Poplar trees for bio-drainage [Киргизстан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Abdybek Asanaliev
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: Hayot Ibrakhimov
- Хянагчид: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
bio-drainage, reduce salinity, favourable microclimate for for plant growth
technologies_1098 - Киргизстан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Kyrgyz Agrarian University (Kyrgyz Agrarian University) - Киргизстан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
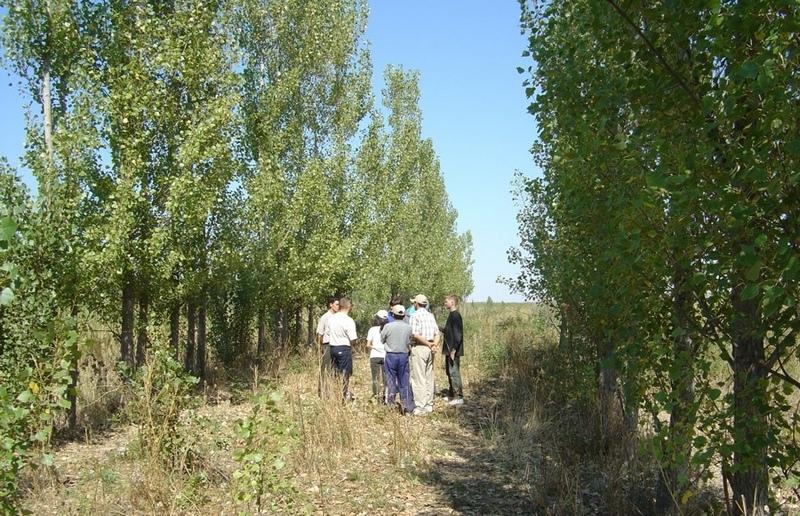
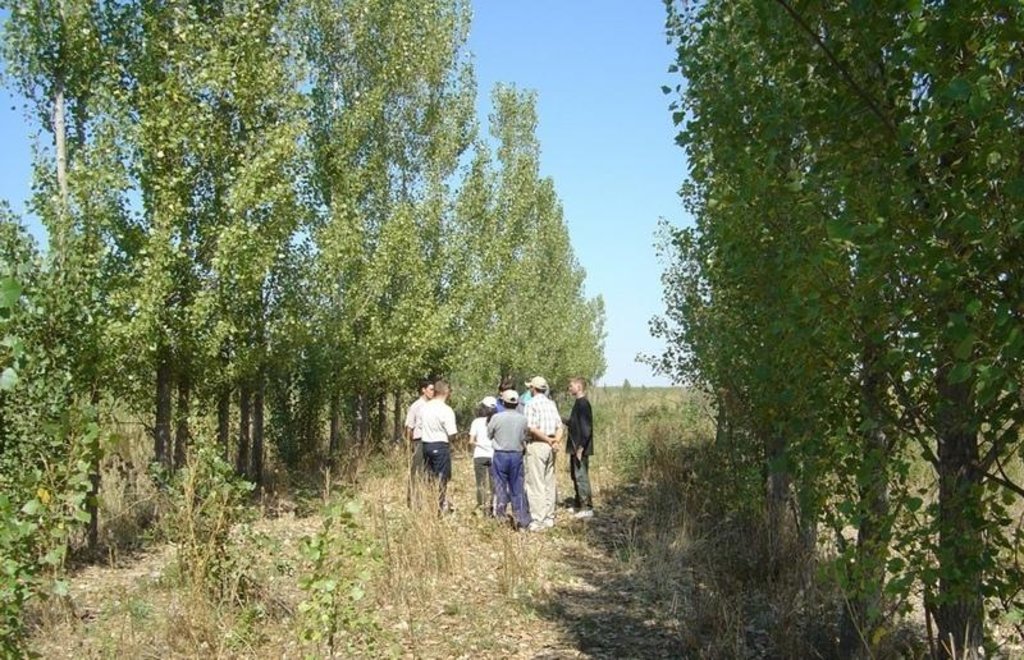
Poplars planted to lower the ground water table and reduce salinity where irrigation drainage systems have broken down; lucerne cultivated between the tree lines.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
In irrigated areas of Central Asia, the drainage system introduced during soviet times has broken down due to lack of maintenance. As a result, water tables have been rising and soil salinity increasing. In the Chui Valley, which is the main crop production area in Kyrgyzstan, approximately 90% of the cultivated land is irrigated for wheat, maize, sugar beet, lucerne and vegetables. Of this, approximately one third (ca. 320,000 ha) is degraded due to loss of fertility, salinisation and waterlogging.
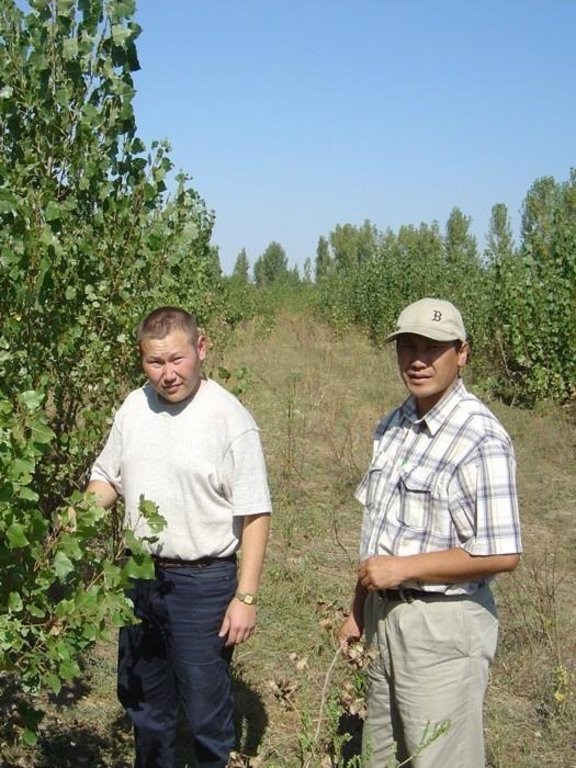
The individual initiative described here - poplar planting - has been applied on a degraded plain (about 400 m a.s.l.), under semi-arid conditions on a plot of 5 hectares. Though initially planted for timber, an important side effect was noted by the farmer in question. Poplar trees, well known for their tolerance to waterlogging and salinity, provide ‘bio-drainage’. Excess water is rapidly taken up by the root system and transpired through the dense foliage. Within the plantation the humidity level of the lower layers of air is increased, thus reducing the influence of the dry, hot winds. A more favourable microclimate for plant growth is thus created. Simultaneously the original purpose of planting - to obtain cheap timber and firewood - is achieved through the rapid growth of the trees: there is a severe shortage of wood locally.
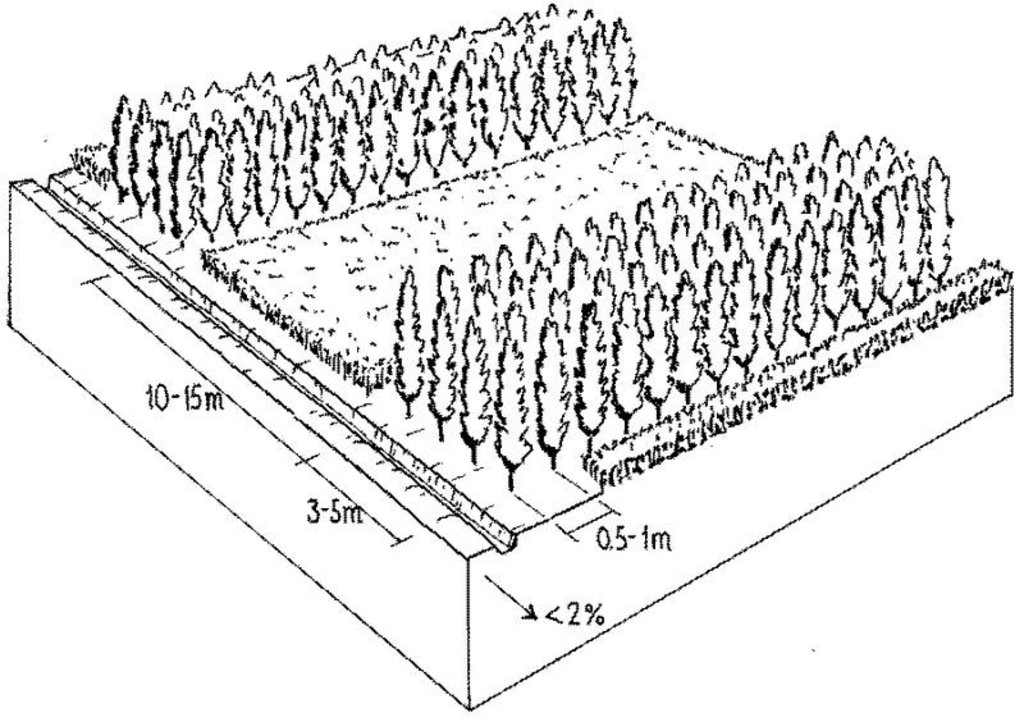
The varieties used include the local Populus alba and Populus nigra as well as a hybrid from Kazakhstan, P. pyramidalis. The trees are planted in rows about 5 metres wide, separated by 10-15 metre strips planted with Medicago sativa (lucerne) and Bromus inermis (a grass), both of which are grown for hay (see technical drawing). Around 3,000 saplings are needed per hectare. The young poplars require irrigating during the first year before their roots can reach the water table. The trees are weeded and their lower branches pruned to encourage straight and fast growth. They are thinned twice before they are 14 years old: these thinnings can be sold. The poplars then remain until they are 20-25 years old and suitable for felling. The output of commercial timber of a poplar plantation is 3,000 m2 per hectare (1 m2 per mature tree). Slow-growing/sick trees, as well as pruned branches, are used as firewood - which can amount to 20-30 m3 per hectare. The cycle begins again after approximately 10 years, when new saplings are planted between the existing, thinned, lines of poplars. Desalinisation of the soil takes 10 years or a little longer, when it again becomes suitable for irrigated cereal cropping.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Киргизстан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Besh-Terek, Chui valley,
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
0.05
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.05 km2.
Map
×2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- ХАА-н ойжуулалт

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- тэжээлийн ургамал - царгас
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - Sep

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
Модны төрөл:
- Улиасны төрөл зүйл
Тайлбар:
Major food crop: Poplar, lucerne (alfalfa), wheat
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Irrigation drainage systems have deteriorated (silted up, choked with weeds and reeds) due to lack of maintenance. This has led to a raised water table, waterlogging and increased salinity, thus seriously affecting productivity and making cultivation of some crops impossible. Farmers’ incomes have significantly reduced as a result.
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- таримал ойн менежмент
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг
Тайлбар:
Type of agronomic measures: legume inter-planting
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
- Cs: Давсжилт / шүлтжилт

хөрсний физик доройтол
- Pw: Усны түвшин нэмэгдэх буюу намагших
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Alternating strips of poplar trees for bio-drainage, and lucerne for fodder. Drainage channels (left) are spaced at 50 metres apart.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: lower ground water level, decrease waterlogging & improve soil fertility, reduce risk of salinisation
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed, increased air humidity & cooling effect
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Poplars (Populus alba, Populus nigra, P.pyramidalis)
Зохиогч:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Set up tree nursery one year before planting: take cuttings about | |
| 2. | Demarcate lines in field. | |
| 3. | Dig drainage trenches in the marshy area (50 cm deep, 50 cm wide, | (end of summer, early autumn) |
| 4. | Plough where seedlings of the poplars are to be planted. | |
| 5. | Transplant tree seedlings from the nursery to the field . | in spring |
| 6. | Irrigate the seedlings by furrow for one year. | |
| 7. | Protect the area from animals. | |
| 8. | Plant lucerne . | in first year after planting of poplars |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | All the Labour | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 1.0 |
| таримал материал | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 1.0 |
| таримал материал | Nursery | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 1.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 920.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 920.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prune lower branches of the trees to encourage tall and straight | |
| 2. | Continue protection of the plot (because of lucerne). | |
| 3. | Cut lucerne for hay . | /4 times per year |
| 4. | Weed control (main weeds are Chenopodium album, |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | All the labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 30.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 30.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: shovel, axe, saw
Labour for establishment and maintenance are provided by the farmer and his family. After 10–15 years trees are
thinned for timber and the cycle begins again – with reduced establishment costs: new saplings are planted between the
existing, thinned, lines of poplars. On two sides the plot is protected by a drainage ditch and a concrete canal protect the plot respectively. Furthermore, there is an agreement with the neighbours not to let the animals graze the lucerne. However after the last cut of lucerne animals are allowed to graze the plot.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is very low - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- худалдаа наймааны/ зах зээлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: this individual is an employee of the regional agricultural department and has a small business
Market orientation of production system: Thinned poplar saplings, timber and firewood from prunings for market
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Lucerne between tree lines
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Lucerne between tree lines
модлогийн бүтээмж
Орлого, зарлага
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
ажлын хэмжээ
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
input contstraints
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Not all the farmers have enough resources for introduction of this technology (equipment,
main benefit
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
However, short-term benefit from lucerne as fodder and from firewood through pruning
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
түймрийн эрсдэл
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
soil fertility
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to lucerne: 100–130 kg of N
biodiversity
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
General drop of water table
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
1 household
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A single farmer has developed this technology. It should be possible to spread the technology among other farmers but financial support (eg interest-free credit) will need to be provided. A recent assessment has showed that there is growing interest in the system by farmers in the region. Additionally, in the lower Yanvan Valley of Tajikistan, a similar bio-drainage system has been described - using poplars and mulberry trees. In that situation wheat is planted in association with the trees.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Positive ecological effect: salinity and area of marshy land can be reduced and waterlogged soils reclaimed How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness raising and training of farmers to show the effect of poplar trees on reduction of waterlogging and salinisation. |
|
Rapid benefit through the production of lucerne and grass. Long-term production of valuable firewood and timber (both are in short supply) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Show the economic benefits of additional lucerne production and timber and firewood; demonstrate marketing opportunities. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The implementation of the technology is not possible for all land users due to input and labour constraints |
Financial support, better organisation/ share of equipment. |
| Major benefit from timber production comes only after 25 years |
Create awareness about additional short-term benefits, especially firewood and fodder, as well as the long-term effects and the sustainability of the system. |
|
Cannot be replicated by all farmers in the valley at the same density as the market for trees (timber, firewood) will be saturated, and trees can never completely take the place of irrigated food crops: nevertheless the benefits will extend to those growers through the drainage function of the poplars |
A new overall production system will have to be worked out for the region. |
|
The case reported here works in its current design because of its isolated ‘island effect’: if more farmer grew poplar, the same bio-drainage effect could be achieved over the whole valley at a lower density of trees per unit area, implying a larger proportion of cultivable land. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Budaychiev D (2002) The prospects for hybrid poplar forest plantations. Resolving problems and the strategy of reformingagrarian science. News of Kyrgyz Agrarian Academy Vol. 2, Issue 3, 4.1 Bishkek
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна