Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [Замби]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Silenga Wamunyima
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1187 - Замби
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Замби
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Замби
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - Замби1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Participatory Research and Development [Замби]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Arthur Chomba
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
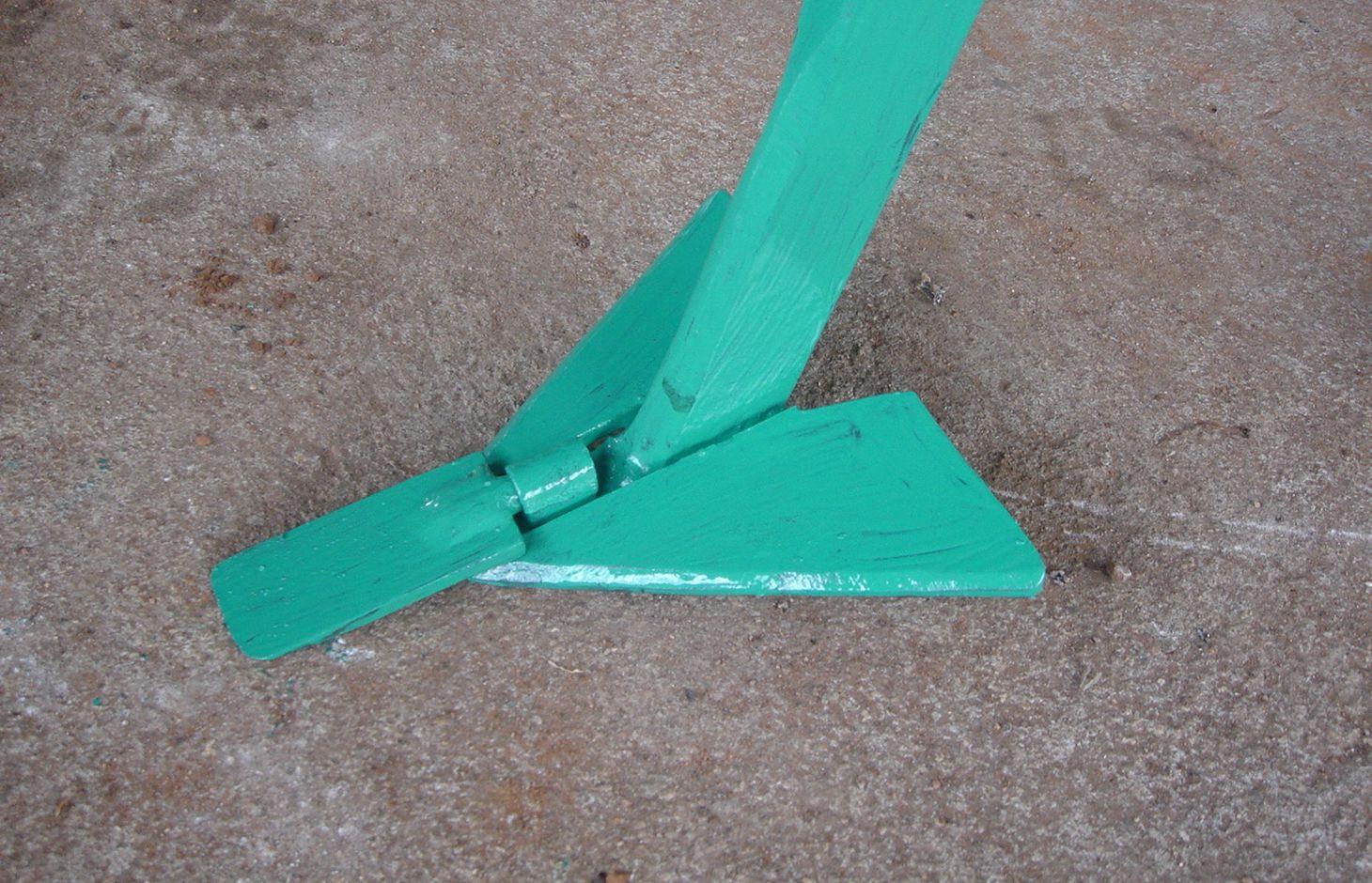
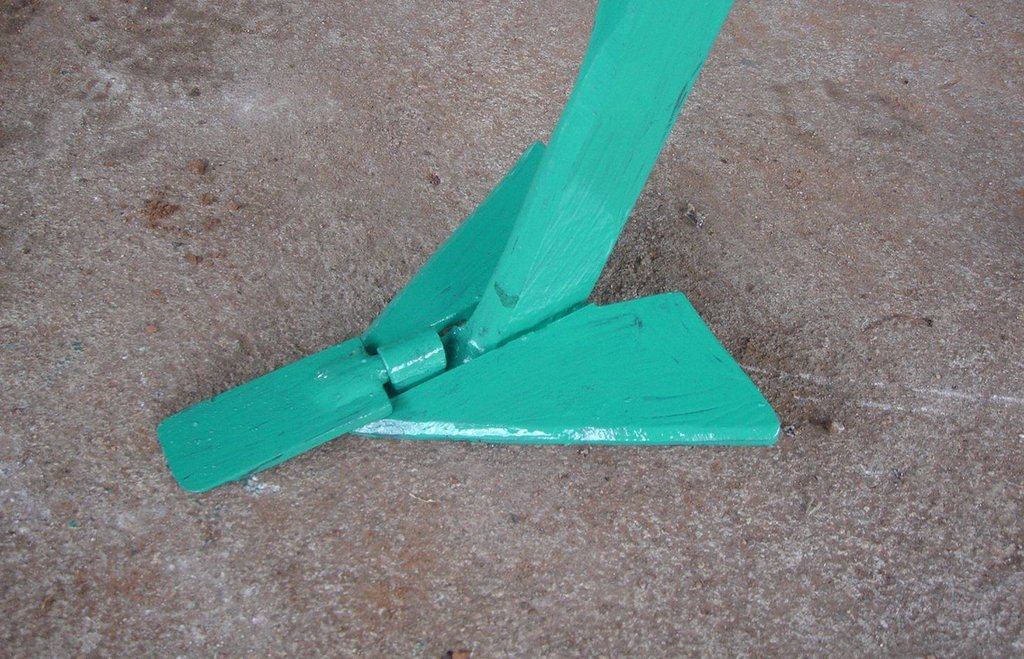
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Замби
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Zambia/Southern Province
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Mazabuka/Magoye
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - эрдэнэ шиш
- даавууны таримал - хөвөн
- тосны ургамал - газрын самар
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March

Бэлчээрийн газар
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- үхрийн аж ахуй - цагаан идээ
- ямаа
- тахиа

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
Тайлбар:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрсийг бага гүнд боловсруулах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах
- А6: Хагд өвсний менежмент
- А7: Бусад
А3: Хөрс боловсруулах тогтолцоог ялгана уу:
А 3.1: Тэг боловсруулалт
А6: Хагд өвсний менежментийг тодорхойлно уу:
А 6.1: шатаасан
Тайлбар:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах
- Pi: хөрс хагсах

биологийн доройтол
- Bl: Хөрсөн дэхь амьдрал алдагдах
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
Тайлбар:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
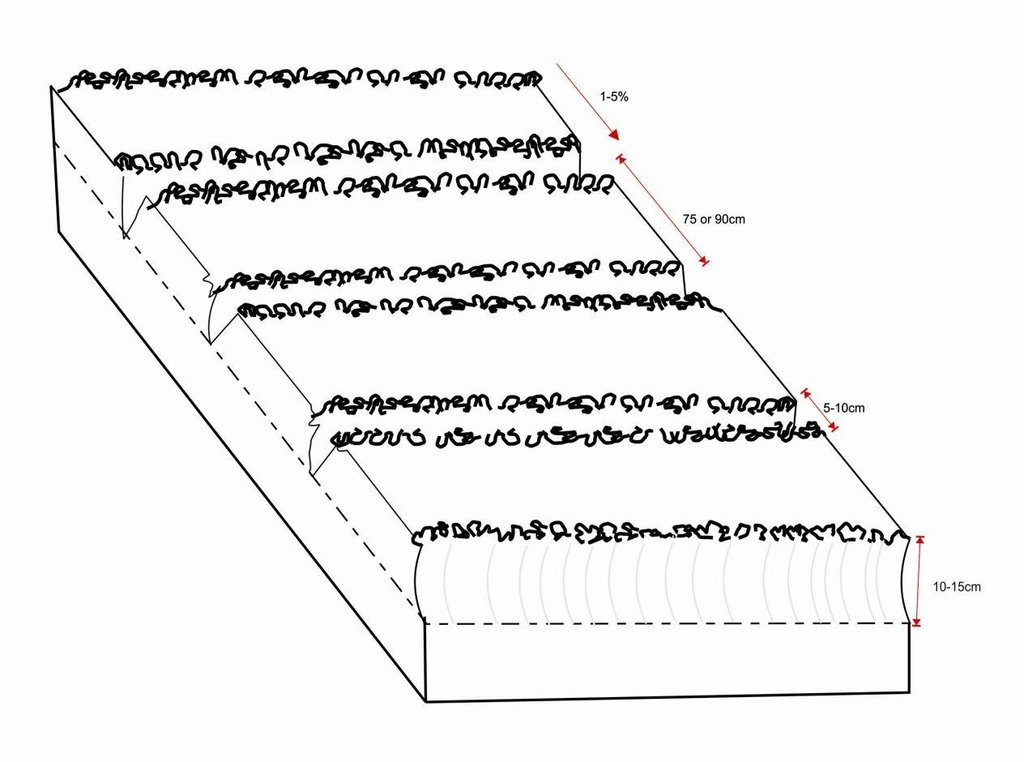
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Зохиогч:
Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
2.40
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | |
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 580.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 580.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | April-May |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8.0 | 2.5 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4.0 | 2.5 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24.0 | 1.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | kg/ha | 20.0 | 2.5 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400.0 | 0.8 | 320.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Herbicides | l/ha | 5.0 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Lime | kg | 1000.0 | 0.042 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 4.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 4.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 621.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 621.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Summer rains from November to March
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
> 50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- хувь хүн
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
3tons/ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
5tons/ha
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to early planting
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Residues needed for soil cover
бүтээмж буурах эрсдэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Better resistance
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
2-3ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
>10ha
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More time and labour freed for other activities
ажлын хэмжээ
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to incresed yields
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
амралт, рекреацийн боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Less time spent on farm operations
олон нийтийн институц
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to better soil cover
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to better soil cover
усны урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Improved soil structure
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to good drainage
ууршилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to better soil cover
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to better soil cover
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to non-inversion tillage
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
хөрс хагарах/ хагсах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
хөрс нягтрах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to deep tillage
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
давсжилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to good drainage
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
хортон шавж/өвчний хяналт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Resistance to chemical weed control
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Ground water contamination
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Only if applied over an extensive area
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Only if applied over an extensive area
голын адагт үерлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Only if applied over an extensive area
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Only if applied over an extensive area
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | сайн |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | мэдэхгүй |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- > 50%
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
FAO
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Participatory Research and Development [Замби]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Arthur Chomba
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна