Vegetated earth-banked terraces [Испани]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joris De Vente
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
Terrazas de tierra vegetadas (Spanish)
technologies_1516 - Испани
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
López Carratala Jorge
+34.950.281045
carratala@cebas.csic.es
Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Estación Experimental de Zonas Áridas (EEZA-CSIC)
General Segura 1, 04001; Almeria; Spain
Испани
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - Испани1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
05/04/2011
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Regional rural development programme [Испани]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joris De Vente
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
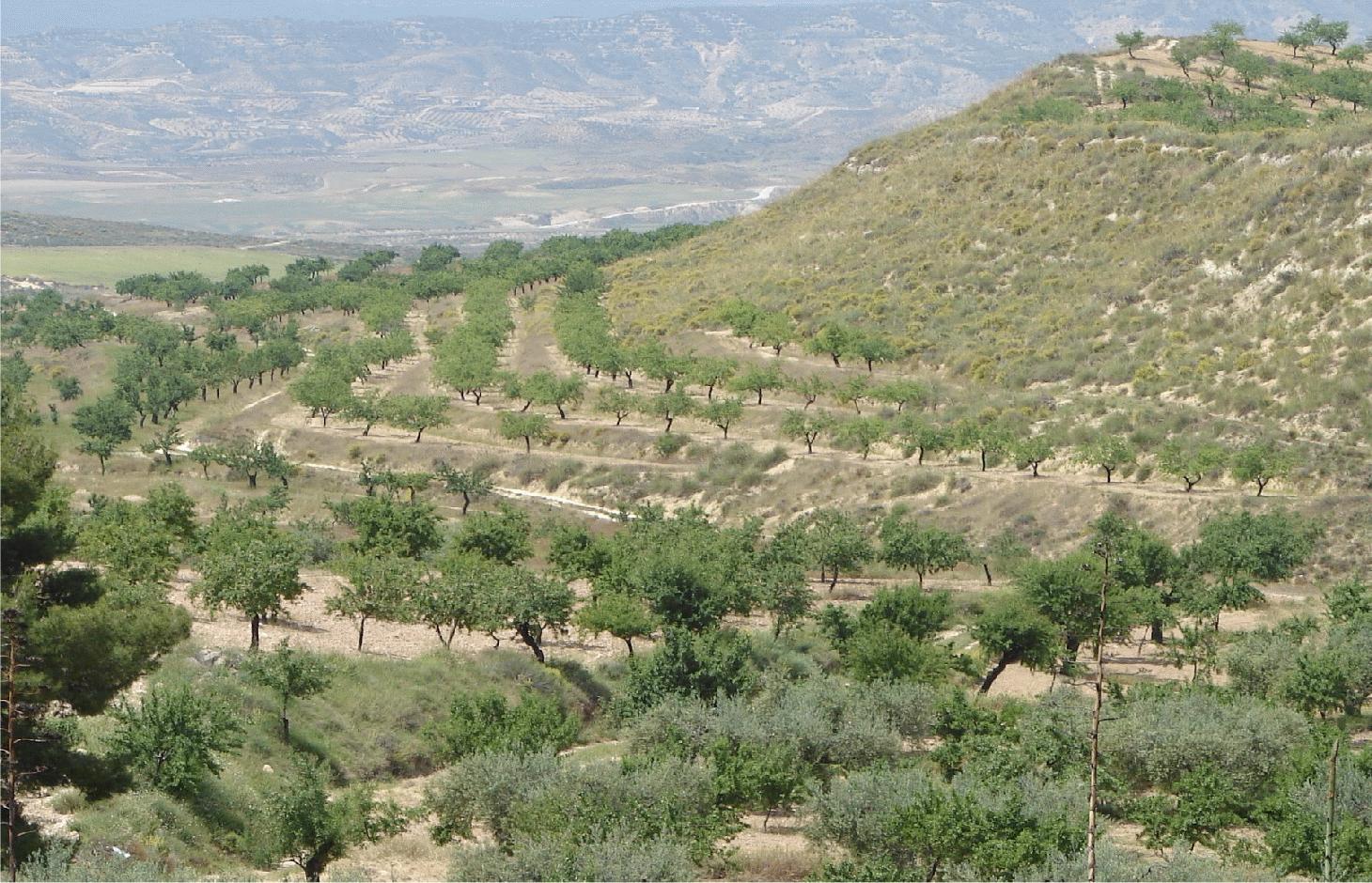
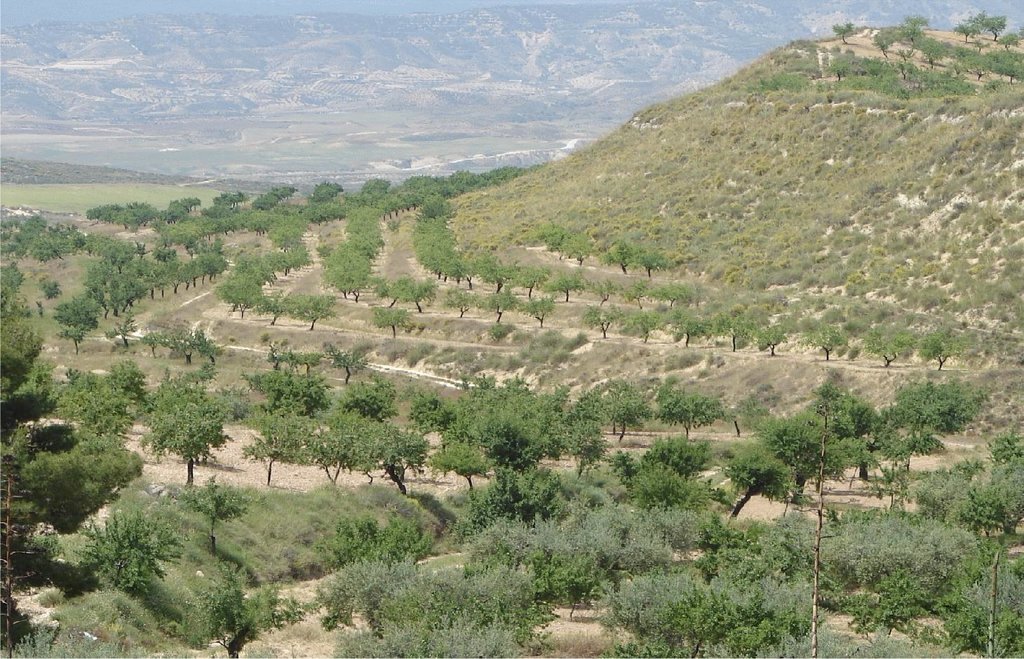
Earth-banked terraces in cereal and almond cropland covered with drought-resistant shrubs.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
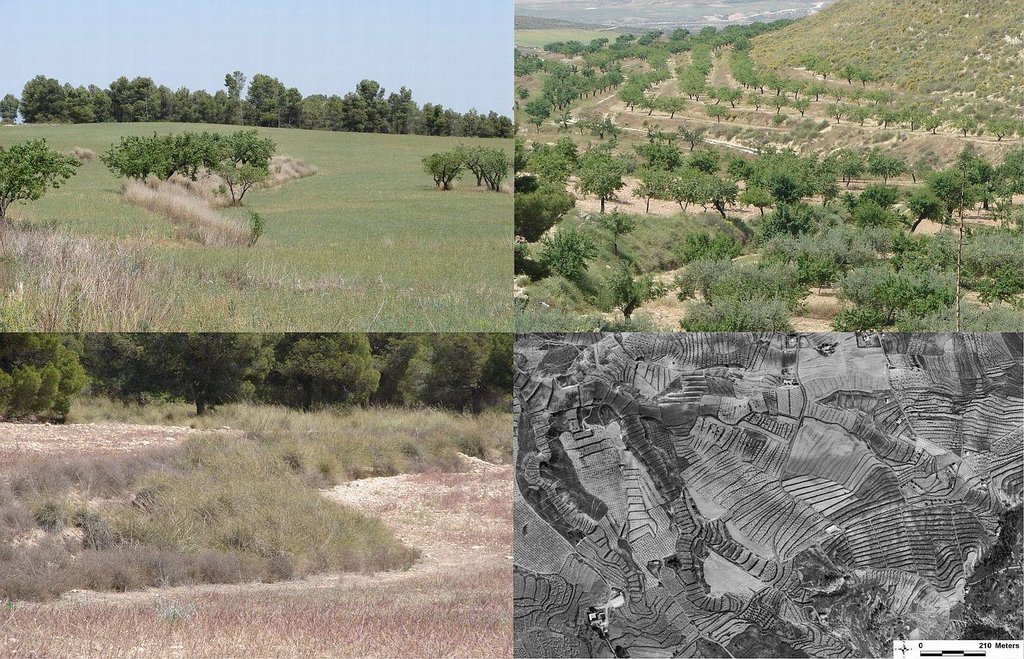
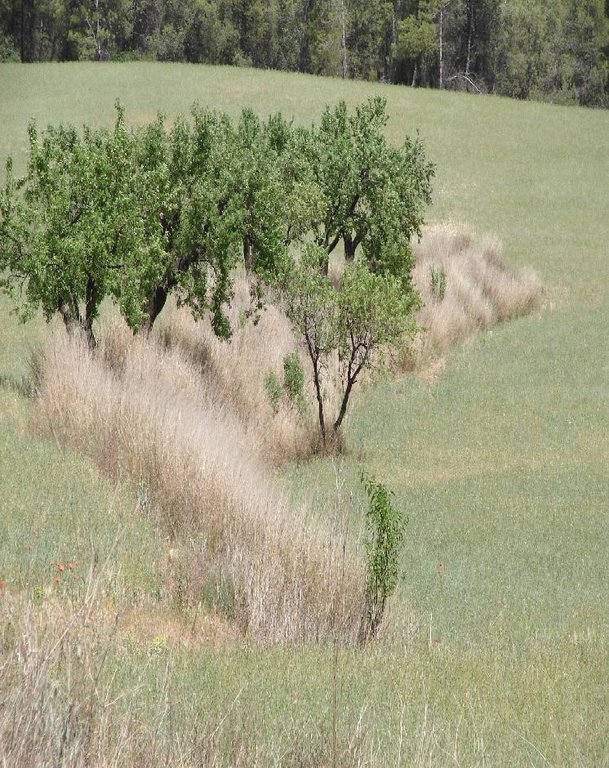
Earth-banked terraces are constructed by carefully removing a superficial soil layer (~10-20 cm) from one part of a field, concentrating it on the lower end of that field in order to reduce slope gradient and length. Another terrace is created directly downslope to form a cascade of terraces. Terrace risers have to be of restricted height (~50-150 cm) to prevent steep and unstable terraces. Stones from the fields can be used to reinforce the terrace ridge. After terrace construction, fields should be gently sloping (<3%) in the direction of the main slope. The distance between terraces must be enough to allow tractor movement during normal cultivation activities and it depends also on the slope gradient. The steeper the slope, the shorter is the distance between terraces. Terraces reduce the formation of gullies and retain water from upslope. The terraces are made with locally available machinery (tractor, small bulldozer). The terrace ridges are optimal locations to plant olives, almonds or fruit trees. Moreover, to be most effective, the terrace ridges are vegetated with shrubs adapted to semi-arid conditions and with a good surface cover (>~30%) throughout the year (e.g. Stipa tenacisima, Rosmarinus officinalis, Thymus vulgaris, Ulex parviflorus, Rhamnus lycioides, Pistacia lentiscus). Natural regeneration of vegetation is allowed without limitation on the terrace ridges, so no herbicide application or burning are carried out to remove weeds. Where possible, regeneration should be stimulated by planting the same adapted species in at least 25% of the terrace ridge. Optionally, in the other 75% of the terrace ridge, cereals or other leguminous species can be sown, but should not be harvested or used for grazing.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology reduces flooding, damage to infrastructure and siltation of water reservoirs, while maintaining (or slightly increasing) crop productivity. This is achieved by reducing runoff, soil erosion and hydraulic connectivity through a decreased slope gradient and an increased vegetation cover. The terrace ridge functions as a sink for runoff within fields and reduces runoff velocity. The vegetation leads to increased soil organic matter content below plants, producing an improved soil structure and a higher infiltration capacity. The use of stones from the fields to reinforce the terraces is optional, but facilitates crop production in the fields and makes the ridges more resistant to higher runoff velocities. The technology requires an initial investment in the construction of the terraces. Terraces can best be located on thalwegs and on areas where gully formation is often observed. Maintenance consists of filling up possible bank gullies developed in the terraces after important rainfall events and, if needed, substitute decayed shrubs with new ones.
Natural / human environment: The technology is generally applied on soils of shallow to medium depth (20 – 60 cm), and slopes are gentle to moderate (5-15%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, peaking in summer commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanized and market-oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately-owned.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Испани
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Murcia
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Guadalentin catchment
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Most of the earthen terraces are already much older than 50 years. Recently, the regional administration is promoting clearly defined vegetated strips with minimum dimensions in order to apply for subsidies.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа

Холимог (тариалан/бэлчээр/мод), үүнд. ХАА-н ойжуулалт
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and loss of soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: November to June
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 10-100 км2
Тайлбар:
The exact area is not known, but the technology is widely applied throughout the province of Murcia and the district of the upper Guadalentin.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Almond and cereal fields often have a relatively low surface cover by vegetation during long periods of the year, leaving the soil unprotected against raindrop impact and rill or gully formation), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Reduced infiltration capacity causing runoff and soil erosion), other human induced causes (specify) (Cropping of relatively steep slopes sensitive to erosion because of slope gradient), governance / institutional (spatial planning of land use results in formation of too large fields without field boundaries)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (High intensity erosive rainfall is common), droughts (Dry periods and dry years require higher water availability)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
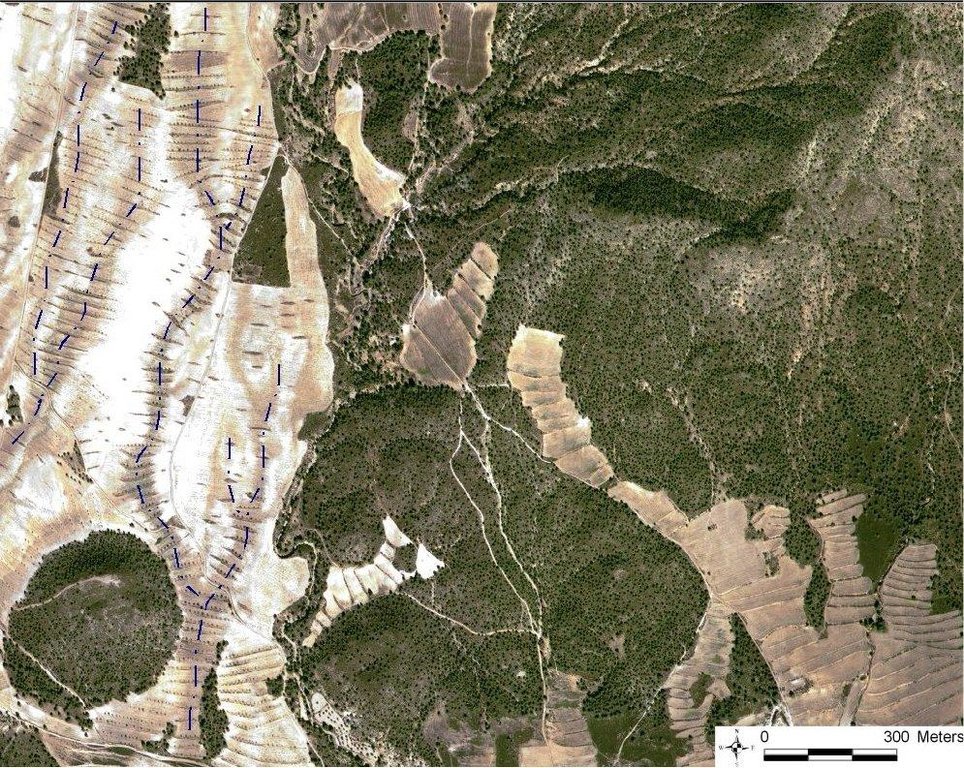
Quickbird satellite image showing the concentration of terraces along natural drainage lines (thalwegs) where runoff concentrates. Drainage lines are indicated with dotted lines.
Location: Torrealvillla. Murcia
Date: Satellite image 2003
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Design of the terraces and selection of the location requires some technical knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Practical implementation of the terraces does not require a high level of knowledge)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 42
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-7
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: alligned: contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): >30% cover
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-100
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Fruit trees / shrubs species: natural regeneration of shrubs with possible additional plantation of almond trees and/or woody shru
Grass species: Natural regeneration assisted by seeding of legiminous species and cereals
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 30-100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-200
Construction material (stone): Only when many stones are present in the fields
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5-15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: <3%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
EURO
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
0.63
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
79.00
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plantation of shrubs and cereals or Leguminous species (optional) | Ургамлын | Autumn - winter |
| 2. | Construction of terraces | Барилга байгууламжийн | autumn or winter |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 270.0 | 270.0 | 10.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 428.0 | 428.0 | 12.0 |
| таримал материал | shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1.0 | 218.0 | 218.0 | 10.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 916.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replace died shrubs (optional) | Ургамлын | autumn-winter |
| 2. | Filling up bank gullies in terraces | Барилга байгууламжийн | twice a year or after heavy rainstorms |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 10.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 10.0 |
| таримал материал | Shrub seedlings and seeds | ha | 1.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 10.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 74.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: For initial construction a large tractor or small bulldozer is required. For maintanance a normal tractor can be used.
The costs were indicated assuming a distance between terraces of 50 meter, meaning two terraces of 100 meter long per hectare. Prices are for spring 2008. Subsidies are foreseen for the installation of the vegetated terraces and for maintenance during at least 4 years if all requirements are fullfilled that are described in the regional development programme.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Price of fuel and labour are the most important determinants of the costs.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
300.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Dry period in summer during 3-4 months (June – August/September)
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хотгор нөхцөл
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Landforms: Hill slopes-footslopes (mostly on concave slope segments)
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: >50m (There is a lowering of groundwater table due to overexploitation for irrigation purposes)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (excess: sporadically there are flash floods during extreme rainfall events)
Water quality (untreated): For agricultural use only (irrigation) (groundwater)
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who don’t. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory, or office.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
All cropland is privately owned. Some shrubland or forest is state property. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the Segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Depending on local conditions yield may be the same or increase slightly
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Field paths become shorter, so more tractor movement is required (not more kilometres!)
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Implementation of terraces is considered relatively expensive
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Depends on crop yield.
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less damage to fields due to less gully formation
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less damage to neighbours fields by gullies and flooding
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
There is less damage to fields and to infrastructure due to gully formation and flooding.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
On the long term higher infiltration capacity of the soil
гадаргын урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Vegetation on the terraces increases vegetation cover
хөрс алдагдах
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Provided by the vegetation on the terraces
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Terraces provide corridors connecting fields and provide shelter
ашигт төрөл зүйл
амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
нийтийн/хувийн хэвшлийн дэд бүтцэд учрах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/экстрим үзэгдлийн төрөл | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | муу |
Тайлбар:
The crop type is sensitive to changes in water availability under the semi arid conditions
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Тайлбар:
Implementation of the terraces is relatively expensive. Additionally planting of shrubs is also relatively expensive and requires a subsidy. Once installed, maintenance is not expensive and pays off because of less damage to fields and infrastructure.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 10-50%
Тайлбар:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Terraces are traditionally widespread in the region. Most of them were installed without external support. Nowadays there are subsidies for construction and maintenance of vegetated strips and terraces.
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is acceptance, but it is not growing. In some parts terraces are removed to make larger fields, and some new ones are also constructed. Recently installed subsidies may change this
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The terraces prevent gully formation and damage to the fields and to their neighbours How can they be sustained / enhanced? maintenance is needed and should be promoted. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
This technology is very effective at reducing surface runoff and erosion by reducing slope gradients and connectivity. In addition, it has a water harvesting effect. So it reduces on-site and off-site erosion problems and potentially increases water retention in the fields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology can be enhanced by providing more info and publicity so that existing terraces are maintained. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| It is considered relatively expensive to implement and particularly the optional planting of woody species is considered complicated in dry years | Subsidies for terrace construction and planting of woody species as well as cooperation between farmers to reduce costs of maintenance when subsidies stop. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The technology does not significantly improve farm income and has a significant implementation cost. | Provide information on all the advantages that include many costs for society (including floods, reservoir siltation etc.). The subsidy for implementation already solves the problem of implementation costs. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Garcia-Fayos, P. and Gasque, M., 2002. Consequences of a severe drought on spatial patterns of woody plants in a two-phase mosaic steppe of Stipa tenacissima L. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(2): 199-208.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
internet
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Hooke, J.M., 2006. Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region. Geomorphology, 79(3-4): 311-335.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
internet
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Kirkby, M.J., Bracken, L.J. and Shannon, J., 2005. The influence of rainfall distribution and morphological factors on runoff delivery from dryland catchments in SE Spain. CATENA, 62(2-3): 136-156.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
internet
7.3 Цахимаар олж болох хэвлэлийн холбоос (ж.нь ном, тайлан, видео г.м.)
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
CARM 2008. Programa de Desarrollo Rural de la Región de Murcia 2007-2013 Tomo I. 508pp
URL:
http://www.carm.es/neweb2/servlet/integra.servlets.ControlPublico?IDCONTENIDO=4689&IDTIPO=100&RASTRO=c431$m1219
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Regional rural development programme [Испани]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Joris De Vente
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна