Reduced livestock numbers [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1343 - Тажикистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Газар ашиглагч:
Sahdullo
Karsang 1
Тажикистан
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Киргизстан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
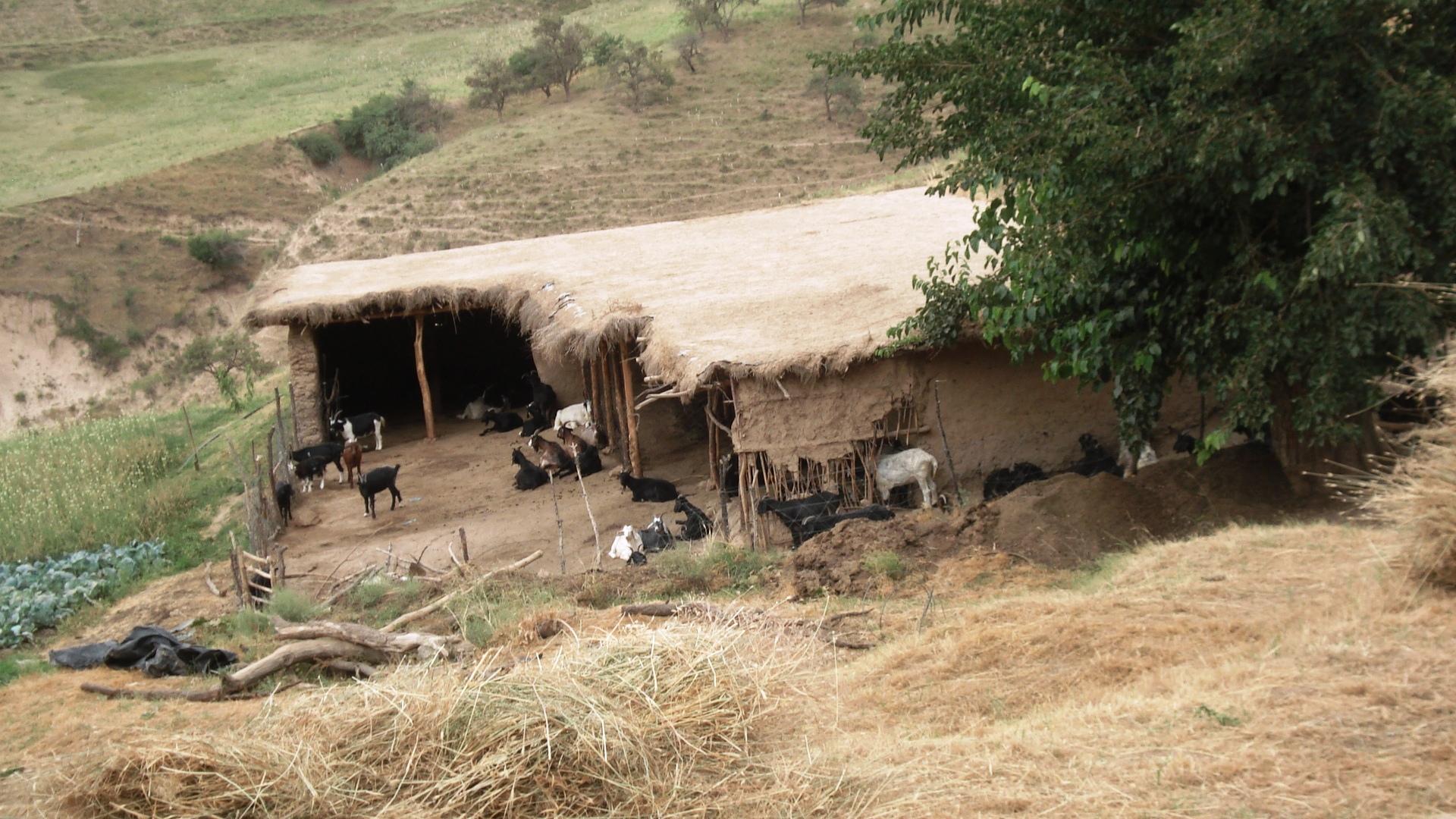
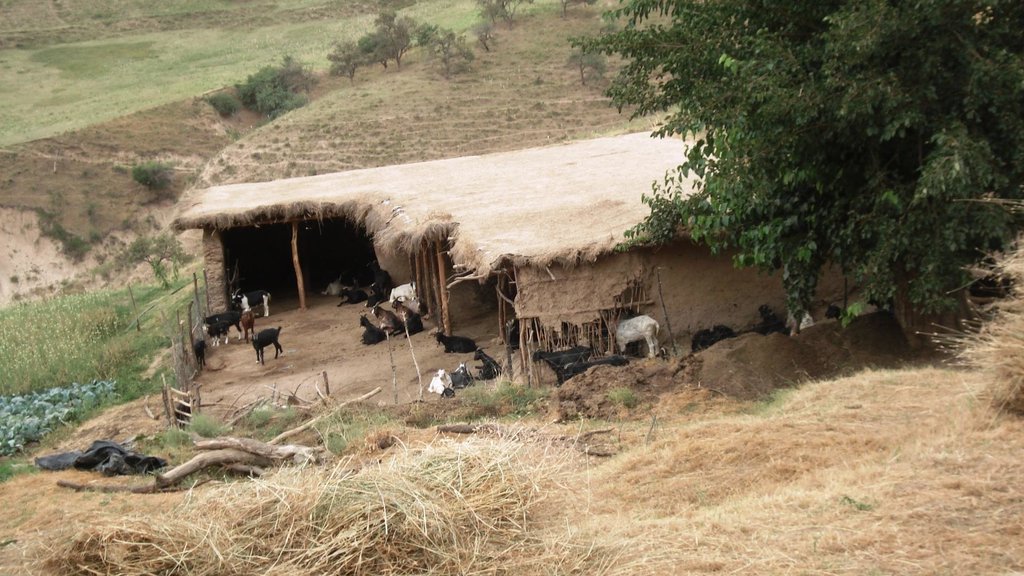
The grasslands are used as pastures by a reduced number of livestock belonging to an individual land user.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
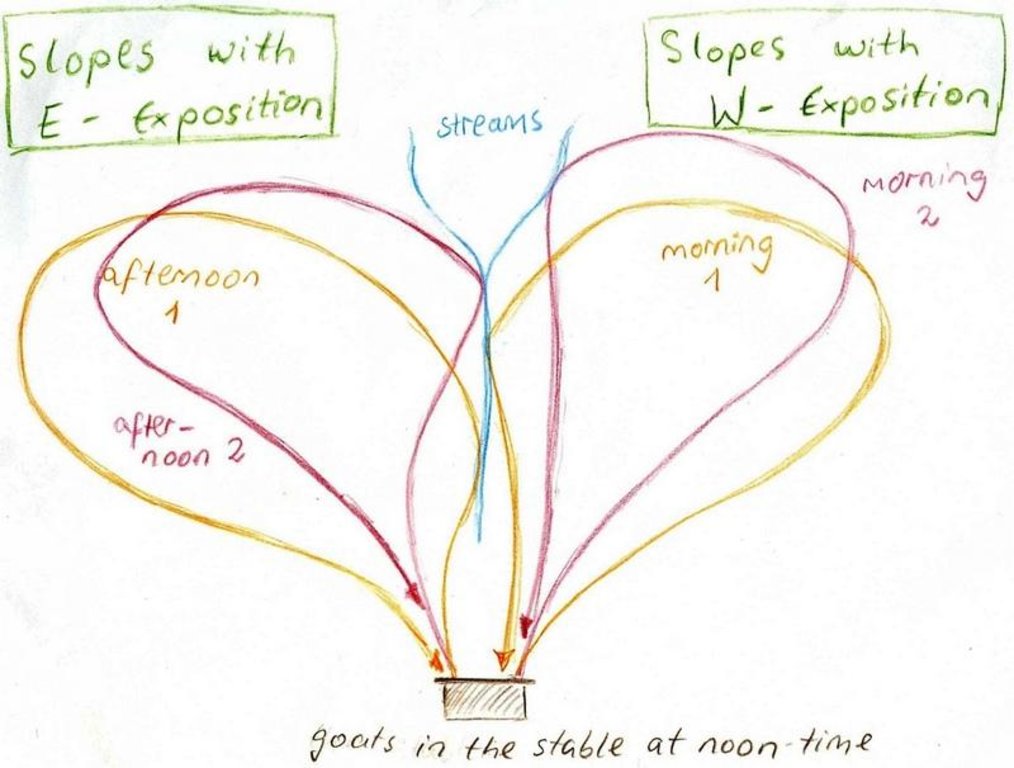
The around 50 goats are brought to the pastures early in the morning and will be brought back to their stable from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. After this, they will be accompanied to the pastures again. In the morning the west-exposed and in the afternoon the east-exposed pastures are visited. The same rotational scheme is applied over the whole year, which means that the same pastures are visited daily. The pastures are exclusively used by the land user fror more than the half of the year (from autumn to spring). In summer the pastures are also used by the village herd of the nearby village (Karsang). Herding is mostly the task of the land user's sons but sometimes he will accompany the animals by himself. Cows are let out on the pastures in the morning and come back in the evening by themselves.
Purpose of the Technology: The reason for west-facing grazing in the morning and east-facing in the evening is that grass is moist at these times of day. This is also why at noontime animals are not on the pastures. The animals are led slowly by the herder as to not tire them, to make them fatter and to avoid damages on vegetation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: No special pasture maintenance activities are undertaken.
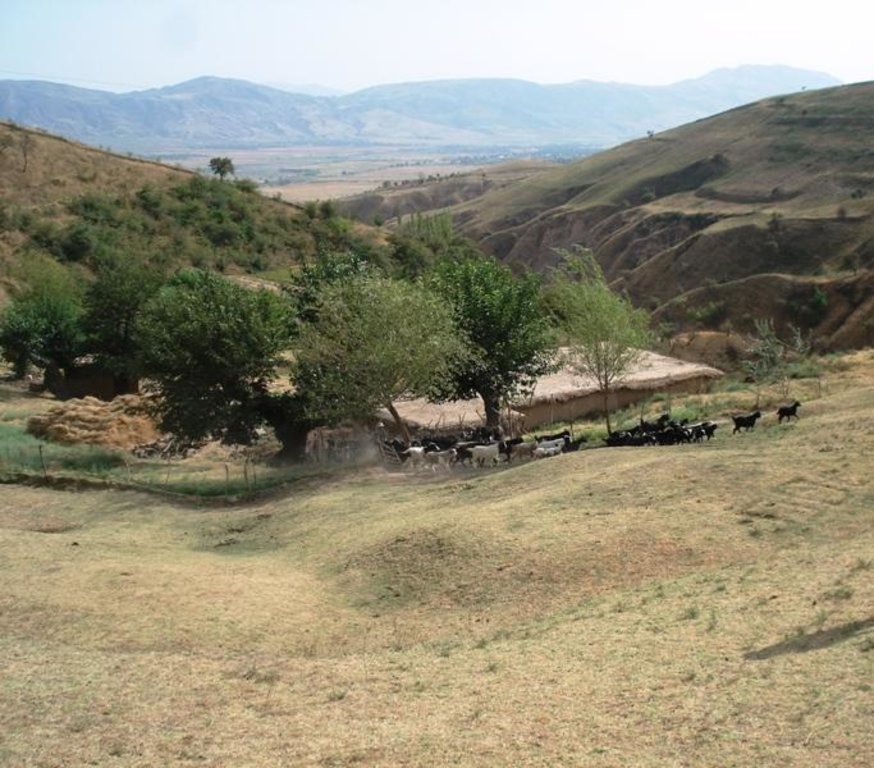
Natural / human environment: The area is around one hour away from the village which actually controls the pastures (communal pastures). In addition snow lies longer in spring than further down. This means that the village herd only comes here from late spring to late summer, which decreases the pressure on the pastures. Together with the situation in a small depression that protects from high radiation in summer this contributes to the generally better pasture quality (greener, more grasses) compared with the village pastures in proximity to the villages. An important factor contributing to the generally good conservation state are the reduced livestock numbers. They are only reduced because the land user is close to these more distant pastures and the village is quite far away.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Region of Republican Subordination
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Faizabad
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.5 km2.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The land user has rented land for the establishment of a self-sufficient agropastoral system after independence (early 1990ies). A part of the area was used as cropland when there was still a village (in the middle of the 20th century) whereas other parts of the land were also used as pastures.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Ранч
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- ямаа
- cows
Төрөл зүйл:
ямаа
Тоо хэмжээ:
50
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Especially in the places where animals pass regularly and where they stay for longer times physical degradation of soils (compaction, crusting) together with the degradation of vegetation (cover and biomass) are major problems. In addition, low fertility is also a problem for vegetation growth.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water erosion problems associated with wood chopping. And trees wood be very important for climate regulation.
Ranching: Goats, cows
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах
- Pi: хөрс хагсах

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Big herds passing daily), other human induced causes (specify) (Inappropriate soils used for grazing), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional (Incapacity of government to implement soil conservation.)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Daily rotation on pastures of the village Karsang.
Location: Above Naobad. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 25.08.09
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user developed his own rotational scheme.)
Technical knowledge required for herders (sons and grandsons of land user): low (They just need to apply the scheme.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase in organic matter, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Reduced livestock numbers
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Somoni
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
3.42
4.4 Establishment activities
Activity Type of measure Timing
1. Buying livestock Management Reduced livestock numbers
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
Specify input Unit Quantity Costs per Unit Total costs per input % of costs borne by land users
Other Buying livestock Goats 50.0 87.7 4385.0 100.0
Total costs for establishment of the Technology 4385.0
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
Activity Type of measure Timing/ frequency
1. Herding Management Daily
2. Giving salt to livestock Management Twice per week
3. Fodder for livestock Management In winter
4.7 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Specify input Unit Quantity Costs per Unit Total costs per input % of costs borne by land users
Labour Herding daily days 365.0
Other Salt for animals for one year 1.0 12.0 12.0
Other Fooder for livestock winter 1.0
Total costs for maintenance of the Technology 12.0
Comments:
The only effective costs mentioned by the land user is salt for animals. Other inputs - be it labour or winter forage - does not have to be paid, respectively bought.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour input is decisive: As long as work is done by family members costs are restricted on alimentation. If external labour is hired, wages have to be added.
5. Natural and human environment
6. Impacts and concluding statements
Links and modules
Expand all
Links
Modules
Primary recommended database
UNCCD
Зохиогч:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Somoni
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
3.42
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying livestock | Reduced livestock numbers |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Бусад | Buying livestock | Goats | 50.0 | 87.7 | 4385.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 4385.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 1282.16 | |||||
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Herding | Daily |
| 2. | Giving salt to livestock | Twice per week |
| 3. | Fodder for livestock | In winter |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Herding daily | days | 365.0 | |||
| Бусад | Salt for animals | for one year | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | |
| Бусад | Fooder for livestock | winter | 1.0 | |||
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 12.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 3.51 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The only effective costs mentioned by the land user is salt for animals. Other inputs - be it labour or winter forage - does not have to be paid, respectively bought.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Labour input is decisive: As long as work is done by family members costs are restricted on alimentation. If external labour is hired, wages have to be added.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility: Mainly medium, but also low
Soil water storage capacity: low - medium
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: Mostly no groundwater, since very hilly.
Water quality (untreated): Good source water, since no diarrhae after drinking it.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Many medical plants
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are implied in housework, whereas men are working as herders, because of traditions.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: The land user only depends on the rented land, cultivated together with his two sons and their families.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
The household has much more grazing land than average village households.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
Pastures are in theory used by village communities, but enforcement of rotational grazing in remote ares is difficult. These pastures are therefore something between communal and open access pastures. The water is used by the land user without any restrictions.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
малын бүтээмж
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
His animals yield higher prices on the market than average livestock.
эдийн засгийн ялгаат байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The productive success of the land user lets him appear richer than the rest of the village.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Having a big herd on a big pasture area is a guarantee for better self-sufficiency.
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially in the establishment phase there was jealousy about the success, especially in fruit-production.
Livelihood and human well-being
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially biomass is reduced by daily grazing.
хөрс алдагдах
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Especially the proportion of grasses is higher compared with other village pastures
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | муу |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
On the long term benefits of animal husbandry might be slightly reduced due to damages on vegetation (and soils) by the own and by the animals of the village herd.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The only land user with this form of management known is the one interviewsd
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: This form of management combines an exceptional personal spirit of innovation and financial means to lease land as to establish a self-sufficient system in the hills. It is also necessary to have a truck and / or car to transport goods to the market and to stay in touch with the rest of the family in the village, since it is too small to offer space to all the household members.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Self-sufficiency is the main success for him. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It requires high labour inputs and motivation, which for the land user are necessary to have success in the post-USSR setting. |
| The animals yield a higher price because they are fatter than the other animals. |
| The geographic location is clearly an advantage, because the land user is far away from the negative impact of village herds. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
At the same time quite positive for soil and water conservation and productive in terms of meat and sold livestock. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the land user could rent (parts of the) pastures the interest of planting trees as a measure of rehabilitation would increase. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Trees cannot recover because of constant grazing. | Only if the land user is sure that investments will profit him, that is if land tenure is clarified, will he invest into active conservation measures. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Especially at the crossing-points of the land user's herd with the village herd degradation phenomena (trampling paths) are visible. | By an agreement between the village (land commitee) and the land user the land use could be reglemented clearer. |
| This form of land use is difficult to maintain for young people who want to participate in social life. And it is not sustainable because it does not permit allvillagers to practice such forms of herding that require much land. | The land user should be able to rent a part of the pastures (smaller than the actually grazed 50 ha) where he would be need to conserve soils and vegetation (for instance. by tree-planting or more sophisticated rotation. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна