Organic Agriculture with Reduced Tillage [Украин]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Natalia Prozorova
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Organic Agriculture
technologies_7440 - Украин
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Prozorova Natalia
National Scientific Center «Institute for SoilScience and Agrochemistry Research, named after O.N. Sokolovsky»
Украин
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Delft University of Technology (TU Delft)1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологийг газрын доройтлыг бууруулж, газрын тогтвортой менежментийг хангахад тохиромжтой гэж үзэж болох уу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
This organic agriculture technology combines reduced tillage with organic farming practices to enhance soil health, increase carbon sequestration, and maintain sustainable agricultural productivity.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
This example of organic agriculture is applied primarily in the central Poltava region of Ukraine, which is characterized by undulating plains within the Poltava Plateau. The region’s fertile chernozem soils provide an ideal environment for sustainable farming practices. These soils are predominantly deep, medium-humus, medium-loam chernozems, known for their agronomically favourable physical and chemical properties, including high organic carbon content (around 3% in the upper layer) and excellent water retention capacity. The natural fertility of these soils, combined with their relatively high nitrogen and exchangeable potassium content, underpins their suitability for organic farming.
Organic agriculture in this context combines two land management technologies (LMTs): reduced tillage and organic farming. Reduced tillage minimizes soil disturbance, which preserves soil structure and reduces erosion, while organic farming eliminates synthetic inputs and relies on crop rotations, organic fertilizers, and biological pest control to maintain soil health and ecosystem balance. The purpose of these practices is to enhance soil carbon sequestration, mitigate climate change impacts, and support sustainable agricultural productivity.
Farming is certified as a producer of organic plant products in accordance with the standards equivalent to Council Resolutions (EU) 834/2007 and 889/2008.
Under this system, shallow tillage is carried out to a depth of 4–6 cm, which helps preserve the natural structure and capillarity of the soil. It employs Horsch cultivators of the "Agrosoyuz," "Scorpion," and "Quant" models. The enterprise also extensively uses disc harrows from the French manufacturer Grégoire Besson, such as the DXRV and DXRV-HD models, which are employed for green manure incorporation. These tools operate at a precisely determined depth, regardless of the micro-relief of the field. Thus, PE "Agroecology" does not use ploughs for inversion tillage but instead prioritizes shallow tillage with cultivators and disc harrows.
The main crops grown include winter wheat, soy, corn, sunflower, and perennial herbs such as sainfoin. The combination of these crops supports soil fertility and biodiversity while maintaining agricultural productivity. Land Mitigation Technology (LMT) refers to practices and technologies designed to reduce or offset the environmental impact of land use activities. It includes strategies for restoring degraded ecosystems, preventing soil erosion, conserving biodiversity, and managing resources sustainably. LMT is often applied in agriculture, construction, and land development to balance development needs with environmental protection.
Key activities to establish and maintain the technology include transitioning from conventional to organic farming practices, adapting tillage methods to reduced-intensity operations, and maintaining organic soil fertility through natural inputs. These activities require significant initial effort and investment, including soil testing for nutrient content and organic carbon stocks, stakeholder engagement for field planning, and long-term monitoring of soil health indicators. The establishment process also involves collaboration with scientific institutions, such as ISSAR and Bioclear Earth, to ensure effective implementation and validation of the technology.
The primary benefits of this technology include improved soil structure, increased biodiversity, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and enhanced carbon sequestration. The technology has demonstrated the potential to sequester up to 0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹, with minimal yield trade-offs. Additionally, the resilience of the chernozem soils supports similar crop yields in both organic and conventional systems, thanks to their natural fertility and lower input rates in conventional agriculture. Farmers particularly value the long-term sustainability and ecological benefits of organic farming.
Land users face challenges with this technology. Transitioning to organic farming can result in temporary yield reductions, requiring adaptation in farm management practices. Furthermore, reduced tillage demands specific equipment and techniques, which may present a financial barrier for some farmers. The implementation of organic farming also requires significant effort in pest and weed management due to the absence of chemical inputs.
Overall, this form of organic agriculture represents a promising approach to sustainable farming in Ukraine, particularly in the fertile Chernozem region. Its ability to enhance carbon sequestration while maintaining comparable yields to conventional systems highlights its potential to contribute to climate mitigation and soil restoration goals. Further research and field validation are needed to refine the understanding of its impacts and optimize its implementation.
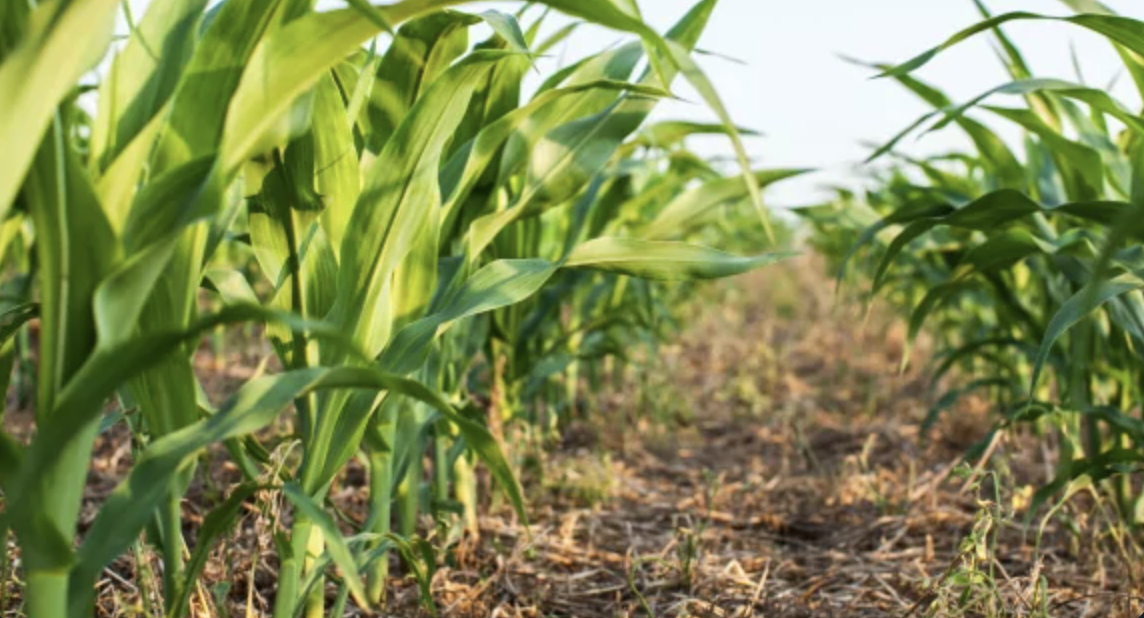
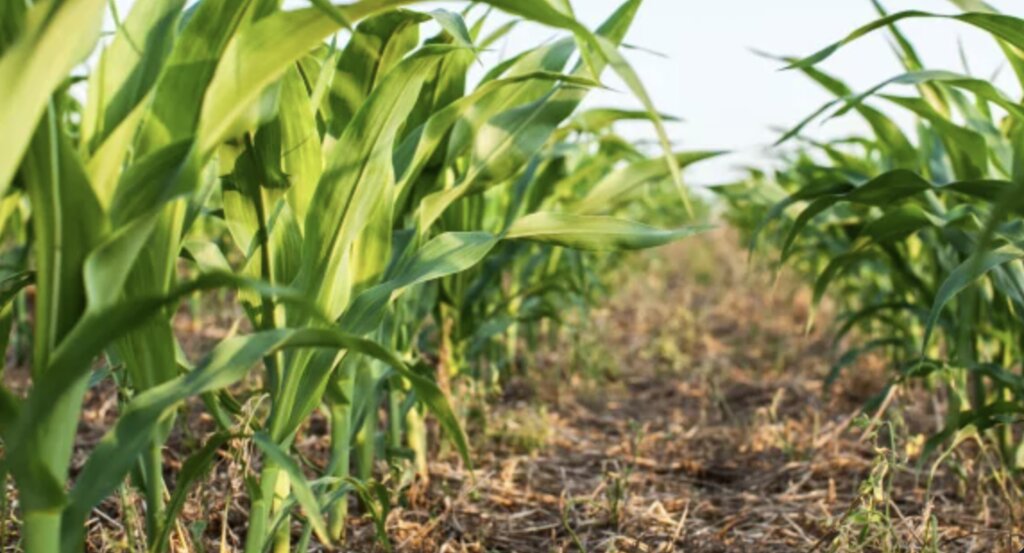
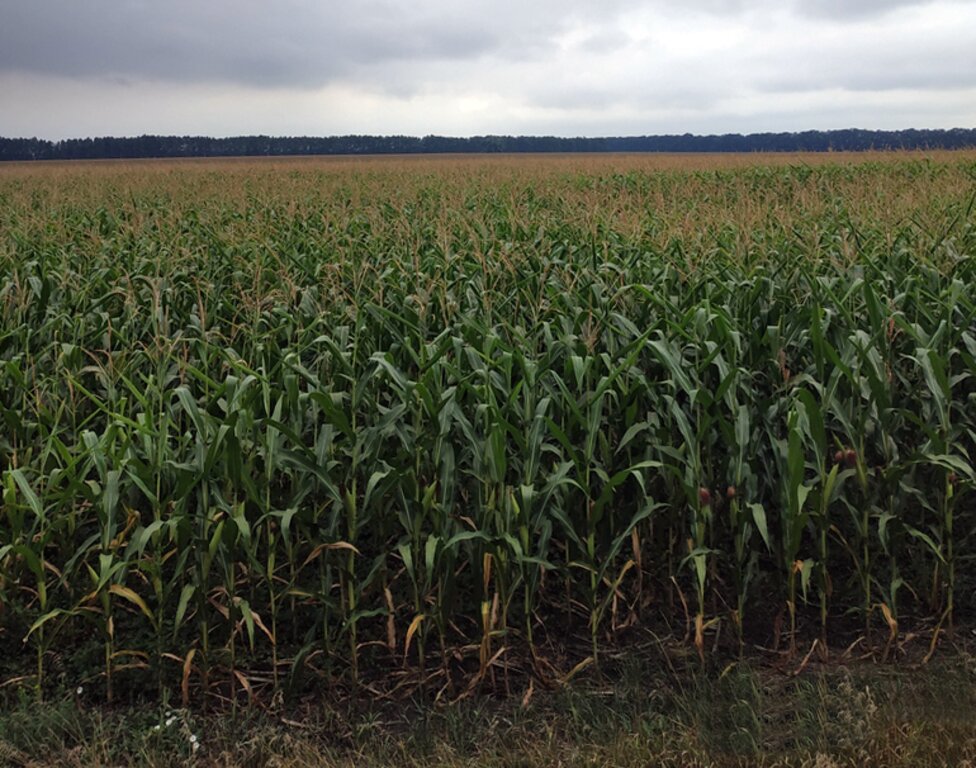
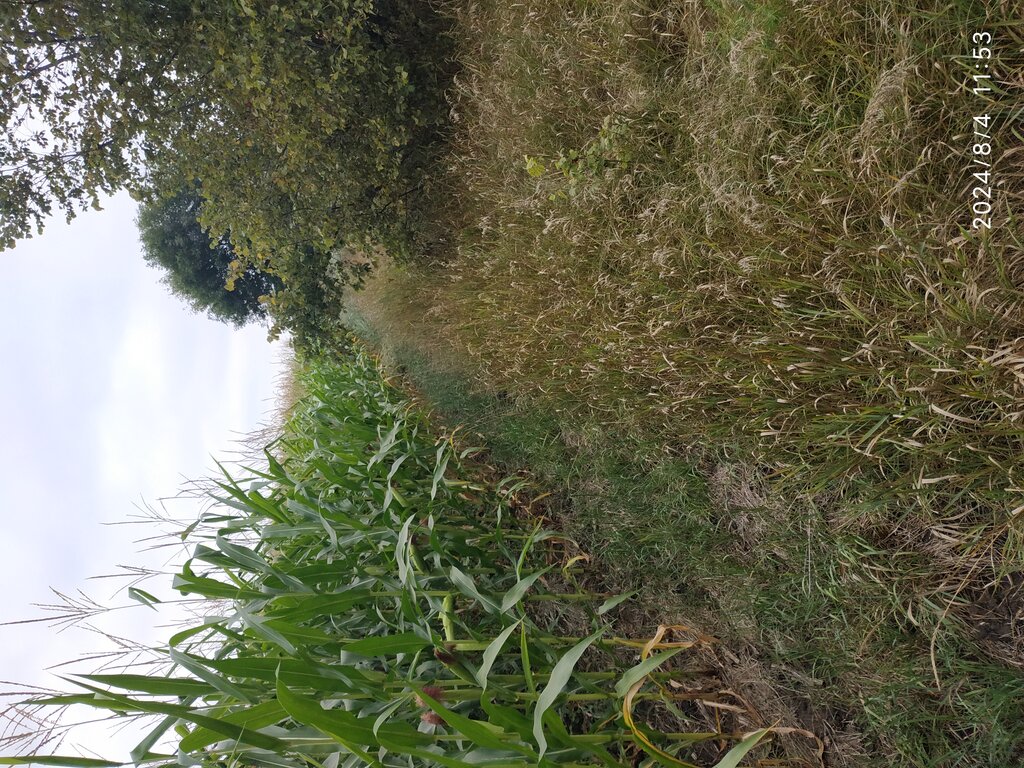
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
Гэрэл зурагтай холбоотой ерөнхий тэмдэглэл:
The photos provide a detailed view of the agricultural practices in the field, highlighting the healthy state of the maize crops in central Ukraine. These images capture the natural environment where organic farming techniques are being applied, showcasing the crops' growth, the quality of the soil, and the overall ecological balance. The close-up shots emphasize the care taken to maintain soil health and biodiversity, aligning with the principles of organic farming. The visuals also illustrate the sustainable land management practices that promote environmental stewardship and high agricultural yields.
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Украин
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Poltava region, Shishaky area
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Poltava region on the left bank of the river Psyol, in 20 km from urban-type settlement Shishaky and in 80 km to the regional center Poltava
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 1,000-10,000 км2
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Үгүй
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
- chernozem productivity assessment between conventional and traditional agriculture
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Perennial herbs
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - гурвалжин будаа
- үр тариа - улаан буудай (өвлийн)
Тариалалтын тогтолцоо:
Улаанбуудай эсвэл тэжээлийн ургамал/бэлчээр ээлжилсэн
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Spring/Summer Season; Autumn/Winter Season
Сөөлжлөн тариалалт хийгддэг үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар таримлыг сөөлжлөн тариалдаг вэ?
Intercropping involves a combination of perennial herbs (such as sainfoin) with annual crops like buckwheat or sunflower. This practice helps optimize resource use, improve soil fertility, and enhance field biodiversity.
Таримлыг ээлжлэн тариалдаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
The crop rotation system includes a diverse mix of:
Annual crops: Buckwheat, winter wheat, soya, corn, and sunflower.
Perennial crops: Sainfoin, spelt, and other forage herbs.
This rotation is designed to Maintain soil fertility, Reduce the risk of pests and diseases, Optimize nutrient use, and Support sustainable farming practices. The rotation is adapted to the specific soil and climatic conditions of the region to ensure long-term productivity and environmental health.
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээр газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- Хөрсний үржил шимийн нэгдсэн менежмент
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим
- А3: Хөрсний гадаргыг сайжруулах
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

бусад
Тодорхойлно уу:
Some water and wind erosion (but almost no erosion at all)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
Тайлбар:
The organic agriculture system in Poltava prevents land degradation through sustainable practices, including:
Reduced tillage: Maintains soil structure and minimizes erosion.
Use of mulch: Organic mulch, such as crop residues, is applied to protect the soil from wind erosion, conserve moisture, and reduce surface runoff.
Crop rotation and intercropping: These practices improve soil health, reduce nutrient depletion, and promote biodiversity.
Green manure incorporation: Enhances soil organic matter and strengthens soil resilience against degradation.
This proactive approach ensures that the fertile chernozem soils remain productive and sustainable for future generations while reducing the risks of erosion and nutrient loss.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
Dimensions of Structures or Vegetative Elements:
Raised Beds/Planting Rows: Typically range from 10–30 cm in height and 30–60 cm in width, depending on crop and soil type.
Plant Spacing: Varies by crop; cereals (e.g., wheat, barley) are spaced 20–30 cm apart, while row crops (e.g., sunflower, corn) are spaced 50–80 cm apart. Cover crops are planted more densely, up to 200 plants/m².
Vertical and Lateral Gradients:
Contour Planting and Terraces: Applied in areas with slopes of 5–15°. Terraces or contour planting are spaced at 5–20 meters vertically to reduce erosion and enhance soil stability. The lateral gradient is maintained at ≤1% through contour plowing or vegetation strips, following natural land contours.
Slope Adjustment:
Before and After Technology Implementation: Initial slopes (5–15°) are slightly leveled or terraced, reducing slope gradients to improve soil stability and prevent erosion.
Machinery for Reduced Tillage:
The technology employs Horsch cultivators (e.g., AgroSoyuz, Scorpion, Quant) and disc harrows from Gregoire Besson (DXRV and DXRV-HD models). These tools are precisely calibrated to a shallow tillage depth of 4–6 cm, ensuring minimal soil disturbance.
These machines operate efficiently, incorporating green manure while preserving the soil's natural structure and capillarity. They eliminate the need for plowing, which is traditionally associated with significant soil disruption.
Species Used and Plant Densities:
Legumes: Clover, vetch, sainfoin.
Cereals: Winter wheat, barley, spelt.
Row Crops: Sunflower, corn.
Cover Crops: High-density planting up to 200 plants/m² for effective soil coverage and nutrient cycling.
Plant Densities: 150,000–200,000 plants/ha for cereals and legumes; 30,000–50,000 plants/ha for row crops.
Materials Used:
Construction materials include loamy soil, organic mulches, compost, and locally sourced biomass.
Зохиогч:
Larisya Shedei
Он, сар, өдөр:
12/04/2023
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Талбайн хэмжээ ба нэгжийг тодорхойл:
7000 ha, it represents a large typical farm in Ukraine. It’s also a convenient size for scaling up agricultural solutions or technologies.
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Ам.доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
depending on local conditions and the type of labor required (e.g., general farm work vs. skilled machinery operation)
4.3 Бий болгох үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil testing (chemical & biological) | Pre-season |
| 2. | Transition planning (certification) | Pre-season (2-3 months before planting) |
| 3. | Cover crop seeds (e.g., clover, vetch) | Pre-season (1-2 months before planting) |
| 4. | Compost/organic amendments | Pre-planting (2-3 weeks before planting) |
| 5. | Reduced tillage equipment upgrade | Pre-season (1 month before planting) |
| 6. | Labor for initial setup (e.g., planting cover crops) | Pre-season (1–2 weeks before planting) |
| 7. | Miscellaneous inputs (mulches, fencing, etc.) | Pre-season (1–2 weeks before planting) |
| 8. | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | Annual (pre-planting) |
| 9. | Cover crop replanting | Annual (during planting season) |
| 10. | Reduced tillage operations | Annual (during planting season) |
| 11. | Organic pest and weed management | Annual (growing season) |
| 12. | Labor for maintenance activities | Annual (during planting season) |
| 13. | Miscellaneous (repairs, small inputs) | Annual (as needed throughout the year) |
Тайлбар:
Establishment costings include the first year of operations
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Consulting fees, planning materials | session | 10.0 | 2500.0 | 25000.0 | 50.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor for planting cover crops | Day | 4200.0 | 50.0 | 210000.0 | 20.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor for weeding, pest management, maintenance | Day | 4200.0 | 50.0 | 210000.0 | 15.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Equipment rental or purchase | machine | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Reduced tillage equipment use | ha | 7000.0 | 150.0 | 1050000.0 | |
| таримал материал | Cover Crop Seeds (e.g., clover, vetch) | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 25.0 |
| таримал материал | Replanting of cover crops | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 20.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost/Organic Amendments | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 35.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Organic fertilizers | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 25.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Organic pest control (biocontrols, organic pesticides) | liter | 35000.0 | 30.0 | 1050000.0 | 25.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Mulches, fencing | unit | 7000.0 | 2.5 | 17500.0 | 15.0 |
| Бусад | Soil Testing (chemical & biological) | test | 7000.0 | 20.0 | 140000.0 | 30.0 |
| Бусад | Small repairs, inputs like mulches | unit | 7000.0 | 2.5 | 17500.0 | 10.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 4705000.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 4705000.0 | |||||
Хэрэв зардлыг нэр төрлөөр тодорхойлох боломжгүй бол технологийг бий болгоход зарцуулсан хөрөнгийг тоймлон оруулна уу:
4705000.0
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
The land user is responsible for 60% of the total costs, The remaining 40% could be covered by government subsidies, agriculture support programs, or sponsorships from private companies involved in the agritech or sustainable farming sectors.
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cover crop replanting | Annually (during planting season) |
| 2. | Reduced tillage operations | Annually (during planting season) |
| 3. | Organic pest and weed management | Annually (growing season) |
| 4. | Labor for maintenance activities | Annually (during planting season) |
| 5. | Miscellaneous repairs and small inputs | As needed throughout the year |
| 6. | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | Annually (pre-planting) |
| 7. | Soil health monitoring (e.g., soil testing) | Every 2-3 years (or as needed) |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Organic pest and weed management | ha | 1000.0 | 50.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labor for maintenance activities | day | 7000.0 | 50.0 | 350000.0 | 80.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Reduced tillage operations | Equipment | 1.0 | 200000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| таримал материал | Cover crop replanting | kg | 175000.0 | 1.6 | 280000.0 | 100.0 |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Organic fertilizers (compost/manure) | ton | 7000.0 | 100.0 | 700000.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Miscellaneous repairs & small inputs | Unit | 70000.0 | 2.5 | 175000.0 | 100.0 |
| Бусад | Soil health monitoring (soil testing) | test | 7000.0 | 20.0 | 140000.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 1895000.0 | |||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 1895000.0 | |||||
Хэрэв зардлыг нэр төрлөөр тодорхойлох боломжгүй бол Технологийг бий болгоход зарцуулсан хөрөнгийг тоймлон оруулна уу:
1895000.0
Хэрэв газар ашиглагч нийт зардлын 100% -иас бага хэсгийг төлсөн бол хэн голлох зардлыг гаргасан бэ:
remaining costs covering by government programs, investors, depending on the context and support mechanisms available.
Тайлбар:
For Soil Health Monitoring, the cost is distributed over 2-3 years (based on testing frequency).
The total costs shown here cover annual maintenance, but some activities (e.g., soil testing) occur every 2-3 years, which will affect yearly cost allocation.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
The costs of implementing and maintaining organic agriculture combined with reduced tillage as a land management technology are influenced by a combination of local factors, including labor, equipment, inputs, land conditions, certification, environmental factors, and scale of operation. Understanding these factors helps in estimating costs more accurately and planning for efficient resource use.
1. Initial Soil Testing and Amendments: Costs are influenced by the condition of Chernozem soils and the need for specific amendments to support organic farming practices.
Labor for Establishment and Maintenance: Seasonal labor demand for planting cover crops, applying organic fertilizers, and managing pests affects overall costs.
2. Specialized Equipment: Upgrading or accessing reduced tillage equipment tailored to this technology adds to establishment expenses.
3. Certification Requirements: Transitioning to certified organic farming involves costs for documentation, inspections, and compliance with standards.
4. Material Inputs: Price and availability of cover crop seeds, compost, and organic pest control products impact both establishment and recurrent costs.
5. Weather-Driven Costs: Unpredictable weather can lead to increased use of inputs like organic pest management and irrigation.
6. External Support: Grants, subsidies, or cost-sharing arrangements can reduce the burden on land users but are variable depending on donor or government programs.
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
500.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Selyaninov’s Hydro-Thermal Coefficient 0.81-1.05, precipitation XI-III 140-150
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Cold period 120-133 days, assimilation of precipitation in the cold period 47%
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- хамааралгүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- их (>3 %)
- дунд (1-3 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Typical chernozem medium-, low-humus (Haplic Chernozem)
5.4 Усны хүртээмж ба чанар
Гүний усны түвшин:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
сайн
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ба газрын доорхи ус
Усны давсжилтын асуудал бий юу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үерт автдаг уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Биологийн олон янз байдал
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- дундаж
Хүйс:
- эмэгтэй
- эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- дунд нас
- ахимаг нас
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ талбай том, жижиг, дунд алинд хамаарах вэ (орон нутгийн нөхцөлд харгалзуулна уу)?
- том-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- компани
Газар ашиглах эрх нь уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилсан уу?
Тийм
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
боловсрол:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
техник зөвлөгөө:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зах зээл:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
эрчим хүчний хангамж:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
зам тээвэр:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
усан хангамж ба ариутгал:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- ядуу
- дунд зэргийн
- сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбайд үзүүлсэн нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Crop yields increased by ~60% due to improved soil fertility and organic farming practices.
газрын менежмент
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн бусад үр нөлөө
Enhanced marketability of products due to organic certification
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын мэдлэг
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Increased awareness and adoption of sustainable practices in the local community.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах карбон
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Improved organic matter content (+50%) and reduced soil compaction.
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Carbon sequestration potential of 0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹ observed
Талбайд илэрсэн үр нөлөөг үнэлнэ үү (хэмжилт):
Soil organic matter measured at 5.5% after implementation, compared to 3.6% previously.
Water infiltration tests showed a 30% improvement over two seasons.
Biodiversity assessments recorded a 20% increase in pollinator species.
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хөрш зэргэлдээ газарт учирах хохирол
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Reduced erosion and runoff benefit adjacent landowners
хүлэмжийн хийн нөлөө
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Net GHG reduction due to carbon sequestration and reduced fertilizer use (0.4 t C ha⁻¹ yr⁻¹)
Талбайн гадна илрэх үр нөлөөллийн үнэлгээг тайлбарлана уу (хэмжилтүүд):
Carbon footprint analysis identified a positive balance through sequestration and input optimization.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, цаг агаарын гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | муу |
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
Уур амьсгалд хамаарах бусад үр дагавар
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Soil degradation | муу |
Тайлбар:
Land users have observed a significant increase in extreme heat and drought events over the past decade, which have directly impacted crop yields and soil health. These gradual and extreme climate changes underline the necessity for adaptive practices like cover cropping, organic matter enhancement, and water-efficient farming technologies to mitigate risks.
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Бий болгох зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
нөлөө үл мэдэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
бага зэрэг эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
- > 50%
Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн хүмүүсээс хэд нь өөрийн хүчээр технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн бэ, өөрөөр хэлбэл гадны тусламж дэмжлэг авалгүйгээр?
- 91-100%
Тайлбар:
Most adopters implemented the technology spontaneously, driven by its potential to enhance soil health, reduce input costs, and improve long-term productivity. Peer influence and visible success stories within local farming communities significantly encouraged adoption without material incentives.
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Бий болсон өөрчлөлтөд зохицуулан технологийг өөрчилсөн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Land users see the technology as a sustainable solution that improves soil health, reduces input costs in the long term, and offers potential market advantages through organic certification, leading to higher-value crops and improved land productivity. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| From the key resource person’s perspective, the technology promotes long-term environmental sustainability, increases resilience to climate change, and contributes to carbon sequestration, while aligning with broader policy goals for sustainable agriculture and reduced environmental impact. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Initial high costs: The transition to organic agriculture and reduced tillage involves significant upfront investment in equipment, labor, and materials. | Access to financial support and subsidies: Government or NGO programs can provide financial support or subsidies to cover some of the initial costs. |
| Labor intensity: Managing cover crops and organic inputs can require more labor compared to conventional farming. | Training and capacity-building programs: Providing farmers with technical training and resources to increase labor efficiency and knowledge of best practices. |
| Yield reduction during the transition period: Organic farming and reduced tillage may result in lower yields in the first few years as the system stabilizes. | Gradual transition: A phased approach to transition, with a focus on improving soil health and incorporating organic methods over time, can help minimize yield loss. |
| Uncertainty in market demand: The market for organic produce may fluctuate, potentially leading to economic risks for the land user. | Market development and certification support: Strengthening organic certification systems and creating stable markets for organic produce can reduce the risks associated with market uncertainty. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
Conducted surveys with 25 informants, including farmers and local community members, to gather practical insights and observations on the technology's implementation and impacts.
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Held structured interviews with two big farm owners actively using the technology to understand their experiences, challenges, and benefits observed.
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
19/03/2024
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Practices for Ukrainian Agriculture, ISSAR Team, 2022, 978-1234567890
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
https://issar.com.ua/shop/
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Carbon Sequestration through Organic Farming in Chernozem Soils, Dr. O. Ivanov, NSC ISSAR, 2021, 978-9876543210
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Publication portal, https://issar.com.ua/shop/
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Impact Assessment of Climate-Resilient Agricultural Technologies, M. Kuznetsov, NSC ISSAR, 2023, 978-5432167890
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Publication portal, https://issar.com.ua/shop/
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
National Scientific Center "Institute for Soil Science and Agrochemistry Research" (NSC ISSAR) Official Website
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Sustainable Land Management Practices in Ukraine
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/sustainable-land-management
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт:
Organic Farming Transition Guidelines
URL:
https://issar.com.ua/en/organic-farming-guidelines
7.4 Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
The questionnaire and database provide a valuable platform for documenting technologies, but integrating more dynamic features and ensuring accessibility will further strengthen its utility for land users, researchers, and policymakers.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна