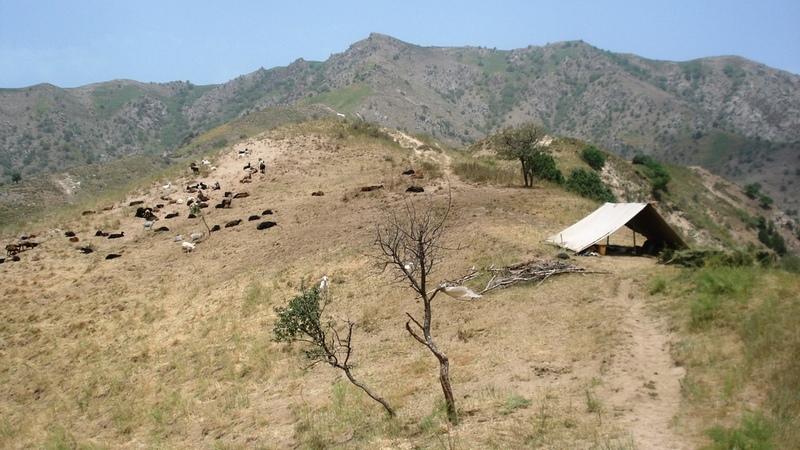
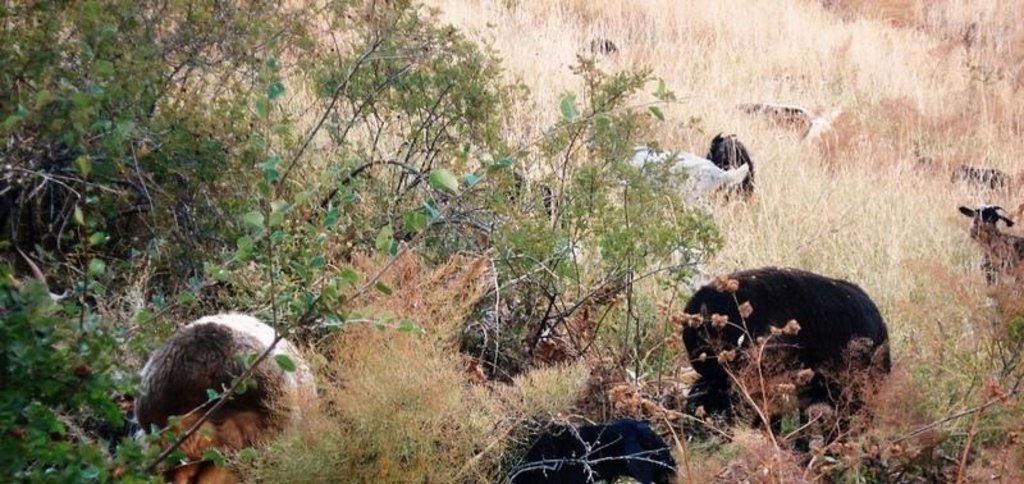
Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Тажикистан]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Dajmardei Kaspi (professional herder)
technologies_1407 - Тажикистан
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Киргизстан1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)
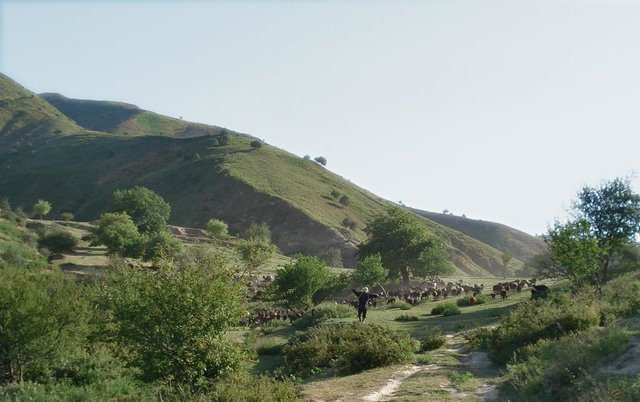

Seminomadic individual herding [Тажикистан]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
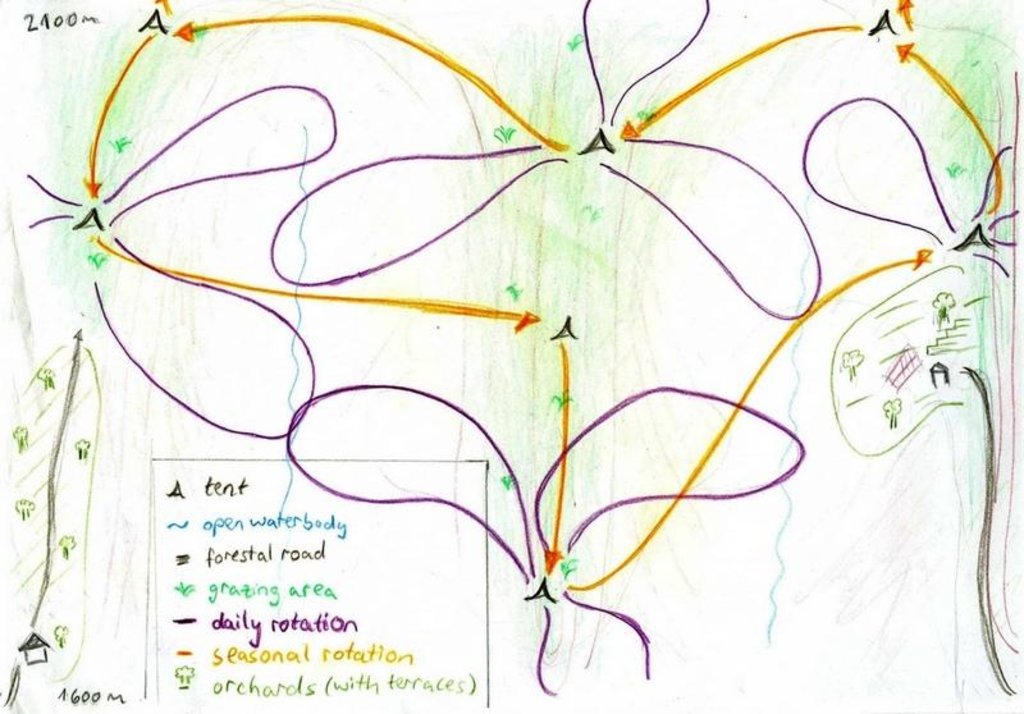
Half-year herding with 500 sheep, goats and cows (very few), with 7-8 different locations of the herder's tent. The herder visits each place twice to thrice per grazing season and stays in one place for one week to maximally one month (during the Ramadan period, due to limited forces). The area is grazed from the higher zone (around 2000m) to the lower zone (around 1600m) twice per season, in a sort of circle. Every day the herder starts in another direction from his tent and leads the animals to the pastures, once in the morning and once in the evening. He passes a stream once (autumn) to twice (summer) a day.
Purpose of the Technology: The grass should not get dusty and dirty, explaining why the herder daily changes the pastures, only revisiting the same places every two to three days.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After accompanying his father as a child and a kind of an apprenticeship (of one year) later on, M. is considered by the villagers as a good herder and they give him their animals for herding. But M. applies for land on the forest department only after working as a guardian and as a tractor driver for 20 years. For the herding profession observing the animals precisely is necessary, in order not to lose any of them. And the maintenance of the pastures is guaranteed by the strict rotational scheme.
Natural / human environment: The pasture-area is in a generally well-conserved state. Moderate to high values of fractional vegetation cover can be observed and only few signs of recent erosion processes (through water) are visible. The area is characterised by steep slopes where still signs of past tree-planting during the USSR period are visible by some trees, many little platforms made for tree-planting and a few terraced areas. Eventhough, many trees have been grazed and do not stand anymore. Besides steep areas there are small, quite flat areas (where the herder installs his tents), that used to be cultivated (wheat) till 1966. These areas generally have low cover-values and signs of rill-erosion, which the herder attributes to the past tilling activity. However, it might also be the trampling and sitting of the animals (staying near the herder's tent at noon-time and during the night) causing this erosion. Nutrient management is provided for by the dung of the animals which is not collected, contrarily to the pastures near the villages.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Тажикистан
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Region of Republican Subordination
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Faizabad
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
The half of the herded area is rented by another person from the village, who gives his animals to the herder. Apart from the interviewed herder there are varying numbers of other semi-nomadic herders with similar management practices, some of them from other regions.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
There are traditional herding peoples like Kuagwates, Kaleks, Lakais, Duramanes, Kurtshaliks), not Tajiks. These often move around with their whole families.
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- ямаа
- хонь
- cows
Төрөл зүйл:
ямаа
Тоо хэмжээ:
500
Төрөл зүйл:
хонь
Тоо хэмжээ:
500
Тайлбар:
Livestock density (if relevant):
< 1 LU/km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The trampling of the animals near the tent, the feeding on young trees and the daily passage of the herd of a limited number of streams (eutrophication).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): No major land use problems due to good management. Only the first rain that cannot be absorbed by the dry soils is a problem.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: sheep* / goats* / cows
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
Тайлбар:
Specify:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jun
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М1: Газар ашиглалтын хэлбэрийг өөрчлөх
- M4: Үйл ажиллагааны цаг хугацаанд том өөрчлөлт орно
Тайлбар:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

биологийн доройтол
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Causing Pc, Bc, Wt), droughts (Causing Pk, Pc, Ha), degradation of near-village pastures (The pressure on more distant areas increases)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (passed tilling with impact on Wt), floods (Intensive rains causing Wt), land tenure (Little interest in tree-planting if land can only be rented annually)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
Тайлбар:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Daily and seasonal rotation.
Location: Above Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 05.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Obeying to what the herder says)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is necessary to know how to lead animals, more than in the case of the common pasture-area)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of fires, palatable fodder
Change of land use type: From afforestation and limited use as cropland to extensive grazing
Major change in timing of activities: Introduction of a strict rotational grazing scheme
Зохиогч:
Christian Wirz, Switzerland
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
6.10
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a herd | constantly investing |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Бусад | Buying a herd | animals | 50.0 | 87.7 | 4385.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 4385.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 4385.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rent fee for land of forest department | once per year |
| 2. | Salary of an assistant herder (normally, but not in 2008) | at the end of the season |
| 3. | compensation for dead animals | at the end of the season |
| 4. | Animal medecine | if necessary |
| 5. | Salt | daily |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Salary of an assistant herder | Days | 120.0 | 6.1 | 732.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Rent fee for land of forest department | 300ha/d | 180.0 | 0.4888888 | 88.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Compensation for dead animals | animals | 2.0 | 44.0 | 88.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Animal medecine | per year | 1.0 | 88.0 | 88.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Salt | kg | 1000.0 | 0.08 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 1076.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 1076.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
The costs are valid for a herd of 250 animals kept by the herder alone for six months and additional 250 animals kept during summer holidays with the help of additional workforce. The salary indicated was not valid for 2008 (the grandsons helped the herder), but for years when M. hires external workforce. For all costs, including 50 own animal, prices in 2008 are taken.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Buying an own herd and looking for the animals are the most expensive factors, expecially if there are sick or dead animals.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Mainly in spring and also in autumn, with a trend to decrease
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitudinal zone: Pasture area around 1600 to 2000 m
Landforms ridges: Small, not so steep areas where the tent of the herder is installed
Landforms mountain slopes: The pasture area is generally very steep
Slopes on average steep (31-60%): The areas mostly frequented are steep
Slopes on average very steep (>60%): The areas dominating spatially are very steep
Slopes on average hilly (16-30%): Ridge areas
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average shallow: Most grassy areas
Soil fertility is low: on the surface of 300 ha the summed up dung of 500 sheep and goats cannot compensate for the loss of topsoil by wind and water
Soil drainage / infiltration is good: Generally high infiltration capacity enhanced by high vegetation cover values
Soil water storage capacity medium (dominatig the area): Loamy soils and high cover values, but generally little trees and dried vegetation in August
Soil water storage capacity can also be good: Near the streams higher water retention, according to herder
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
зөвхөн газар тариалангийн зориулалтаар ашиглах (усалгаа)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Water quality (untreated): Locals drink the water, but are affected by diarrhoea
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Diversity higher than near the villages, but not comparable with biodiversity hot-spots
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- чинээлэг
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Herding is considered as a male profession, inherited from father to son. In nomadic peoples the whole families are mobile and women are responsible for domestic work.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are rich (100).
Off-farm income specification: The herder claims to nourish himself and his wife with the income from herding. But, once he willl not be able to work as a herder anymore, he might depend on off-farm income from his children (remittances)
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
3 households can afford to pay the services of the professional herder (clearly a minority of village population)
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- түрээсийн хэлбэрээр
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Higher vegetation cover and biomass values than for village-pastures
тэжээлийн чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Much less impalatable species' frequency
малын бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The animals get much fatter and are sold for around 50% higher price than animals from common pastures
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The herder says that tree density has decreased, due to livestock but also to chopping. Additionally chopping of living trees is generally forbidden (since the 1960s, when the forest department was created as a new land use type), not making possible the
үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The use of the land for fruit production is not possible with animals grazing, but this was also the case before, as to the herder's opinion
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
тариалангийн усалгааны усны чанар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to reduced stocking rates in comparison with village-pastures (and the soviet times), better water quality
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
амралт, рекреацийн боломжууд
Livelihoods and human well-being
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Better control of runoff, but steeper land
усны урсац
Хөрс
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
40%
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
80%
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Higher cover than on village-pastures
Биологийн олон янз байдал: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
ГТМ хэрэгжихээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
36 species
ГТМ хэрэгжиснээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
47 species
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
More plant systematical diversity
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
түймрийн эрсдэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
According to forest department the area above Karsang, due to ist trees, is more prone to fires than other areas
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
Тайлбар:
A possible adaption to dryer conditions would be smaller herds.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Тайлбар:
4 Years ago a herd of 400 animals had to be sold due to disease. Since then M was able to rebuild a herd of 500 animals. On a short term investing into animals is expensive but pays quickly. The maintenance costs are finally decisive, but quite constant.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- жишээ/ туршилт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
1 Household
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The herder gets paid by the villagers for taking care of their animals
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: According to the herder, young people do not (want to) bear the very physical work.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Grazing stabilises the soils and is thus a prevention against gully erosion in areas with low cover (former cropland). Animals have the same effect as the terraces built years ago. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing activity should continue, once M. is too old for working. |
| The animals provide for soil fertility by their dung, instead of the fertilisers used in Soviet times. This positively influences the share of palatable plants and cover in general and, by this, soil moisture. |
| The area on the forest department is a good alternative to the much too small pasture-area near the village |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Form of land use making it possible to take some pressure from the common pastures without great damages. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It needs to be assured that also poorer families, who depend even more on livestock breeding than richer ones, can give their animals to M. or other professional herders. This could be realised by engaging herder assistants from poor families |
|
The rotational scheme is much more elaborated than in the case of the villages' pastures, which can be explained by more land available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land users like M. should be addressed by forest administration to elaborate legal forms of herding with little damages on natural resources on this land. This will probably require land reforms. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Tree planting is not possible as long as the area is used for grazing. | By giving people land for longer periods (than one year) and with more freedoms in its use, people would gain interest in diversifying use: They would split up "their" land into haymaking, orchard and pasture areas. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| The main problem of this form of grazing is that it doesn't allow the regrowth of trees. | Changing the areas use for grazing, respectively haymaking, every few years. |
| Cover is markedly reduced around the places where tents are installed. | By changing the camping place (but: limited flat areas!) or not keeping the animals in the same place at noon time and during night time, these areas might recover. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Seminomadic individual herding [Тажикистан]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Christian Wirz
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна