Green cover in vineyards [Швейцар]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Nicole Guedel
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Begrünung von Rebflächen (im Direktzug / in der Falllinie bewirtschaftet)
technologies_1018 - Швейцар
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Weissenbach Peter
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture -FAW
Швейцар
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Spring Jean-Laurent
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture-RAC
Швейцар
Газар ашиглагч:
Louis Hannes
Louis Weinbau
Швейцар
Газар ашиглагч:
Hasler Lukas
Hasler Weinbau
Швейцар
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture (FAW/RAC) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцар1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Farmer initiative within enabling environment [Швейцар]
Initiative and innovation of land users, stimulated by government's technical and financial support.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Nicole Guedel
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Naturally growing or sown perennial grasses/herbs providing cover
between rows in sloping vineyards, where the vines are usually oriented up and down slope.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
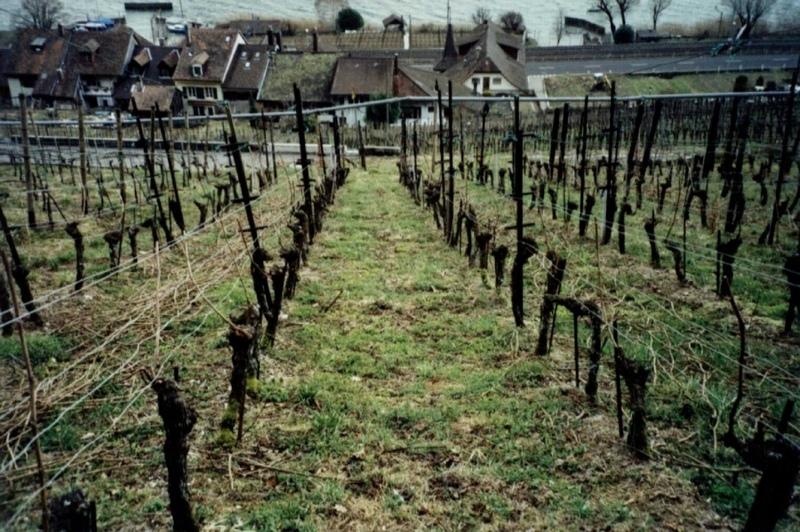
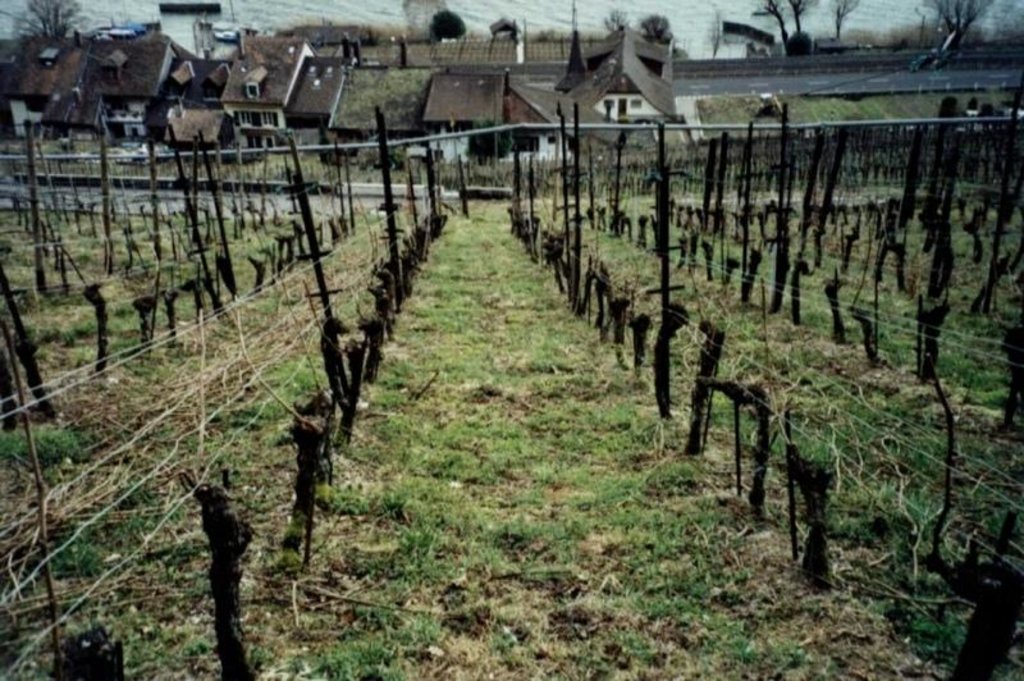
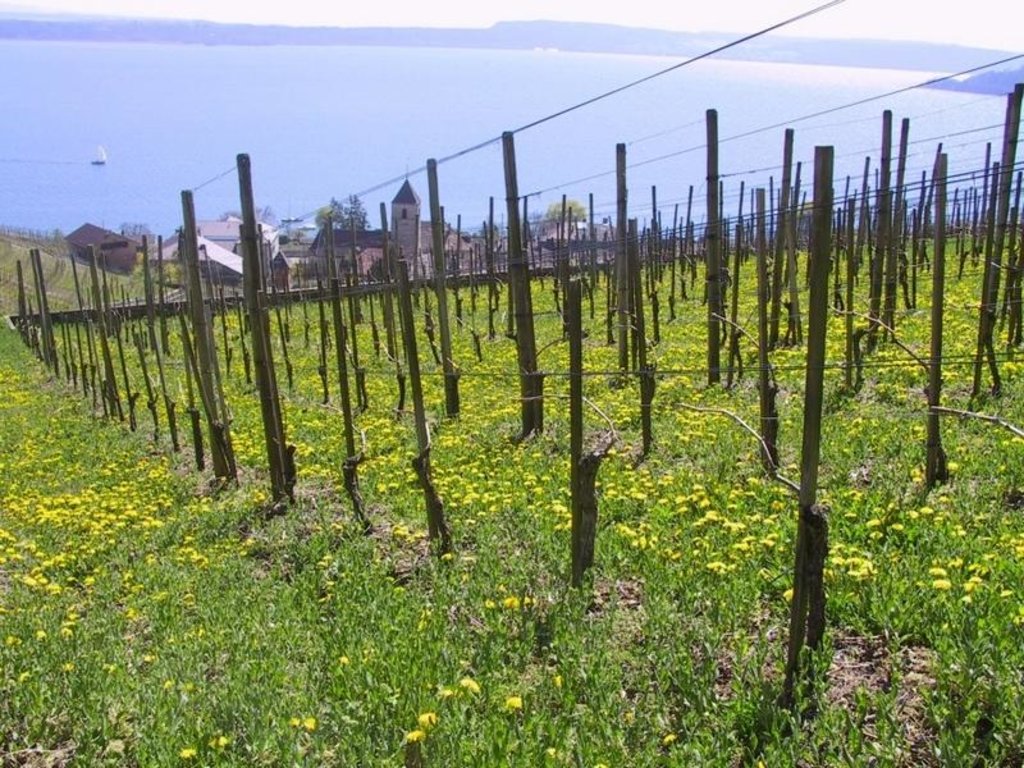
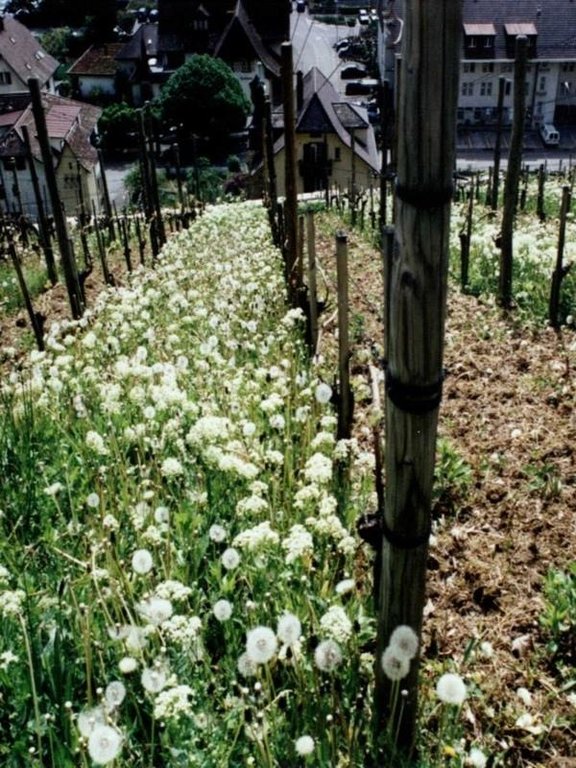
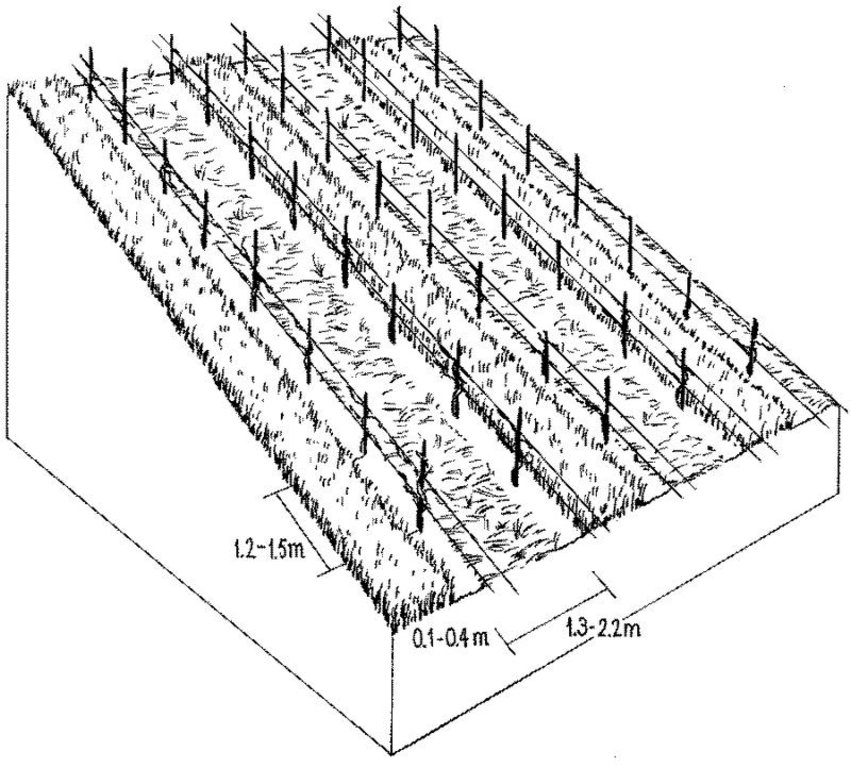
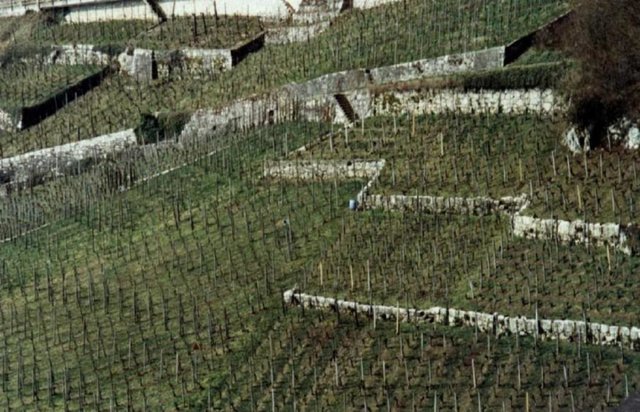
The area around Lake Biel has a strong wine growing tradition dating back several centuries. The vineyards are, for micro-climatic reasons, sited on the southwest facing slope close to the lake. Annual rainfall is about 1,000 mm, with at least one erosive storm per year, and the soils are highly erodible. In conventional viniculture all weeds are controlled chemically. The ‘green cover technology’ comprises sown, or naturally occurring, perennial grasses and herbs which form a biodiverse green cover - a ‘living mulch’ - over the soil surface between vine rows. In this region, rows are generally oriented up and down the slope for ease of machine operation. Green cover may also be applied where vines are grown on narrow bench terraces. The purpose is the prevention of soil degradation, especially soil erosion by water. Secondary purposes include protection of the soil surface from compaction when using mechanised equipment, and promotion of biodiversity.
Green cover is generally established naturally - except on contour-planted terraced vineyards, where cover is planted for immediate stabilisation of the terraces. To avoid competition, a 10-40 cm diameter zone around the freshly planted vines is kept free from vegetation: during the three year establishment period it is removed by hoe, later it is controlled with herbicides (either as a strip along vine rows or around individual vines). The topsoil between the vine rows is ripped every few years with an implement pulled by a small caterpillar tractor. The green cover vegetation is cut, chopped and left as mulch several times using special mulching machines. These operations are not carried out over the whole field at once: alternate rows are left untouched to ensure that some vegetation remains to maintain biodiversity. When these rows redevelop their green cover, the others are then treated. This is effectively a minimum tillage system, building up organic matter in the soil. Cutting and mulching, in addition to ripping, serves to circulate nutrients. Mineral fertilizer and herbicides are applied once a year around the vines. Experiments with the technology started in the 1970s, but green cover has now become standard practice.
Supportive measures include not removing crop residues (from vineyards) which are chopped later - simultaneously with the cover crop (grass) - to protect the soil surface, and irrigation in dry years.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Швейцар
Улс/аймаг/сум:
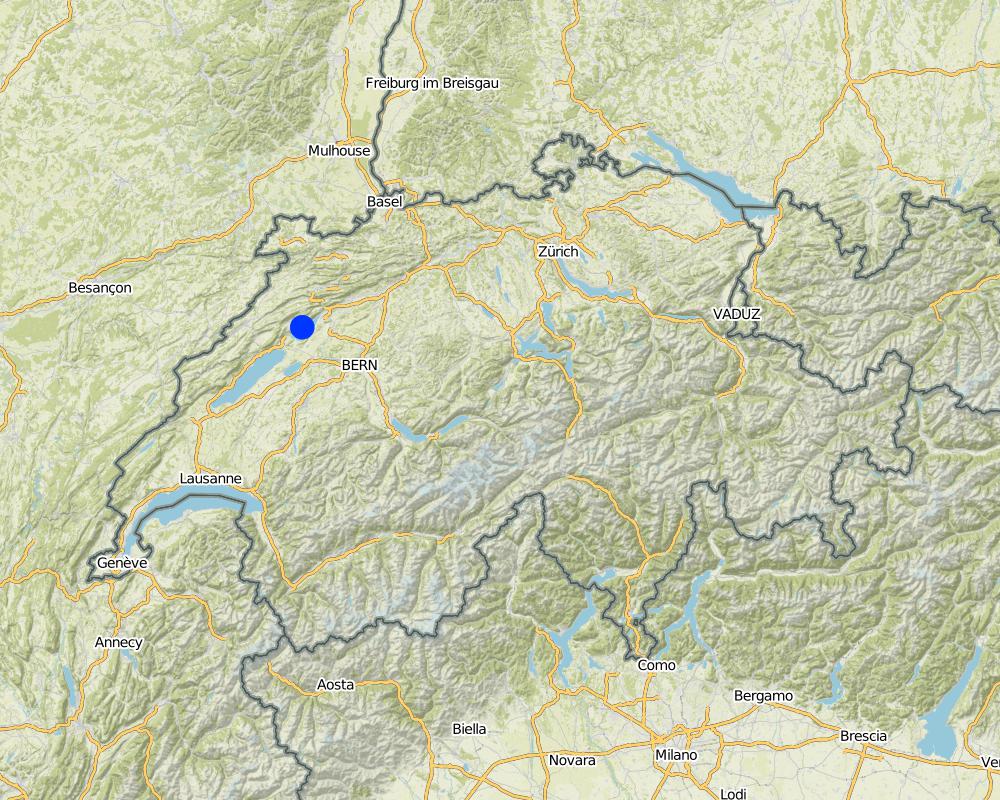
Canton of Berne
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Lake of Biel
Тайлбар:
The technology is applied in all wine growing regions of Switzerland, but under different conditions
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The development of green cover in vineyards was (also on the international level) essentially promoted and supported by the Federal Research Station for fruit-growing, viticulture and horticulture in Wädenswil (Canton of Zürich)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Мод, бут тариалах - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- усан үзэм
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 210Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main problem was decreasing soil fertility, especially through soil erosion by water, caused by lack of soil cover and intensive cultivation. There were associated negative offsite effects including sand/sediment deposition and contamination of groundwater by nutrients. This became a serious problem from the 1960s when the traditional labour-intensive methods were superseded by a mechanised-industrial agricultural system.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: a vine plantation is established for a period of 20-40 years (lifetime of a vine). Some farmers make one year of fallow between the destruction of the old and the establishment of a new plantation.
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Тайлбар:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А7: Бусад

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V5: Бусад
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures
Specification of other agronomic measures: minimum tillage: cutting & mulching, ripping
Specification of other vegetative measures: cover cropping
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking compacted topsoil
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
- Cp: Хөрсний бохирдол

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Cp: soil pollution
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Pk: sealing and crusting
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes: fast changing basic conditions of viticulture in the last 100 years), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), fast changing basic conditions of viticulture (economy, laws)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
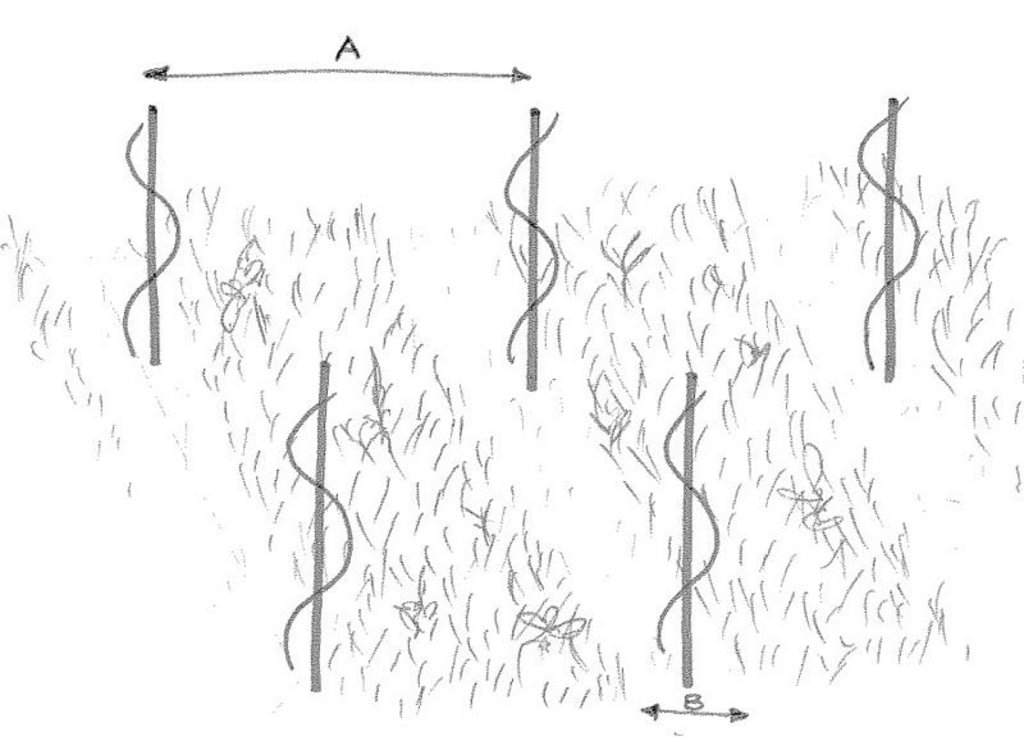
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Technical drawing of green cover on parcel with vine rows oriented up and down the slope. A = distance between vine rows (130-220 cm), B = zone of application of herbicides (10-40 cm).
Location: Twann, Lake of Biel. Canton of Berne
Date: June 2003
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, improvement of soil structure
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: cut or chopped cover vegetation
Remarks: dispersed over the whole surface; if possible cutting/chopping only every second row (alternating)
Agronomic measure: removing less vegetation cover
Material/ species: cut or chopped cover vegetation, vine leaves and cut branches
Remarks: between vine rows
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: compost
Remarks: only sporadically (every 5-10 year or less)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: nitrogen
Quantity/ density: 0-50 kg/ha
Remarks: normally rather little nitrogen
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers: potassium
Quantity/ density: 0-20 kg
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers: magnesium
Quantity/ density: 0-25 kg
Agronomic measure: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers: phosphorus
Quantity/ density: 0-20 kg
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: if possible: only every second row (alternating)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: different grass species, taraxacum, veronica, legumes, calystegia, geranium...
Зохиогч:
Nicole Güdel, Berne, Switzerland
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Swiss Franc
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
0.75
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allow natural cover to establish. | winter/spring, usually at the same time as a new plantation is established |
| 2. | Weeding around base of vines to reduce competition, 2–4 times during | during season (Mai – October), 2 - 4 times, when necessary. |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 13800.0 | 13800.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| таримал материал | Seeds of natural vegetation | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 15000.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 20000.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cuting and not removing vine leaves and branches | winter / annual |
| 2. | Apply mineral fertilizer to the vines (particularly K, N, P, Mg) | April/May / annual |
| 3. | Cut cover vegetation with a portable motor scythe or mower with | during cropping season (first time April/May) / each row 2-4 times during cropping season |
| 4. | cuting and not removing vine leaves and branches | during cropping season / several times during cropping season |
| 5. | Minimum tillage (rip topsoil) of alternating inter-rows with machine | April/May / each row every 4-8 years |
| 6. | Application of herbicides (glyphosates) | beginning of season (May), if necessary second time in Aug./Sept /once (if necessary twice) during s |
| 7. | Cut/chop vine leaves and wood for mulching | during growing season, 2-4 times |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 1500.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 650.0 | 650.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 90.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 2300.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 3066.67 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: e.g.: hoe, mower with tracked vehicle or portable motor scythe, spading machine with tracked vehicle; knapsack sprayer or biocide tank transported by
Costs are calculated on the basis of vine rows being oriented up and down the slope, a distance between rows of
1.3-2.2 m and 6,500 vines per ha on a slope of <60%. Establishment costs have been estimated and are representative of the situation when green cover is encouraged to establish at the same time as new vines are planted (normal practice). This means that the estimated costs include all the annual agronomic and vegetative inputs within the first 3 years during the establishment phase. If green cover is implemented more than 3 years after planting new vines, establishment costs are much reduced, because the vines are bigger, competition with the green cover is less, and the vines are not so sensitive to herbicides, which permits the replacement of labour intensive manual weeding by application of herbicides. Maintenance costs are based on one typical winegrower in the region. Initial investments in machinery and costs directly attributable to ‘plant capital’ (the vines) are not included.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Labour is the major cost component, since wage levels are very high in Switzerland.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Average: Biel: 1200 mm. Region of Bielersee: 1000 - 1200 mm. Neuchâtel: 930 mm.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitudinal zones: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (For climatic reasons vines grow hardly above 600 m a.s.l. in Switzerland )
Landforms: Hill slopes (most of them southeastward sloping hills (part of the Jura mountain range) )
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average: Deep (81-120cm) (Soil depth is very irregular, at some places limestone rocks appear at the surface, at other places soil can be quite deep).
Soil fertility is medium (Vines are normally grown on rather marginal spots. Compared to the general productivity these soils have a medium fertility. (If measured at the vine itself, soil fertility is sufficient/high).
Topsoil organic matter is medium (1-3%) (without / before SWC (green cover)
Soil drainage/infiltration is mostly good, at some points medium (at some spots medium (depressions; when high percentage of clay).
Soil water storage capacity is medium (without / before SWC (green cover)), high (without / before SWC (green cover)) or low (without / before SWC (green cover). Depressions; when high percentage of clay)
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- механикжсан / мотортой
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
100% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: This is representative for the full time winegrowers. The majority of winegrowers do winegrowing beside a regular off-farm job (partly 10-50% of income with salary from off-farm work) as a hobby. Nearly all winegrowers have implementeted the SWC technology. Probably there is no difference in hobby-winegrowers and full-time-winegrowers concernring implementation of the SWC technology.
Level of mechanization is manual labour (most of the work in the vineyard is done by hand (especially harvest)) or mechanised (some of the activities are carried out with fuel driven equipment. But mechanisation is moderate since big and heavy machines cannot been applied in these vineyards)
Market orientation is: Commercial/market (in the region of the lake of Biel the majority of grapes are pressed to wine an then and sold directly from the farm's wine cellar)
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha (only winegrowing land!)
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
10–20% due to competition for water/nutrients
үр тарианы чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Quality of wine decreased when strong competition of water and nutrients happens and nothing is done against it.
бүтээмж буурах эрсдэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to competition of water and nutrients and higher susceptibility to fungal decay (due to higher evapotranspiration rate with green cover and therefore humid microclimatic conditions). Little danger of frost only in depressions or plains (due to higher evapotranspiration rate)
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
(Indirectly due to less erosion damage in the long-term – also due to subsidies related to green cover,marketing under the label of ‘ecological agricultural production’, and other criteria)
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More and specific knowledge necessary. Weeing, cutting, ripping
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Machine use
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Special machines needed, mechanisation is almost a must to be economically successful in the long term
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Healthier than without SWC, less application of biocides
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increased exchange of knowledge and contacts in winegrowers society
үндэсний институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Research stations gained new knowledge and attention
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Among winegrowers, but perhaps also slightly among consumers (through an ecological marketing argument) or walkers (walking through a green vineyard may arise interest in green cover).
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Between generations or between farmers applying green cover and others. Reason: farmers are differently attached to traditional values and norms (i.e.: traditionally every plant 'out-of-place' was seen as unuseful weed and fought with a hoe)
Personal satisfaction / challenge
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Many farmers apply green cover see green cover as a personal satisfaction or challenge for an ecologically and economically sustainable viticulture
Acceptance by society
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Landscape and appearance of vineyard as cultural heritage. Reason: different values an norms of "how a vineyard should look like". Traditionally vines were planted very dense with no vegetation cover in between.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially through improved water retention capacity (due to improved soil structure)
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс нягтрах
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
түрэмгий, харь зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially mice
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through beneficial animals
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Soil fertility
Biodiversity
Soil erosion through wind
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
And groundwater
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Nearly all of the land users have adopted green cover independently of the direct incentives received for growing vines. The spontaneous spread of green cover occurred before these incentives were tied to ‘ecological production’. Note: Swiss agriculture in general is highly subsidised (see approach).
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Personal satisfaction/challenge for ecologically and economically sustainable viniculture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote ecologically sustainable agriculture. |
|
Increased exchange of knowledge and contacts in winegrowers’ associations How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustain/strengthen farmers’ institutions. |
| Improved knowledge/awareness regarding SWC/erosion: among winegrowers, but perhaps also to some extent among consumers (through ecological marketing) or walkers passing by. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Prevention of erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain green cover |
|
Improvement of soil quality (fertility, organic matter, moisture retention, soil structure) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ensure that cover vegetation doesn’t compete with the vines; improve soil properties by applying mentioned agronomic measures. |
|
Contribution to a better balanced and more stable ecosystem (with living space for a wider range of organisms) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Specific management of cover crops (alternating treatment of inter-rows; find solutions to replace application of herbicide). |
| In the long-term economically beneficial because of cutting costs of restoration of soils and fertility loss after heavy erosion events. |
| Possibilities of farm income increase through marketing wine under the ‘vinatura’ label, certifying ecologically produced wine. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| General competition of water and nutrients depending on climate, soil depth and species of cover vegetation | Eliminate/reduce competitive effect of cover vegetation by cutting/mulching vegetation or ripping/ploughing soil. |
| Application of herbicides around vines because of undesirable vegetation in proximity of vine | Find alternative solutions, or minimise application of herbicides. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Farmer initiative within enabling environment [Швейцар]
Initiative and innovation of land users, stimulated by government's technical and financial support.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Nicole Guedel
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна