Sub-Surface Dams (SSD) [Кени]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Guyo Roba
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Brigitte Zimmermann, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Donia Mühlematter, Hanspeter Liniger, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_3340 - Кени
- Бүрэн хураангуйн PDF хувилбар
- Бүрэн хураангуйг PDF-ээр хэвлэх
- Хөтөч дэх бүрэн хураангуй
- Бүрэн хураангуй (форматгүй)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 22 6-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 07 5-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 17 7-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 15 8-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Surface Dams (SSD): 05 12-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Sarface Dams (SSD): 03 9-р сар 2018 (inactive)
- Sub-Surface Dams (SSD): 02 11-р сар 2021 (public)
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
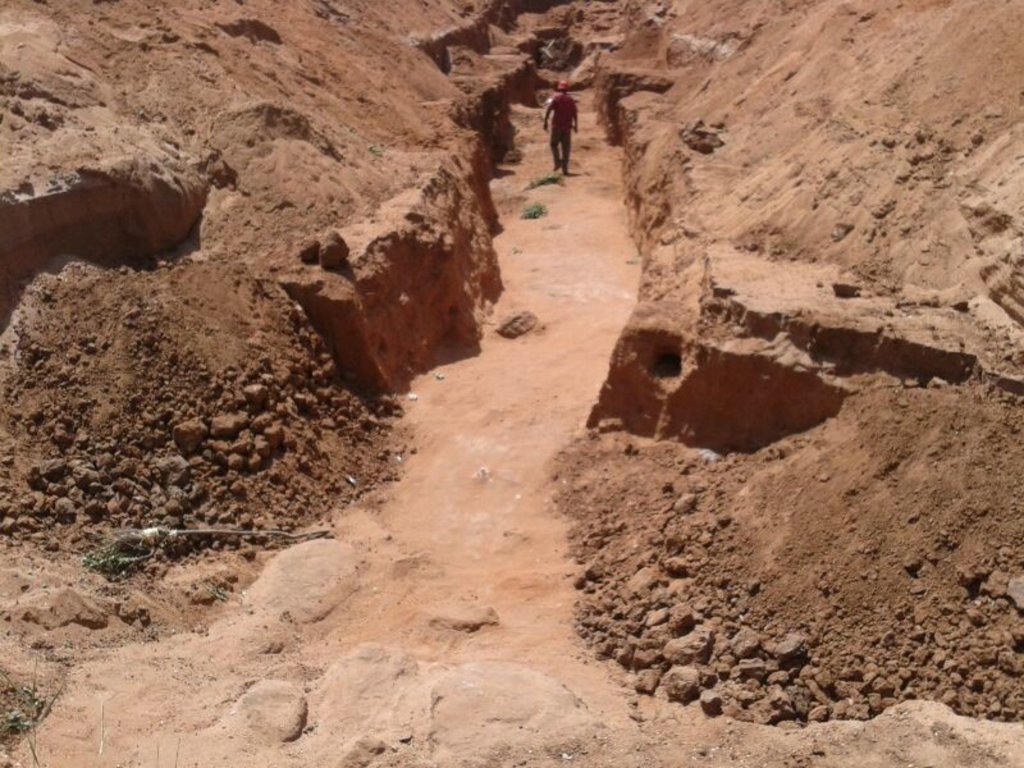
These are constructions stretching across the sand filled dry riverbed, down towards the impermeable floor of the riverbed. They are totally submerged into the ground. For example by fully covering after construction by sand. This are done along dry rivers with huge sand deposits, which has high yield potential and where water can be easily extracted. The aim is to raise groundwater tables and increase the storage capacity for water withdrawals.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
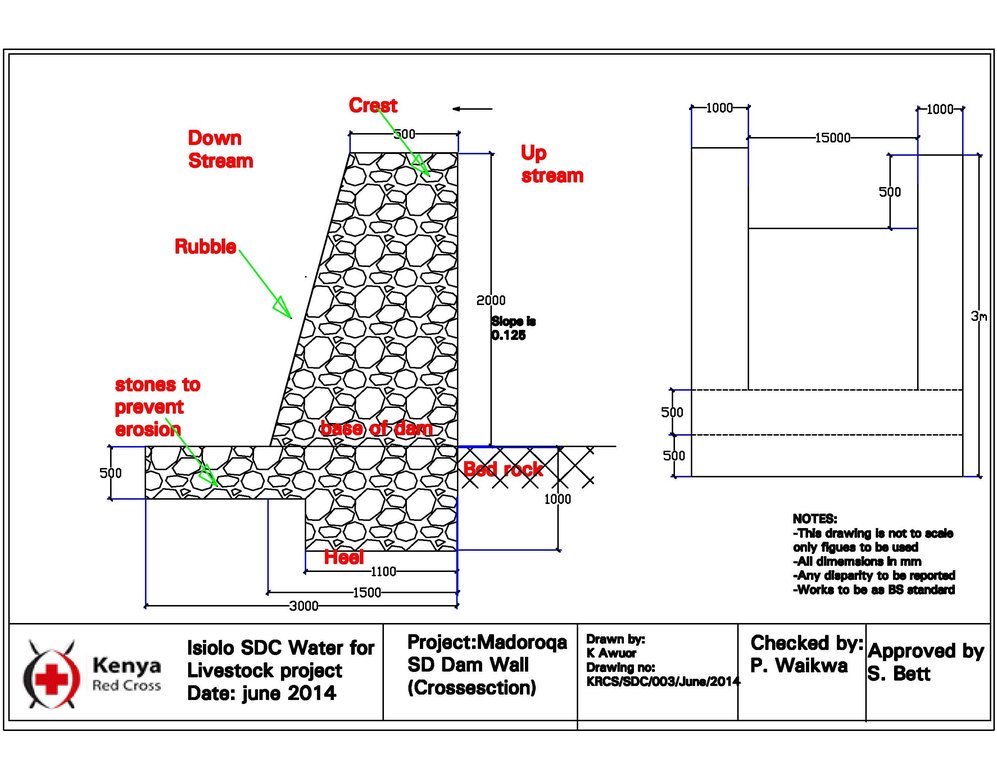
The technology is applied in northern rangeland of Isiolo County which is managed under communal management systems. The aim of technology to reduce pasture and water availability imbalances. The dimensions of sub-surface dam include: a length of water spread (103m),width of the dam (15m), width of water spread (18m), effective dam height (2m), volume of retained sand (103 x 0.5(15 +18) x0.5 x2.0 = 5098.50m3) and the volume of water that can be abstracted from the sand bed (25/100x 5098.50m3 = 1274.6.36m3).
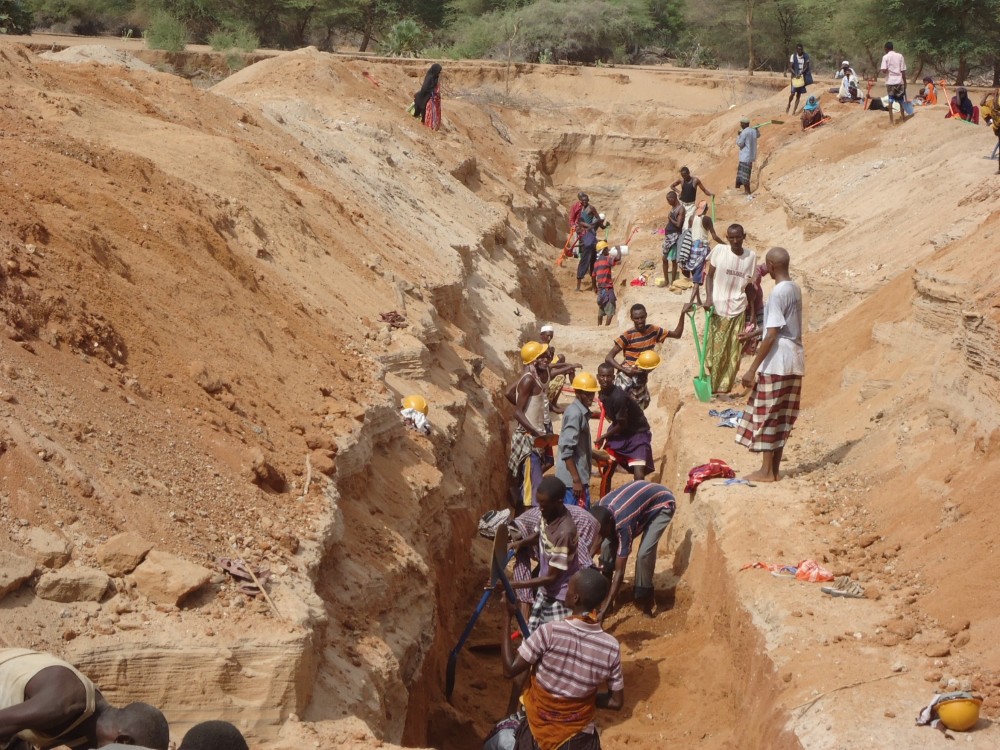
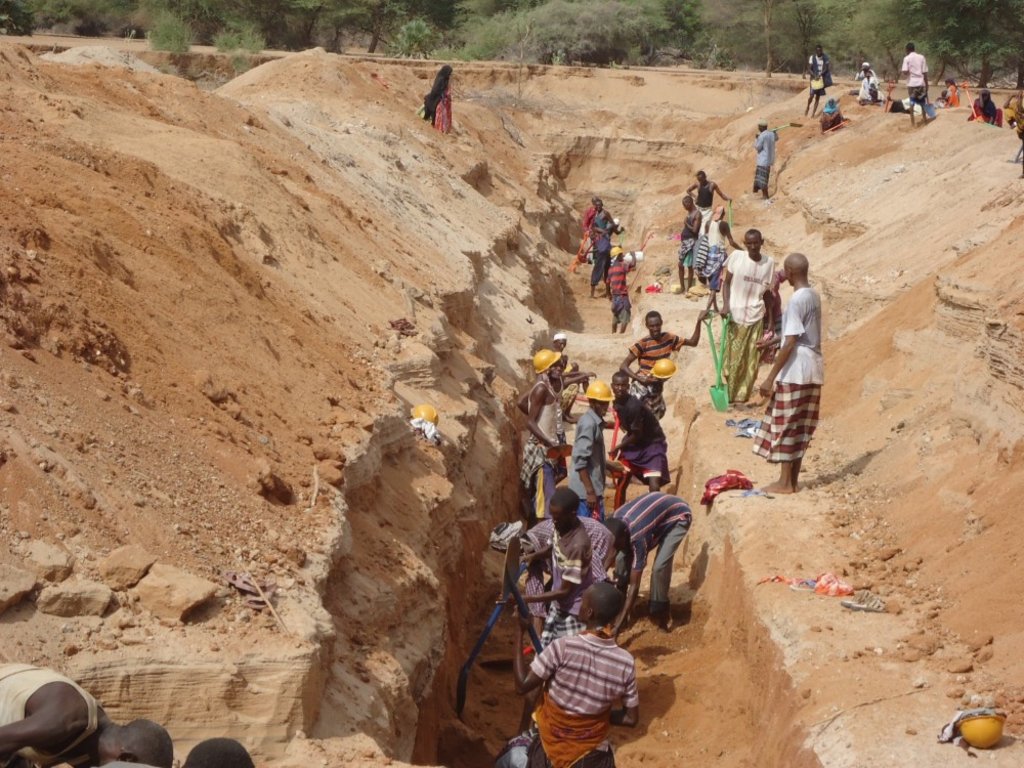
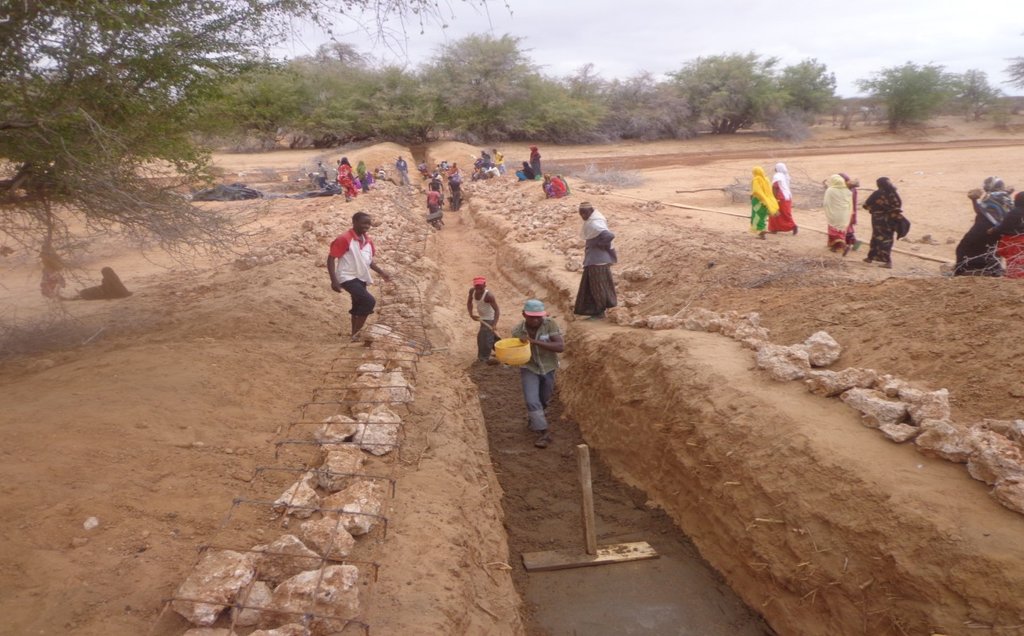
The technology functions as underground water storage infrastructure and the typical activities include, excavation of top porous soil, excavation of sample pits within the excavated area, checking filtration rates of soil, compaction of soil on which dam liners are laid, smoothing the sharp liners along which the dam liners are laid, making grooves to anchor the dam liner, laying the dam liner, anchoring the dam liner with a mixture of cement, water proof and sand with water (motor) and finally drying of the motor and filling back of sand.
The development of Sub-Surface Dams (SSDs) was done through Cash for Work program where local labours comprising of 40-50 persons are engaged in excavation, compactions and developing the liners. Farm tools like jembe, panga, spades and human labour are required to develop the SSD. The technology improves water supply/availability, thereby extending the period of livestock grazing in areas where typically water is depleted before the pasture hence improves water access for livestock in ways that support wider management and utilization of the rangeland and as such strength the resilience of pastoralists to droughts. This effectively gives pastoral groups, an extra grazing time (typically 2 extra months), a period usually not too long to encourage land degradation through over-grazing but long enough to enable pastoralist utilize the remaining pasture in wet season grazing areas. In so doing, the technology enable balanced use of vast communal lands without livestock retreating to dry season grazing areas.
In the process of the landscape level participatory planning with the communities: i) they identified different challenges, including need for decommissioning certain water points that they consider are contributing to over grazing and also attracting other communities, hence drive frequent conflicts, secondly, ii) they mapped areas in the rangeland where there is mismatch between water and pasture availability, most of these areas are in wet season grazing areas. So the next discussion was on what strategic water infrastructures that will enable herders to graze for 2 -3 extra months to enable them utilize the grass before they migrate to the traditional dry season grazing areas. So by design, the technology should only yield water that can allow settling for those extra months, not longer to the detriment of the rangeland
The technology was instrumental in fostering both balanced utilization of land and strengthening sustainable use of the vast rangeland by ensuring that herders utilize available pastures in the wet seasons grazing areas before moving to dry seasons grazing areas. The water stored through the technology stays longer, in this case study, the water lasted for 5 months after the end of the rainy season .
The area receives bimodal rainfall, long rain in March-May and short rain in November-December. With changing seasons/climate, the dry seasons can last up to 1 year in case of rainfall failure. Typically, dry seasons are 6-7 months (May- November).
Normally, the water is depleted within 2 months after the rainy period. The technology is also cheap and easy to understand and construct (especially in areas with clay as the underlying impermeable material) with a possibility of the communities to be taught how to identify suitable site and the entire process of construction. However, in areas without clay soil, the excavation of clay and transportation can be labour intensive and expensive.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Кени
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Northern Kenya
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Garba Tula, Isiolo County
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Map
×2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
- нийгэмд үзүүлэх үр нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Бэлчээрийн газар
Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй:
- Хагас нүүдлийн бэлчээрийн аж ахуй
Тайлбар:
Communal grazing area that is shared by 2 and more pastoral groups
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Бэлчээрийн мал аж ахуй ба бэлчээрийн газрын менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S5: Далан, усан сан, цөөрөм
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

бусад
Тайлбар:
Mismatch of pasture and water resources - there are areas where pastures are plenty but surface rain water is depleted earlier than pasture.
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
The SSD technology increase water availability is period immediately after the rain, hence ensuring better pasture utilization and more sustainable use of land.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
chamber
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
3.5 USD per day
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removing sand over dyke and man-days for excavating and transporting soil to dam site | 21 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 2. | Building and compaction soil in dam wall | 3 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 3. | Supplying water for compaction | 0.5 day for 45 casual labourers |
| 4. | Back-filling sand on dam | 1 day for 45 casual labourers |
| 5. | Supplying water for compacting clay in dam wall | 2 days for 45 casual labourers |
| 6. | Compacting soil and placing liners | 12 days for 45 casual labourers |
Тайлбар:
The construction of SSD was done through “Cash for work” which is participatory process that involves community mobilization, identification of beneficiaries and formation of “Cash for work” committees, registrations and verification of beneficiaries and implementation/supervision of the work.
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | tools - jembe, spade etc. | pieces | 80.0 | 5.33 | 426.4 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Removing sand over dyke and Man-days for excavating and transporting soil to dam site | per day | 945.0 | 4.0 | 3780.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Building and compaction soil in dam wall | per day | 135.0 | 4.0 | 540.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Supplying water for compaction | per day | 22.5 | 4.0 | 90.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Back-filling sand on dam | per day | 45.0 | 4.0 | 180.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Supplying water for compacting soil in dam wall | per day | 90.0 | 4.0 | 360.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Compacting soil and placing liners | per day | 540.0 | 4.0 | 2160.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 7536.4 | |||||
Тайлбар:
As stated, the cash for work approach means that people get paid 4 USD per day for working on SSD until completion. There are phases where people participated in preliminary phases in meetings and consultation without payments but the actual work was done on cash for work basis.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training of communities to manage and maintain the structures | yearly |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour for site protection and maintenance of hygiene | per site | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 1000.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Water User Associations on the sites are trained on the management of the structures on behalf of the community e.g. on the protection of structure and hygiene maintenance.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Distance of the sub-surface dam from villages, extent of destruction by floods and human activities
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
because of the climate change, the rainfall is becoming more erratic.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Isiolo
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хотгор нөхцөл
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- бүдүүн/ хөнгөн (элсэрхэг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
сайн чанарын ундны ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Их
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Их
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Хагас-нүүдэлийн
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- бүлэг / олон нийтийн
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- том-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- нэгдлийн/ тосгон
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
малын бүтээмж
газрын менежмент
Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
мал услах усны хүрэлцээ
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
гангийн нөлөө
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Усны хүртээмж
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул (гамшиг)
Уур амьсгалын гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| ган гачиг | сайн |
Усзүйн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | сайн |
Тайлбар:
The technology copes very well with floods as the construction is embedded in the sand and thus very well protected.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
The technology has limited running and maintenance costs once its done fairly well.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The technology created opportunity to graze in wet season grazing areas for an averge extra 2 months period after rainy seasons. The technology has provided additional water that gave herders extra days to graze in wet season areas and utilize the pasture that would have been unutilized due to water constrains. In so doing, the land users utilized the pasture without retreating to traditional dry season grazing areas. |
| The extra grazing months has reduced overall livestock mortality during droughts and also improved resilience of pastoral community. |
| The distance travelled and effort required to access water was reduced. Community members reported reduced distances covered and time spent in search of water for livestock. In some instances the distance reduced from 12-15 Km to 3 Km. Community members also mentioned reduction in conflict incidences over water resources in some areas due to adequate supply of water as a result of construction of water infrastructure. |
| The balanced utilization of the grazing area through SSD water provision, enables herd to graze in wet season grazing for slightly longer period and utilize pasture optimally, this however, does not mean that during that garzing period, there will be overgrazing. The volume of water available restricts the number of animals sustained by the grazing area. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The technology has created an opportunity to optimally use the grazing area and overall reduced land degradation. The technology Improves access to water for livestock in ways which promote more sustainable management of rangeland resources and as such strengthening the resilience of local communities. |
| The validation process prior to construction of the SSD is draws critical lessons of identifying and agreeing on where to construct the SSD in a way that fit within broader sustainable rangeland management in a manner that ensured sustainable and efficient utilization of pasture and browse resources in targeted areas. The increase in water supply allowed livestock to graze additional 2-3 months in target areas before shifting to dry grazing areas where previously they migrated before exhausting the pasture and browse resources due to water scarcity. The dry season grazing area is towards Merti, in Kom and Sabarwawa where there are deep boreholes, under, lock and key and only opened during dry seasons. In typical year, the dry season period is about 7 months. But when one rain season fail it goes to about 11 months. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| When the construction season for SSD is not well planned, there is likelihood/risks of the dams being washed away by flash floods. | Better planning and timing of the development of SDD, just slightly before the onset of rainfall. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
11/01/2018
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Promoting resilience by influencing water infrastructure development in community managed rangelands of Kenya
URL:
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2014-088.pdf
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Balancing water infrastructure in community-managed rangelands in the arid and semi-arid lands of Kenya
URL:
https://portals.iucn.org/library/sites/library/files/documents/2014-089.pdf
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна