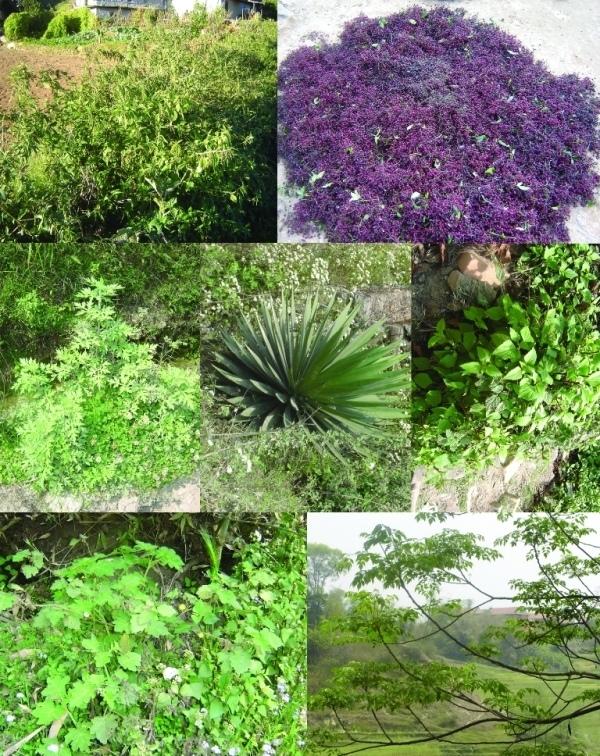
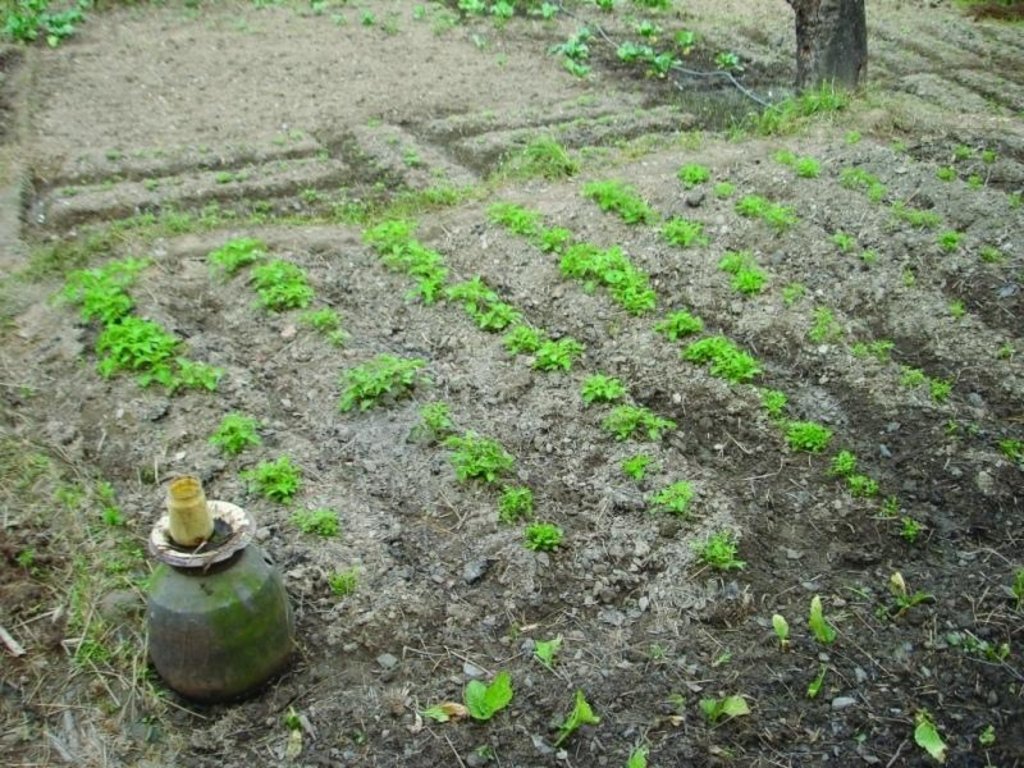
Organic pest management [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: David Streiff
Jaibik rogkira byabasthapan (Nepali)
technologies_1755 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Director
+977 1 5520314
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Team Leader
+977 1 5543591
ssmp@helvetas.org.np
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
06/11/2008
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Promotion of botanical pesticides for organic pest management and liquid manure
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Production of fresh vegetable is often hampered by pests which may reduce production and badly affect farmers’ income. Chemical pesticides are available and are used, sometimes excessively, to combat these pests in parts of Nepal’s midhills. Botanical pesticides prepared from a variety of plant ingredients soaked and fermented in cattle urine provide a suitable alternative to chemical pesticides, at least for subsistence and semi-commercial vegetable producers. These pesticides are based on farmer’s traditional knowledge and are emerging as alternatives to the
application of chemical pesticides.
All the ingredients for these pesticides are available locally; in some cases the plants are considered as weeds. Crofton weed (banmara) grows in abundance along roads and paths, and on forest floors and suppresses the growth of other more valuable species. It is believed to have pesticidal effects and is often used in botanical pesticides. The Nepali names of other plants commonly used in the tonics are asuro (malabara tree), titepati (mugwort), bakaino (Persian lilac), timur (Nepali pepper), patina (field mint), tulsi (sweet basil), neem, sisnu (stinging nettle), ketuke
(century plant), and khirro (tallow tree). In general it is said that herbs and plants that are bitter, pungent, or ‘hot’ or that produce a strong odour are most effective in botanical pesticides.
The botanical pesticide is diluted with water before applying to vegetable crops. The dilution ratio depends on the age and type of the plant being treated with a higher dilution for seedlings in nurseries than for mature plants. While botanical pesticides do not kill all pests, they do combat soft-bodied insects such as aphids and act as a repellent against larger insects like cutworms, various larvae, and red ants. They are not usually effective against plant diseases.
In some places innovative farmers have started to produce and sell botanical pesticides for pest management and as a liquid manure for foliar application.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Midhills districts of Nepal
Map
×3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- Cheaper pest management
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices and the increasing demand for fresh and off-season vegetables have increased the
incidence of pests. These pests are controlled mainly by chemical pesticides where available, and where they are not
available entire crops can be destroyed and farmers’ livelihoods endangered.
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Хортон ба өвчний нэгдсэн менежмент (органик газар тариаланг хамруулна)
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- M7: Бусад
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction in application of chemical pesticides, reduction in application of chemicalfertilisers
Secondary technical functions: supplementary irrigation
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.00
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Different plants with pesticidal properties are collected and chopped into small pieces. Only tenderparts should be used to facilitate decomposition. | Менежментийн | |
| 2. | Other materials like ginger powder, green chilli, ash, and mustard cake are mixed with the chopped plant material | Менежментийн | |
| 3. | The material is placed in a plastic drum or earthen pot and soaked in cattle urine at the rate of about one kilogramme of solid material per 2 litres of cattle urine. | Менежментийн | |
| 4. | The drum is close as air-tight as possible and put in a shady place. | Менежментийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | Persons/day | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Drum | pieces | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 10.0 | |||||
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The botanical pesticide needs to be stirred with a wooden stick about every 15 days. | Менежментийн | |
| 2. | The prepared pesticide is normally ready for field application after about 35-40 days of fermentation/preservation. | Менежментийн | |
| 3. | The pesticide is diluted with water 1:4 (1 part pesticide solution: 4 parts water) for mature plants and 1:8 for nurseries and applied with a jug, sprayer, or broom. | Менежментийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
Тайлбар:
Cost as in January 2007
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
Sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Labor- intensive preparation of botanical pesticides. Need to be prepared fresh for each crop, therefore demanding labor often at inconvenient times
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Pest incedence and destruction of crops
Crop health
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
due to additional fertilizer
Organicproduction of crops
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
Social prestige as use shows user to be a progressive farmer
Acceptance of the fertilizer
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
May not be accepted due to urine in the mixture ( especially if human urine is used)
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Application of agrochemcals
Soil biology health
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduction of chemical pesticide contamination of water bodies
Dependence on oncostly external inputs
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: It is adopted by small to medium scale, 50% of SSMP trained/organised groups and 10% of local farmers from outside the SSMP groups were using the technology.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Organic pest management using botanical pesticides reduce the expense of pest control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the benefits of organic pest management |
|
Organic pest management reduces the negative impact of chemical pesticides How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the benefits of organic pest management |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive preparation often at inconvenient times as the botanical pesticide has to be prepared fresh for each crop and can only be stored for a limited amount of time | Develop methods that reduce labour requirements and highlight possibilities for bulk production and adequate storage without losing effectiveness |
| The reagents that are effective in the botanical pesticides have not been identified |
Carry out applied research into the different reagents and their effect on different pests |
| The botanical pesticides are not effective against all pests | Carry out applied research into and document the effects of different botanical pesticides on different pests |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Neupane, F.P. (2056 BS - 1999/2000) Insect Control by Herbs. Kathmandu: Sajha Publications
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
SSMP
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Several pamphlets on different tonal tonic compositions are available in Nepali from SSMP
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
SSMP
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна