Improved trash lines [Уганда]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Эмхэтгэгч: Unknown User
- Хянан тохиолдуулагч: –
- Хянагчид: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger, Joana Eichenberger
Emikikizo (Lukiga)
technologies_990 - Уганда
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн:
Miiro Henry Dan
Ministry of agriculture animal industry and fisheries - Uganda
Уганда
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - Уганда1.3 ВОКАТ-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн:
Тийм
1.5 ГТМ Арга барилын Асуулга (ууд) руу хандах (ВОКАТ ашиглан баримтжуулсан)

Promoting farmer innovation [Уганда]
Identification of farmer innovators in SWC and water harvesting, and using them as focal points for visits from other farmers to spread the practices and stimulate the process of innovation.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Kithinji Mutunga
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
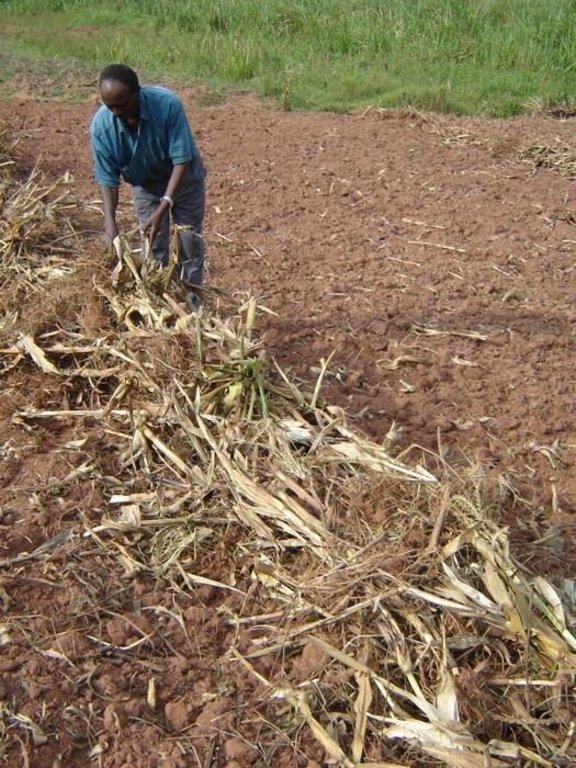
Weeds and crop residues laid in bands across the slope of annual crop fields to conserve soil and water, and to incorporate organic matter into the soil after decomposition.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт
Тодорхойлолт:
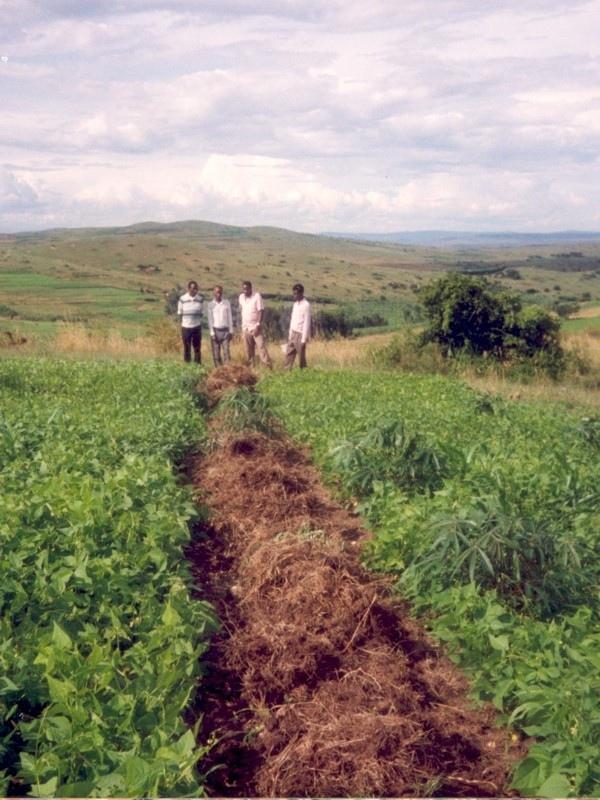
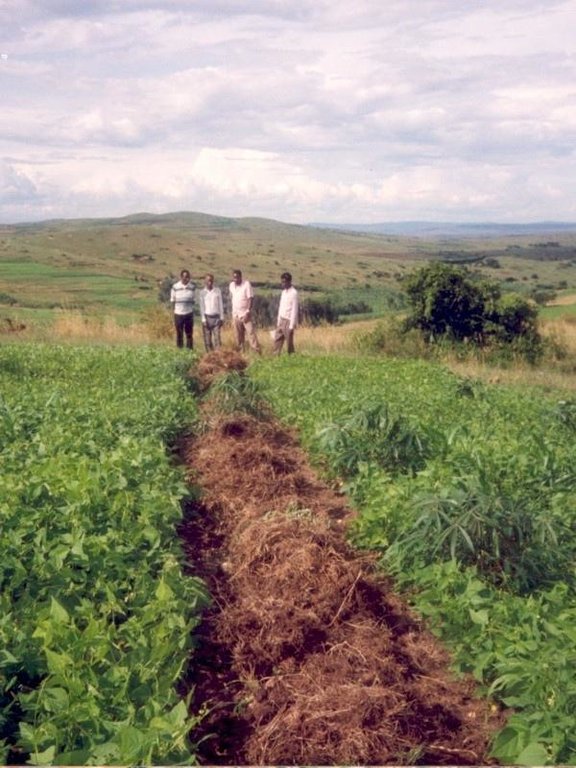
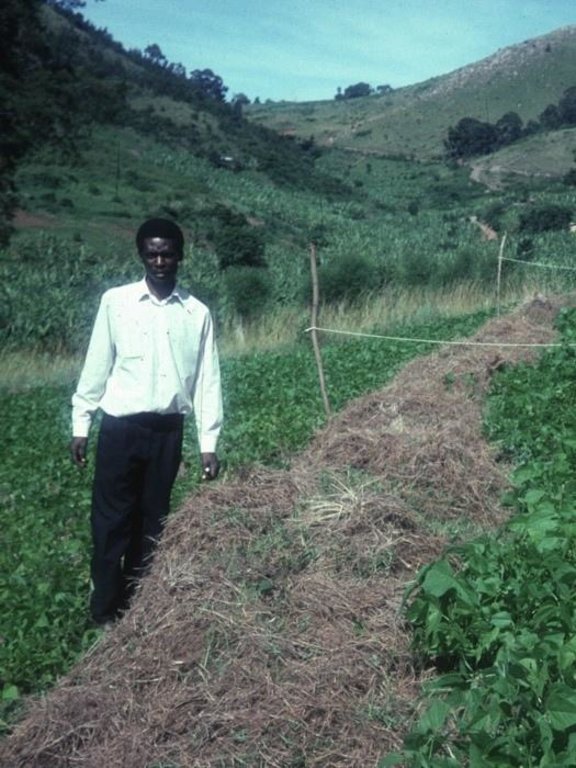
Trash lines of organic material across the slope constitute a traditional land husbandry practice in south-west Uganda. These traditional, ‘unimproved’, trash lines are beneficial, but even better is an improved version designed through Participatory Technology Development (PTD). Improved trash lines are smaller, closer spaced, and of longer duration than the traditional type. They are more effective in controlling runoff and maintaining soil fertility.
All trash lines (improved and traditional) are composed of cereal stover (straw) and weeds that are collected during primary cultivation (hand hoeing), and heaped in strips along the approximate contour. Creeping grasses should not be used in trash lines: they can alternatively be decomposed in bundles, and then used as mulch in nearby banana plantations. Trash lines are used in hillside fields where annual crops, including sorghum, finger millet, beans and peas, are grown. The recommended spacing between the improved trash lines is 5-10 m, depending
on the slope: the steeper the closer. The amount of material available determines the cross section of each trash line (typically ±0.5 m wide and ±0.3 m high). Improved trash lines are left in place for four seasons (there are two seasons a year in Kabale) before they are dug into the soil. Much of the material used has, by this time, decomposed or been eaten by termites. Through incorporation into the topsoil, they improve soil fertility acting effectively as ‘mobile compost strips’. New trash lines are then established between the sites of the former lines. Upkeep comprises removal of weeds that sprout within the lines - before they set seed - and the addition of more trash during each new cultivation and weeding cycle.
Improved trash lines are multipurpose in retarding dispersed runoff while, as discussed, maintaining soil fertility. They are a low-cost option for soil and water conservation. However, they need to be complemented by other measures on the steeper slopes. The climate in this part of Uganda is subhumid, with a bimodal rainfall regime, and average annual rainfall of around 800 mm. Hill tops are used for grazing, the lower slopes are cultivated with annual crops (where the trash lines are found) and the valleys are dedicated to bananas and other cash crops. Families are large: 8-10 persons, and the population density is high, at nearly 200 persons/km2.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон/ бүс нутаг/ байршил
Улс:
Уганда
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kabale
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kabale district
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу:
- 0.1-1 км2
Тайлбар:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.25 km2.
it is an indeginous technology. Widely used in various fields and at different slopes.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжсэн хугацаа
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- >50 жилийн өмнө (уламжлалт)
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Уламжлалт системийн хэсэг (> 50 жил)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (ууд)
- үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ экстрим байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
3.2 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(үүд)

Тариалангийн талбай
- Нэг наст үр тариа
- Олон наст (модлог биш) үр тариа
- Мод, сөөг тарих
Нэг наст үр тариа - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- үр тариа - шар будаа
- үр тариа - жирийн сорго
- буурцагт ургамал - шош
- буурцагт ургамал - вандуй
Олон наст (модлог биш) тариалан - Таримлыг тодорхойлно уу:
- банан/плантан/абака
- Eucalyptus
Жилд ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 2
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: Feb - Jul Second longest growing period in days: 120 Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Jan
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Continuous cultivation of annual crops on slopes prone to erosion, with little or no restitution of fertility through manures
or fertilizers.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): continous cultivation without fallow due to small sizes of farms
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах вэ
- хөрс/ ургамлын бүрхэвч сайжруулах
- Налуугийн арга хэмжээ
- Ус хуримтлуулах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ
3.7 Технологид харгалзах газрын доройтлын төрөл

хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал

хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим ба ялзмаг буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
Тайлбар:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (lack of communication), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of spread of knowledge)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах
Тайлбар:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжүүлсэн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
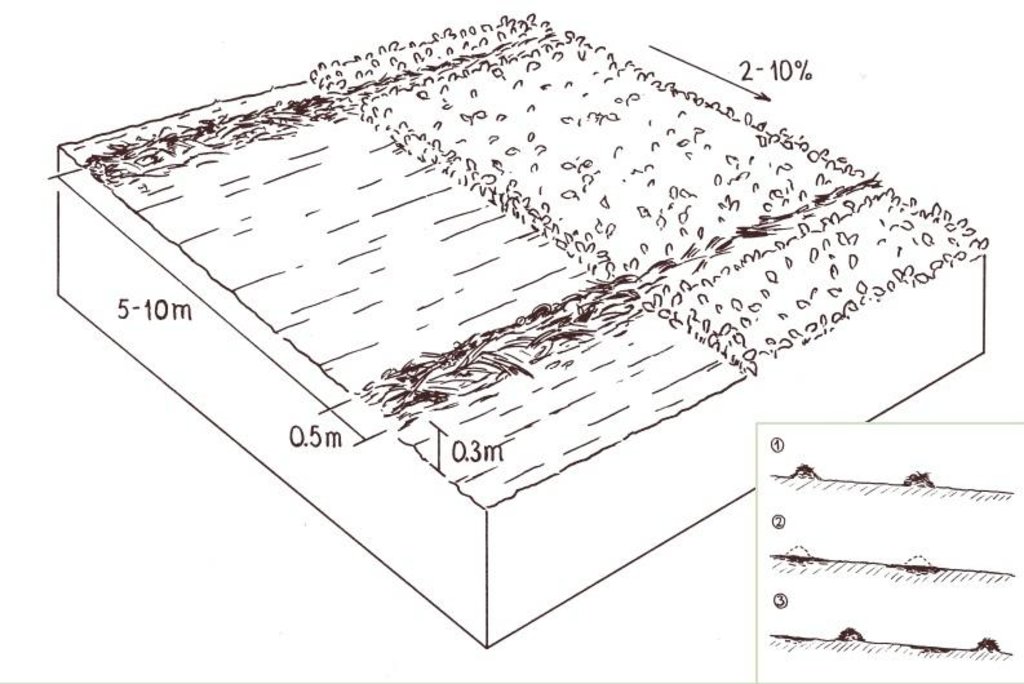
4.1 Технологийн техник зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зургийн тайлбар):
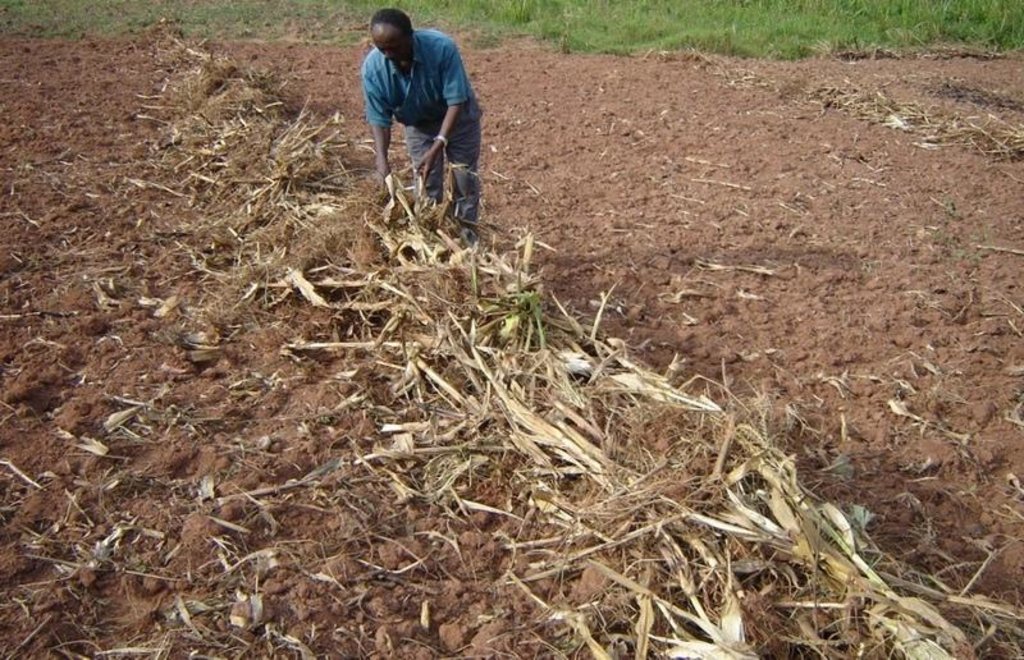
Trash lines without crops (left)
and with crops (beans; right).
The insert shows the stages of the technology: regularly spaced trash lines are kept place for four seasons (1); then decompose over time and are incorporated into the soil (2); and finally new trash lines are placed between the previous strips (3).
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase in organic matter, improvement of soil structure, sediment harvesting
Agronomic measure: mulching, trash lines
Material/ species: weed residue, sorghum
Remarks: along contour
Зохиогч:
Mats Gurtner
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
Uganda Shillings
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
1000.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өдрийн цалингийн хэмжээг тодорхойлно уу:
1.00
4.4 Бий болгоход шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 30.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 0.03 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Duration of establishment phase: 36 month(s)
4.5 Арчилгаа/ урсгал үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | During land cultivation, existing (old) trash lines are dug. 2. New trash lines are then created exactly between the (cross-slope) | Dry season / each cropping season |
| 2. | The size of the trash lines depends on the amount of trash available, | Dry season |
| 3. | Weeds are added to the trash lines, and, in preparation for the second | Second season |
| 4. | Trash lines are kept free of growing weeds and built up with more | Third and fourth seasons |
| 5. | Trash lines are kept free of growing weeds and built up with moretrash. Full cycle for improved trash lines: 4 seasons (2 years) |
4.6 Арчилгаа/урсгал ажилд шаардагдсан зардал, хөрөнгийн өртөг (нэг жилд)
Тайлбар:
Machinery/ tools: hand hoe
These figures are approximate, representing a typical situation with 1,500 running metres of improved trash lines, per hectare, at a spacing of 7 m apart on a 10% slope. The 1st year (first and second seasons) involves more work than the
2nd year (third and fourth seasons): the figure given is an annual average of all work associated with trash lines. The costs of the traditional, larger and wider spaced trash lines are about 50% more than these given above - because trash has to be carried further.
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг, зардалд нөлөөлөх гол хүчин зүйл:
Labour, need to collect and heap the trashlines material in lines above the slope
5. Байгаль ба нийгмийн нөхцөл
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
800.00
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- чийглэг
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Гадаргын хэлбэр
Дундаж налуу:
- хавтгай (0-2 %)
- бага зэрэг налуу (3-5 %)
- дунд зэрэг налуу (6-10 % )
- хэвгий (11-15 %)
- налуу (16-30 %)
- их налуу (31-60 % )
- эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- тэгш өндөрлөг / тал
- нуруу
- уулын энгэр
- дов толгод
- бэл
- хөндий
Өндрийн бүслүүр:
- 0-100 д.т.д. м.
- 101-500 д.т.д. м.
- 501-1,000 д.т.д м.
- 1,001-1,500 д.т.д м.
- 1,501-2,000 д.т.д м.
- 2,001-2,500 д.т.д. м.
- 2,501-3,000 д.т.д. м.
- 3,001-4,000 д.т.д м.
- > 4,000 д.т.д. м.
Гадаргын талаархи тодорхойлолт ба бусад тайлбар:
Slopes on average: Also rolling and hilling (both ranked 2)
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- нимгэн (21-50 см)
- дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- зузаан (81-120 cм)
- маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- дундаж (элсэнцэр, шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсөнд агуулагдах ялзмаг:
- дунд (1-3 % )
- бага (<1 % )
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil texture: Medium (the trash material modifies the organic matter content of the areas applied)
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1) and low (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Low (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын тухай мэдээлэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Бусад эх үүсвэрээс олох орлого:
- Нийт орлогын 10-50 %
Чинээлэг байдлын түвшин:
- ядуу
- дундаж
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- гар ажил
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
1% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
24% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
55% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: some farmers are involved in trade with nearby Rwanda and there are also a number of families who receive remittances from family members who work in Kabale or as far away as Kampala
5.7 Газар ашиглагчийн технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын дундаж талбайн хэмжээ
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Тайлбар:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha (ranked 2) and 2-5 ha (ranked 3)
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- хувь хүн, өмчийн гэрчилгээгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
- хувь хүн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.4 Өртөг ба ашгийн шинжилгээ
Арчилгаа/урсгал зардалтай харьцуулахад ямар ашиг өгсөн бэ (газар ашиглагчийн бодлоор)?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нэвтрүүлэлт
Тайлбар:
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: the technology is indeginous. There is some evidence of growing spontaneous adoption.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Improved trash lines have small but significant advantages over the traditional trash lines (which are beneficial themselves) in terms of (a) less labour (b) improved crop performance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue with farmer-to-farmer visits for this to be explained. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The technology is very simple and uses locally available material. It is easy to understand, being a modification of an existing tradition How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue with farmer-to-farmer visits for first hand learning. |
|
Multiple ecological and SWC benefits: improves soil fertility, reduces erosion, increases infiltration etc How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue to encourage adoption of (and further farmer experimentation with) the improved trash lines. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах арга зам
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Source of weeds | Pull out weeds before they set seed and don’t use stoloniferous or rhizome-forming (creeping) grasses in trash lines (see picture). |
| trash line harbours pest and diseases | use entirely dry grass or material |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Where land is limiting, agricultural land which would be used, is lost | uses it as a crop rotation basis |
| The trash lines are not enough on their own to control erosion on the steeper slopes | Introduce/promote supplementary structural remedies such as earth bunds. |
| Competition for crop residues which have an alternative use as livestock fodder and, especially, mulch in banana plantations | Grow hedgerows of shrubs/grasses to increase availability of material for fodder, trash lines and mulching. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан арга/эх үүсвэр
7.2 Ном, хэвлэлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Briggs SR et al. Livelihoods in Kamwezi, Kabale District, Uganda.. 1998.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Silsoe Research Institute, UK
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Mutunga K and Critchley W. Farmer’s initiatives in land husbandry Technical Report No 27. 2001.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Regional Land Management Unit, Nairobi, Kenya
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Critchley W and Mutunga K .Local innovation in a global context: documenting farmer initiatives in land husbandry through WOCAT Land Degradation and Development (14) pp 143–162. 2003.
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг дэлгэх Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Promoting farmer innovation [Уганда]
Identification of farmer innovators in SWC and water harvesting, and using them as focal points for visits from other farmers to spread the practices and stimulate the process of innovation.
- Эмхэтгэгч: Kithinji Mutunga
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна