Agroforestry to improve soil fertility, water retention, and sustainable income for local communities [Афганистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Ahmad Zia Jalalzai
- Хянан тохиолдуулагчид: Mohammad Amin Nesar, Megha bajaj, Mir Wali Khan Lakanwal
- Хянагчид: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
د خاورې د خاصلخيزۍ ودې، اوبو ذخيره کولو او محلي ټولنو له پاره د دوامداره عايد په موخه د کرنيزې ځنګلدارۍ قطعو جوړول /ایجاد پلات زراعت جنگلی برای بهبود سلامت خاک، نگهداری آب و تأمین درآمد پایدار برای جوامع محلی
technologies_7443 - Афганистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Andar Ahmadullah
FAO Afghanistan
Афганистан
Газар ашиглагч:
Mohammad Haider
Ghaibi Rangeland Management Association (RMA)
Афганистан
Газар ашиглагч:
Ghullam Sakhi
Qarcha Rangeland Management Association (RMA)
Афганистан
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Community-based sustainable land and forest management in AfghanistanТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - Афганистан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
This technology is applied with a focus on land restoration and conservation and is not problamatic with regard to land degradation.
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
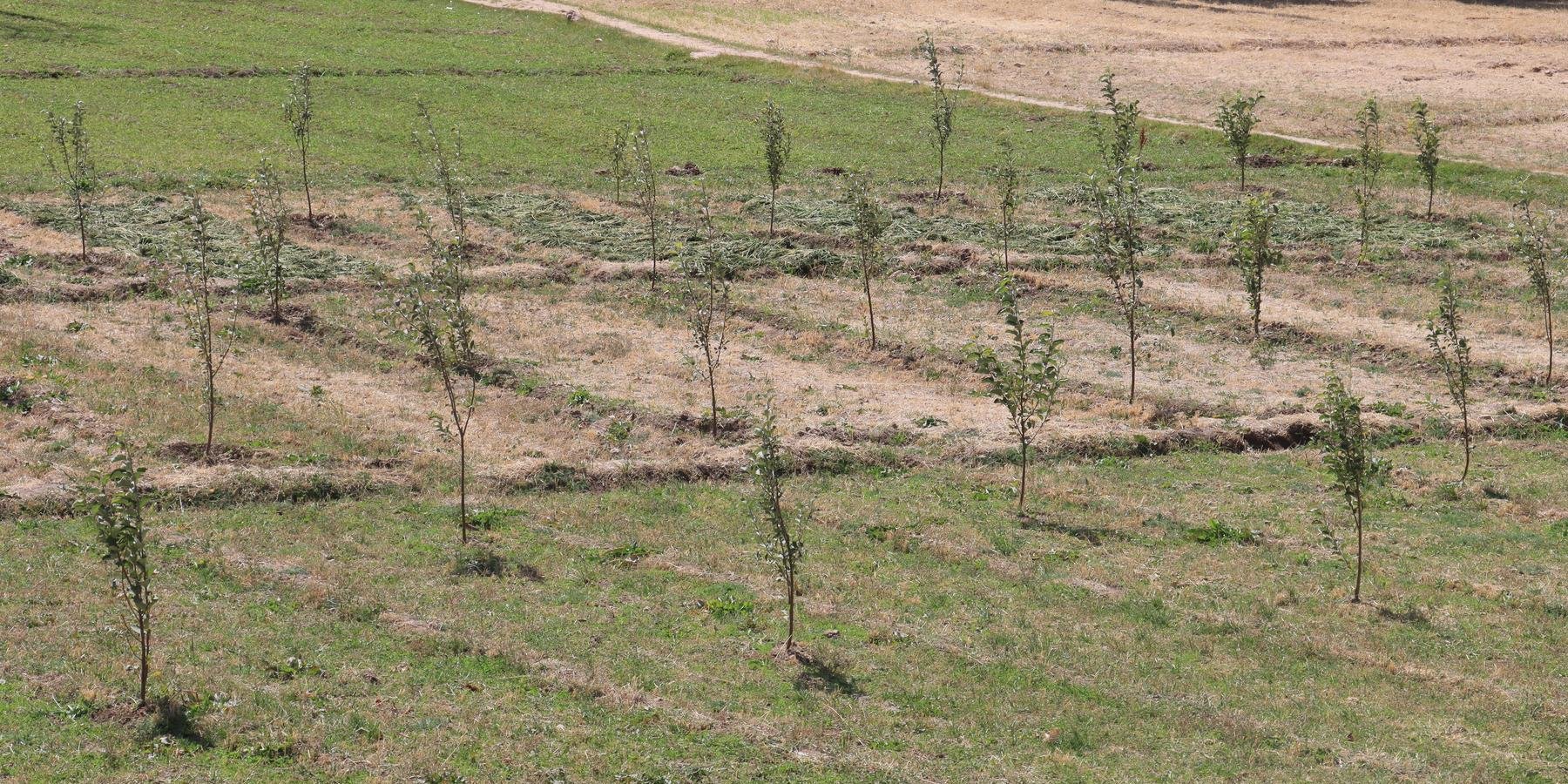
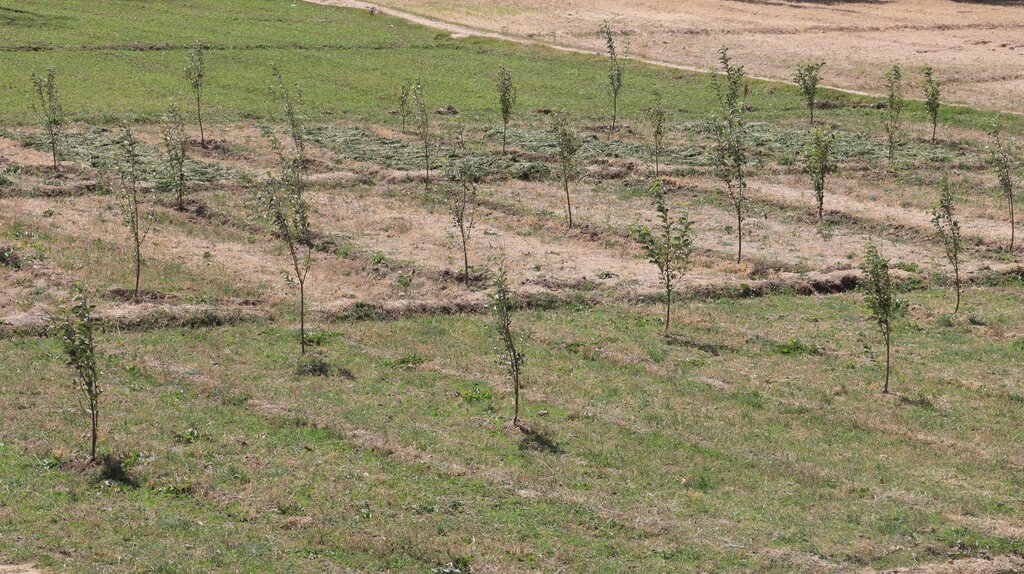
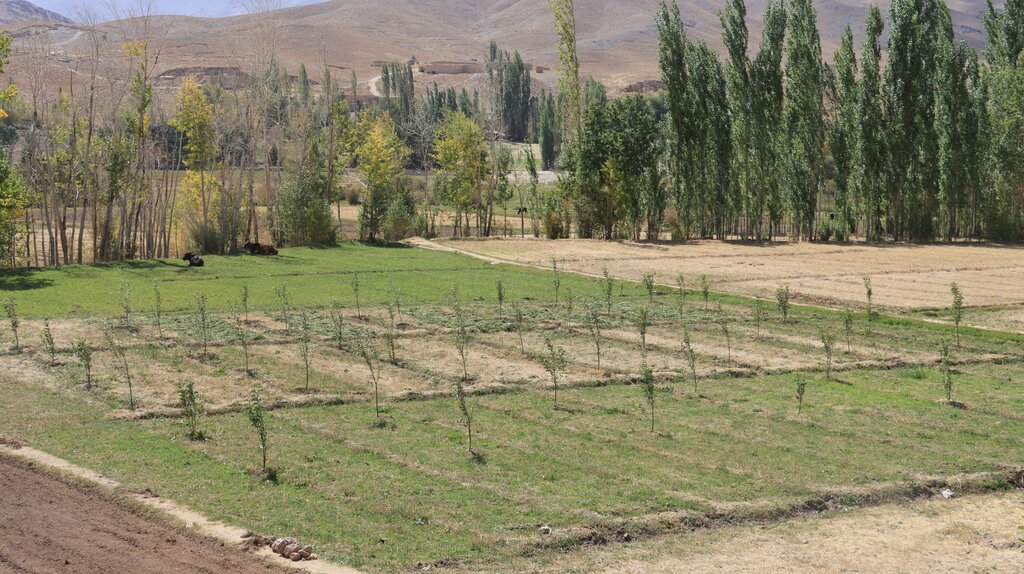
The Agroforestry system in Malistan district combines traditional practices with support from the Community-Based Sustainable Land and Forest Management project in Afghanistan. This initiative provides technical support, training, and resources like apple trees, fertilizers, and alfalfa seeds to establish 400 orchards (1,000 m² each). The goal is to enhance community livelihoods by reducing dependence on rangelands, helping to preserve local ecosystems.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
The agroforestry system adopted in the mountainous districts of Ghazni province, particularly in Navor and Malistan district is an innovative approach that is transforming the way local farmers cultivate their land. This system integrates agricultural crops, tree cultivation, and livestock farming to maximize land productivity while promoting environmental sustainability. At the heart of the system are apple orchards, alfalfa seeds, and fertilizers, which work together to enhance food security, provide livestock feed, and improve soil fertility. Supported by modern agricultural techniques, the project includes a total of 400 orchards, each covering 1,000 square meters, helping to alleviate pressure on overgrazed rangelands while improving local livelihoods.
This agroforestry method is particularly well-suited to Ghazni’s rugged terrain, where farming communities rely heavily on livestock and rangelands for sustenance. However, the region’s dry climate, frequent overgrazing, and ongoing land degradation have made traditional farming increasingly unsustainable. By introducing apple trees and alfalfa cultivation, farmers now have an alternative source of income and animal feed while actively restoring degraded lands. Alfalfa serves as a nutrient-rich fodder for livestock, and in return, livestock manure is used as fertilizer, creating a self-sustaining agricultural cycle that enhances soil health.
Beyond its environmental benefits, this system plays a crucial role in improving livelihoods. By diversifying agricultural production, it enhances food security and generates additional income for local farmers. More importantly, it helps alleviate the burden on fragile rangelands by offering an alternative source of livestock feed, reducing overgrazing and preventing further land degradation. Through natural nutrient recycling, alfalfa provides essential fodder for livestock, while their manure replenishes soil nutrients, ensuring long-term soil fertility.
To successfully implement and maintain this system, several key activities and inputs are required. Local farmers receive specialized training and technical support to equip them with the necessary skills. Essential supplies, including apple saplings, fertilizers, and alfalfa seeds, are provided to help establish the orchards. Additionally, proper maintenance, such as irrigation, pruning, and weed control, ensures that the orchards remain productive. Soil and water conservation efforts, such as constructing contour banks and water diversion structures, further safeguard the land against erosion and water loss.
The impact of this technology extends far beyond the fields. Environmentally, it significantly reduces soil erosion, improves water retention, and restores soil health. Economically, it increases household income by boosting apple production and generating sales from alfalfa as livestock feed. Socially, it strengthens community resilience by offering a reliable source of food and income, while encouraging the adoption of sustainable farming practices.
While many farmers appreciate the system for its cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and diverse benefits, some challenges remain. Because of the duration for fruit production of apple trees are typically taking three to four years to bear fruit, patience and long-term planning is crucial. Additionally, the dry climate means that farmers must invest extra time and effort in irrigation, especially during drought periods, to ensure optimal growth and fruit yield. Despite these challenges, the agroforestry system in Malistan and Navor presents a promising solution for sustainable land management and rural development.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.4 Технологийн дүрс бичлэг
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт:
Artificial reseeding plays a vital role in the restoration of degraded rangeland ecosystems. Reseeding of local palatable fodder species in degraded rangeland is a restoration technique aimed at reintroducing native plants that support soil health and local biodiversity. This process enhances forage availability for grazing animals, stabilizes soil, and helps combat desertification by promoting sustainable vegetation cover. By using palatable, locally adapted species, artificial reseeding improves the health and productivity of degraded rangeland ecosystem.
Он, сар, өдөр:
20 october 2023
Байршил:
Malistan district Mokly village.
Зураглаачийн нэр:
Ahmad Zia Jalalzai
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Афганистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Southeastern Ghazni province
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
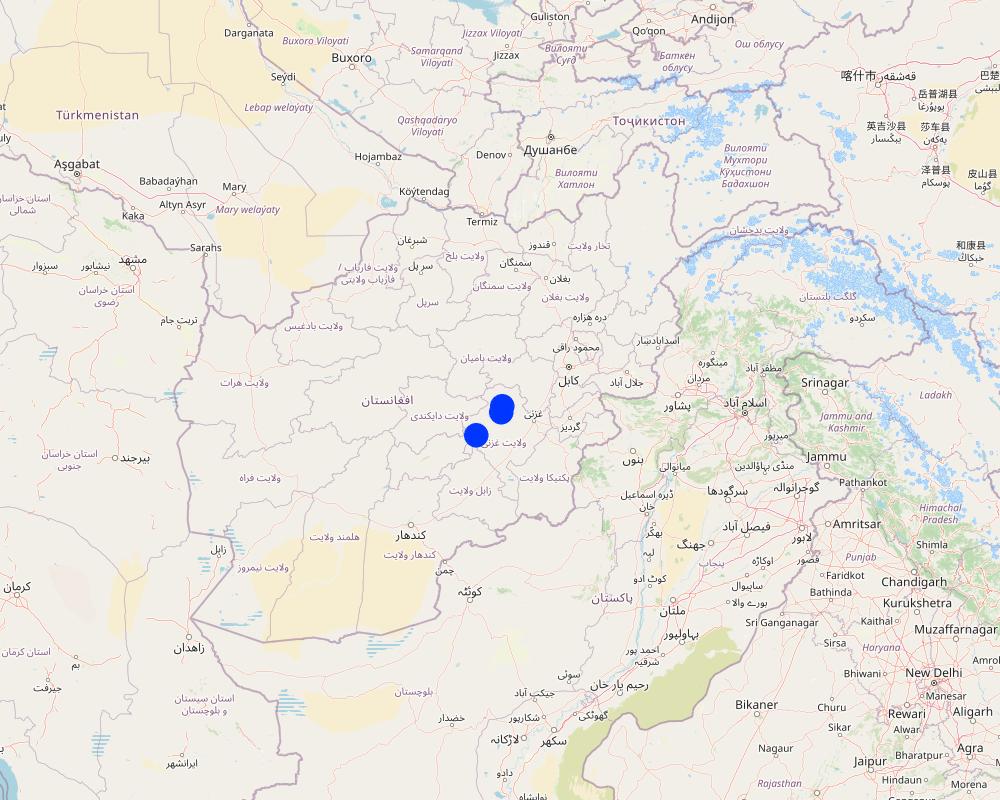
The technology is applied in 44 villages through 7 Rangeland Management Associations (RMAs). Hemat and Faqir are sample villages reflected in the map.
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
This project established 400 agroforestry plots (for 400 land users); the coordinates represent the samples locations for 400 orchards.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2022
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
The agroforestry system was introduced as an innovative, community-driven approach, offering an environmentally friendly alternative. This initiative was developed in response to the community's call for sustainable solutions that enhance livelihoods while preserving natural resources.
The agroforestry system integrates apple tree plantation with alfalfa intercropping, enhancing land productivity and sustainability by providing both fruit and forage. This technology improves livelihoods and promotes soil fertility and moisture retention for long-term environmental benefits
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
- нийгэмд үзүүлэх үр нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- цэцэгт таримал - олон наст
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
summer and fall season
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар таримлыг сөөлжлөн тариалдаг вэ?
Alfaalfa is mainly used for intercropping
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- үхрийн аж ахуй - сүүний ба махны чиглэлийн (жишээ нь зебу)
Тариалан-мал аж ахуйн нэгдсэн менежмент хэрэгждэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
Animal manure is added in the fall season
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- эдийн засгийн аюулгүй байдал, хөрөнгө оруулалт татах чадвар
Төрөл зүйл:
үхрийн аж ахуй - сүүний ба махны чиглэлийн (жишээ нь зебу)
Тоо хэмжээ:
1345
Тайлбар:
In autumn, people in the community graze their land with animals like cattle, sheep and goats. To manage and control the grazing, they use stakes and ropes to fence a specific area of land and ensure that the saplings are not damaged.
Planting of fruit trees helps to reduce pressure on rangeland grasses and shrubs to support landscape restoration.
Most land users plant apple trees and alfalfa. Some land users, who do not have animals, cultivate legumes instead of alfalfa.
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- цэцэгт таримал - олон наст
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар таримлыг сөөлжлөн тариалдаг вэ?
Earlier, wheat was planted only on the cropland and the only grazing land that was overgrazed and it became degraded. Now there is a mixed system agro-pastoralism in place due to the application of the technology.
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- үхрийн аж ахуй - сүүний ба махны чиглэлийн (жишээ нь зебу)
Тариалан-мал аж ахуйн нэгдсэн менежмент хэрэгждэг үү?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
Most land users plant apple trees and alfalfa seeds. Some land users, who do not have animals, cultivate legume intercropping instead of alfalfa.
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаатай арга хосолсон
Тайлбар:
Out of the 400 agroforestry plots, some have full water availability, while others have 80% water availability. About 10% of the agroforestry plots receive only 40% to 60% of the required water. The saplings are mainly irrigated by spring rainfall. In a few plots, additional irrigation is provided two to three times during the warm season by transporting water from the canal using animals.
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
- Тариалан-мал аж ахуйн нэгдсэн менежмент
- Хөрсний үржил шимийн нэгдсэн менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- M6: Хог хаягдлын менежмент (дахин боловсруулах, эргүүлэн ашиглах эсвэл бууруулах)
Тайлбар:
Residue management of trees is used for fuel, and alfalfa is utilized as livestock fodder in winter.
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрс салхиар эвдрэх
- Et: Хөрсний гадаргын зөөгдөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
- Ca: Хүчилжих
- Cp: Хөрсний бохирдол
- Cs: Давсжилт / шүлтжилт

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pc: Хөрс дагтарших
- Pk: Гадарга дээр хагсах, хагарах
- Pw: Усны түвшин нэмэгдэх буюу намагших
- Ps: Хөрсний органик үе давхаргын алдрал, гадаргын суулт

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bh: Амьдрах орчин доройтох
- Bq: биомасс буурах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
- Bl: Хөрсөн дэхь амьдрал алдагдах
- Bp: Хортон шавьж/өвчлөл ихсэх, махчид цөөрөх

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
- Hg: Гүний ус / уст үеийн усны түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
- Hp: Гадаргын усны чанар муудах
- Hw: Ус намгархаг газрын буферлэх буюу хаах чадвар багасах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
Тайлбар:
This project reduced the land degradation by applying this agroforestry technology.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
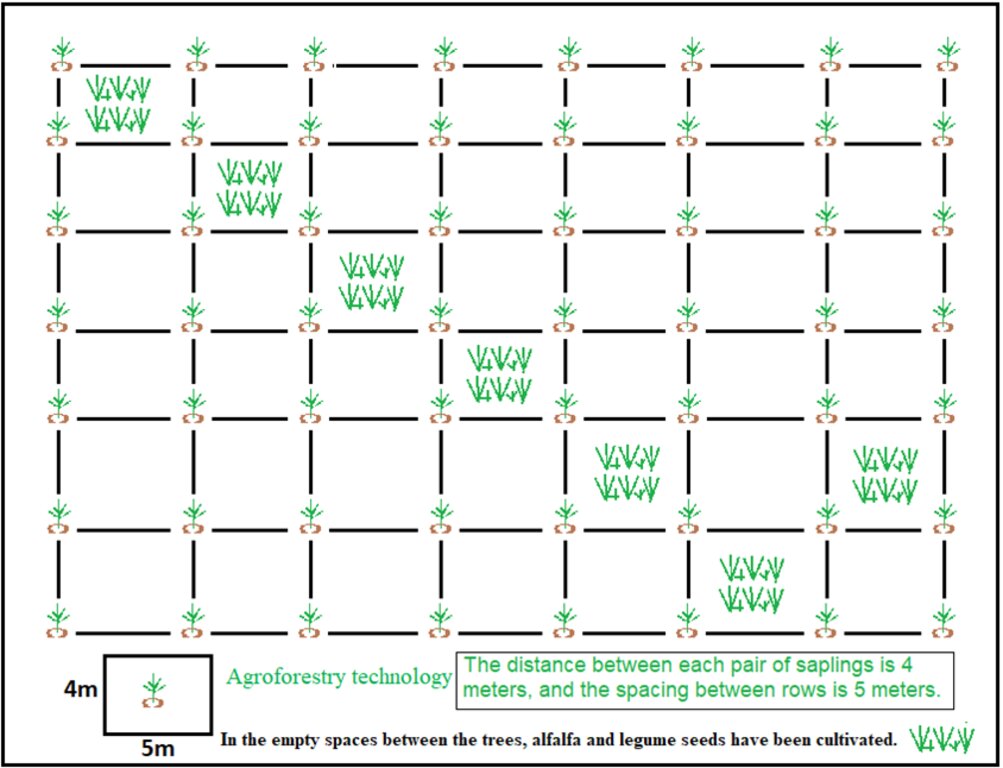
Saplings are planted in plotted areas with widths ranging from 4 to 5 meters. The outlines of the plots measure 40 × 50 meters, depending on the land structure. The spacing between saplings is 4 meters, with 5 meters between rows. Alfalfa and legume seeds are planted in the gaps. Small plots of 0.1 hectares were used, each containing 50 saplings.
Зохиогч:
Ahmad Zia Jalalzai
Он, сар, өдөр:
16/10/2024
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
0.1 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
5 USD
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and site selection follow by feasibility study | December to January |
| 2. | Procurement sapling and equipment | December and January |
| 3. | Levelling plots, cleaning from weeds | March |
| 4. | Designing layout | March |
| 5. | Digging planting pits | March |
| 6. | Planating apple saplings | spring |
| 7. | Irrigating | April to September |
| 8. | Training and pruning of orchard | October and Noverber |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour for preparation of plots levelling, digging pits and cleaning weeds | Person/day | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour for plantation | Person/day | 5.0 | 8.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | Number | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Rope | Meter | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Hoe | Number | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Pruning scissors | Number | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Wheelbarrow | Number | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Alfalfa seeds | Kg | 4.0 | 3.0 | 12.0 | |
| таримал материал | Apple sapling | Number | 50.0 | 1.0 | 50.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | DAP | Kg | 25.0 | 3.0 | 75.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Urea | Kg | 25.0 | 1.0 | 25.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 272.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 272.0 | |||||
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Applying manure for growth of crops and trees(refers to using organic animal waste (such as cow, horse, chicken, or sheep manure) to improve soil fertility and promote plant growth.) | in fall season |
| 2. | Disc ploughing and harrowing | in fall season |
| 3. | Chemical fertilizer application to crops | at the time of observing needs |
| 4. | Pest management with chemicals | in spring season |
| 5. | Irrigation of sapling | As per needed time |
| 6. | Mulching trees (humus cover)refers to the practice of covering the soil around trees with organic material, such as humus, straw, leaves, wood chips, or compost. | In a hot summer and lack of water, dry year |
| 7. | Pruning trees | in spring season |
| 8. | Operation and maintenance | spring, summer and fall |
Тайлбар:
Inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Unskilled labour | Person/day | 20.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | ploughing | person/day | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | apply of fertilizer and manure | person/day | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | form pest management | person/day | 3.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | planting of annual crops / perennial alfalfa | person/day | 2.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Uprooting dry sapling and replacing to fresh sapling. | Number | 2.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Shovel | Number | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Organic fertilizer | M3 | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | DAP | |||||
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Urea | |||||
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Pesticides | |||||
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 160.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 160.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
After establishment, all responsibilities for maintenance, operations activity, care, and management belongs to land users.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Usually, the land users are farmers, and all the activities are performed by the land users. The project team provides technical support and capacity building. The most important factors affecting the cost in the project are the materials’ accessibility in the field such as saplings, chemical fertilizer, and pesticides.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
As the technology have been applied in a 400 different topography plots, some of the plots are in a flatted, gentle and hilly slop and most of the technologies are applied in flatted area.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
In Ghazni province, the primary soil types include Aridisols in arid regions, Entisols on slopes, Sierozems in desert areas, and fertile Alluvial soils in valleys that support agriculture. Soil pH levels in the region range from 6.33 (slightly acidic) to 8.52 (alkaline), indicating varying degrees of acidity and alkalinity. The Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC), nitrogen levels, and salinity vary across these soil types, influencing agricultural productivity and land management practices. For more detailed information, including specific nutrient content and soil characteristics, resources such as the FAO’s Agro-Climatic Atlas can be consulted.
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалттай
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ба газрын доорхи ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
тохиолдлын
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
In years with heavy snowfall, water availability increases, and springs are replenished. Conversely, during drought years, water resources decrease significantly. From July to September, a water shortage is commonly experienced, prompting farmers to transport water from canals using animals. Additionally, some farmers rely on groundwater specifically for irrigating saplings. This seasonal variation in water supply is critical for agricultural practices in the province.
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- нэн ядуу
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
- ахимаг нас
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- дунд-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Everyone individually has possessed land ranging from 0.5 hectares to 2 hectares in communities. However, land users has allocated only 0.1 hectares of land for the application of this technology.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
Тодорхойлно уу:
The traditional system refers to a record that recognizes land ownership and is issued based on the customs and traditions of local communities. This document is not legal but is used within the community to validate ownership.
Тайлбар:
The land in this area is privately owned, while the rangeland is government-owned and accessible for public use. However, some individuals have encroached the rangeland, converting it into agricultural land and claiming it as their own property, despite lacking legal ownership documentation.
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
0
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
Now we have 400 apple orchards
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In the past, there were no apple orchard in this area. The community mostly relied on the rangeland, and the animal feed was limited then. Due to the application of these technologies, the apple orchard has increased, and alfalfa intercrops have been expanded for animal feeding. As a result, pressure on the rangeland has decreased.
үр тарианы чанар
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
less then 10 orchard. No alfaalf crops
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
400 orchards with Alfaalfa crops
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Alfalfa intercrops have become friendly feeds for animals, along with other grasses harvested from the rangeland.
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
less then 10 plots of Alfaalfa
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
400 plots
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Crops production specifically grown to feed livestock. It plays a crucial role in ensuring a steady supply of nutritious feed for animals, especially in dairy and meat production systems.
малын бүтээмж
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
мал услах усны хүрэлцээ
мал услах усны чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны хүртээмж
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
It is not distinguishable for now
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
It is not distinguishable for now
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops has significant environmental, economic, and agricultural benefits. When grown together in an agroforestry system, they create a sustainable and productive farming model.
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops has significant environmental, economic, and agricultural benefits. When grown together in an agroforestry system, they create a sustainable and productive farming model.
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
It is not distinguishable for now
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
It is not distinguishable for now
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops has significant social benefits, contributing to rural development, employment, food security, and community well-being.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
less then 10 orchard
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
400
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Food security is achieved when people have consistent access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to maintain a healthy life. The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops plays a crucial role in enhancing food security by ensuring the availability of fruits, livestock feed, and sustainable agricultural income.
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
less then 10 orchard
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
400 orchard
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops has a direct and indirect impact on human and animal health. These crops provide essential nutrients, improve environmental conditions, and contribute to sustainable food systems that enhance overall well-being.
амралт, рекреацийн боломжууд
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
less then 10 orchard
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
400
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops not only provides food and economic benefits but also creates various recreational opportunities. These activities promote tourism, community engagement, and overall well-being, contributing to rural development and environmental appreciation.
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops plays a significant role in Sustainable Land Management (SLM) by improving soil health, preventing degradation, and enhancing ecosystem services. Properly managed apple orchards and alfalfa fields help restore land fertility, prevent erosion, and support long-term agricultural sustainability.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops has significant effects on soil moisture due to their respective water demands, root systems, and overall impact on the surrounding ecosystem. Both crops, when properly managed, can help retain moisture in the soil and improve its structure, but if mismanaged, they can also lead to issues like water depletion or soil erosion.
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops can have significant effects on soil cover, which plays a crucial role in protecting the soil from erosion, enhancing water retention, and promoting overall soil health. Proper management of soil cover is essential for ensuring sustainable agricultural practices and maintaining soil fertility over time.
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops plays a significant role in the accumulation and dynamics of soil organic matter (SOM) and below-ground carbon (C). Both of these components are essential for soil fertility, carbon sequestration, and overall ecosystem health. The management of these factors has critical implications for sustainable farming practices, climate change mitigation, and long-term soil productivity.
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ашигт төрөл зүйл
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
үер усны нөлөө
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Floods are one of the most significant climate-related risks that can affect agricultural systems, particularly in regions prone to heavy rainfall or where irrigation infrastructure is inadequate. Both apple orchards and alfalfa crops are vulnerable to flood impacts, which can result in loss of yield, soil degradation, and cause damage to the overall ecosystem. However, with effective disaster risk reduction strategies, the negative impacts of floods on these crops can be mitigated.
гангийн нөлөө
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
apple orchards and alfalfa crops are highly sensitive to water stress, and prolonged drought conditions can reduce crop yields, degrade soil quality, and negatively affect the overall health of these plants. Understanding the impacts of drought on these crops and implementing appropriate water management strategies are crucial for maintaining agricultural productivity in drought-prone areas.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops, especially when enhanced by technology, can have significant off-site impacts on water availability. These impacts stem from how irrigation systems, water management practices, and agricultural technologies influence local and regional water resources, hydrology, and ecosystems. Off-site effects include changes to water quality, water use efficiency, and the sustainability of water resources in surrounding areas.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Тайлбар:
The cultivation of apple orchards and alfalfa crops is highly sensitive to both gradual climate change and climate-related extremes like floods, droughts, and temperature fluctuations. These climate impacts affect not only the crops' growth and yield but also the technologies used in managing these crops. Understanding the exposure and sensitivity of these agricultural technologies to such climate factors is crucial for farmers and land users to ensure long-term sustainability.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
Before the project was implemented, the land was either used for wheat cultivation or left fallow. With the introduction of the agroforestry project, tree seedlings were planted, and alfalfa was grown. In some plots, legumes were cultivated instead of alfalfa. In the first year, the production of alfalfa and legumes significantly outpaced the wheat yield, resulting in high levels of satisfaction and happiness among the local communities.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 11-50%
Тайлбар:
In addition to the 400 gardens established through the project, local communities independently created 50 small and large gardens without any financial assistance. They purchased saplings from the market and, having previously received capacity-building training from the project team, applied agroforestry practices on plots of various sizes, tailored to their available land.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Integrated systems that combine apple trees with alfalfa and legumes offer several benefits. Farmers appreciated the enhanced biodiversity, which supports pest control and improves pollination, leading to healthier crops and increased yields. The intercropping of legumes is particularly valued for its role in improving soil fertility through nitrogen fixation, reducing dependence on synthetic fertilizers, and promoting sustainable farming practices. |
| Economically, farmers find that this system provides diversified income sources, as they can sell both fruit and forage crops, which mitigates risks associated with crop failure. Additionally, the ability to optimize land use while maintaining ecological balance is a significant advantage. This resource efficiency, coupled with the adaptability of practices to different climates and soils, enables farmers to achieve resilience against climate variability. |
| Furthermore, land users recognize the opportunities for community engagement and knowledge sharing to promotes agroforestry. As these systems gain popularity, farmers are increasingly accessing markets for sustainably produced goods, enhancing their profitability. With supportive policies of sustainable land management, the future of agroforestry initiatives appears promising, benefiting both the environment and local economies. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Integrated systems of apple trees intercropped with alfalfa and legumes are recognized for their multifaceted benefits. They highlight the importance of these systems in promoting sustainable agricultural practices, noting that the biodiversity fostered by agroforestry enhances pest control and supports healthier ecosystems. This ecological balance is crucial not only for soil health but also for mitigating the reliance on chemical inputs, which aligns with global sustainability goals (Nair, 2019; FAO, 2020). |
| Moreover, compilers emphasize the economic advantages of agroforestry. By diversifying income streams, these systems reduce financial risks for farmers and stabilize local economies. The adaptability of agroforestry practices to various climates and soil types allows for broader implementation, making it an attractive option for diverse agricultural settings (Schroth et al., 2004; Somarriba et al., 2016). |
| Key resource persons also note the social dimension of agroforestry, as these systems encourage community engagement and collaboration. This participatory technology fosters knowledge sharing, leading to improved agricultural practices and strengthening local capacities. With increasing support from policies advocating for sustainable land management, agroforestry initiatives are well-positioned for growth and development, contributing to both environmental health and economic resilience (Pretty, 2018; Wang et al., 2020). |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Initial costs and investment risks | The project team provided seedlings, fertilizers, and Alfalfa seeds at the start of the technology. Land users were responsible for carrying out physical activities such as digging holes, planting seedlings, and irrigation, which helps reduce costs and fosters a sense of ownership among the participants. |
| Low knowledge of the technology and skill gaps | To address educational gaps, the project’s field team conducted capacity-building programs and workshops before implementing the technology. This initiative has enabled land users to become familiar with new methods and enhance their capabilities in agroforestry |
| Market access and economic viability | The project team established agroforestry committees and facilitated direct market communication and improved access for land users to sell their produce. It has provided sales skills training to land users, allowing them to make more profit from their produce |
| 4) Pest and disease management: | 4) The project's field team has educated land users about common pests and diseases in the area and provided them with preventive management strategies. In case of new issues, they have been linked with the Department of Agriculture to ensure timely and effective support. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Provision of Resources and Local Engagement: | Importance of equipping land users with essential materials, such as sapling and fertilizers, to lower initial barriers and encourage participation. Enhance ownership to ensure sustainability when the project pulls out |
| Addressing educational gaps | Realizing that knowledge gaps could hinder the project’s success, the team implemented pre-launch training workshops. These sessions were aimed at familiarizing land users with innovative agroforestry, helping to ensure their understanding and effective implementation of new techniques. |
| Market connections and economic benefits | Key resource personnel highlighted the importance of establishing market access for sustainable success. By Rangeland management Association and offering training in market engagement, the project helped land users gain market literacy, empowering them to maximize income potential from their produce. |
| Support for pest and disease management | The project team prioritized proactive pest and disease management by training land users in common pest prevention techniques. The creation of a support network with the Department of Agriculture ensures that land users have access to timely guidance for any emerging issues, ensuring resilience and adaptability in their practices. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
Field visits and field surveys by project team
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
About one per agroforestry plot by project team
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
Three people - project implementation unit.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Field reports and documents.
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
16/12/2024
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна