Improved compost preparation [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Sudhariyeko compostmal nirman (Nepali)
technologies_1750 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
Непал
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
Непал
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Improved compost preparation using a range of biomass and waste to produce high value fertiliser
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
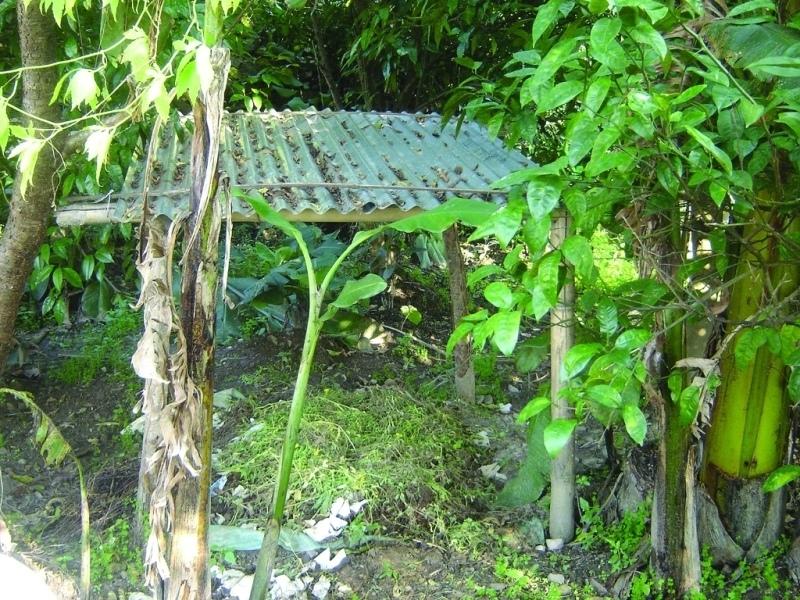
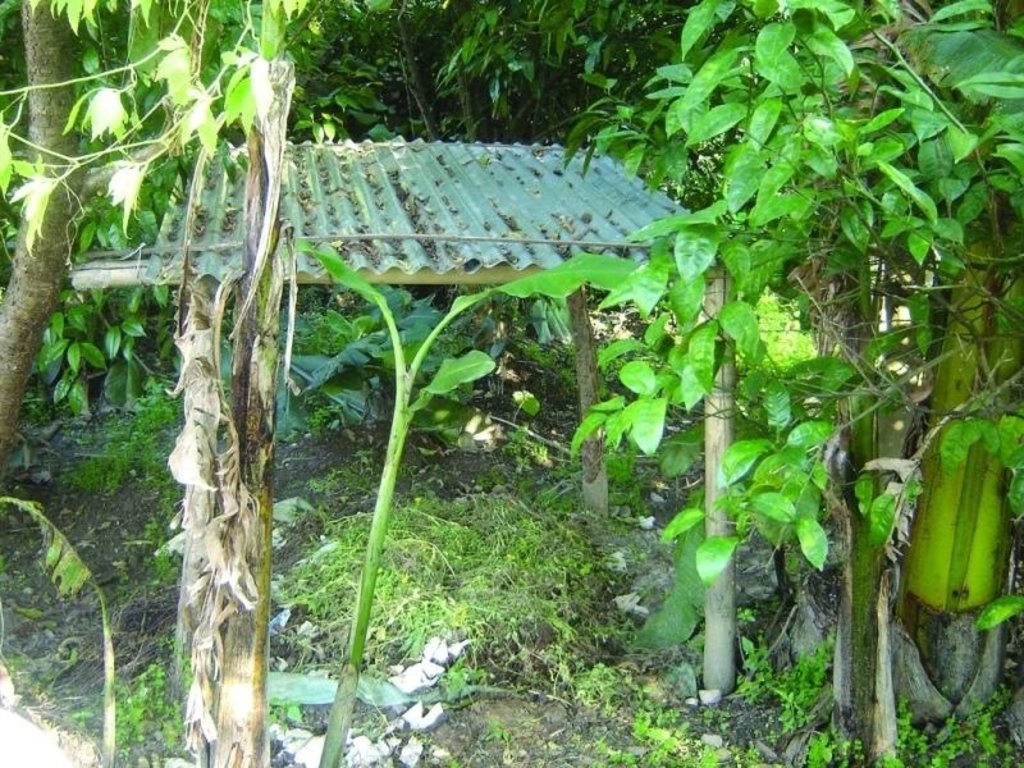
Compost can be prepared from a wide range of organic materials including dead plant material such as crop residues, weeds, forest litter, and kitchen waste. Compost making is an efficient way of converting all kinds of biomass into high value fertiliser that serves as a good alternative to farmyard manure, especially for crop-growing households without livestock. The compost is often mixed with forest soil, ripe compost from the previous batch, or even a small amount of animal dung as a starter for the decomposition process. The mix of materials determines the quality of the final compost as much as the management of the composting process. Nitrogen-rich fresh materials such as legume residues and many types of weeds and shrubs are mixed with carbon-rich forest litter and cereal residues. Small amounts of wood ash, lime, or mineral fertiliser can help increase or balance the overall nutrient content of the compost.
The compost needs to be turned every 30-50 days depending on the mix and the outside temperature. It should be protected from direct sunlight, rainfall and runoff so as to reduce volatilisation and leaching of nutrients. The material must remain moist at all times to avoid slowing down decomposition and hindering the efficiency of the micro and macro-organisms involved in decomposition. Heaping the compost or collecting the material in a pit helps the compost to reach the temperatures needed (700C) to destroy pests and weeds.
Once the compost is well decomposed and has an earthy smell, it can be applied directly or stored for later application. It can be applied as a crop fertiliser in rows or to individual plants for improving general soil fertility and organic matter content, thus improving the soil structure and its water holding capacity.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Midhills districts of Nepal
Map
×3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- Improve compost production
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) the inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) the application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, and losses of fertiliser in surface runoff and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds or groundwater.
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Хөрсний үржил шимийн нэгдсэн менежмент
- Хаягдлын менежмент/хаягдал усны менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- M7: Бусад
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
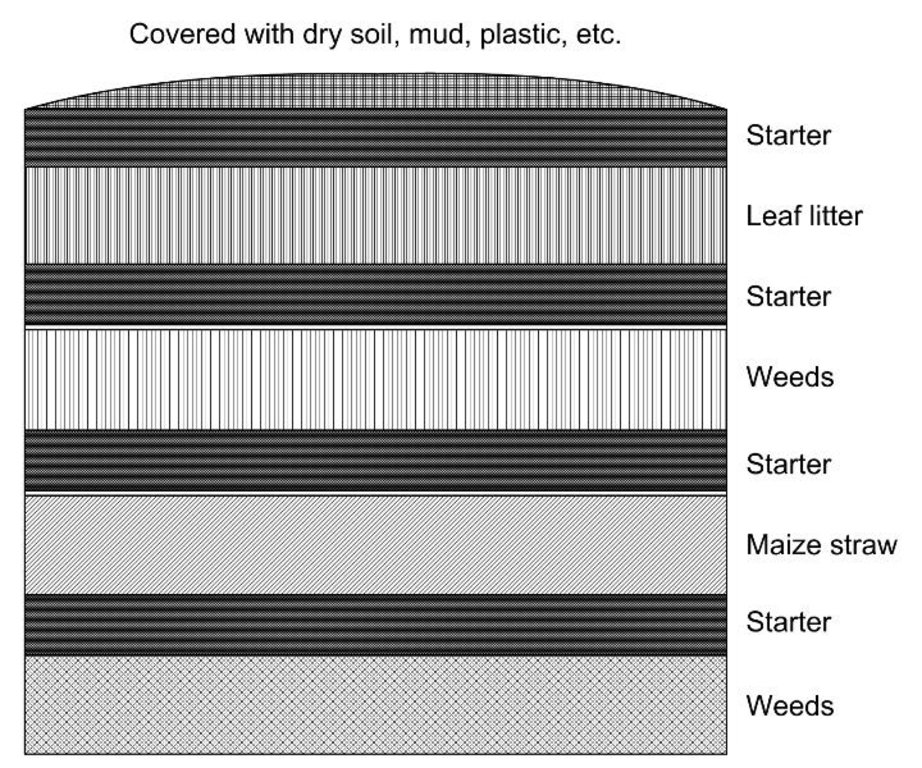
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Layering of the different materials in a compost pit
Note: This is just an example and need not be followed exactly. The important aspects are:
- the need for a starter such as forest soil or manure
- place weeds in the centre of the pit so that they are fully decomposed
- cover dry materials with moist material and material that only decays slowly with easily decaying material.
The pit can be 1 to 2m in diameter and about 1m deep. The size depends on the available biomass for composting and the amount of compost required.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in soil fertility and productivity, increase in soil organic matter content, improvement in physicalsoil conditions, increase in soil water holding capacity
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.00
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig a 1-2m diameter and 1m deep pit using a spade or shovel | |
| 2. | Collect crop residues, grass, tree leaves, ash, lime, and animal urine | |
| 3. | Put a layer of ash at the bottom of the pit followed by tree leaves, grass, crop residues, and a layer of forest soil (as it contains the necessary microorganisms – bacteria, fungi, etc. – and quickens the decomposition process) | |
| 4. | Add more tree leaves, crop residues, and grass until the pit is full and contains a healthy mixture of dry and fresh/moist materials | |
| 5. | Cover the compost heap with a fi ne layer of ash or mud and a cap of |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Preparing compost pit | Persons/day | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 4.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 4.0 | |||||
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dispose of domestic and household wastewater and cattle urine in the pit to keep it moist (but not saturated/soaked) until it is fully decomposed. | |
| 2. | The compost needs to be turned every 30-50 days depending on the mix and the outside temperature. | |
| 3. | Depending on the location, it takes about 3-6 months for the compost to be fully decomposed. |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintaining compost | Persons/day | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 2.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 2.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Cost as in January 2007
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
Sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced expenses on chemical fertilisers
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Preparation of compost is labour intensive
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Soil fertility
Organic crop production
Application of fertilizer
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduction of nutrient influx into water bodies
Dependence on external inputs
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
The high cost of mineral fertilisers means that the establishment costs are soon recovered. In the long-term, a major reduction in costs leads to large benefits.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: About 30% of the participants of SSMP activities related to compost making, and about 20% of farmers that were
not part of the programme have adopted the technology.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The use of compost reduced the need for mineral fertiliser thus reducing production costs and outside dependence How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further promote the technology to increase this impact |
|
Compost making does not require any livestock How can they be sustained / enhanced? Its low cost and use of local materials makes it the fertiliser of choice for poor households |
| In-situ composting saves labour involved in transporting compost to the fields |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The preparation of compost is not appropriate for commercial use (except in nurseries) | Compost improvement should go hand-in-hand with promoting alternatives for the other requirements |
| Compost requires a large amount of biomass which may otherwise be needed for fuel, fodder, or animal bedding |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
STSS; SSMP (2001) Farmyard Manure and Compost Management (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Soil Testing Services Section, Department of Agriculture andSustainable Soil Management Programme
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
SSMP
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [Непал]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [Непал]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- Эмхэтгэгч: Richard Allen
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна