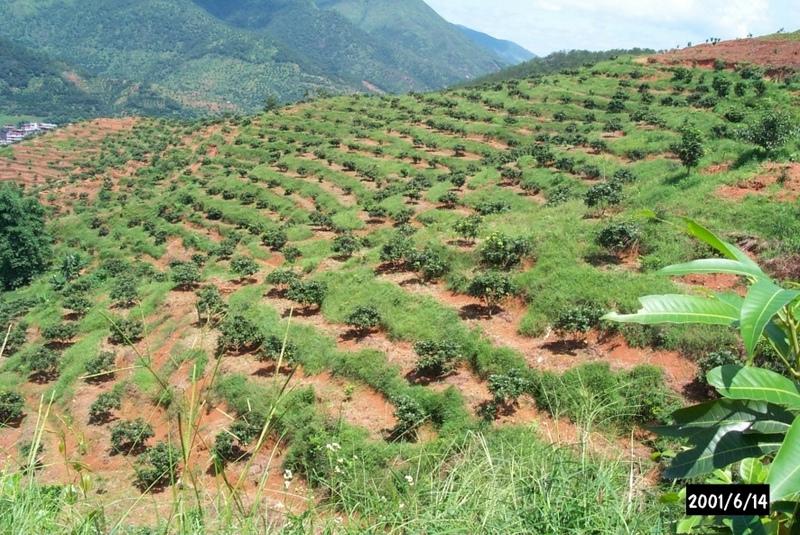
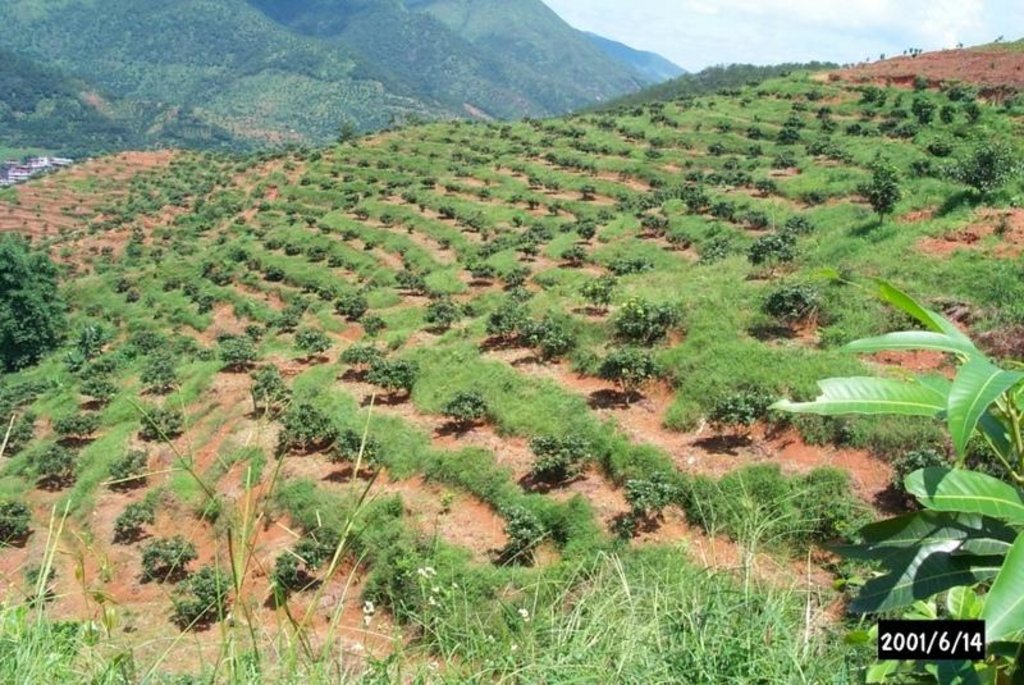
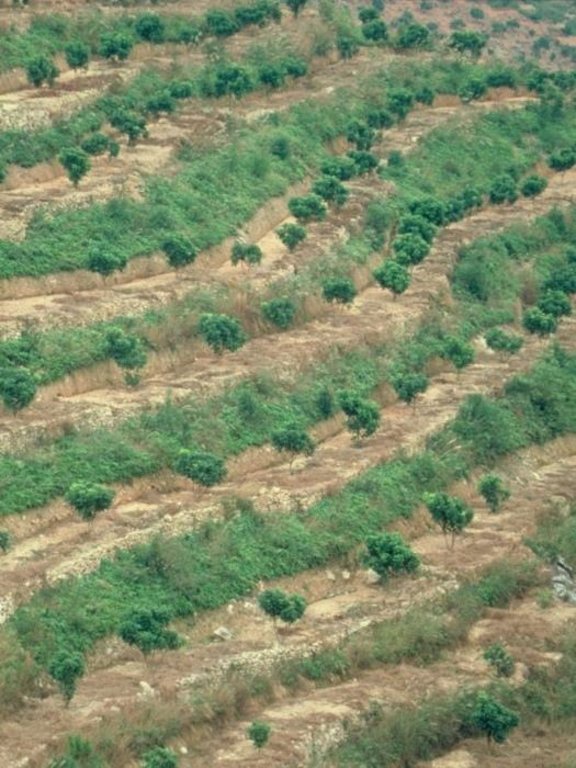
Orchard terraces with bahia grass cover [Хятад]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Zhanguo Bai
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Bahia grass interplanted in orchard
technologies_1106 - Хятад
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Liu Zhengming
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
Хятад
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Nie Bijuan
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
Хятад
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Yang Xuezhen
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
Хятад
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - НидерландТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun (SCOY) - ХятадТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office (Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office) - Хятад1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
16/06/2001
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Rehabilitation of degraded hillsides through the establishment of fruit trees on slope-separated orchard terraces, with bahia grass planted as protective groundcover.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
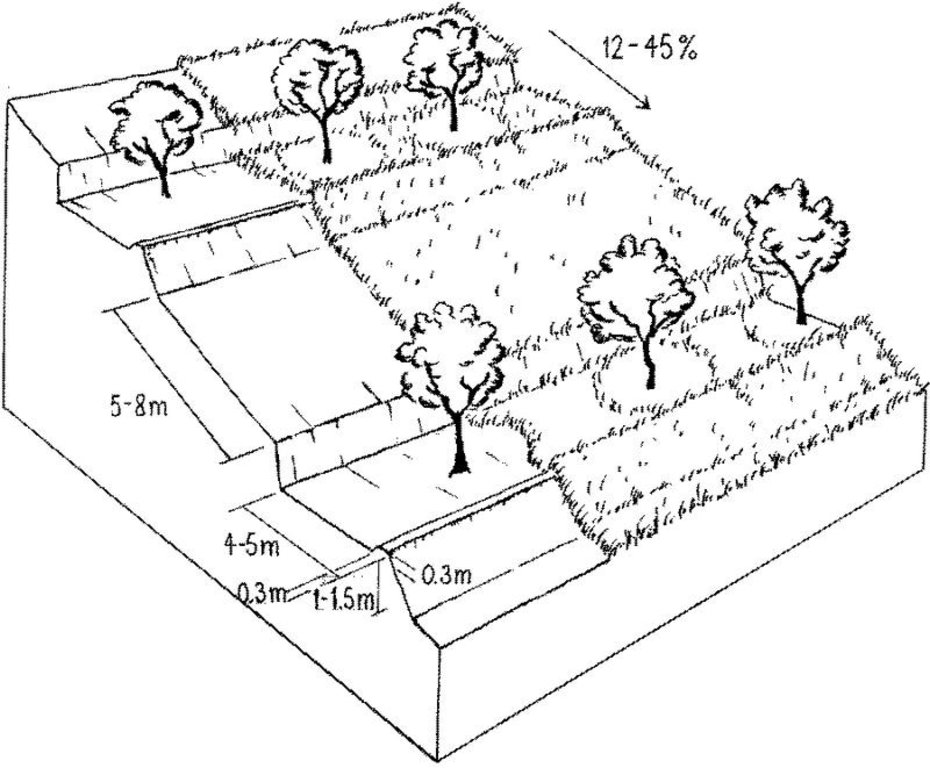
In this case study orchards were established between 1991 and 1992 on degraded and unproductive hillsides (wasteland), with slopes of 12-45%. This was achieved by constructing level beds on the contour, mainly as continuous slope-separated orchard terraces, but in some cases as individual planting platforms. Terrace construction was generally undertaken by hand using hoes and shovels.
Purpose of the Technology: A typical terrace has a 4-5 m wide bed and a 1.0-1.5 m high riser. Commonly, a raised earth lip (0.3 m high) is constructed on the terrace edge to retain rainwater. The terrace riser walls are not protected. Even before terrace construction there was little topsoil and in some places the upper subsoil had been lost to erosion. The establishment of fruit trees (lychee, Litchi chinensis and longan, Dimocarpus longan) therefore required deep planting holes (1 m3), filled with organic matter/manure, into which seedlings were planted. In subsequent years additional large quantities of organic matter/manure were applied in circular trenches to the side of the trees, succeeding trenches being gradually further away as the trees grew. Bahia grass (Paspalum notatum) was planted for SWC purposes as a cover crop, to stabilise terrace risers and to improve soil fertility. It has not been used for fodder in this case. The germination rate of bahia grass seeds is comparatively low; therefore instead of direct seeding, nurseries were established to produce seedlings. The bahia grass seedlings were transplanted onto the terrace risers and beds (leaving a space around each fruit tree) and on the hillside slopes between the terraces. The grass grew and spread quickly, restoring a protective vegetative cover following terrace construction.
Natural / human environment: The primary overall purpose of the technology was to rehabilitate degraded hillsides through the planting of economically valuable fruit trees. Terracing reduces soil erosion while retaining most of the rainwater. The application of organic matter creates improved rooting conditions, while restoring and maintaining soil fertility. The bahia grass further provides protective groundcover preventing splash erosion, increasing surface roughness, and thereby slowing down runoff velocity, while contributing to the restoration of the soil’s biological, chemical and physical properties. Irrigation ditches dug along the terraces help to reduce erosion further. This project was planned by SWC specialists: around 6,000 families were allocated orchard plots and provided with seedlings at a subsidised price.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Хятад
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Fujian Province
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Yongchun County
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The technology comes from the soil conservation theory books and accumulated experiences over years.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
Tree and shrub cropping: lychee, longan

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Жимс, самар
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Degraded and unproductive hillside slopes (wasteland), with low and declining soil fertility, subject to severe soil erosion
(sheet, rill, gully and mass movement) during periods of heavy and prolonged rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low fruit yield and little income after consideration of input.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The farmers\' consciousness of soil conservation are gradually improved and their ability of forest protection are also increased.
Forest products and services: timber, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Constraints of wasteland (before SWC)
Forest/ woodlands: Also nature conservation / protection
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- hillside stabilizing and restoration
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 10-100 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 55 m2.
This is a part of the comprehensive development of Shan Huxi small watershed.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А6: Бусад

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V5: Бусад

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wm: Хөрсний нуралт, шилжилт

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), land tenure (land subdivision)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Fruit trees on slope-separated terraces with a spacing of 5-8 metres between (dependent on slope). Terrace risers and beds are protected by the fast spreading bahia grass (right): note a grass-free space is maintained around each tree.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, control of dispersed runoff
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure
Agronomic measure: organic matter application
Vegetative measure: aligned trees
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: dispersed grass
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: longan, lychee
Grass species: bahia
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 16.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 12.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 9.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4-5
Construction material (earth): Using earth for the construction can reduce investment.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 6%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:20
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: Changing land use patterns - Mountain and hilly areas closure for recover of the forest and grass.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
3.00
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.On each terrace one line of fruit trees was established. Deep planting | Ургамлын | winter of 1991 |
| 2. | 2.Fruit tree seedlings were planted. Spacing between trees was | Ургамлын | spring of 1992 |
| 3. | 3.Bahia grass was transplanted onto the terraced hillside | Ургамлын | spring of 1992 |
| 4. | Terraces were constructed by hand.Soil was excavated from the upper portion of the terrace and used to build up the lower portion behind the terrace riser wall to create a level platform (bed). Part of the excavated soil was used to build a terrace lip. | Барилга байгууламжийн | winter of 1991 |
| 5. | land preparation for the grass planting | Барилга байгууламжийн | winter of 1991 |
| 6. | hill closure | Менежментийн | Nov. 1999 |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1.0 | 840.0 | 840.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Bahia transplants | ha | 1.0 | 435.0 | 435.0 | |
| таримал материал | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 60.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 145.0 | 145.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1840.0 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
NA
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.Digging trenches by the side of the fruit trees and filling with organic | Агрономийн | |
| 2. | prune, fertilize, pest control for the fruit trees of Longan and Litchi | Ургамлын | spring, autumn and winter /3 times/year |
| 3. | grass plantation, fertilizaion | Ургамлын | spring and summer /3 times/year |
| 4. | Filling any gaps in the bahia grass. | Ургамлын | |
| 5. | In the first 1–2 years maintenance also involves replacing any fruit tree | Ургамлын | |
| 6. | Weeding around the trees. | Ургамлын | |
| 7. | Repairing terraces damaged by storms. | Барилга байгууламжийн | after raining season/4 times/year |
| 8. | regular inspection and management | Менежментийн | Jan. 1991 / 6 times/year |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1.0 | 144.0 | 144.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Bahia transplants | ha | 1.0 | 58.0 | 58.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 36.0 | 36.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 84.0 | 84.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | biocides | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 44.0 | 44.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 376.0 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
NA
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel
For establishment: 200 person days for terrace construction, 100 for digging pits and planting trees, 50 for transplanting
bahia grass. For maintenance: 15 person days for terrace maintenance, 40 for digging organic matter trenches, 5 for
bahia grass gap filling. The SWC department produces bahia transplants in nurseries; these are then distributed to the
farmers.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
steep slope and lots of civil work.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
- чинээлэг
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
40% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income is mainly from factory labour
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ажлын хэмжээ
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
input constraints
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
organic matter/manure
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
үндэсний институц
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
rainwater retention
гадаргын урсац
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
70
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
35
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
24.3
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
3
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
erosion due to raindrop splash
competition between fruit trees and bahia grass
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 50 -иас их %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
6593 Households (56 percent of the area)
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 10-50%
Тайлбар:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5755 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
784 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a slow spontaneous adoption of the technology, based on the fact that bahia grass is remarkably helpful in controlling soil erosion.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
An increase in vegetative cover reduces erosion, improves the ecological environment, increases soil fertility and organic matter content, improves How can they be sustained / enhanced? Control weeds and fertilize well. |
|
The combination of structural and vegetative measures has a quick impact on reducing soil erosion and preventing mass movement on hillside slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? ncrease the vegetative cover and improve soil properties through the addition of plenty of organic matter/manure. |
|
Improved land management practices bringing back degraded wasteland sites into economic production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Demonstration and extension while also improving the enabling legislative environment. |
|
Editors’ comments: In China, large areas of degraded hillsides have been brought back into production by constructing terraces on which fruit trees are planted. In this example the technology has been further improved through planting of bahia grass, as a groundcover, to restore the structure and increase the soil organic matter. On a much smaller scale a case of degraded land conversion is presented from Tajikistan. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Orchard development can extend too far up the slope, onto steep mountain sides | Reserve the upper slopes for forest, and restrict orchards to the lower slopes. |
| Potential competition for water and nutrients between the bahia grass | Clean weed (bahia grass included) in the area immediately around the fruit tree. |
| Increase in farm income becomes very positive only after fruit trees start | Consider replacing bahia grass with a more palatable perennial fodder plant to improve farm income in the short term. |
| Low germination rate of bahia seeds | Expand experimental studies (seed treatments, cuttings, taking splits, etc). |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Acceptance Materials of Shan Huxi Small Watershed.. 2001.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна