Rainfed paddy rice terraces [Филлипин]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагч: Deborah Niggli
Palayan
technologies_1422 - Филлипин
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Rondal Jose
joserondal@yahoo.com
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Elliptical Road, Diliman, 1100 Quezon City, Philippines
Филлипин
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
08/09/2003
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
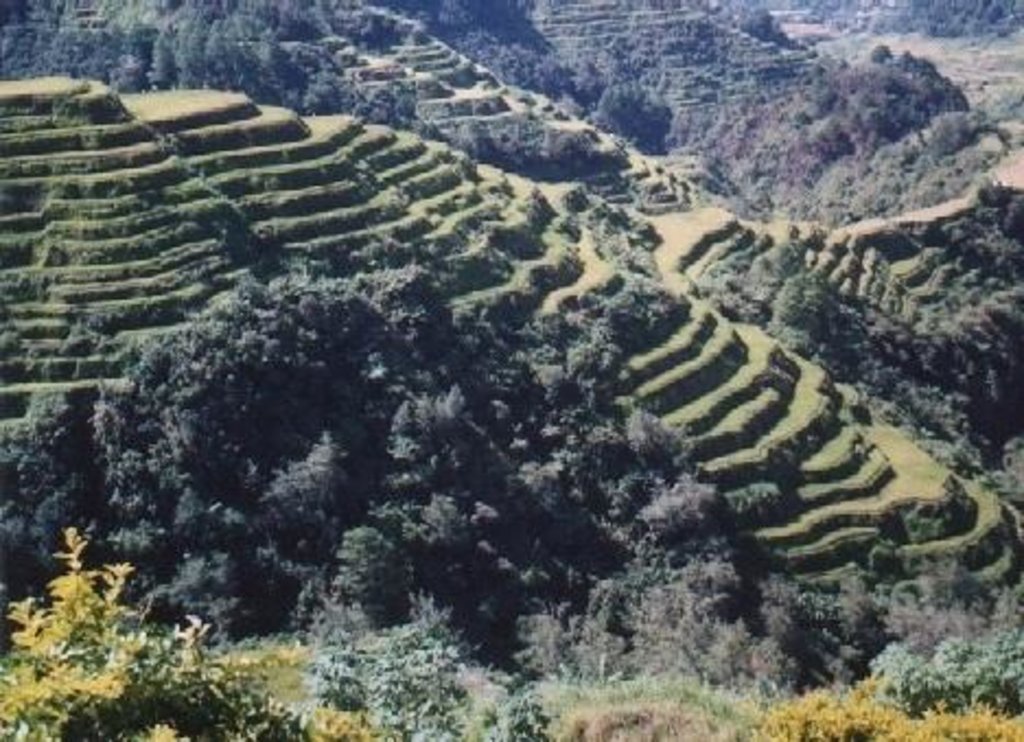
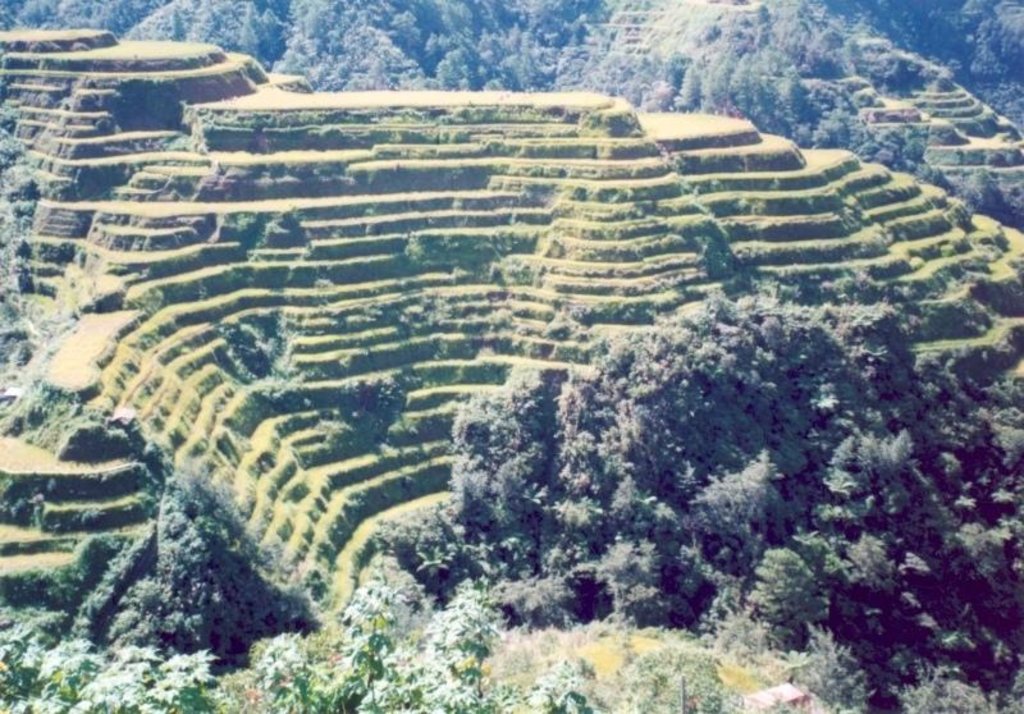
Terraces supporting rainfed paddy rice on steep mountain slopes: these have been in existence for more than a thousand years.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
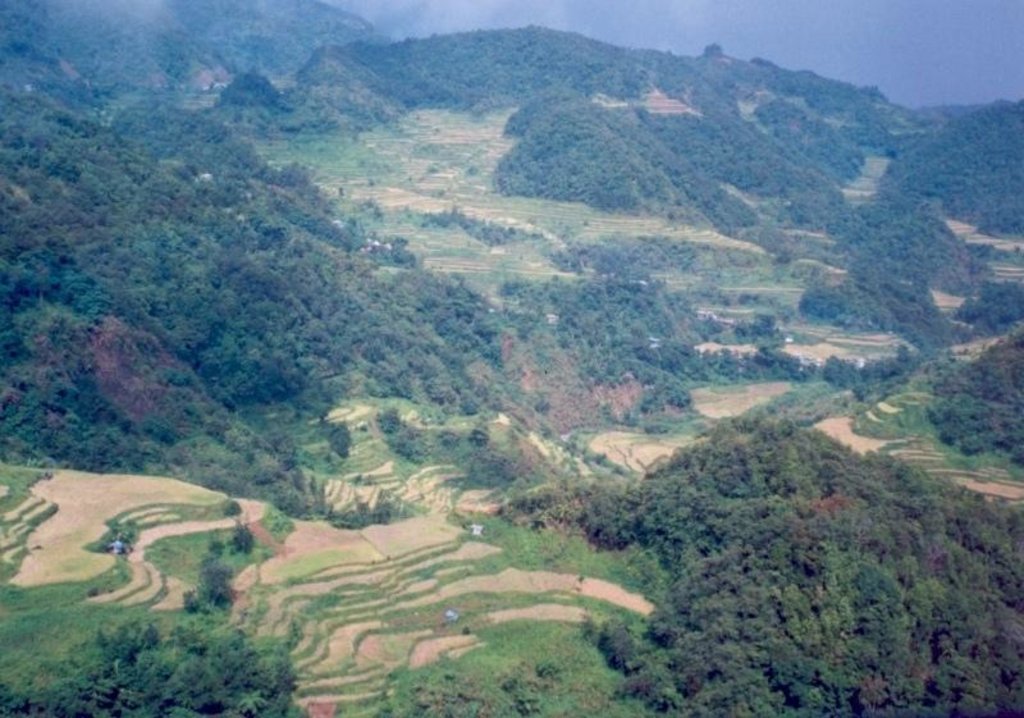
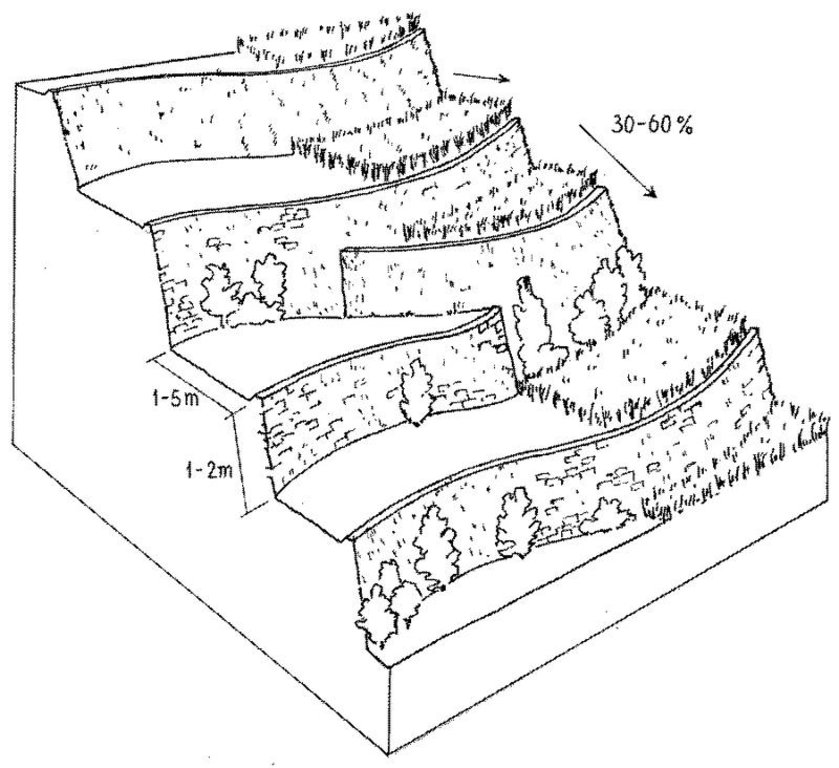
Terraced paddy rice on steep mountain slopes is the main method of rice cultivation in Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) of the Philippines. This is a traditional technology: most of the terraces are at least a thousand years old. The terraces were constructed manually on steep hill slopes (30-60%) with small portions located in narrow valley bottoms. Farmers generally own one hectare or less of terraced land, and cultivation is intensive. The terraces (‘paddies’) curve along the contour, and are narrow, ranging from one to five meters in width, depending on the slope. The height of the riser is between one and two meters. Water supply for the rice crop depends on rainfall, and only one rice crop is grown
per year.
The terraces impound rainwater - average rainfall is around 2,000 mm - and thus prevent soil erosion. Soil fertility is largely maintained because the impounded water and a zero rate of erosion preserve organic matter levels. Some nutrient loss occurs however with each harvest. The terraces are multi-functional: in addition to their agricultural use, they assist in environmental protection through flood mitigation, and they contribute to biodiversity. Furthermore they have become a tourist attraction.
Land preparation is mainly manual. Farmers puddle the soil with their bare feet. Excess water is drained to the terrace below by a small opening in the lip on top of the riser. Maintenance consists basically of repairing breached bunds/risers. Every planting season, a few centimetres of soil is added. To strengthen the bunds, some farmers plant grasses, which may be cut and carried for animal fodder: napier grass (Pennisetum purpureum) is an example. It is important not to disturb the soil of the bund, as this may encourage breaching.
The area where the technology is practiced is mostly between 2,000 and 2,500 m. Because of the cool climate caused by the high elevation, crop maturity takes longer than in the lowlands. In some cases, vegetables such as cabbages and sweet potatoes are grown after the rice is harvested. The farmers, indigenous to the area, have a distinct culture that is different to lowland rice farmers. Rituals connected with farming are widely practiced. There is an added economic benefit from tourism, as people from all over the Philippines - and beyond - travel there for the spectacular views and mild climate.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Филлипин
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Cordillera Region
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Cordillera Region
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Devised by the land users themselves due to extreme necessity
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The terraces allow crop cultivation in an area characterised by steep slopes and high rainfall. However, farming in this marginal areas is labour intensive, mechanisation is not an option on the narrow paddies, and even animal traction is rarely possible due to the steepness of the terrain and the high terrace risers. Non-terraced hill slopes are prone to very high runoff and soil erosion, production is zero.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): High runoff and soil erosion, zero productivity.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 240
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- > 10,000 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15000 m2.
The above provinces are basically dependent on terraced paddy rice. Most of it are rainfed with some areas under irrigation
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
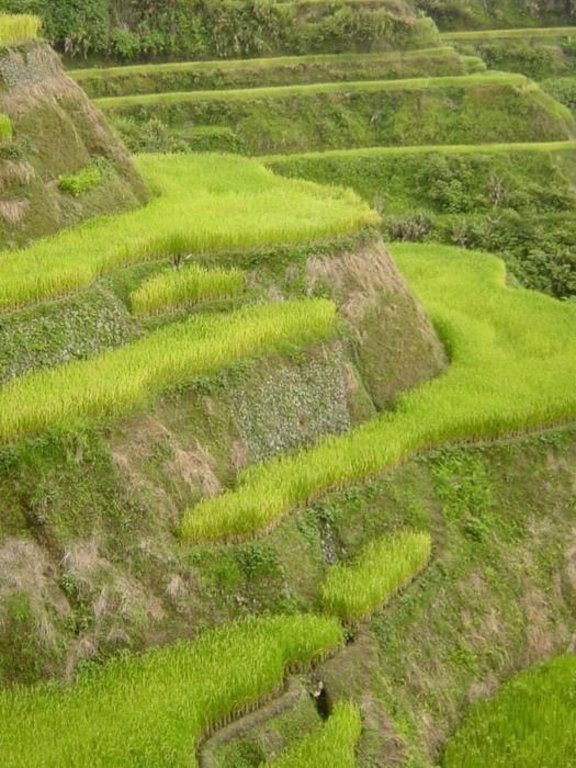
Layout of rainfed paddy rice terraces. The level terraces allow cultivation of paddy rice (right) on steep slopes. In some places the terrace risers are as tall as the beds are wide.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, indirect maintenance of fertility
Vegetative measure: grass on bunds/risers (supp.)
Structural measure: level bench terrace
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determination of contour lines by eye. | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 2. | Levelling by moving soil from the upslope to the downslope part | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 3. | Construction of bunds (lip at the terrace edge) of about 50-100 cm | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 2700.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding by cutting grasses on the bund/riser using hand tools. Hoeing | Ургамлын | |
| 2. | Repairing breached portion of the bunds. Adding a few centimetres | Барилга байгууламжийн | |
| 3. | Land preparation by puddling. In most cases, the use of animal tractionis not possible because of the steepness of the slope and heightof the risers. | Барилга байгууламжийн |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | labour | ha | 1.0 | 30.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | tools | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 40.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The costs of establishment are estimates - as new terrace construction no longer takes place. The land has already been terraced for centuries. The 800 person days are for land levelling and bund construction, which comprises the main activity. The calculation was based on a land slope of 30-60%. The maintenance figure assumes regular light maintenance - and does not include major repairs to bunds.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: carpentry, trading, labour for neighbouring farms, overseas employment, transport services, activities associated with tourism
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
compared with zero in the non-terraced scenario
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
conflicting with other income generating opportunities
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
үндэсний институц
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрс алдагдах
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. The technology is widely accepted. As the terraces were constructed hundreds of years ago and construction of new terraces is no longer done the question of ‘adoption’ is not relevant.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Know very well the agronomy of rice production |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Low maintenance cost |
| Farmers are well versed (very familiar) with the rice production system – it is part of their culture |
| Terracing allows paddy rice production on very steep slopes, which are prone to very high erosion and water loss in such a monsoon area. It transforms steep unproductive slopes into productive land |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Lack of irrigation facilities | Construction of water harvesting structure |
| Declining yield | Fertilizer application |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Lack of moisture for about six months | Moisture conservation (mulching): construction of water harvesting structures for supplementary irrigation. |
| Continuous mono-cropping | Crop diversification. Other crops (such as sweet potato, cabbage, chilli) could be grown after rice towards the end of the rainy season through minimum or zero tillage. |
| Severe soil fertility decline in some locations – and therefore declining yields | Fertility enhancement using organic and inorganic sources (manure, crop residues, compost, fertilizers etc). |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Breemen van N, Oldeman LR, Plantinga WJ and Wielemaker WG (1970) The Ifugao Rice Terraces. In: Miscellaneous papers (7) 1970,eds. N van Breemen et al Landbouwhogeschool, Wageningen, The Netherlands.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна