Legume integration [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Bali pranali ma kosebali samabesh
technologies_1753 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Director
+977 1 5520314
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Team Leader
+977 1 5543591
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
11/05/2008
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
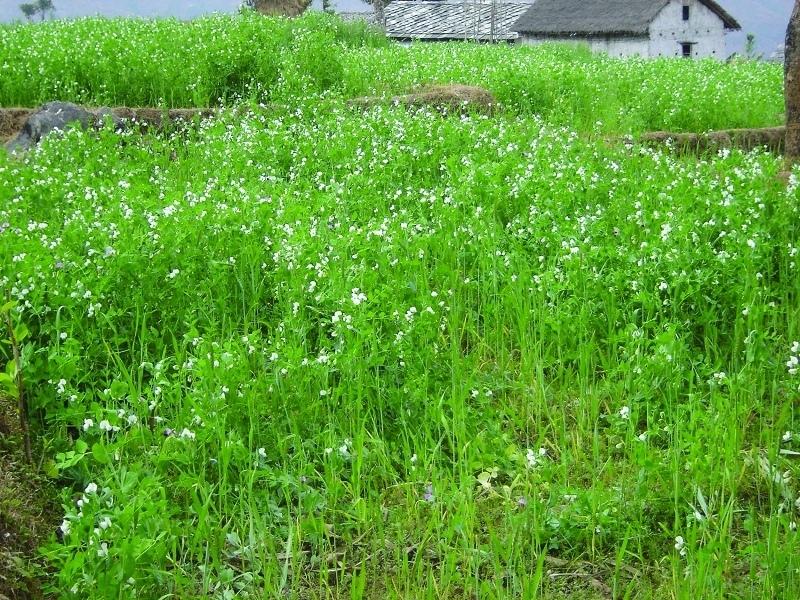
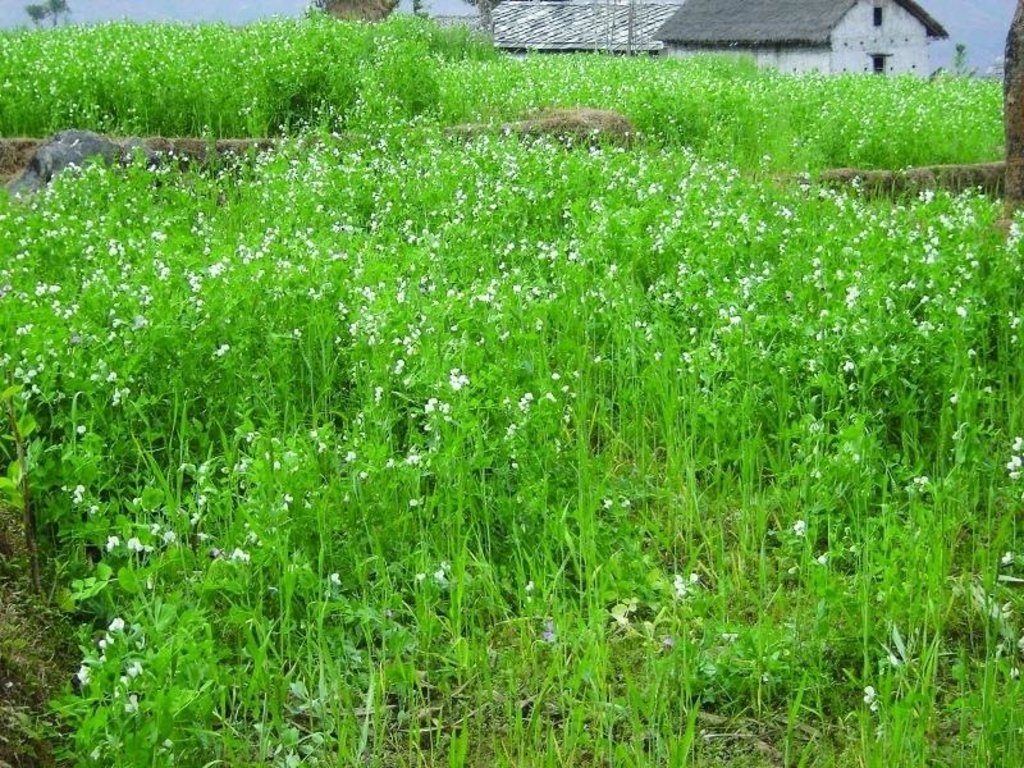
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Legumes are widely grown across the hills of Nepal, with the most common being soybean, lentils, black gram, cow pea, beans, horse gram, field peas, and rice bean. They are mostly intercropped or relay cropped with cereals such as maize, millet, and rice. They are also planted on the edges of terraces and rice paddy bunds. Depending on the species, they may be grown in rain-fed or irrigated fields during the winter or summer seasons.
The majority of the legumes grown by farmers are used for food or as a cash crop. The planting of fodder legumes has become more popular with the expansion of stall-feeding and the development of a dairy industry. The planting of legumes, with the main objective of improving soil fertility is a more recent development in Nepal’s hills.
Nitrogen is the main plant nutrient element and is usually applied through commercial fertiliser where available. Legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen through bacterial nodules on their roots, then nitrogen subsequently becomes available to the following crops. It is important, therefore, not to uproot the legume crop during harvesting - it should be harvested by cutting the above ground parts leaving the roots (and the nodules) in the soil. The crop residues can be fed to livestock, used as animal bedding, applied as green manure directly to fields, or incorporated in compost. In this way most of the nitrogen that was fixed by the legume crop is returned to the soil.
Details about the different legume species and their different characteristics and uses are described in detail in SSMP, PARDYP and SSD-NARC (2000).
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Midhills districts of Nepal
Map
×3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- improve soil fertility
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil
fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) the application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems
through excessive leaching, losses of fertiliser in surface runoff, and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams,
ponds, or groundwater.
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Хөрсний үржил шимийн нэгдсэн менежмент
- ургамлын сорт / малын үүлдэр сайжирсан
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
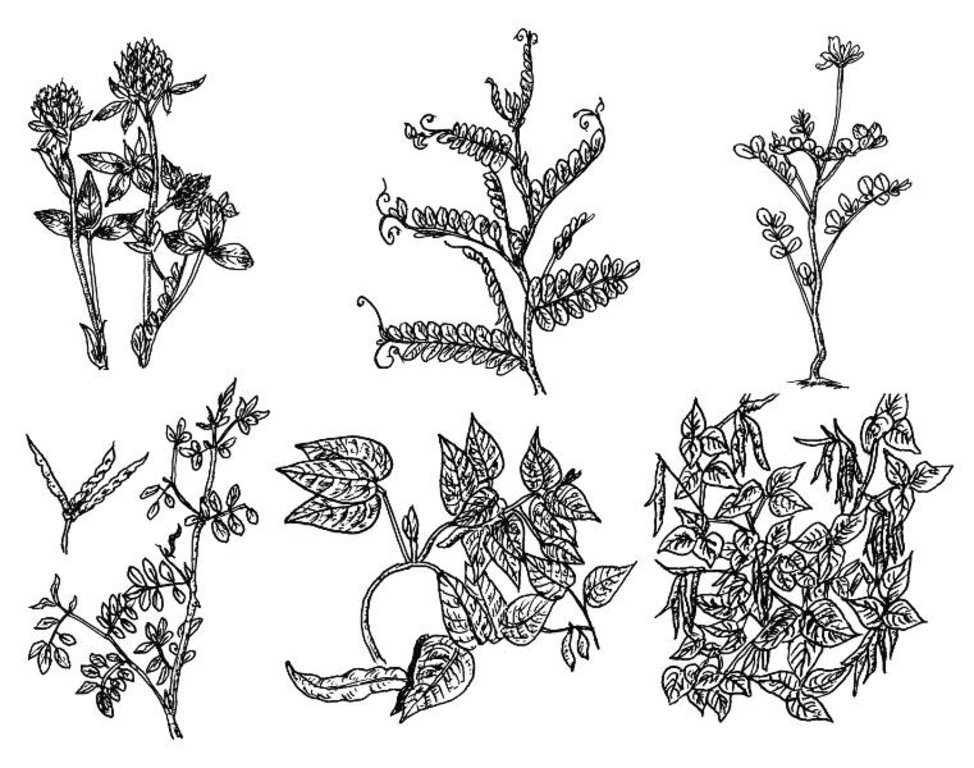
A number of species are presented
in the legume integration decision
support guide (SSMP, PARDYP, SSDNARC 2000). Here only a selection of useful legume species are presented (from top left corner to lower right corner):
- red clover (Trifolium pratense)
- hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth)
- Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus)
- rice bean (Vigna umbellata)
- velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens)
- tephrosia (Tephrosia spp.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in soil fertility (nitrogen in particular), increase in soil productivity & decrease in soil erosionon terrace bunds, nutritius and high value crops
Secondary technical functions: fodder and green manure availability & income
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.00
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | Persons/day | 2.5 | 2.0 | 5.0 | |
| таримал материал | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 6.5 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Depending on the type of farm niche - broadcast, line sow, or spot | Агрономийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
Тайлбар:
Cost as in January 2007
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Slopes on average:Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced expenses for nitrogen fertilizers
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Livestock fodder nutritiousness
Value and nutritiousness of crops
Crop in terms of main yield
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрс алдагдах
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Highly susceptible to diseases and pests
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Application of fertilizer
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced nutrient flux into water bodies
Dependence on outside
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
On average a benefi t of US$ 40 to 50 per ropani can be expected from the production of legume species
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: About 80% of participating farmers used/had adopted the technolog. It has also been adopted by farmers who have not directly participated in SSMP activities.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Cost effective in terms of inputs and management practices in comparison with other commodities |
| Needs less agronomic practices and care (i.e. can be cultivated in zero or reduced tillage) |
| Has multiple uses: food crop, feed crop, fodder, soil building |
| Can be integrated in varying niches on farms and therefore does not need additional land |
| Rich indigenous knowledge exists |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Highly vulnerable to diseases and pests | Skip planting time (i.e. preponing planting of crops to get around life cycle of pests) , use location specifi c species, resistant varieties |
| Very susceptible to waterlogging | Only plant in well-drained soils |
| In high fertility conditions, nitrogen fixing rhizobium does not work leading to less nitrogen fixation | For very specifi c and new species, the soil needs to be inoculated with the correct strain of bacteria |
| Legumes generally do not respond to nitrogen fertiliser | Do not apply nitrogen fertiliser to legumes |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
SSMP (2005) Legume Integration Manual (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
SSMP
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
SSMP; PARDYP; SSD-NARC (2000) LegumeIntegration into Hill Farming Systems, Decision Support Guide Kathmandu: Sustainable Soil Management Programme, People and Resource Dynamics Project and Soil Science Division-Nepal Agricultural Research Council
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
SSMP
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна