Introduction of Crop Rotation [Гүрж]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Hanns Kirchmeir
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: Kety Tsereteli
- Хянагч: Ursula Gaemperli
technologies_4275 - Гүрж
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
хамтран эмхэтгэгч:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Applying Landscape and Sustainable Land Management (L-SLM) for mitigating land degradation and contributing to poverty reduction in rural area (L-SLM Project)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Regional Environmental Centre for the Caucasus (REC Caucasus) - Гүрж1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
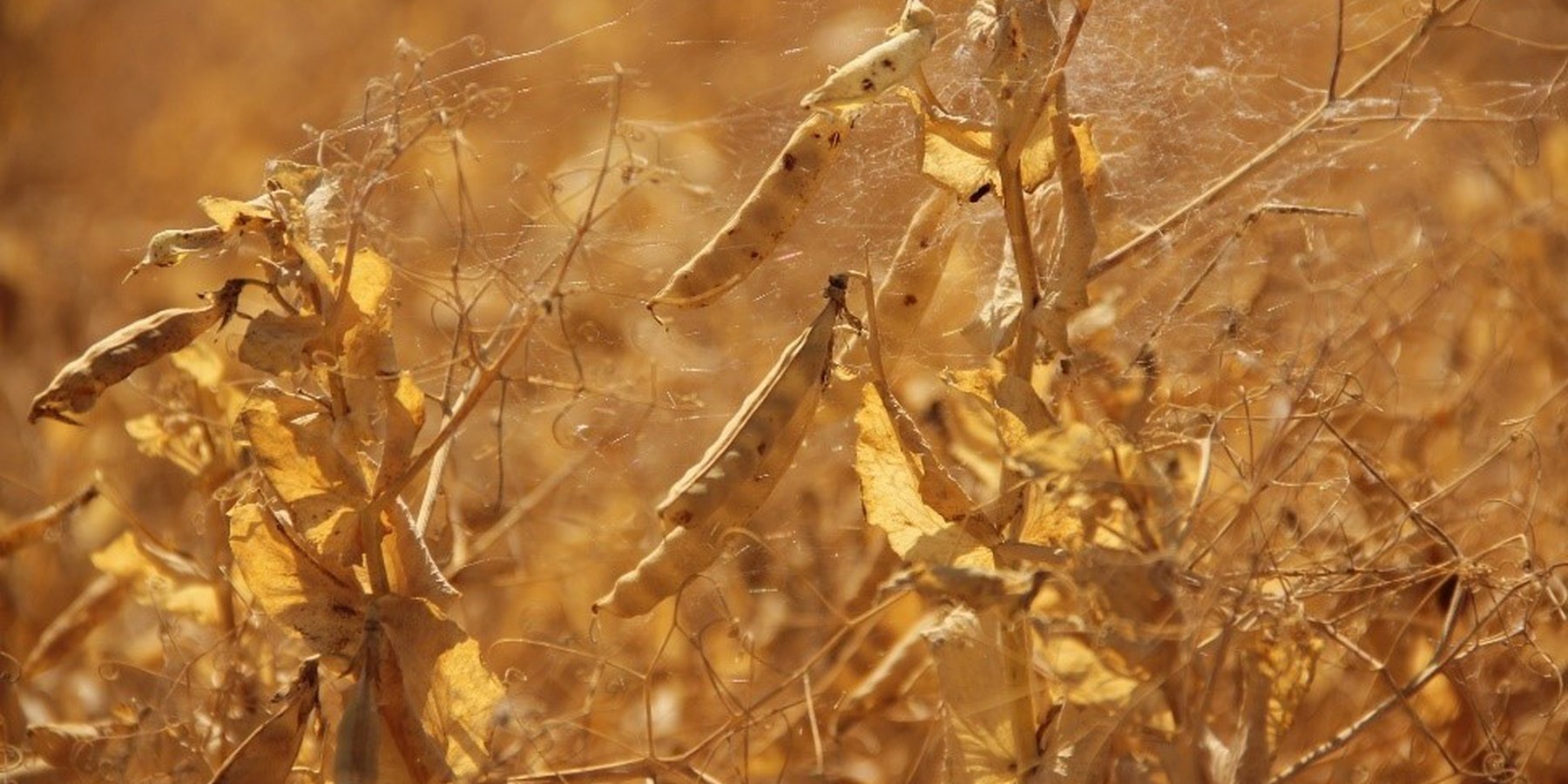
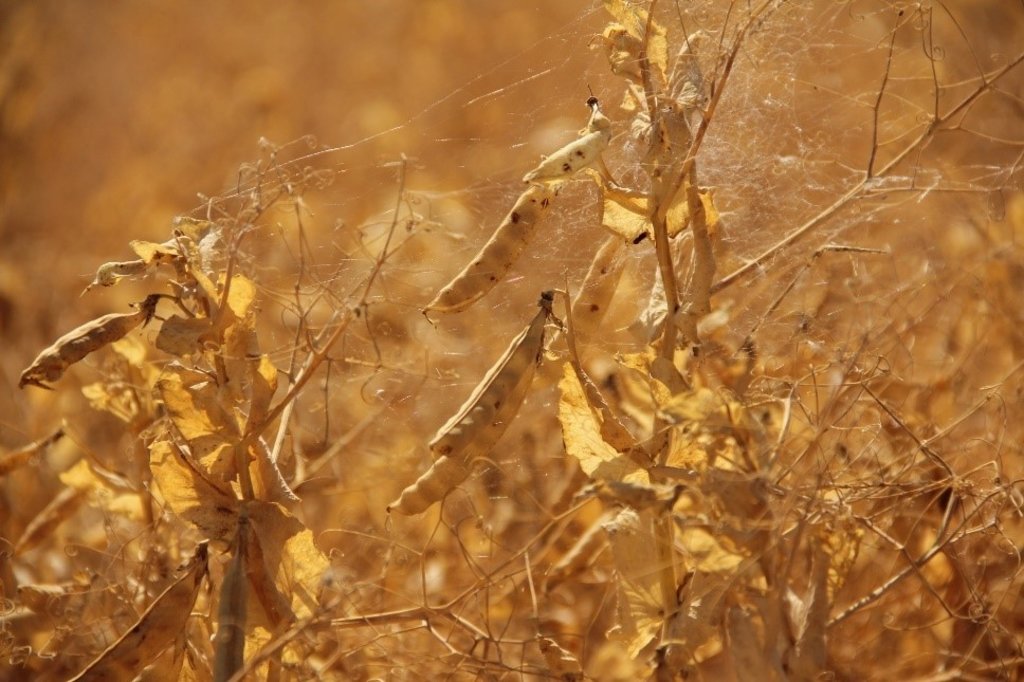
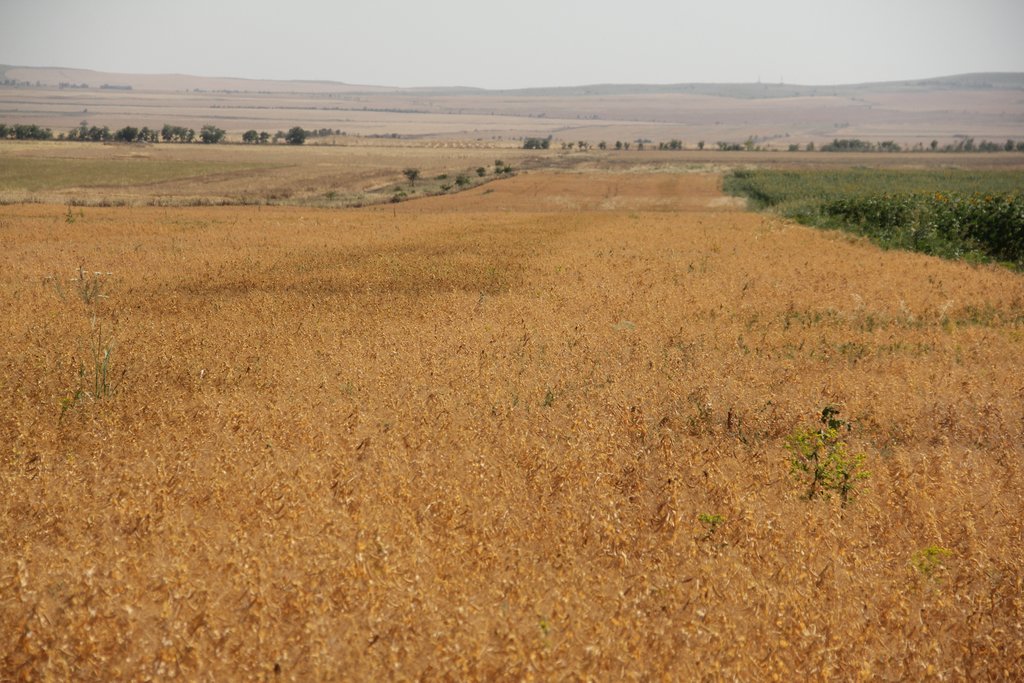
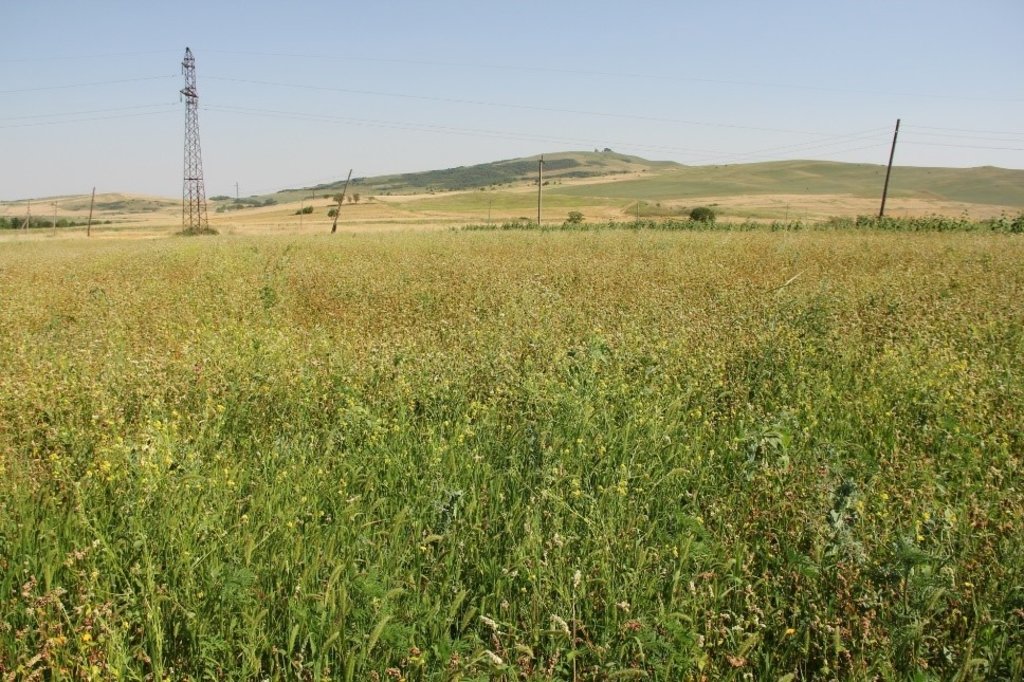
In the municipality of Dedoplistskaro, Georgia, 100 ha of land have been cultivated with peas on approx. 25 fields (each 1-10 ha in size). The introduction of peas as an alternative crop that is now used in rotation with wheat, helps to increase soil fertility sustainable and ecologically.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
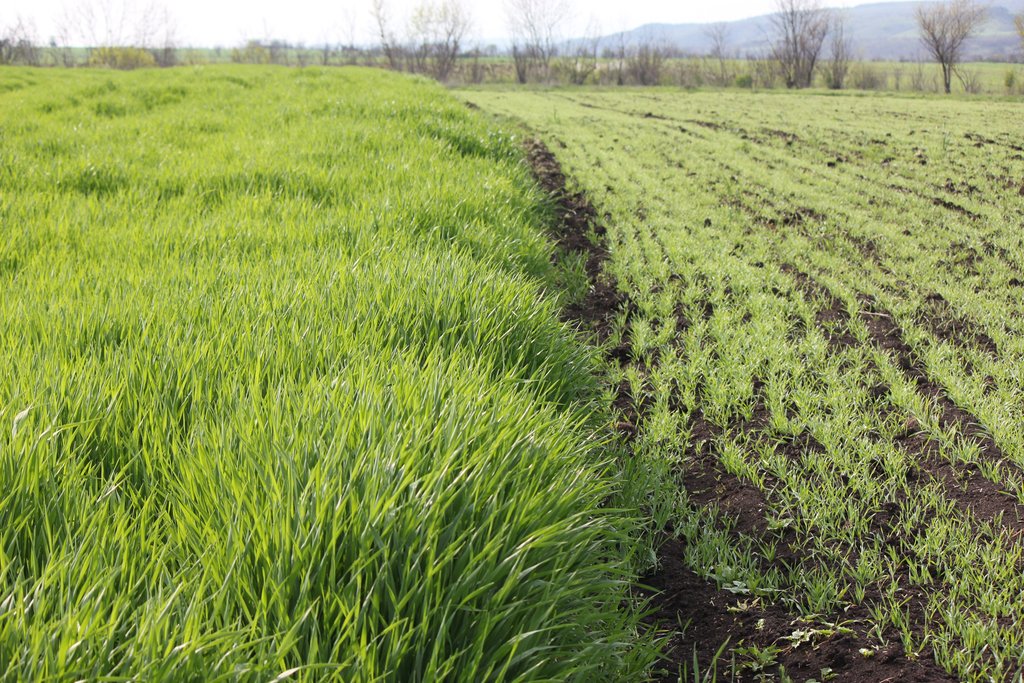
Dedoplistskaro is located in the Shiraki Plain, in eastern Georgia, and consists of steppes, where grain crops are cultivated and livestock is grazed in the winter. The steppic soils are dominated by Chernozems and Kastanozems, the climate is warm and temperate and the small-scale land (2-5 ha) is in individual ownership. The labour including plowing, seeding and harvesting is fully mechanised, the machines are mainly borrowed from agricultural machinery cooperatives and less often from private machinery suppliers. For the inhabitants of Dedoplistskaro municipality, agricultural production is an important source of income. 74% of the Georgian wheat production is located in the Kakheti region. Shiraki valley has a great share of this. The area of wheat production in Dedoplistskaro is 13,693 ha (Census 2014). Securing the productivity of arable land and stopping degradation due to the loss of soil fertility is of local and national importance. The introduction of pea as an alternative crop, which can be used in rotation with wheat or other crops, should help to increase soil fertility in a sustainable and ecologically viable way. Pea is a plant from the legume plant family. The root system of Pea can thus fix nitrogen from air by symbiotic bacteria. This helps to increase the C/N ratio in the soil leading to higher decay rates of organic carbon (e.g. from straw residuals) and higher fertility of soils. Most farmers sowed on 23 and 24 March 2018 - some until 29 March 2018. Later sowing led to lower yields.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Гүрж
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kakheti
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Dedoplistskaro
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Технологи газар нутгийн хэмжээнд жигд тархсан бол түүний эзлэх талбайг тодорхойлно уу (км2-аар):
1.0
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2018
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- үр ашигтай эдийн засгийн нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (эрт ургацын)
- буурцагт ургамал - вандуй
- buckwheat
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Үгүй
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
Crop rotations with wheat, pea and buckwheat. Different systems, one example: Year 1: Wheat, Year 2: Pea, Year 3: Wheat, Year 4: Wheat, Year 5: Buckwheat, Year 6: Wheat, Year 7: Wheat, Year 8: Pea, Year 9: Wheat
Тайлбар:
Before the implementation of the technology wheat was cultivated without intercropping or crop rotation.
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Тийм (Технологи хэрэгжүүлэхээс өмнөх үеийн газар ашиглалтын талаархи асуулгыг бөглөнө үү)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (эрт ургацын)
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Үгүй
Тайлбар:
It is envisaged to continue with crop rotation in the following years.
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- Ээлжлэх тогтолцоо (таримал ээлжлэн тариалах, уриншлах, өнжөөн тариалах)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
Тайлбар:
The nitrogen fixing capabilities of the pea-roots will increase fertility of the soil additionally to the crop-rotation effect.
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)
Тайлбар:
The permanent cultivation of wheat on the same field leads to degradation of fertility.
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
The crop rotation will reduce and/or prevent from land degradation by permanent wheat cultivation.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Proposed rotation schema for wheat, pea and buckwheat
Зохиогч:
Hanns Kirchmeir
Он, сар, өдөр:
07/02/2018
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
100 ha
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
20
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of farmers and fields according to the selection schema and signed subsidy contracts to all farmers | Until January 2018 |
| 2. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2017-Novembver 2018 |
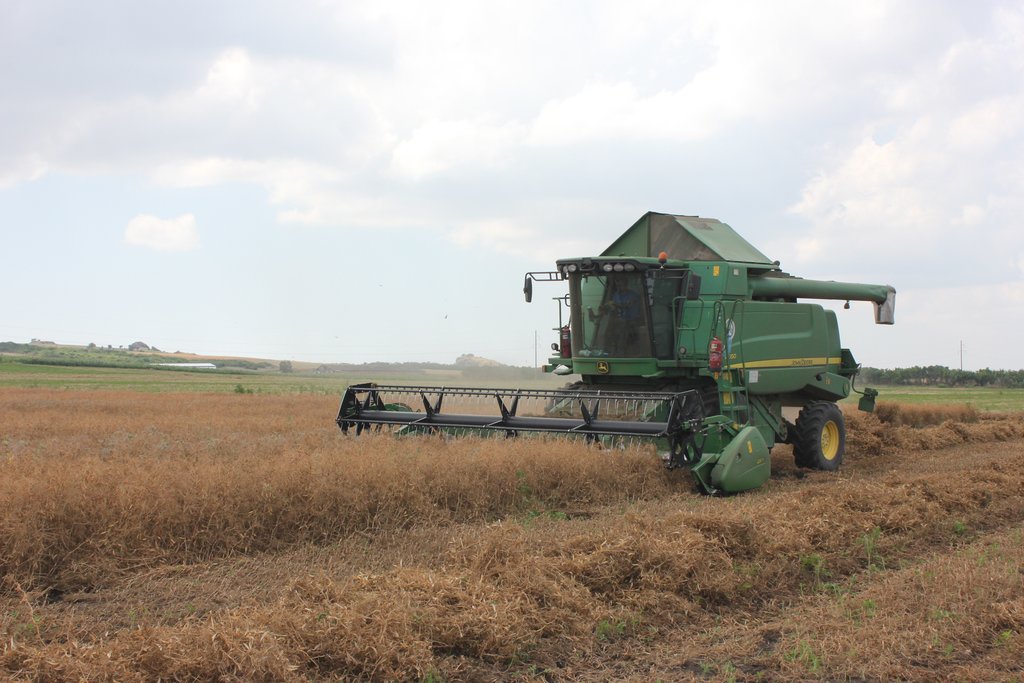
| 3. | Seeding, maintaining and harvesting | March-October 2018 |
| 4. | Scientific assessment of soil fertility before seeding | October 2018 |
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | plowing | ha | 100.0 | 35.71 | 3571.0 | 40.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | harrowing | ha | 100.0 | 14.29 | 1429.0 | 40.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | seeding | ha | 100.0 | 8.93 | 893.0 | 40.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | harvesting | ha | 100.0 | 35.71 | 3571.0 | 40.0 |
| таримал материал | pea-seeds (250kg) | ha | 100.0 | 133.93 | 13393.0 | 40.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | herbicide (1l) | ha | 100.0 | 5.36 | 536.0 | 40.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 23393.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 23393.0 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
60% of the cost have been added as a subsidy payed from GEF project funds.
Тайлбар:
The funding was organised in a public call. Farmers from the Dedoplitskaro region have been invited to apply for a 60% co funding of the pea/buckwheat planting.
The costs stated in the section "Labour" for plowing, harrowing, seeding and harvesting include costs for labour and for equipment. The work was done partly by the farmers themselves and partly by an agricultural contractor such as for driving the harvester. The machines are mainly borrowed from a local machinery cooperative, but also from private machinery suppliers.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
Тайлбар:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
Тайлбар:
The full production cycle (plowing, harrowing, seeding, harvesting including the application of pesticide have been included in the 'establishment' section.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
It was a challenge to organised the high amount of pea-seeds, as they are not commonly available in the region.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
697.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
The driest month is January, with 25 mm of rainfall. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June, with an average of 108 mm. The difference in precipitation between the driest month and the wettest month is 83 mm.
Холбогдох цаг уурын станцын нэр:
Dedoplistskaro Met. Station
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- хагас хуурай
The climate is warm and temperate in Dedoplistskaro. The average annual temperature in Dedoplistskaro is 11.3 °C. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.7 °C. The lowest average temperatures in the year occur in January, when it is around 0.1 °C.
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- нарийн /хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- их (>3 %)
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
In the region steppic soils are dominating (Chernozems and Kastanozems)
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
хангалтгүй/ байхгүй
Усны чанар (цэвэршүүлээгүй):
муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар гэж:
газрын доорхи ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Биологийн олон янз байдлын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
The landscape is intensively used by agricultural purpose. The former network of windbreaks was massively reduced in the last decades. Re-establishing could support the habitat diversity significantly.
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10 %-иас доош
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- механикжсан / мотортой
Хүйс:
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
The local farmers-association was an important partner in promoting the imitative.
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээтэй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Үгүй
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The average yield of peas 3 t/ha, 98 t pea yield was taken from the pilot plots. Some of the farmers will sow the peas in other plots to improve soil fertility on another land under their ownership. Buckwheat was sown only on 2 plots, 450 kg at all. The farmers who had opted for the concept of starting the crop rotation with buckwheat cultivated the green mass in the soil to improve their fertility. The harvest of peas/buckwheat was very variable between the different farmers depending on their timing of measures: 1. The farmers who could not use the possibility to seed the crops in March - 1 farmer, because of rainy weathers afterwards, seeded pea later , in the middle of April. This farmer could not get yield from the plot. The others (2-3 farmers) who could not harrow the soil after seeding (as we recommended to harrow), they got the small yield.
Талбайд илэрсэн үр нөлөөг үнэлнэ үү (хэмжилт):
When peas are used as a intercrop between winter wheat cultivation, this would have a positive effect on wind erosion. Since the implementation of the crop rotation just started in 2018, evidence-based further impacts are only expected in the following years, e.g. impacts on soil quality.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Талбайн гадна илрэх үр нөлөөллийн үнэлгээг тайлбарлана уу (хэмжилтүүд):
No off-site effects are expected.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Тайлбар:
Maintenance costs were not applied.
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- 1-10 %
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 0-10%
Тайлбар:
It is a very new technology. But success of the first year will help to spread it across the region.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The project gave farmers the opportunity to try the new crops (peas and buckwheat) for the community of Dedoplistsakro, as they only sow wheat and barley over the years. They had the opportunity to get advice on how to sow peas and buckwheat and how to improve the soil fertility of their land. They invested through ploughing, harrowing and maintenance, as well as by taking over the yields. They were also interested in maintaining the yield from the proposed crops, using this seed for further plots next year and passing on the knowledge to other farmers. Some farmers sold harvested peas as forage, some gifted others for the same purposes to improve soil fertility. |
| The farmers, who sow the peas in time and cultivate them with appropriate agrotechnical measures, harvested 3.5-4t/ha. The profit was 12 250 - 14 000 GEL/ha. The yield rate was as follows: 3.5.5 t/ha yield - 4.8 yield rate; 4 t/ha --- 5.5 yield rate. |
|
The expected yield of barley per hectare in the years following pea sowing will be 7-9 tonnes. Income ratios - 9.6 for 7 t/ha yield; 12.4 for 9 t/ha yield. The expert calculated the expected yield on the basis of yield data from the davit Nateladze area in Dedoplistskaro, where peas were sown in 2017 and then 5.5 t barley/ha instead of 1.5 t barley/ha (in previous years before peas were sown) was harvested. As part of the pilot project, 23,750 kg of peas were sown on 92 ha in Dedoplistskaro in 2018. 98 t of peas were harvested in mid-July in the municipality of Dedoplistskaro. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| The machinery for preparing the soil and seeding are available. |
| Especially pea has a very positive effect on soil fertility. |
| Most of the farmers used the technology for next year(2019). They seeded the harvested pea in spring 2019 at another plots in Dedoplistsakro municipality (about 100 ha). This confirms the positive impact of the approach on soil fertility and guarantees the sustainability of the project. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Some farmers (2-3) sow the pea later than others. They did not get a good yield because of the sowing in April. The reason for the delay was 1. rainy weather; 2. lack of machinery. Timely harvesting was also the problem because of the lack of machinery, since Dedoplistskaro is called the barn of wheat and there are not enough machines in the community. The problem of the realization of peas and buckwheat was also the problem because of the lack of companies for peas and buckwheat not only in the municipality but throughout the country. | The farmers asked for a support for the municipality in the development of such enterprises to process the mentioned crops for realization. |
| Of the 3 schemes proposed, 19 farmers choose the first scheme to sow the peas in the first year. The second scheme was not chosen at all. The 3rd scheme to start crop rotation in the 1st year with buckwheat was chosen by 2 farmers. A farmer ploughs the yield of buckwheat as a green mass in the soil and improves the fertility of the soil. Another harvested and prepared 120 hay presses. The farmers improved the soil, but the expenses were at 1 ha / 2 645 GEL, 1 press / 7 GEL, the income ratio 0,31. The sowing of buckwheat to prepare the press is ineffective to benefit from the harvest. The farmers who opted for the third scheme (start of croprotation with buckwheat) were geared towards improving soil fertility, but most farmers prefer to do the rotation in order to benefit from the yield. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| There is no local marked or seller for peas and it is difficult to sell the product for the local farmers. | It needs national support to develop a pea-processing industry. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
Two field visits.
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
Interviews with the implementing national field expert.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Documentation from the field expert
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
12/09/2018
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна