Biogas system at household level fed daily with cattle manure [Камбодж]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christoph Kaufmann
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
ប្រពន្ធ័ឡជីវៈឧស្ម័នប្រើសំរាប់គ្រួសារប្រចំាថៃ្ងដោយប្រើលាមកគោ (Khmer)
technologies_1645 - Камбодж
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Khun Lean Hak
SOFDEC/LAREC, www.sofdec.org
Камбодж
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Pith Khonhel
LAREC
Камбодж
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Bin Sreytouch
SOFDEC
Камбодж
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Say Mesa
SOFDEC
Камбодж
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Society for Community Development in Cambodia (SOFDEC) - КамбоджТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre (LAREC) - Камбодж1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
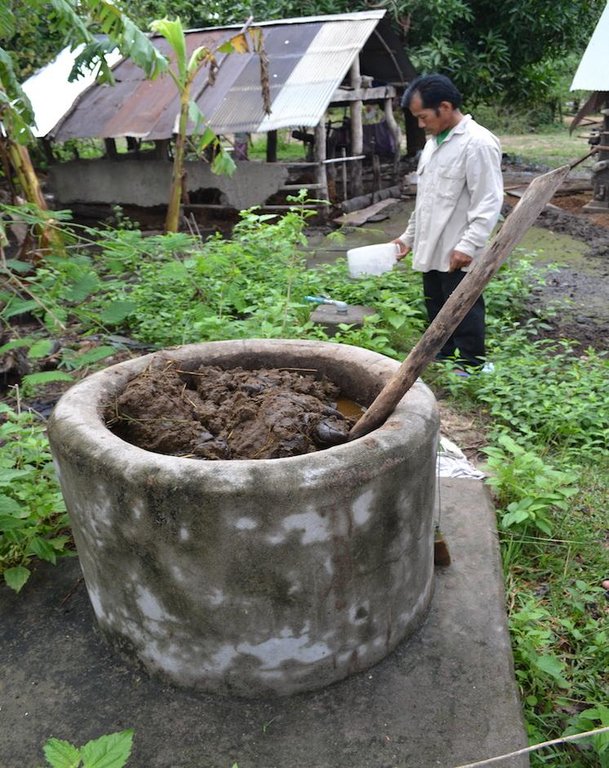
Small-scale biogas systems fed with cow manure and water are implemented in order to supply the household with energy for cooking and lighting, as well as to produce fertilizer.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
In this case-study, a small-scale biogas system was introduced in order to generate both energy for home consumption and fertilizer. Small-scale biogas systems are implemented in different parts of the world, however the layout thereof varies considerably.
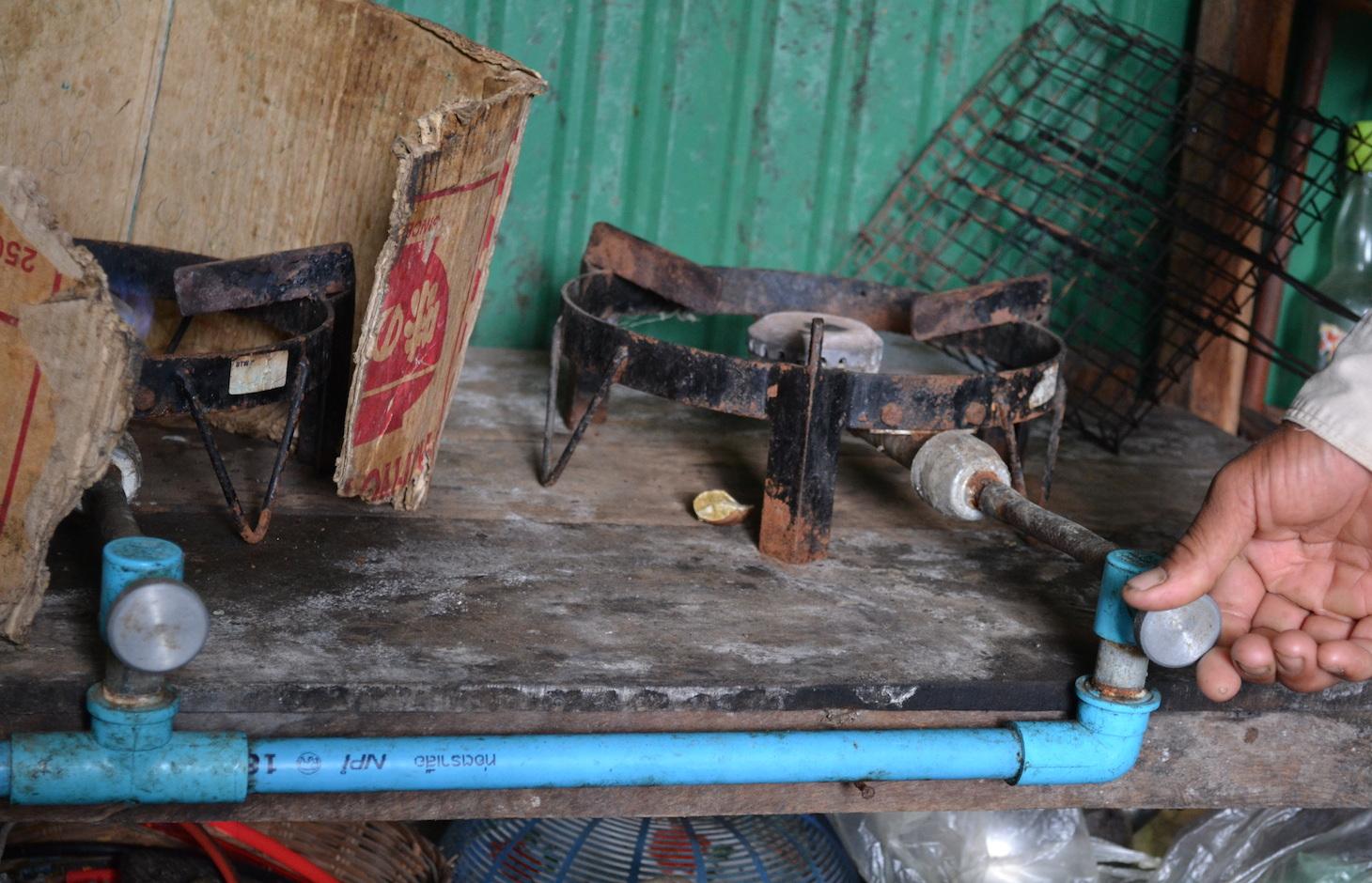
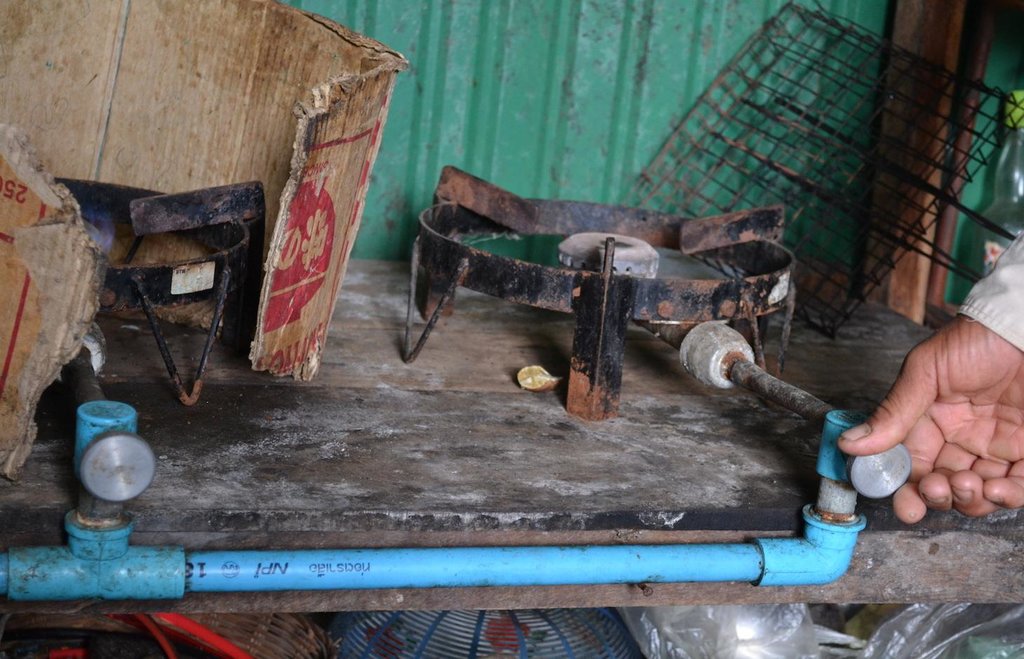
The model used in this case-study consists of different components (cf. technical drawing). First, there is an inlet where the land user puts cow manure mixed with water. On the bottom of the inlet, there is a board which closes the access to the bio-digester situated beneath the inlet. The board can be opened manually by pulling a string. Once the board is open, the fluid components go through a pipe which leads to the bio-digester. In the bio-digester, bacteria transform the organic matter into biogas (mainly methane and CO2) and slurry. At the other end of the digester, there is another pipe (outlet). The outlet is lower than the inlet, and due to the difference in pressure, the slurry is pushed out of the digester. The slurry is dried and applied to the fields two to three times a year with the help of an ox cart. It has similar effects on the plant growth as chemical fertilizer as it does not build up the soil organic matter as much as compost. The biogas, however, is pushed to the pipe situated on top of the digester and can be utilized for domestic uses. The gas is used for cooking and lighting.
The use of biogas allows reducing the expenses on charging batteries for the lighting, as well as reducing the firewood use (usually from deforestation) for cooking. The slurry reduces the expenses on chemical fertilizer in the fields and has the advantage of killing the weed and rice seeds present in the manure and crop residues.
For building the biogas system, there is governmental and NGO support. These two actors finance half of the construction costs. The other half is paid by the land user. Building a biogas system is quite costly, with about 400 $, and not all of the land users in the area can afford paying 50% of its price. However, the costs borne by the land user are paid off within a few years due to reduced expenses on firewood, chemical fertilizer, and charging batteries. The construction itself was undertaken by local companies.
The costs are paid off within a few years due to the reduced expenses on firewood, chemical fertilizer and battery charging.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter (low soil fertility, acidification, small amount of cattle, area has been deforested a long time ago) and the groundwater table is rather high (1-3 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), the cattle are released to the paddy fields. The cattle is often replaced by hand tractors, which effects the production of manure but allows a higher amount of crop residues on the fields.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge which different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Камбодж
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kampong Chhnang
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Sre Ouk Samlor Sap/Taing Krasaing/Rolear Pha,er
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
There are only 4 households in this village which apply the technology (lack of money and/or cattle). However, similar Technologies are introduced in other provinces – yet it is difficult to estimate the area covered. Estimation for this village.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
LWS (a Dutch NGO) in joint efforts with specialists from the National Biodigester Program NBP. Implementation in 2012
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June-December

Суурьшил, дэд бүтэц
- Хот суурин, барилга
- biogas system
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of organic matter, lack of water retention in soil, irregularity of rainfall, low soil fertility (sandy soil), monocultures, bare soil during dry season, ploughing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low soil fertility, lack of water.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Эрчим хүч хэмнэх технологи
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S11: Бусад

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- M6: Хог хаягдлын менежмент (дахин боловсруулах, эргүүлэн ашиглах эсвэл бууруулах)
Тайлбар:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
- Ca: Хүчилжих

биологийн доройтол
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing, soil is left bare for several weeks), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Rice monoculture (rice as staple crop)), change of seasonal rainfall (More erratic beginning of wet season), droughts (On dry soil, rice cannot be planted and if already planted, rice cannot grow), labour availability (High migration rates from the villages to garment industry, cities or abroad, influence agricultural activities (e.g. broadcasting instead of transplanting of rice seedlings)), education, access to knowledge and support services (Khmer Rouge regime in the 1970s, a lot of knowledge got lost)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Rice straw is removed for different domestic uses (cattle, mushroom cultivation, etc.)), overgrazing (Cattle eats rice straw left after harvest, less organic matter on the field, grazing is not managed), change in temperature (More hot days), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (Some incidents of land grabbing, land use rights not clear, corruption), poverty / wealth
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
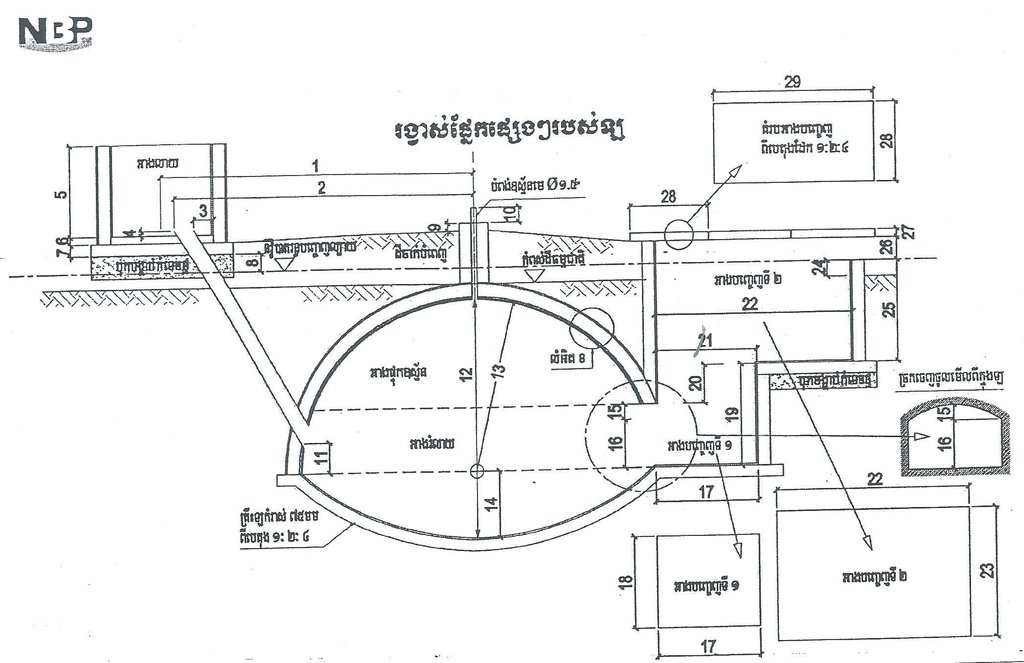
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Biodigester. Inlet: top left; gas outlet: top centre; digestion chambre: centre; and outlet: right. For the comlete building instructions contact the NBP.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The most challenging part is the construction of the construction of the Biodigester.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter
Structural measure: Biodigester. Round shape. Tiles and concrete.
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4 m^3
Structural measure: Connecting pipes made of plastic
Construction material (concrete): Tiles are covered in concrete.
Construction material (other): The most challenging part is the construction of the Biodigester.
Other type of management: Change of energy supply system for home consumption.
Зохиогч:
National Biodigester Programm, www.nbp.org.kh
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Riel
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
4000.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
5.00
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of the biodigester by external experts. The land user did not help with the construction, he only paid 200 US$. The other 200 US$ were paid by the National Biodigester Program. | Dry season, when water table is low. |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Барилгын материал | Construction of biodigester | 1.0 | 400.0 | 400.0 | 50.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 400.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 0.1 | |||||
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Add manure and water to the inlet | once per day all year round |
| 2. | Collect residuals from biodigester, spread it out and let it dry, and finally put it on the field. | 3 times/year |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | 1.0 | 121.5 | 121.5 | 100.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 121.5 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 0.03 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Cart to bring residues from the biodigester onto the fields.
The costs were calculated for 1 biodigester with a capacity of 4 m3.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The most costly part of this Technology is the construction of the biodigester. Once the system is installed, the costs borne by the land user are low. Also, the land user can save money since he doesn’t need to buy firewood any more.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
27° to 35°C, 1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water tabel and availability of surface water data during dry seasons. People use water for drinking after filtering or boiling.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Only degraded forests are in the area.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: Handicraft, remittances and factory work.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Тайлбар:
Land ownership is very complex. Most of the land belongs officially to the government, yet many land users hold a paper confirming they applied for a land title – but de iure, this paper is worthless.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Dried residues are put in the garden (cucumber, pumpkin, watermelon) which increases nutrient availability.
эрчим хүчний үйлдвэрлэл
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
He saves 50 $ on chemical fertilizer per year.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
No smoke from open fire.
Contribution to human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
On the long term livelihood is improved, because he saves over 60 $ per year in firewood and battery charging for light, as well as 50 $ for chemical fertilizer.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Pollution of groundwater due to washing out of nutrients.
Хөрс
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Most of the carbon is transformed into methane, not available as organic matter.
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
reduced weed seeds
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Compost usually not completely decomposed, as well as raw manure, contain lots of weed seeds.
energy generation (eg hydro, bio)
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Before the installation of the biogas system, the land user bought firewood.
deforestation for firewood
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Sludge is left to dry outside, nutrients washed out into groundwater. Not measurable.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- > 50%
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
100% or 4 land user families
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
The farmers can ask the National Biodigester Program for subsidies, but need to pay half of it on their own. As the farmers often lack money and need at least 3 - 4 heads of cattle to produce enough manure while they switch more and more to hand tractors, not many farmers are building new biogas digesters.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Fertilizer production (sludge). |
| Saves money and time on the cooking fuel (previously wood) and electricity (charging batteries) for the light. |
| No weed seeds in the sludge compared to compost and raw manure if used as fertilizer. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Less deforestation for firewood. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The residue does not improve the soil as much as compost. | Make compost in addition to biogas to enhance the soil organic matter. |
| The building costs are prohibitive | Increase subsidies from state or NGOs. |
| At least 3-4 heads of cattle or 4-5 pigs have to be kept to produce enough manure. | Diversify production with different animals. |
| Work has to be done each day to produce biogas. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Overgrazing could become a problem as more cattle needs to be kept. | Add slurry as a liquid fertilizer |
| Part of nitrogen is volatilized during the drying of the sludge. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
05/08/2014
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
NBP National Biodigester Program
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
www.nbp.org.kh
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Lam et al. 2009. Domestic Biogas Compact Course. University of Oldenburg.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://www.nbp.org.kh/publication/study_report/2_domestic_biogas%20.pdf
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Gurung. 2009. Review of Literature on Effects of Slurry Use on Crop production. The Biogas Support Program
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна