Terraces with improved seed and fertilizer application [Афганистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Roziya Kirgizbekova
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: Bettina Wolfgramm
- Хянагч: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Palbandi bo tukhmihoi behbudyofta va kud
technologies_607 - Афганистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
Газар ашиглагч:
Mohammad Azim Habibullah
Natural Resources Management Comittee (NRMC)
Sari Joy Village, Takhar Province
Афганистан
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Researcher:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Potential and limitations for improved natural resource management (NRM) in mountain communities in the Rustaq district, Afghanistan (Rustaq NRM Study)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar, Afghanistan (LIPT)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Bern University of Applied Sciences, School of Agricultural, Forest and Food Sciences (HAFL) - Швейцар1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
17/10/2016
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
SLM practices documented in the frame of the Rustaq NRM study were established only recently (1-3 years ago). It is too early for a final judgment on the sustainability of these technologies within the human and natural environment of Chokar watershed.
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
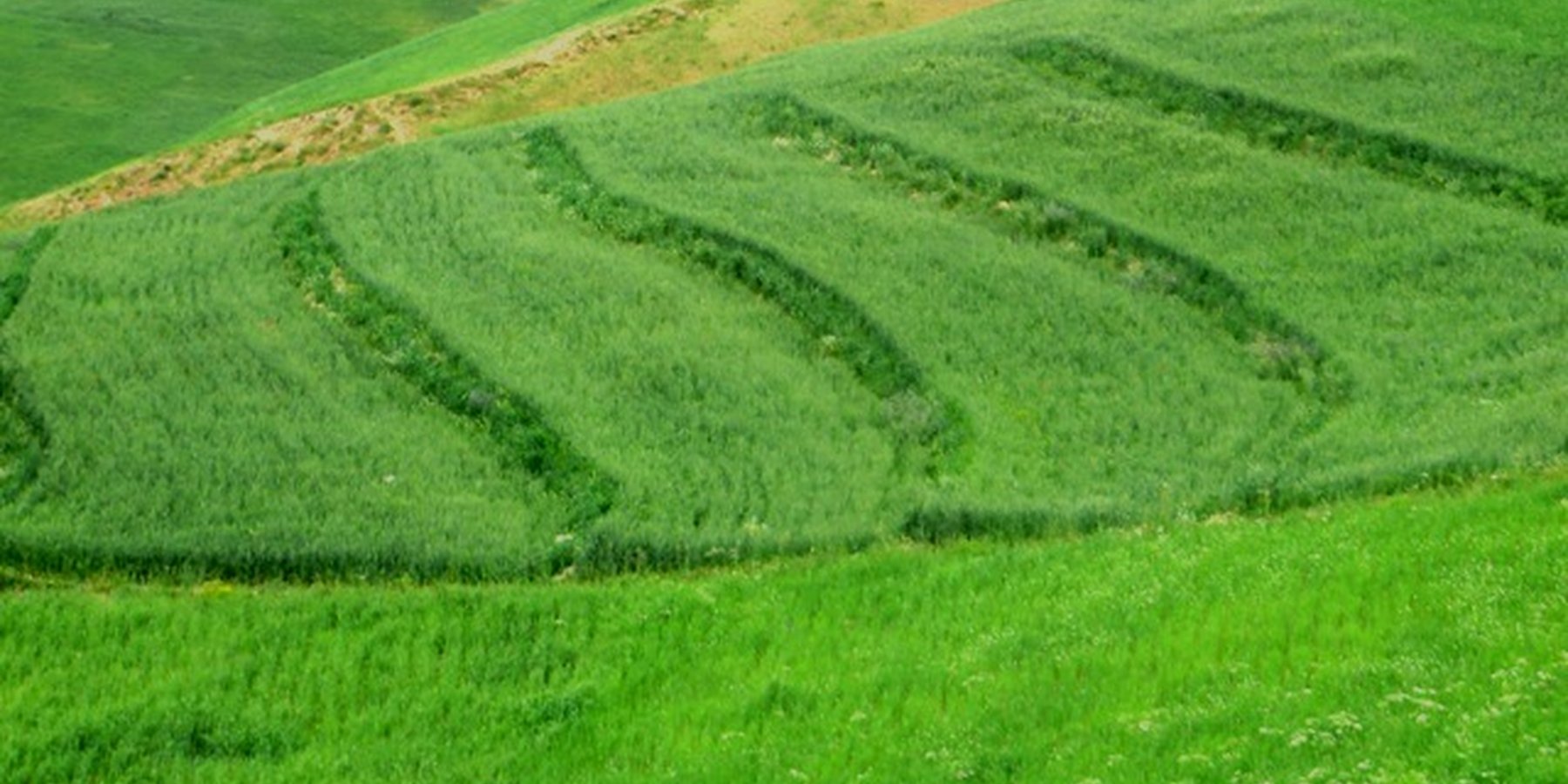
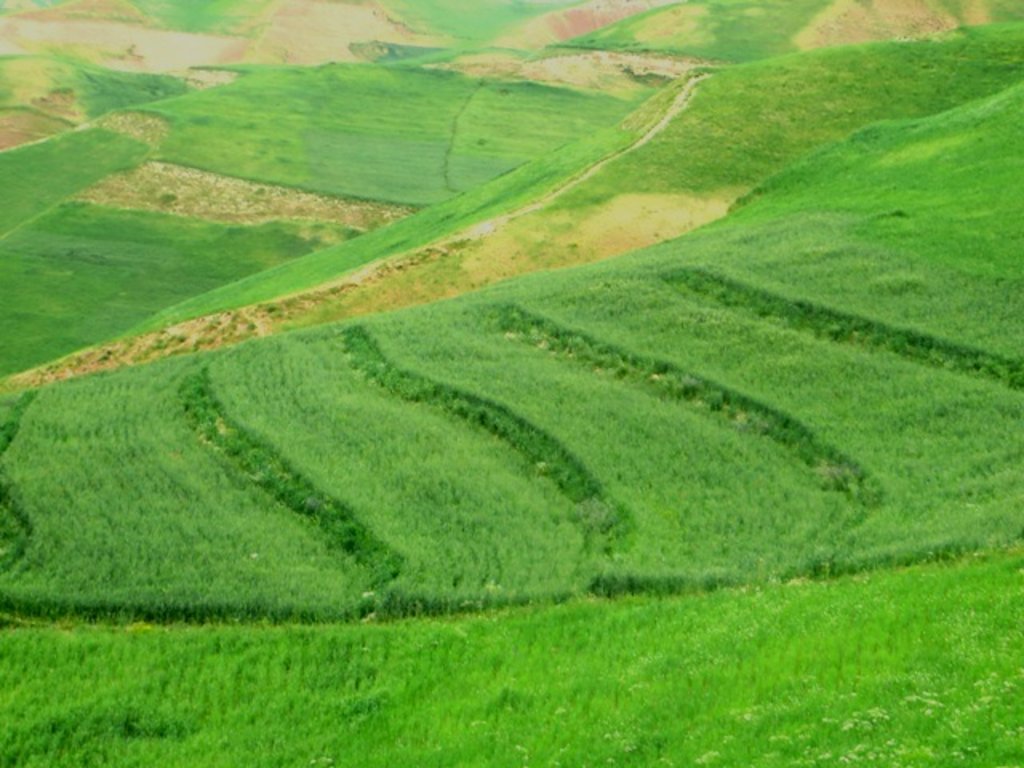
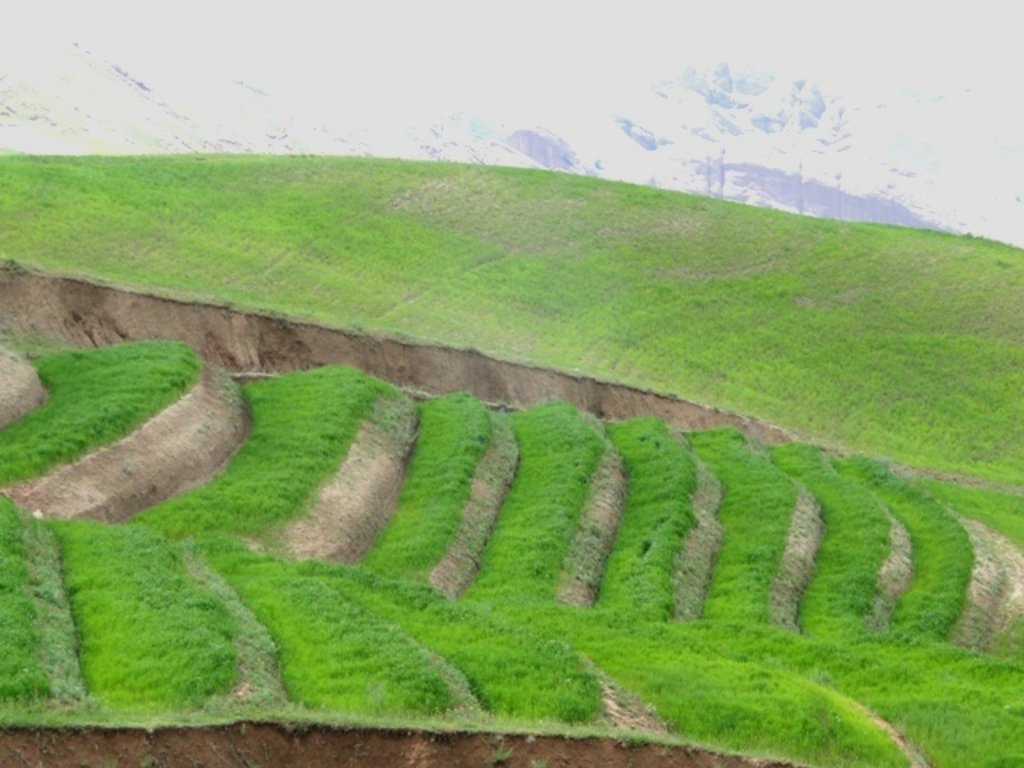
Terraces are established on mountain slopes used mainly for cropping wheat, with the purpose of soil protection from erosion, preserving runoff, sediments and nutrients on-site. Improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on the terraces for increasing crop yield, but also vegetation cover and biomass production, and thus prevent further land degradation.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Project supported implementation of terraces with application of improved seeds and fertilizer has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash floods triggered by heavy rainfall.
The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend mainly on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months.
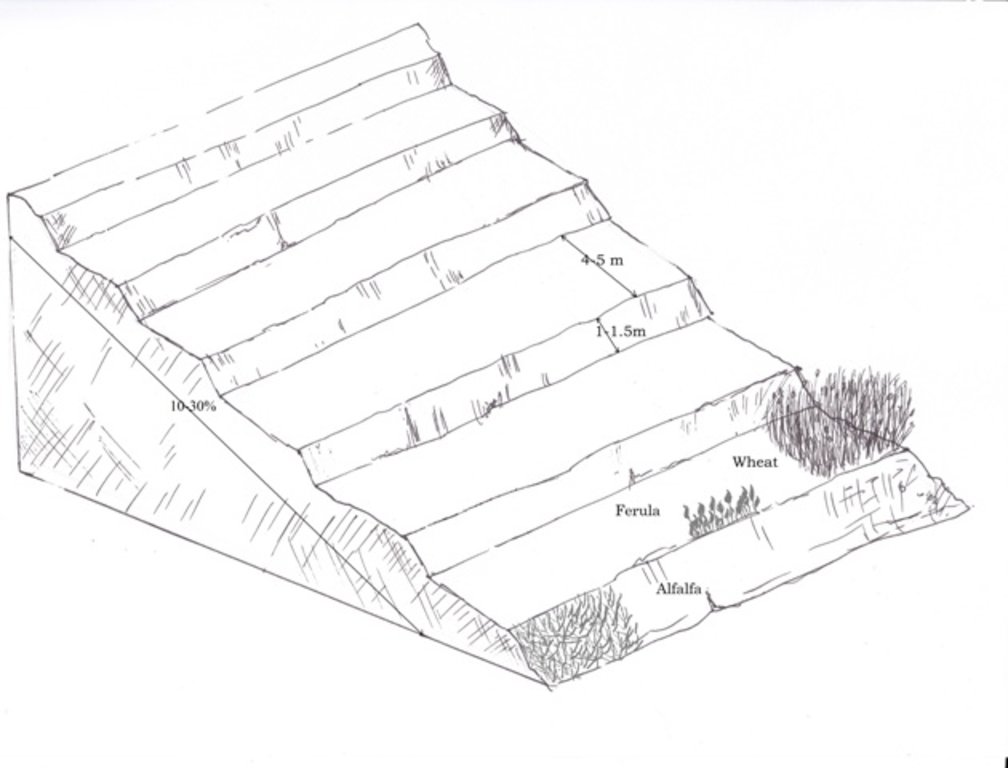
Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions. The project introduced terraces as sustainable land management practices on private plots, situated on rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes to protect the land from soil erosion and prevent the loss of water and fertile topsoil, seeds and fertilizers. The average plot size for terrace implementation is 2 Jerib (0.4 hectares) with contour strips of 40m x 4m. The height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. Terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil above the bench downwards. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, mostly alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs (ferula) are included they are cultivated along the bench contours .
Maintenance activities include small repair work on the riser by adding some amount of soil and re-sowing of alfalfa seeds on those spots.
The terraces allow application of improved seeds and fertilizers without them being washed off. The land-users report noticeable increase of wheat yield from the terraced plot with application of improved seeds and fertilizer compared to the non-terraced plot. An average plot of 0.2 ha on non-terraced hilly cropland used to give about 70 kg of wheat (350kg/ha). On terraces the yield has increased/ doubled to 140 kg on the same plot area (700kg/ha). The expectations regarding terraces remain high as over the time the land user hope their land will become more stable and improved soil moisture and fertility will have positive impact on the productivity as well. However, so far no cost-benefit assessment has been conducted allowing attribution of individual measure to the wheat increase.
Many land users are interested in the terrace technology due to a number of environmental and economic benefits expected, however the costs for building the terrace are considered high by an average local land user. They have to rely on external support in order to have sufficient resources for implementation. Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land (or other villagers land) when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Афганистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Takhar Province, Rustaq District
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Chokar Watershed: Sari Joy (upper watershed), Jawaz Khana (middle watershed), Dashti Mirzai (lower watershed)
Тайлбар:
This documentation is based on the experiences of SLM impementers from Sari Joy (8 terraced plots), Jawaz Khana, (7 terraced plots), and Dashti Mirzai (11 terraced plots) as compiled during FGDs. The terraces located in Jawaz Khana have not been digitized yet. Additionally insights were gained through interviews in all three villages on farmers experiences and observations of terraced plots, with both SLM implementers (46) and observers (28).
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) supported by Swiss Development Cooperation (SDC) from 2012-17
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
Wheat, Alfalfa
Хэрэв технологи нэвтрүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан бол технологи нэвтрүүлэхээс өмнө байсан газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг тодорхойлно уу:
Before implementation of the Technology, only annual crops were cultivated, with wheat as the main crop. Plots were ploughed along the countours mostly by animal traction. In recent years land users are starting to use tractors for ploughing, , where villages and plots are accessible by machinery.
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын тухай нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
May-July
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.5 Технологийн хамрах талбай
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг дундажаар тооцож тэмдэглэ:
- 0.1-1 км2
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Agronomic measures: Terraces increase the economic viability of applying improved seeds and (chemical) fertilizer to badly nutrient depleted cropland.
Vegetative measures: Alfalfa is planted on the risers for stabilizing the terraces, and as an important contribution to fodder cropping.
Structural measures: The leveling of countour strips allows to harvest water and sediments.
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wo: Усны элэгдлийн дам нөлөө

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pi: хөрс хагсах

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: биомасс буурах

усны доройтол
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлт/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Terraces are established predominantly on a privately owned land in a mountainous landscape with varying steepness of slopes.
The average size of a plot is 2 Jerib, which is equal to 0.4 ha. The design of the terrace depends on the steepness of the slope. Mostly rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%) slopes are used for building terraces.
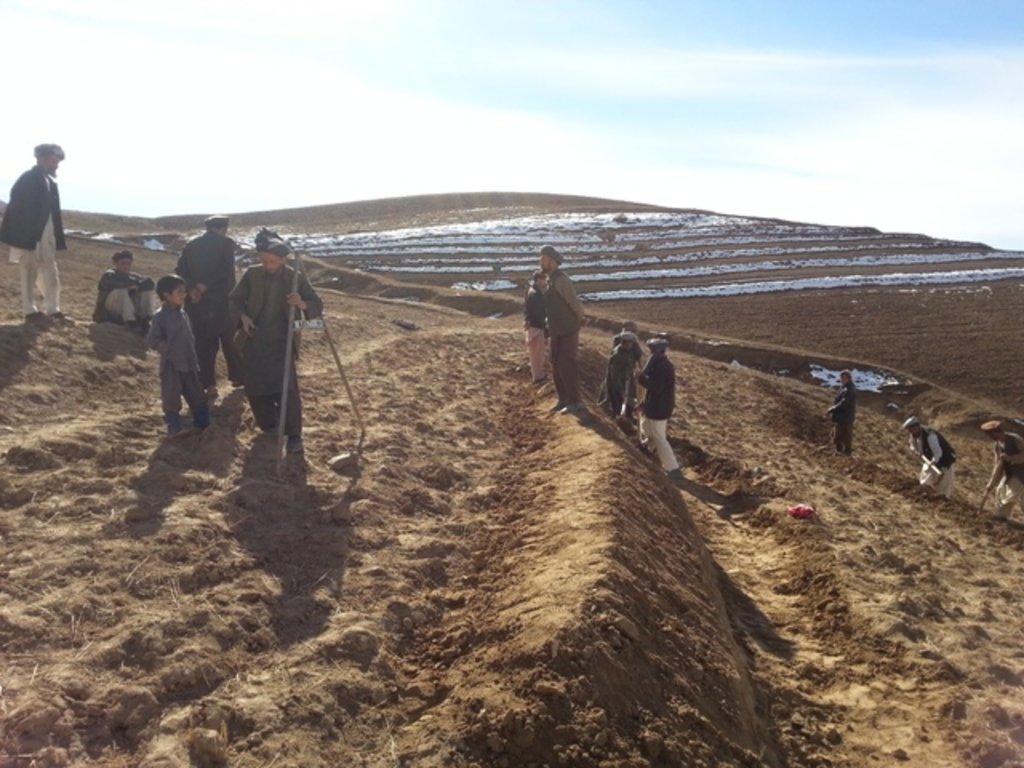
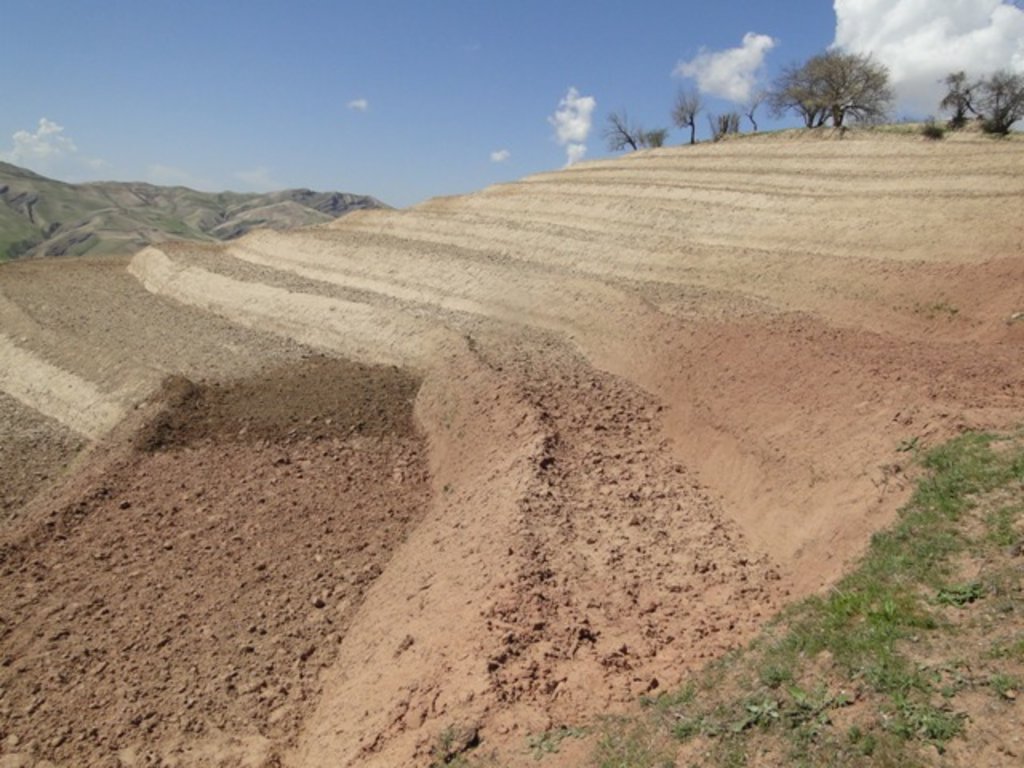
Using an A-frame, the terrace is designed by dividing the slope into contour strips. Depending on the slope steepness, the terrace bench is around 4m wide and the the height of the risers is 1m-1,5 m. The terrace benches are built along the contour by moving the soil of upper bench to the lower bench. The leveled benches of the terrace are cultivated with wheat. The risers of the terrace are mostly used for growing fodder crops, such as alfalfa, which also helps to stabilize the terrace. If medicinal herbs are included, such as ferula, they are cultivated along the bench contours.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
1 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк доллар
Ам.доллар ба үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж хоорондын хөрвөх үнийг тодорхойл (шаардлагатай бол): 1 USD =:
67.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
5.2-5.3 USD
4.4 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of the area for establishing a terrace (Men) | Менежментийн | Autumn |
| 2. | Designing of the terrace using A-frame, assisted by trained technician/project staff (Men) | Барилга байгууламжийн | End of autumn after rainy days |
| 3. | Leveling the soil with a shovel (Men) | Барилга байгууламжийн | Autumn/Winter |
| 4. | Sowing of alfalfa seeds on the risers (Men/women) | Ургамлын | After 20 days of sowing wheat |
| 5. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Агрономийн | Winter/Spring |
| 6. | Sowing of ferula along the contours (Men/women) | Ургамлын | Winter/Spring |
4.5 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Designing of the terrace using A-frame | person-day | 10.0 | 9.0 | 90.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Leveling the soil with a shovel | person-day | 150.0 | 5.3 | 795.0 | 51.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Sowing of wheat and alfalfa seeds | person-day | 10.0 | 5.3 | 53.0 | 51.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Sowing of ferula | person-day | 2.0 | 5.3 | 10.6 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Pick axe | Pcs | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Pitchfork | Pcs | 1.0 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Wheel barrow | Pcs | 1.0 | 38.0 | 38.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | Pcs | 1.0 | 3.8 | 3.8 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Hoe | Pcs | 1.0 | 7.5 | 7.5 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | A-Frame | Pcs | 1.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | |
| таримал материал | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140.0 | 0.42 | 58.8 | |
| таримал материал | Alfalfa seeds | Kg | 17.5 | 0.42 | 7.35 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Ferula seeds | Kg | 2.5 | 6.35 | 15.88 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | DAP | Kg | 125.0 | 0.9 | 112.5 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Urea | Kg | 125.0 | 0.45 | 56.25 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Herbicide | Liter | 50.0 | 0.25 | 12.5 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 1275.48 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
Тайлбар:
Equipment provided by the project was re-used for the implemenation of different SLM practices on different plots. For completness equipment costs are fully accounted for.
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.6 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing the land with animal traction (Men) | Агрономийн | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 2. | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches (Men/Women) | Агрономийн | Winter/Spring/Annually |
| 3. | Application of fertilizer (Men/Women) | Агрономийн | Fall |
| 4. | Weeding (Women) | Агрономийн | Summer |
| 5. | Harvesting wheat (Men and women together) | Агрономийн | Summer/Fall |
| 6. | Harvesting alfalfa (Men and women together) | Агрономийн | Summer/Fall |
| 7. | Collecting and delivering harvested wheat (Men and women) | Агрономийн | Fall |
| 8. | Collecting and delivering harvested alfalfa (Men and women) | Агрономийн | Fall |
| 9. | Repairing terrace risers with a shovel (Men) | Барилга байгууламжийн | Winter/Spring/After heavy rain or snow |
| 10. | Sowing alfalfa seeds on the repaired area (Men/Women) | Ургамлын | Winter/Spring/When required |
4.7 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Ploughing the land with animal traction | person day | 2.5 | 5.3 | 13.25 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Sowing of wheat seeds on benches | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Weeding and Fertilizer application | person day | 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Harvesting and delivering wheat and alfalfa | person day | 70.0 | 5.3 | 371.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Sickle | Pcs | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| таримал материал | Wheat seeds | Kg | 140.0 | 0.42 | 58.8 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | DAP | Kg | 125.0 | 0.9 | 112.5 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Urea | Kg | 125.0 | 0.45 | 56.25 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Herbicide | Liter | 50.0 | 0.25 | 12.5 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 677.3 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des Hommes (Tdh)
Тайлбар:
Costs calculated for a Technology area of 1ha was only done for the purpose of the WOCAT documentation. In reality SLM plots are on average 0.4 ha or 2 jiribs. Costs were simply multiplied by 2.5. The actual costs for a 1ha plot might be slightly different.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Due to the remoteness of the villages where the Technology has been implemented, all the inputs for establishment, such as agricultural equipment, plant material, fertilizers, etc., are purchased in Rustaq town. The expenses for traveling and delivering the inputs affect the establishment costs.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
580.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Average annual precipitation for the area was calculated with 580 mm, with minimums in dry years (2000 and 2001) of 270 mm and maximums in wet years (2009/2010) of 830 mm. The absolute maximum rainfall was calculated for 1986 with 1024 mm. The data series covers the time from 1979 to 2014.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR), http://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Specifications: Derived from the publically available dataset on length of growing period (LGP) (Fischer 2009 / IIASA-FAO). Internet link: http://tiles.arcgis.com/tiles/P8Cok4qAP1sTVE59/arcgis/rest/services/Length_of_growing_period/MapServer
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
The information was derived from two different sources:
- SLM implementers information provided in the Land User Protocol (LUP) during an FGD
- Elevation and slope statistics derived for terraced plots from ASTGTM. ASTGTM is the ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model V002 with a 30 m spatial resolution. More information on ASTGTM is available here: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/node/1079. The data can be downloaded here: https://gdex.cr.usgs.gov/gdex/
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Local land users differentiate between the following soil types where terraces are implemented:
- Light soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); low topsoil organic matter
- Dark soils: moderately deep; texture of topsoil medium (loamy, silty); medium topsoil organic matter
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
дунд зэрэг
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
тохиолдлын
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Floods occur mainly during the rainy seasons in spring and autumn. Availability of surface water differs for the three study villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, and Dashti Mirzai. Sari Joy has sources and good surface water availability. Jawaz Khana has poor water availability as water has to be fetched from a lower laying stream. Dashti Mirzai has good water availability also from an irrigation channel.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
- Нийт орлогын 50 %-иас дээш
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
- ахимаг нас
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчийн өмчилж буй, эзэмшиж буй, түрээсэлж буй эсвэл ашиглаж буй (ашиглах эрх) газрын талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
Those who own land and use water for irrigation are obliged to pay for the water. The payment is made both in kind and in cash to the Mirob, the person in charge of distributing water in the community. The amount of the payment varies from village to village.
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
350 kg / ha
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
700 kg / ha
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The integration of measures including agronomic (improved seed and fertilizer) and structural (terraces to control water flow and loss of top soil, including nutrients and seeds) results in an increase of crop yield already in the first year. The effects cannot be attributed to one or the other measure specifically.
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Alfalfa is planted on the risers.
бүтээгдэхүүний олон янз хэлбэр
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
No change in total area for production, as the riser of the terraces are used for fodder production. However, there is some reduction of area available for annual crop production.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The yield of the main staple crop (wheat)has been reported to be double on terraced plots with application of improved seed and fertilizer. In addition, fodder crops, such as alfalfa grown on the risers, can be harvested.
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Technicians in the villages were trained in the use of A-frames. Implementers of terraces voiced that they themselves would not be able to replicated the designing of terraces.
нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have the opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
in situ water harvesting
хөрс алдагдах
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамалын бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Both an increase in vegetation cover during the growing season when most erosive rains are observed as well as permenant vegetation cover from perennial alfalfa plants can been observed.
газрын дээрхи / доорхи карбон
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
Нөлөөллийн үнэлгээнд хамаарах нэмэлт тайлбар:
These comments apply to 6.1 and 6.2:
- Socio-economic impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the benefits for their Technology. They were asked to indicate production increase of crops; fodder; animals; wood; non-wood forest products; increase in product diversity; or production area. The most important increase they rated with 3, the second most with 2, others with 1 point. Averages of the points given by all SLM implementers are reflected here.
- Ecological impacts and off-site impacts: Based on the Land User Protocols: Individual SLM implementers were asked to rate the on-site and off-site impacts of the Technology on water; soil; and vegetation. They were asked to indicate the strength of impacts with three, two or one points. Averages of the points given by all implementers are reflected here.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | маш сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Тайлбар:
Based on the multi-criteria matrix: SLM implementers from three villages were asked to jointly discuss and rate how much the SLM technology reduced the lands vulnerability to drought and local rainstorms. Only vulnerability to the most prevalent climate extremes (drought and local rainstorms) was discussed. SLM technologies were rated as reducing vulnerability poorly , well, or very well. The average points reflected here are from multi-criteria matrices compiled in three villages where the SLM technology had been implemented.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Тайлбар:
Costs: As larger parts of the establishment of the technology were covered by the project, farmers consideration of the total costs are likely underestimated.
Benefits: Two plots were terraced in 2012, and 5 plots in 2013. However, most terraces were implemented in 2014 (11 plots ) and 2015 (8 plots). The Rustaq NRM study was conducted in autumn 2016. 1-2 years of cultivating the terrace system is too short a period for providing evidence on short- and long-term returns.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
10.7 ha has been terraced within the 3 study villages with LIPT project support.
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
Based on the Land User Protocol: Individual SLM implementers were asked whether they received support for implementing the Technology. Each indicated the type of support he received from the proposed options: "Full Support 100%, Some Support, No Support 0%". 3 implementers claimed full project support, 22 claimed some support, and 1 implementer claimed no project support.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв Тийм бол ямар өөрчлөлтөд дасан зохицсон бэ:
- зах зээлийн өөрчлөлт
Дасан зохицох зорилгоор технологид хийсэн өөрчлөлт (хийц, материал, төрөл зүйл г.м.):
Ferula is planted on the terrace in addition to wheat and alfalfa. The resin-like gum from the dried sap extracted from the stem and roots of Ferula is in high demand as a basic product for pharmaceuticals. Ferula can be sold to local merchants, who resell it to India, and is thus intercropped by some farmers on the terraces.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Notable higher crop yields on the plots where improved seeds and fertilizer are applied on newly established terraces. Farmers have high expectations for the years to come and for yields of annual crops (such as wheat) to remain high. |
| Diversity of crops planted on terraces is valued by the land users. For example, cultivating wheat and alfalfa on the terraced plot provides household with the key crop and also fodder for the livestock and thereby contributes to securing food for the family and maintaining better health of their cattle. Additionally, some farmers have started intercropping Ferula, a medical herb and cash crop. |
| Farmers percieve soil quality on terraced plots with fertilizer application to improve. An improvement in soil fertility (which may relate first of all to the effects of fertilizer application) and increased soil moisture have been reported. Single statements also related to effectiveness of applying fertilizer on terraced plots, as here fertilizer is not washed away during rains. |
| Terraced plots are considered less vulnerable to the effects of rainstorms and dry spells, than non-terraced plots on slopes where annual crops are cultivated. |
| Women considered an advantage that during the establishment phase, men were paid by the project to work on their own land when building the terraces. Thus, there was no need for men to go for seasonal labour migration and they stayed at home. At the same time the terracing of the land is seen as an opportunity to improve the land resources on their families plots. An increase in women's workload related to bringing food to the field during establishment was considered to be acceptable, especially compared to the expected increase in yields. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The application of fertilizer on terraces is expected to show multiple effects: yields from these fertility depleted croplands can be increased. This includes an increase in biomass production, which may be used as green manure on the field or as animal feed or as straw. Further, vegetation cover during the growing period can be increased, which helps to protect the soil from erosive rains. |
| The project paid establishment of terraces on farmers' plots provided 20 days of employment per 2 jerib (0.4 ha) plot for farmers in their home villages. At the same time the terracing is a long-term investment into the land resources. Terracing provides an opportunity to decrease soil degradation and even to rehabilitate degraded lands. Application of improved seeds and fertilizer contribute in the establishment year to increased crop and fodder yields. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
|
The implementation costs are high and land users state that it is impossible for them to cover establishment costs on their own. |
|
| Farmers expectations partly exceeded the actual yield harvested from the terraces in the first years after the implementation. | |
| Both men and women from households that have implemened terraces state that during the establishment year the household experiences an increased workload, that is not well compatible with other on-going household / farm activities. | |
| The production area for annual crops only is slighty reduced. | So far not all farmers seem to use the production area fully. Intercropping with perennial plants is recommended in order to use the risers of the terraces for fodder production. Some farmers have started intercropping of Ferula as cash crop. |
| Sufficient own land is required. | How does the amount of cropland affect the innovation readiness of a farmer? A better understanding is required on farmers willingness to take a risk for investing in a new SLM technology, and especially terracing, and influencing factors. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The technology requires technical knowledge for implementation and maintenance, which is key for successful adoption, replication and upscaling. The project trained technicians to support land users with the design of terraces. While the project aided implementation of terraces has improved the general knowledge and awareness of the land users on the benefits of SLM practices, most farmers will not be able to design terraces on their own. | |
|
Technically correct design of the terrace presents a challenge and might not be always achieved. Forward sloping terrace benches may lead to channeled runoff and have the risk of rills and gully formation. |
|
| There is an attribution gap regarding the increased wheat yields, especially with regard to individual contribution of the terraces, the application of improved seeds and the fertilizer, and the combined effects (role of terraces in making improved seed and fertilizer application effective). | A cost benefit analysis (CBA) needs to be conducted to determine short- and long-term returns of the SLM technology. On farm trials are necessary for assessing impacts of the different measures (agricultural, vegetative and structural measures) before-and-after, as well as with-without the SLM technology. |
| Terrace maintenance is crucial. If not maintained properly for a longer period of time, the damaged terrace can lead to further land degradation through channeled runoff, sever erosion and possible risks of disaster for the surrounding settlements on the slopes. | |
| The technology is established mainly by better-off households, which own more land than the average SLM implementer. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Focus group discussions (FGD) were organized by the CDE team to collect information from SLM implementers. Total of 26 land users who have implemented terraces participated in the FGDs held in the three villages of Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Interviews were conducted by the HAFL team to collect information from persons representing all the three study villages. Very detailed interviews were conducted with 74 persons interested in terrace implementation, of which 46 persons are from households that already have implemented terraces.
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
The technical staff of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq, responsible for the implementation of the technology were consulted on a number of occasions during the compilation of this material.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Information provided in the reports of Tdh LIPT Project in Rustaq served as an initial source of information during the preparatory phase and also solidifying the description of the technology and area of implementation. Other background papers on Afghanistan were referred to for general information on agriculture and natural resource management in Afghanistan.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна