lines
- approximate area covered: 200m2
Note that the drum was not delivered with the drip irrigation set. Mr Basnet uses the same drum for irrigating other crops where drip irrigation is not feasible, in which case he connects a pipe with a rose to the drum.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: supplementary irrigation, constant and slow supply of nutrients, increase in soil fertility & increase in soil productivity
Secondary technical functions: pest control
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
Drip irrigation system
Эзэлхүүн, урт зэргийг тодорхойл (тохиромжтой бол):
200 l plastic drum; 20 bitter gourd plants per line with 1.5m spacing between lines
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.00
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare and place stakes | Менежментийн | |
| 2. | Collect urine (see WOCAT fact sheet ‘Improved cattle shed for improved urine collection – QT NEP1) | Менежментийн | |
| 3. | Grow bitter gourd seedlings | Менежментийн | |
| 4. | Set up drip irrigation set and prepare field | Менежментийн | |
| 5. | Transplant seedlings | Менежментийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Collect urine and prepare irrigation system | persons/unit | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Drip set | unit | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Drum | unit | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Stakes | unit | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 50.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear drip holes | Менежментийн | |
| 2. | Double filter the urine – once when taking out of the collection tank, and again when pouring into the drip irrigation tank | Менежментийн | |
| 3. | Irrigate every alternate day with 160 l water and 40 l urine. | Менежментийн | |
| 4. | Fix shoots to the stakes | Менежментийн | |
| 5. | Raise ridges for better irrigation efficiency | Менежментийн | |
| 6. | Harvest the crop | Менежментийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintain drip irrigatio nsystem and apply urine | persons/unit | 15.0 | 2.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 30.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Cost calculated in January 2007.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Landforms: Also valley floors
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
reduced expenses for agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Allows organic production of high value crops
establishment costs
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
social prestige as a progressive farmer
requires handling of dung and urine
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
application of agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides)
eutrophication, nitrification of water bodies due to uncontrolled outflow of urine
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
reduced influx of nutrients into water bodies
dependence on costly external inputs
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
The high cost of mineral fertiliser and the high price that bitter gourd fetches means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, a major reduction in fertiliser costs and improved income leads to increased benefits.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 90-100 %
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Some farmers in Surkhet district started to use the technology in 2006, after seeing Iman Singh Basnet's innovation of applying urine through drip irrigation in 2005.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Urine as a liquid manure is applied at the same time as irrigation (fertigation) How can they be sustained / enhanced? The link between urine application and drip irrigation or other forms of small scale irrigation needs to be promoted |
|
The on-farm use of collected urine reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thereby reducing cash expenditure and outside dependency How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the technology to increase this impact |
|
Human urine can also be used, but needs to be fermented longer and may be socially less acceptable How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the use of urine and show that there is no problem with using human urine |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The initial establishment costs for a drip irrigation set may hinder adoption |
Prepare a business plan and calculate the cost-benefi t to convince farmers of the technology’s benefi ts |
| Lack of availability of urine may inhibit the commercial application of urine with drip irrigation | Urine needs to be established as a tradeable good produced by livestock farmers and bought by vegetable farmers to apply to their crops |
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна