Traditional irrigated rice terraces [Непал]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Ramanand Bhattarai
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Tari khet (Nepali)
technologies_1099 - Непал
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - НепалТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Непал1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
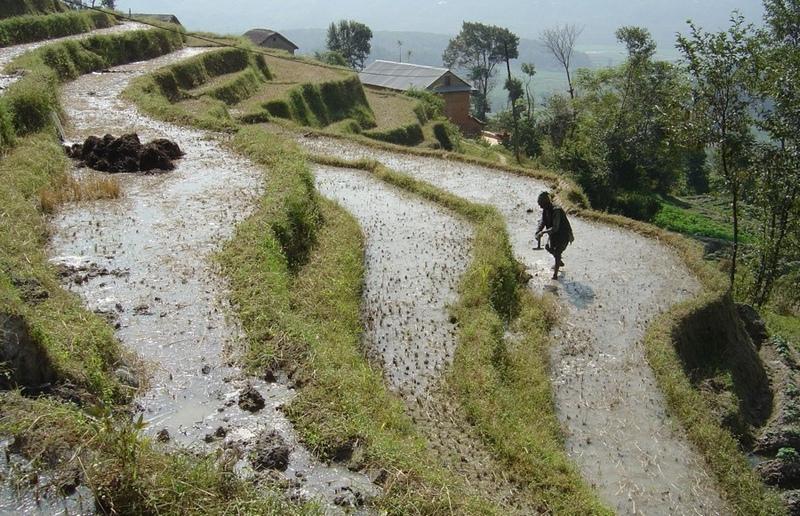
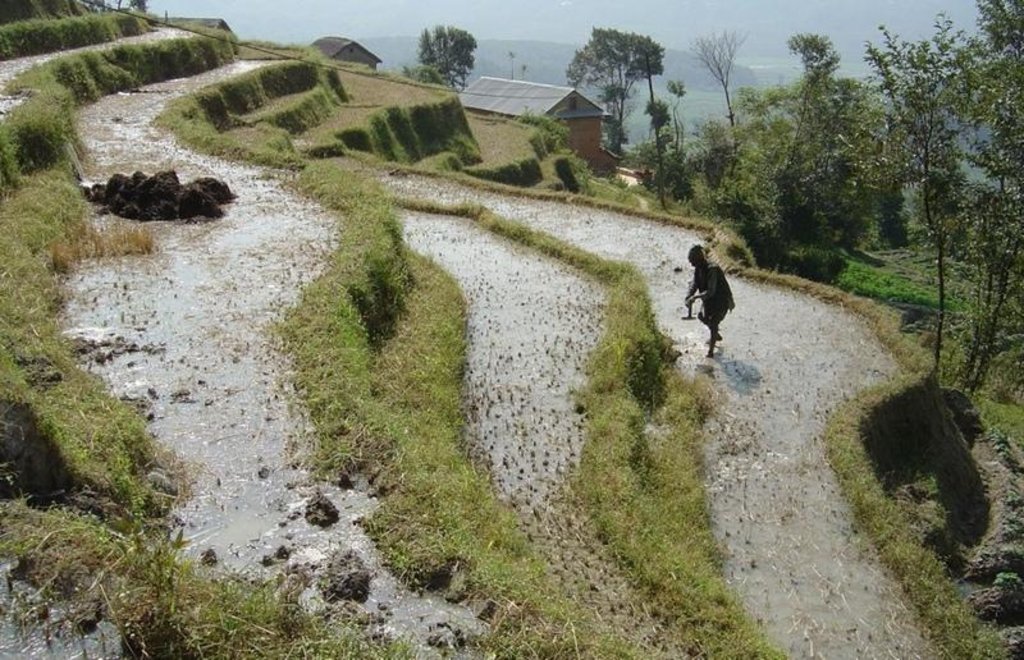
Level bench terraces with risers protected by fodder grasses, used for the irrigated production of rice, potatoes and wheat
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
The level bench terrace is a traditional technology that makes irrigated crop production possible on steep, erosion prone slopes. The majority of such terraces in Nepal were constructed by hand many generations ago, but some new land - mostly already under rainfed cultivation on forward sloping terraces - is still being converted into irrigated terraces. The initial costs for the construction of the terraces are extremely high – and annual maintenance costs are considerable also. The climate is humid subtropical, slopes are steep (30%-60%) and soils generally have a sandy loam texture. Terraces are cropped by farmers who mostly have less than 0.5 ha of land each.
Two to three annual crops are grown per year starting with paddy rice during the monsoon, followed by potatoes and/or wheat.
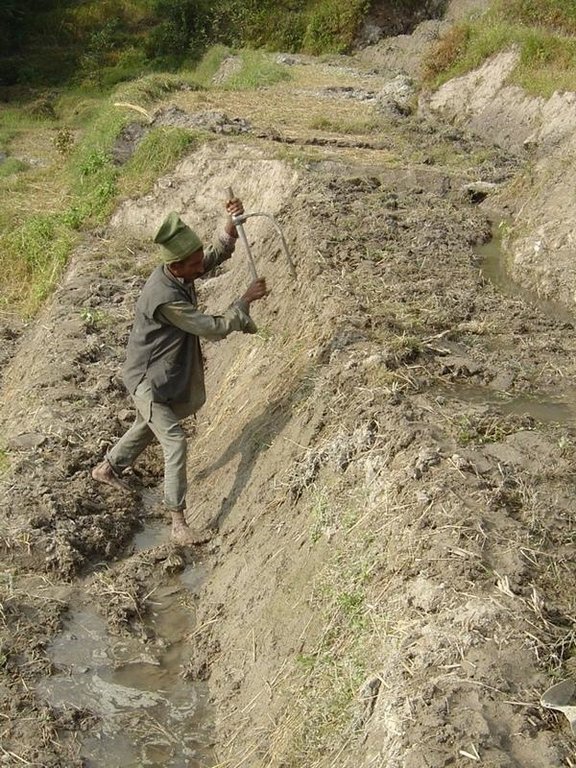
While terrace beds are usually 2–6 m in width, to save labour they are made as wide as they can be without increasing the danger of slips/land slides. Surveying was traditionally done by eye, but now a water-tube level may be used. Risers are 0.8-1.5 m high with a small lip (20-25 cm). The slope of the riser varies from 80 to 160%, depending on the initial gradient of the hill. Stones are incorporated in the risers if available, and grass species such as bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) and napier (Pennisetum purpureum) may be planted for stabilisation and as cattle fodder. The risers are compacted (with hoes) to improve ponding conditions for the paddy rice. Twice per year the risers are scraped with a special tool: (1) at the time of land preparation for paddy rice the lower part of riser is sliced, but the upper part is left protected with grasses against the monsoon rains; (2) at the time of wheat planting the whole riser (including the lip) is scraped and spread as green manure on the terrace.
Terraces are flooded with water for paddy rice cultivation: a smaller amount of water is diverted into the fields for other crops. Excess water is drained to the lower terrace by openings in the lip, which are filled with rice straw in order to filter out sediments. The depth of water for rice - when flooded completely - is normally between 10 and 15 cm. Fertility is maintained by addition of farmyard manure, spreading the scraped soil from the riser, and also through sediment carried in the irrigation water. Nowadays, mineral fertilizers are also applied.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Непал
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kathmandu
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Manmata subwatershed
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
1.0
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1 km2.
Map
×3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - цагаан будаа (чийгт газрын)
- үндэст/булцуут ургамал– төмс
- wheat
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
Тайлбар:
Major cash crop: Potatoes
Major food crop: Rice and wheat
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - steep slopes, not suitable for agriculture in their original state (better for forestry, agroforestry, horticulture, and fruit
trees)
- small and scattered plots of land
- land users find chemical fertilizers and water expensive
- there is water scarcity from September to May and too much rain in the monsoon period (June to August) with the danger of erosion and collapse of the terraces
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V2: Өвс ба олон наст өвслөг ургамал

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S1: Террас
Тайлбар:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wm: Хөрсний нуралт, шилжилт
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
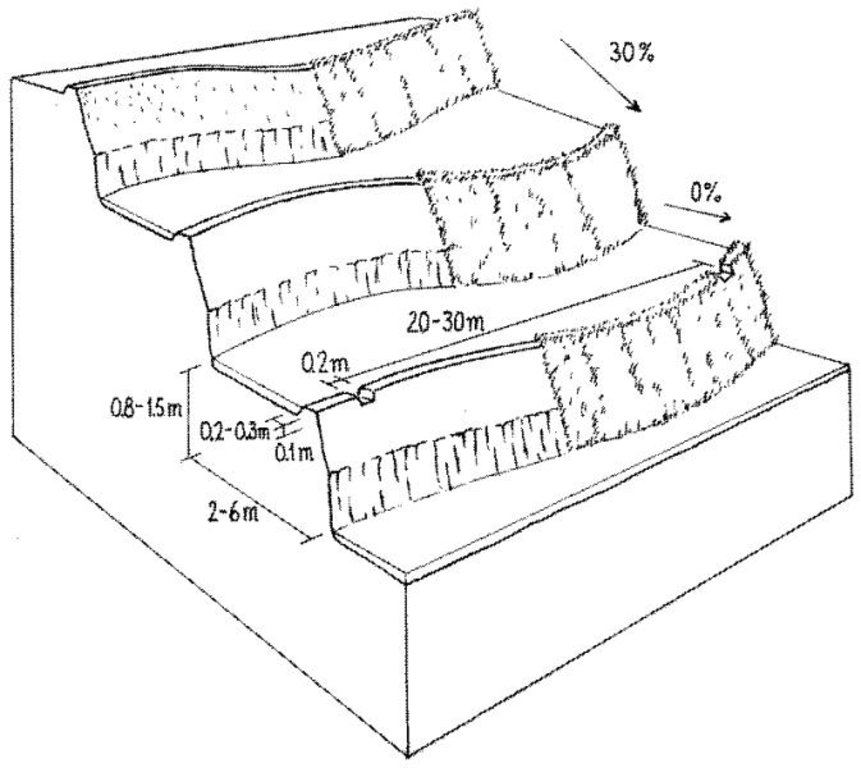
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Layout of irrigated terraces. Openings in the lips drain excess water, grass cover stabilises lips and risers (right). After harvesting of rice, the grass is scraped off the lower part of the risers (left) and spread on the terrace beds
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, control of dispersed and concentrated runoff, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: green/farmyard manure
Vegetative measure: fodder grass at risers
Terrace
Material: earth
Зохиогч:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting grasses including bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon). | during monsoon |
| 2. | Construct bunds (risers) with soil from upper and lower sides | before monsoon |
| 3. | Level terrace beds (soil moved from upper to lower part of terraces). | before monsoon |
| 4. | Make lips on edges of terraces | before monsoon |
| 5. | Compact risers | before monsoon |
| 6. | Construct irrigation canal | before monsoon |
| 7. | Make openings in lips for drainage of excess water | before monsoon |
| 8. | Test-irrigate terrace for accurate levelling | during monsoon |
| 9. | Plant grasses including Bermuda grass (Cynodon dactylon) | during monsoon |
| 10. | After 2–3 years: some narrow terraces may be merged to form single, wider terraces | during monsoon |
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flood the paddy fields .. | (June/July) / Repeated 3–4 times during |
| 2. | Slice/scrape grass and soil on lower part of risers and spread on terraces | (when flooded, June/July) / |
| 3. | Plant rice and apply mineral fertilizer | (June/July). / |
| 4. | Harvest rice | (October) / |
| 5. | Apply manure (cattle manure), after rice harvest | (October). / |
| 6. | Slice/scrape grass and soil from whole of risers and spread on terraces; repairsmall collapses/slumps in risers | (October/November) / |
| 7. | Pprepare land | (November) / |
| 8. | Apply mineral fertilizer | (November/December). / |
| 9. | Irrigate | Nov. / repeated several times during cultivation |
| 10. | Harvest of potato/wheat | (January-March). / |
| 11. | Planting of rice | June,July / |
| 12. | planting of potatoes, wheat | November / |
| 13. | Repair of small collapses/slumps in risers. | (Oct./Nov.)/ |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 185.0 | 185.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/manure | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 840.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 840.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, spade, baskets, (doko), special tool for scraping
Current establishment costs are very difficult to determine since the majority of the traditional terraces were
established a long time ago. Costs depend closely on the present state of the land (forward sloping terraces or uncultivated) and the need for irrigation canals. Farmers say that construction now could cost up to US$ 10,000 per ha if carried out by hand at full labour cost. The cost given for maintening the terraces (approx. US$ 840 per ha) includes all associated annual crop production costs. In this case study, 100% of the construction costs were borne by land users.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good because of the geology and soil texture (loam)
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
- ердийн хөсөг
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Off-farm income specification: hired labour (on other farmers’ fields) or as porters
Market orientation of production system: Subsistence (rice/wheat) and commercial (potatoes)
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
- хувь хүн
Тайлбар:
Land use rights: leased (90% of farmers), individual (10%)
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
the technology is a part of a complex farming system
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
тухайн аж ахуйн орлого
эдийн засгийн ялгаат байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
not everyone has access to land for irrigation
ажлын хэмжээ
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Livestock fodder
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
олон нийтийн институц
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
when the agreed and scheduled water extraction amounts are exceeded
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
усны урсац
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
хөрсний гулсалт/ чулуун нуранги
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
poor maintenance of topmost terraces may cause landslides
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Soil fertility
Biodiversity
Number of crabs in irrigation water make holes in the terrace risers
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
which in turn can cause pipe erosion and riser collapse
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
газар доорхи ус/голын усны бохирдол
Groundwater recharge
Soil moisture and nutrients downstream
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | муу |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | муу |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | муу |
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Income and production increased How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the terraces (including all maintenance activities) |
| Easier to cultivate flat terraces/less labour required (after establishment of terraces) |
|
Work sharing: traditional terraces are part of a long tradition of work sharing within the community with no external labourneeded How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established traditions and norms |
|
Technology is easy to understand/apply. Increased opportunities for irrigation facilities: farmers without level terraces are not allowed (by the irrigation committee at village level) or do not claim irrigation water |
|
The irrigation element of this technology fosters social bonds within the community How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prevent loss of well established norms and traditions. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Decreased grass production (grazing area reduced) | Promote planting of high value grass species on risers (such as bermuda grass). |
| The farmers believe that the terraces are too narrow (for efficient use of tractors); they would like to have wider terraces |
Investigate possibilities of constructing wider paddy rice terraces on steep slopes, which, according to present experience, is not possible. |
| High labour costs for establishment. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
There is considerable literature on the construction and maintenance of irrigated terraces in general, but no references thatspecifically describe the traditional paddy rice terraces in Nepal
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна