No Till [ОХУ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Peter Liebelt
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Нулевая обработка
technologies_1319 - ОХУ
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
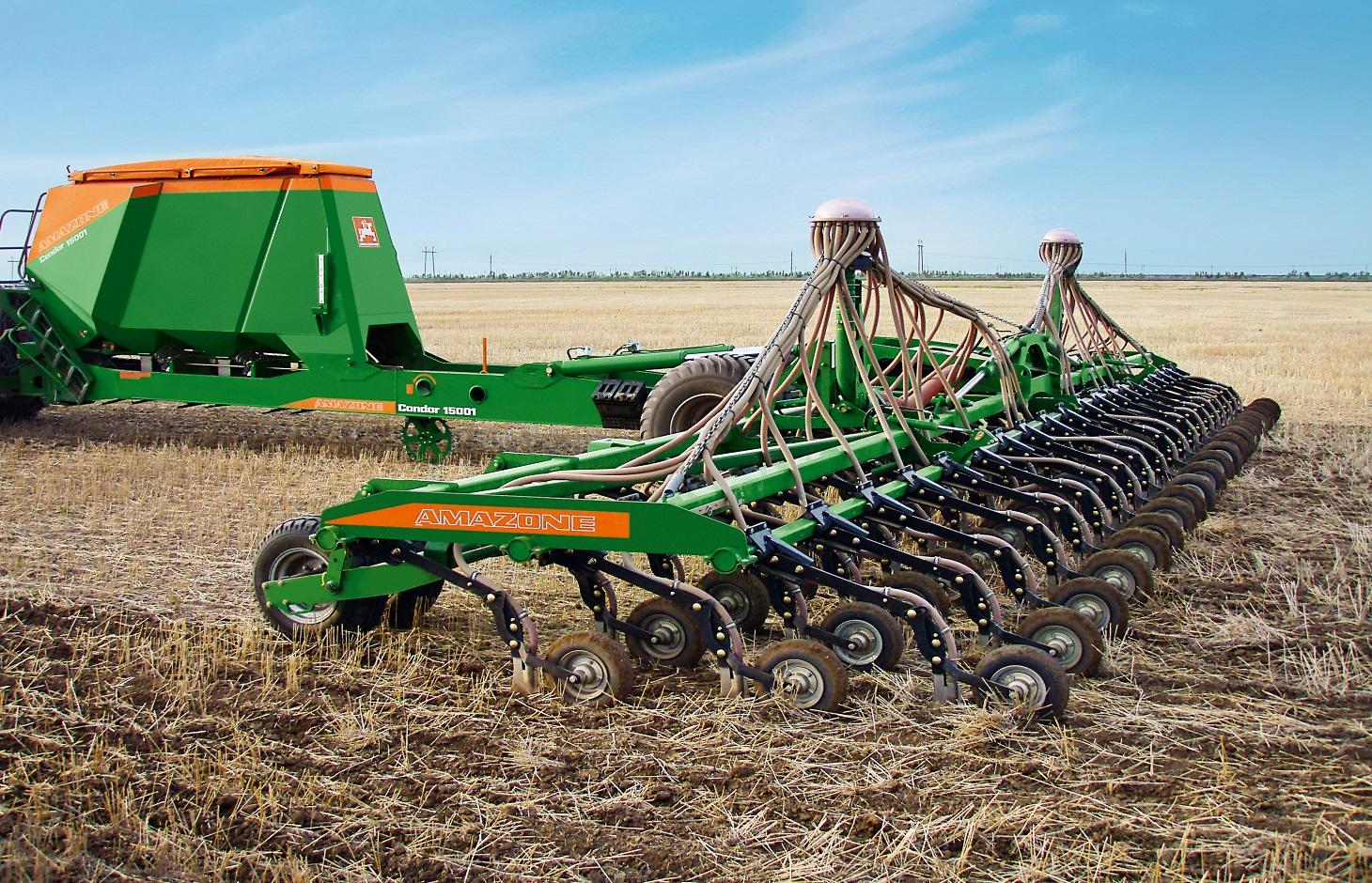
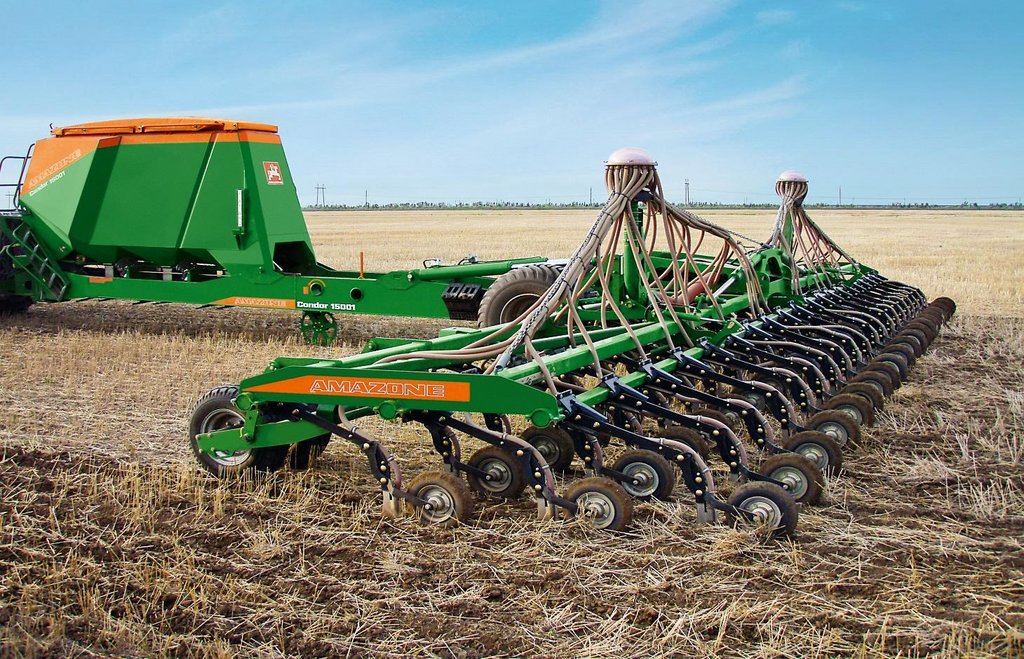
No tillage is based on direct seeding with the innovative/ modern direct seeder Condor and works without any kind of soil disturbance.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
"No-Till" is a key element of the ‘modern cropping system/ Canadian System’ in the Kulunda steppe. In contrast to minimum tillage an innovative modern direct seeding machine is used. The successful implementation of “No-Till” requires an adaptation of the whole cropping system including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. In the study area predominantly spring cereals are grown. The direct seeder ‘Condor tine seeder’ (Amazone) was used for direct seeding. In contrast to the SZS 2.1 seeder used for minimum tillage it has flexible, individually depth-guided tine coulters, which ensure a high precision of seed placement. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the valuable soil moisture remains in the soil, and there is sufficient fine soil to ensure the optimum seed/ soil contact. Straw is safely cleared from the seed furrow, preventing the "hairpinning-effect" which is the pressing of straw by the coulter into the sowing slit. During the sowing period fertilizers are applied and broad spectrum herbicide in autumn and selective pesticides in the growing season are sprayed which help to increase yield.
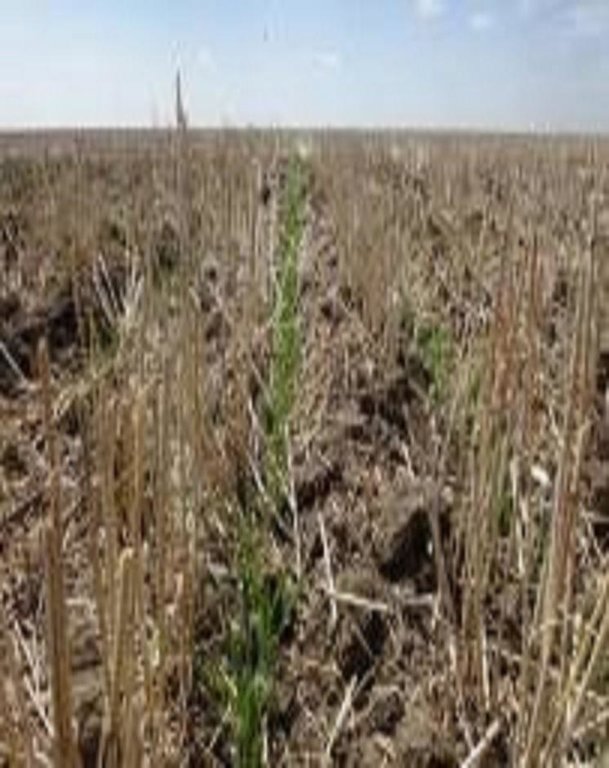
No-till works without intensive primary tillage and stubble cultivation that saves time, fuel and reduces soil water evaporation. No-till increases soil aggregate stability, helps to reduce the risk of soil erosion, leads to a higher soil fertility and reduces soil water losses. Weed control through crop rotation and herbicide application allows to omit mechanical weeding and thus to protect the soil against fertility decline and soil water loss. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under no soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system and until soil organic matter could build up in the soil.
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that no tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The Modern Canadian system caused fixed production costs in form of annual depreciation and also additional costs due to the application of fertilizers and pesticides, the prices of which increased in the last four years. Due to not finalised land rights reforms, uncertain credits and harvest insurance farmers are reluctant to invest in new machines.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
ОХУ
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
Тайлбар:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Since the collapse of the Soviet Union increasingly innovative conservation technologies that are being developed in research experiments are implemented in practice. But the no technology of "No-till" as the most extreme form of conservation tillage is rarely applied in the study area. Thus the tested no-system is highly innovative for the Kulunda steppe.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It's the decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils, topsoil thickness through deflation and soil compaction, which lead to a decrease of soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation and in addition the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation as a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land user that we work with and that implement the our new farming practices have a similar opinion relating the land use problems like the research staff of the project. But there are still a lot of farmer, that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from traditional soil management.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрсийг бага гүнд боловсруулах
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 m2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to our test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha managed by Minimum Tillage; 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах
Тайлбар:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл
- Ed: Хөрсний салхиар үлээгдэх, хуримтлагдах
- Eo: Салхины элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional soil tillage by ploughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow without vegetation cover), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Strong winds and storms - Sukhoveijs - from the southwestern central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cultivated cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production), education, access to knowledge and support services (Need for better know how how to manage no-till systems. Need for more effective measures for knowledge transfer and capacity building.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
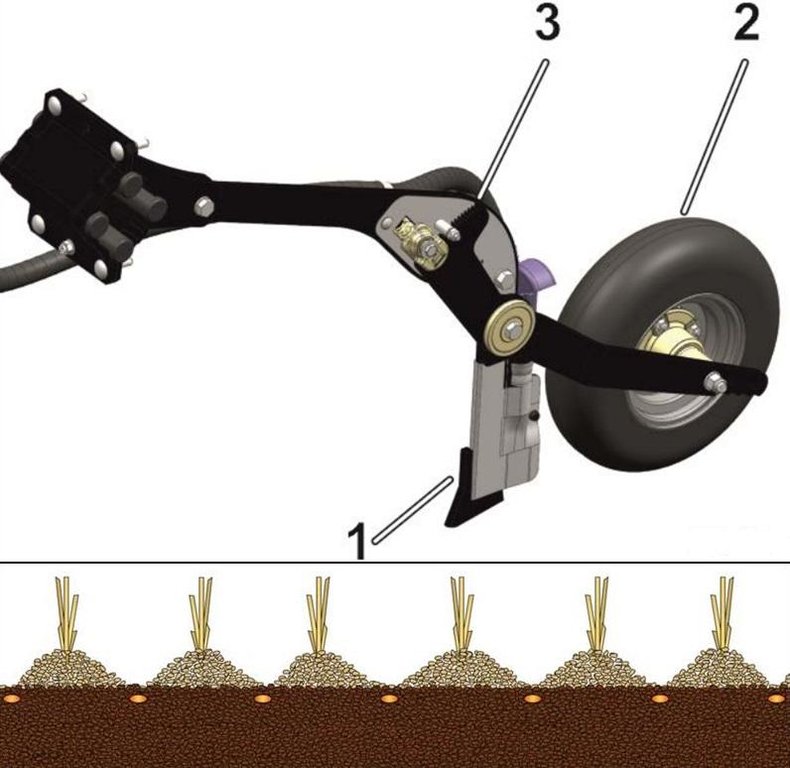
The coulter system of the direct seeder Condor based on an individually depth guided tine coulter. When opening the seed furrow, the narrow coulter moves little soil, so that the soil moisture remains in the soil. The accurate depth control and the packer wheel lead to an optimum contact between seed an soil, which is very important especially in dry regions like the Kulunda dry steppe in Poluyamki. 1-Chisel coulter 2- Packer wheel 3-Air diffuser. Illustration: seed grains placed between the former sowing rows
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Green manure
Material/ species: Pea (once in a rotation)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: 100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg/ha (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-rape
Quantity/ density: 4 years
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Direct seeder Condor (Amazone company)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Direct seeding | Агрономийн | Late april/ early may |
| 2. | Fertilizer application | Агрономийн | |
| 3. | Pest management | Агрономийн | period of vegetation |
| 4. | Harvest | Агрономийн | september |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.12 | 4.12 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 15.96 | 15.96 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | fuel | ha | 1.0 | 25.49 | 25.49 | |
| таримал материал | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 19.37 | 19.37 | |
| таримал материал | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 30.83 | 30.83 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 9.42 | 9.42 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 105.19 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor MTS 1221, Tractor Kirovets K 701, Harvester Don 1500, Direct seeder Condor 15001, Sprayer UX 5200
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
High initial investment in new machines. Compared to the Traditional Soviet System with conventional deep ploughing without fertilizer application fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
- маш чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the in the field of crop production are not so attractive for woman. Traditionally, much more women work in the field of livestock farming.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- том-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Тайлбар:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
бүтээмж буурах эрсдэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Initial costs, first years for herbicides
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
but increase of costs for pesticides and fertilizer, decrease for fuel and labor
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
in general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
ууршилт
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс нягтрах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
There is a lower risk for compaction damage than under under traditional ploughing
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ашигт төрөл зүйл
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
use of herbicide application
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The no-till system works without mechanical weed control, therefore it must be a chemical weed control especially in the first years of no-till system.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
higher content of soil moisture
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms where we have tested the technology of minimum tillage will partly apply this technology on their farming land. But it must be considered that the test farms of the KULUNDA project were interested in conservation technologies already at the beginning at the project and they are able to invest in new machinery to implement the tested SLM technology, that is not representative for the whole Kulunda-region.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. In contrast to the Adapted cropping system (with minimum tillage) the modern Canadian system require new seeding machinery that that means high establishment cost. Therefore the implementation growth is not so significant compared to the adapted system that use already existing Soviet seeding machinery.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through better soil cover |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks. | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation. | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| High initial investment costs for buying direct seeders | share machine and costs with other land users. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна