Afforestation [Кабо Верде]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jacques Tavares
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Arborização / floresta (Portuguese)
technologies_1523 - Кабо Верде
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Varela Larissa
INIDA
Кабо Верде
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Amarós Regla
INIDA
Кабо Верде
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Bentub Jailson
INIDA
Кабо Верде
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
INIDA (INIDA) - Кабо Верде1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Protection des versants [Кабо Верде]
Cette approche consiste à mettre à profit les eaux d'écoulement superficiel
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jacques Tavares
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
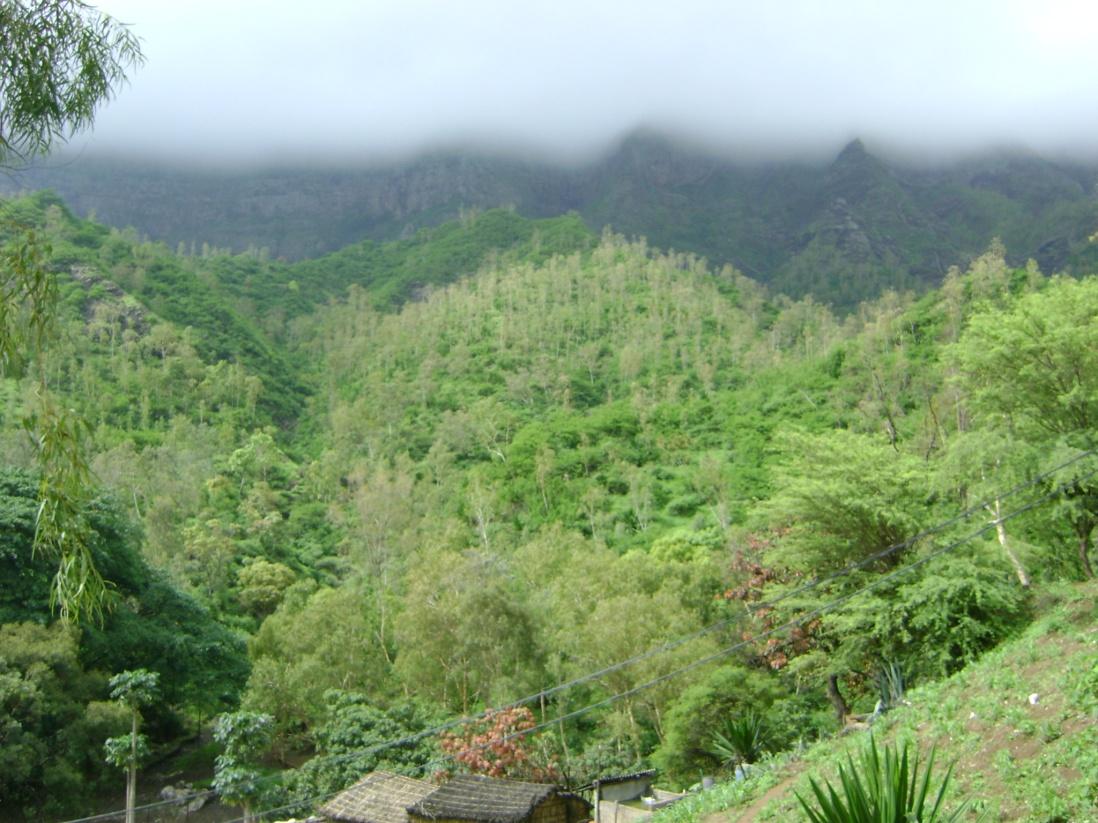
Afforestation is one of the key technologies to address the fragility of ecosystems: it provides better protection against erosion and makes better use of rainfall in order to maintain the sustainability of agricultural systems.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
Mountain forest areas are considered protective due to their role in regulating water (infiltration of storm water, regulation of surface runoff, and ground water recharge) within the watershed. The main species used are Prosopis juliflora, Parkinsonia aculeata, Jatropha curcas, Atriplex spp, Acacia holosericea, Acacia victoriae, Lantana camara and others, in arid areas and Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Grevillea robusta, Pinus and Cupressus ssp. in highland and humid areas.
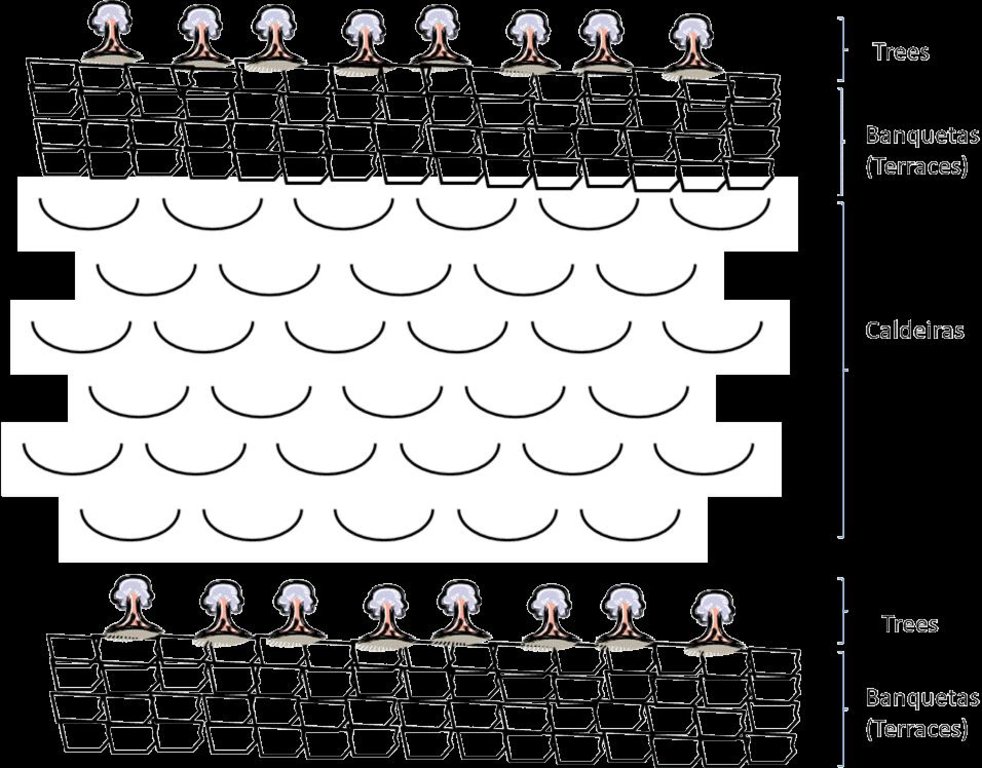
Purpose of the Technology: The climatic conditions are characterized by high spatial and temporal variability of the rainfall. The rains are concentrated in two or three months (August and September or October); the highlands and the N-NE parts are wetter compared to the low lands or coastal areas, which are very dry. The average annual rainfall is about 225 mm over the whole island; it has declined since the 1960s, with negative effects on farming conditions, and water supply. However, in areas located more than 500 m above sea level and exposed to trade winds, rainfall can exceed 700 mm. About 20% of the precipitation is lost through runoff, 13% infiltrates the soil and recharges aquifers and 67% evaporates. The evaporation loss is a limiting factor for any agriculture or forestry. Therefore, it is necessary to adapt the afforestation implementation to the specific local conditions (slope, stone cover, climate, etc). To overcome and minimize the problem of water scarcity, several measures are applied: (a) caldeira or half-moon structures achieved with earth or stone; (b) contour furrows or level bench terraces with stone walls arranged along the contour; (c). small dams to protect gullies. The aim is to maximize retention of water and control surface runoff. This not only allows better infiltration of water for the tree plantations, but also protects against soil erosion and facilitates groundwater recharge.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The success of the reforestation may be indicated not only by the area covered but also by the number of introduced plants. In 1975, there were about 3,000 ha of afforested land. By 2011, there are over 90,000 ha of afforested land with almost 50 million trees. Afforestation has focused mainly on the island of Santiago and Santo Antão, (13% of the total area reforested). Nowadays, more than 20% of the country is afforested. The forest has had a great importance in the context of combating desertification, rehabilitation of vegetation cover, in meeting energy needs and forage production and in developing agrosilvopastoral systems, as well as having undoubtedly contributed to a significant modification of the landscape in Cape Verde. The afforestation activities also contributed to increase biodiversity of some species of birds, including “Galinha di mato” (Numida meleagris), “Codorniz” (Coturnix coturnix), “Passarinha” (Halcyon leucocephala) and others.
Natural / human environment: The forest species are mainly used for land protection and for production of fuel wood and coal. Because of the poor growing conditions, the forest species are not well suited to the construction industry or wood processing.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Кабо Верде
Улс/аймаг/сум:
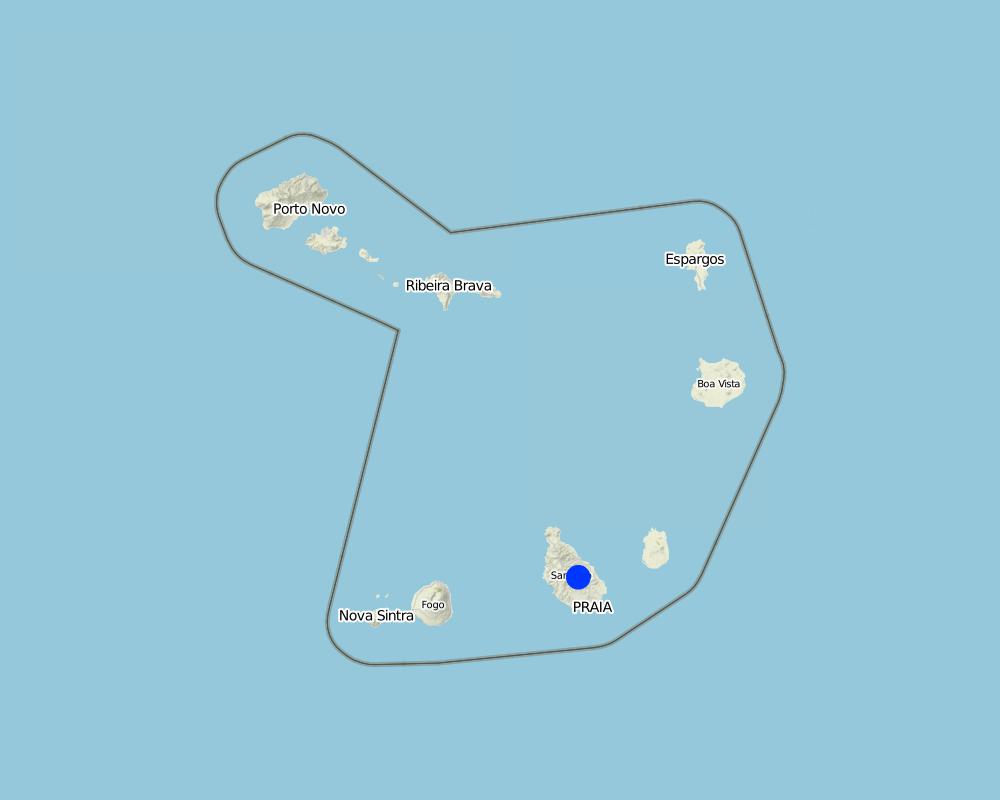
Santiago Island, Cape Verde
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Ribeira Seca
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
71.5
Тайлбар:
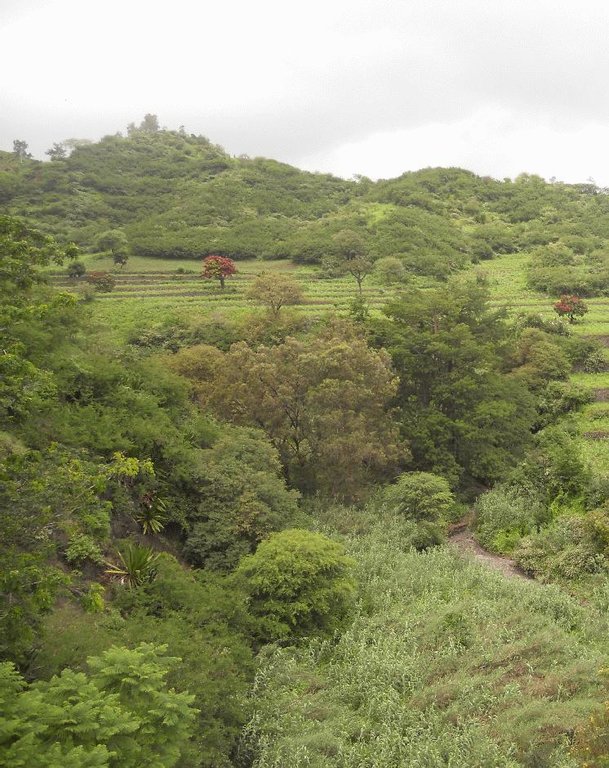
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 71.5 km2
The forest with the greatest density of trees occupies an area of 2.51 km2 and is located in the area of higher altitude. The density decreases with decrease in altitude
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Before 1975, the forestry production was directed to the market of wood, after 1975 began to stock in order to protect the environment
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- экосистемийг хамгаалах
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Ой-мал аж ахуйн систем

Бэлчээрийн газар
Эрчимжсэн мал аж ахуй / тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл:
- Хадлан буюу бэлчээрт ашиглагдахгүй талбай
Амьтдын төрөл зүйл:
- ямаа
- cows

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
- Мод тарьсан, шинээр ойжуулсан
Мод тарих, модгүй газрыг ойжуулах: төрөл зүйлийн гарал үүсэл болон бүтцийг тодорхойлох:
- Холимог төрөл зүйл
Мод тарьсан, шинээр ойжуулсан газрын төрөл:
- тропикийн уулын плантаци - Eucalyptus spp.
- тропикийн уулын плантаци - Pinus spp.
Модны төрөл:
- Хуайсны төрөл зүйл
- Майлсын төрөл зүйл
- Eucalyptus camaldulensis
- Grevillea robusta
- Нарсны төрөл, зүйл
- Prosopis juliflora, Parkinsonia aculeata, Jatropha curcas, Atriplex spp, Lantana camara
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Байгалийн нөөцийг хамгаалах
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The loss of soil by runoff, influenced by its low coverage, reducing their fertility and their thickness
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by runoff, low productive soils, low organic matter, low soil cover, fertility and depth particularly in the agro-systems with rainfed agriculture.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: goats/ cows
Grazingland comments: production is characterized as extensive, although made in a closed expaço
Plantation forestry: Few trees are cut, since the main objective of which is the forest canopy. The dead are removed, make's some clean and plant new trees every year.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Before 1975, date of independence of Cape Verde, began to stock the areas discovered. The forest is more dense at high altitudes but also introduced
Forest products and services: nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
Type of grazing system comments: production is characterized as extensive, although made in a closed expaço
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 90
Longest growing period from month to month: August untill October
Livestock density : 25-50 LU /km2
The main species used are Prosopis juliflora, Parkinsonia aculeata, Jatropha curcas, Atriplex spp, Acacia holosericea, Acacia victoriae, Lantana camara and others, in arid areas and Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Grevillea robusta, Pinus and Cupressus ssp. in highland and humid areas.
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)

Бусад
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Байгалийн ба сайжруулсан ойн менежмент
- Усжуулалтын менежмент (усан хангамж, ус зайлуулалт зэрэг.)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамлын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S2: Далан, хаалт
Тайлбар:
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bh: Амьдрах орчин доройтох

усны доройтол
- Hg: Гүний ус / уст үеийн усны түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
Тайлбар:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: soil management (It is cultivated maize and peanuts on land slopes very pronounced and boot up the plants by the root in end of the cycle), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The cleaning of the crop residues of corn is done pulling them by the root, negatively affecting soil stability), poverty / wealth (Leads sensitized peoples to advocate action against the landscape for survival of the family), education, access to knowledge and support services (Knowledge and technical training increase the options for means of survival of the community that acts on the forest, the degree of attending school is low and the illiteracy rate is 17%)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Creation of the wild animals compact the soil, destroying the structures for the conservation of soil and water exists, and creates conflict), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Sometimes occur heavy rains intensity that associated with poor vegetation cover, increase soil erosion), governance / institutional (Lack of applicability of the laws that manage the land)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Treatment of slope before afforestation
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It's needed sufficient knowledge to choice species according to their suitability to the natural and human environment)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.4
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): land from the local construction of the ditch is used in the construction of banks, that can be rein
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30 - 60%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:3
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Зохиогч:
Jacques Tavares
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Quantification of the area to be afforested | |
| 2. | Production of plants in nursery ( 500 - 1300 plants) | |
| 3. | Treatment of area (slope) with building terraces (15 m / person / day) | |
| 4. | Treatment of area (slope) with: Making half-moons “Caldeiras” (3 / person / day) | |
| 5. | 4.Excavating the pits (10 / person / day): 60x60x60 cm | |
| 6. | Planting (50 /person / day): 5 to 5 metres | |
| 7. | Initial maintenance (8 /persons / day) | |
| 8. | Cleaning and marking on curves level | In April |
| 9. | Construction of the retention / infiltration ditch and opening of the surface of culture | April to June |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 28218.0 | 28218.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 410.0 | 410.0 | 10.0 |
| таримал материал | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 942.0 | 942.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 29570.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 29570.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | forest cleaning | |
| 2. | forest cleaning | In the dry session |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Forest cleaning | ha | 1.0 | 142.0 | 142.0 | 52.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 142.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 142.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: Hoe, machete
Costs are estimated according to the time required for afforestation and the entity contracted for the implementation of the activities.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The labour affects the costs more than other factors. Paid labour is a way to achieve additional income for many people in this area. The employer (Directorate General of Agriculture, Sylviculture and Livestock of the Ministry of Rural Development) provides 90% of the cost of the equipment. The lifetime of the equipment is 10-15 years.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
800.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
- чийглэг
- хагас хуурай
- хуурай
Thermal climate class: tropics. average temperature equal to 26 º C
The exposure and altitude are factors diterminantes for agroclimatic estratização. the higher areas and targeted to the SE are more humid.
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Altitudinal zone: 100-500 m a.s.l. belongs to the stratum semi-arid sub-humid. Is part of the stratum the highest percentage of the area of the basin. 1000-1500 m a.s.l. includes mainly the cliffs and ridges.
Landforms: Also ridges and footslopes. The hazards of a convex situations does not allow its application in mountain slopes.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow is associated with the sloping hillsides used for rainfull agriculture and shaloow is found mainly in the valley bottoms of the downstream.
Soil texture (topsoil): The soil overlay mainly basaltic rocks, piroclastic, conglomerates and aluvial deposits
Soil fertility is medium - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium - low
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар, нөөцийн талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Ground water table: In rain months, it is more superficial than in the dry months
Availability of surface water: There is some just when it rains.
Water quality (untreated): Salinization of water due to over exploitation of wells and boreholes
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
and own 1% of the land (the tecnology is applyed by the state, and the state of that country is poor).
Off-farm income specification: forest production (mainly grass and wood) generate an annual income of approximately $2,500
Market orientation of production system: Mixed:Forest products are quite limited: lumber, firewood, charcoal and fodder from the pods. Firewood is the most important product but marketing is quite limited in time and space and subsistence are families who enter the forest for collection of grass and firewood. It is necessary for their survival. The state sells these products in order to finance other development projects.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- том-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
Also 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha and 100-500 ha,
The forest covers all the household
The grass production is made between the trees across the forest area if it's possible
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- төрийн
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
- Diocese
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээлийн чанар
эрчим хүчний үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Firewood to the community
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
ундны усны хүрэлцээ
Орлого, зарлага
ХАА-н зардал
эдийн засгийн ялгаат байдал
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийн хэрэгцээг хангах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
It reduces the options of land use
соёлын боломжууд
маргааныг шийдвэрлэх
нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Any sex has the same opportunity on the assets of the forest
livelihood and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
It improves air quality, promotes the production of endemic species and its use as medicine
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
ууршилт
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
салхины хурд
Экологийн бусад үр нөлөө
Invasive species
competition
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсац
голын адагт үерлэх
голын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдах
буферлэх / шүүлтүүрийн багтаамж
салхиар тээвэрлэгдэх хурдас
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Цаг уурын гамшигт үзэгдэл
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| орон нутгийн аадар бороо | мэдэхгүй |
| орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | муу |
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | муу |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | мэдэхгүй |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| цргалтын хугацаа багасах | сайн |
Тайлбар:
Tree species more tolerant of the climatic factors can be used, whilst retaining all the benefits that the existing species provide
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The high costs are associated with its implementation; afterwards they are significantly reduced and the technology builds up the benefits.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
None. It's a project of the government
Тайлбар:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Only the state has implemented this technology, because it changes the use of land and, without any subsidies, other land users are not encouraged to agree to it.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: there is a continuing campaign of afforestation of state land. There are voluntary associations working in this technology for a better environment
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Production of firewood and grass How can they be sustained / enhanced? make more forest operations such as pruning or cutting of new seedlings |
|
Protection of soil How can they be sustained / enhanced? strengthen maintenance operations |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Increases the quality of the landscape and reduces the loss of soil by runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? increasing the tree cover in areas with low coverage |
|
Encourages the production of livestock, and fuel wood How can they be sustained / enhanced? integrate the community in managing the forest, and manage it in a sustainable way. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| impossibility of farming in the forest lands | off-farm income creation to compensate |
| Lack of involvement of farmers in the management of forest areas | capacity building of land users in forest management strategies, elaboration of contracts between State and land users for the management of forest perimeters |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Reduces the percentage of land for agricultural production | increase productivity in cultivated land and reduce the need for the use of forest land, and implement new production technologies such as greenhouses |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Desertification at the Santiago Island, DESIRE, 2008
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Relatório de avaliação inicial do impacto das realizações de conservação de solos e água em 1993 do projecto WDP, WDP project, 1995
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
www.ine.cv: Survey of family income and expenditure, INE, 2002
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
OCDE, CILSS, 1982. Análise do Sector Florestal e Propostas para Cabo Verde. Sahel D (82) 179
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Club do Sahel, pp 203.
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
MAAA/DGASP, 1996. Rapport de pays pour la Conférence Technique Internationale de la FAO sur les Ressources Phytogénétiques, Leipzig, 1996, pp 38.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Leipzig, 1996, pp 38.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Protection des versants [Кабо Верде]
Cette approche consiste à mettre à profit les eaux d'écoulement superficiel
- Эмхэтгэгч: Jacques Tavares
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна