Local level participatory planning approach [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Daniel Danano
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2388 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources (MoA) - Etiópia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre tecnologias da GST
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
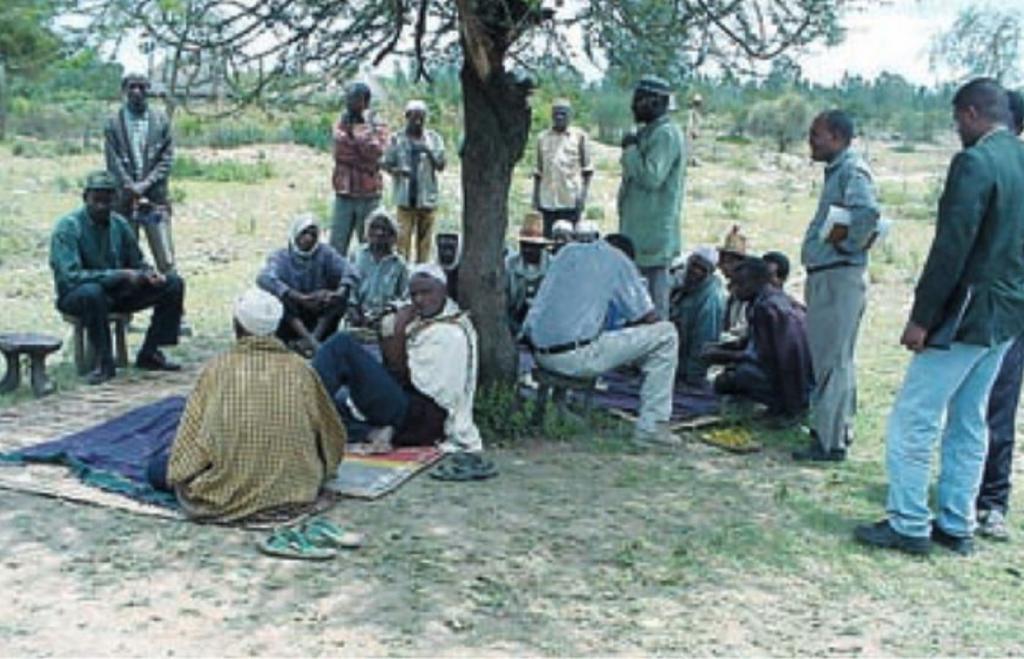
An approach used by field staff to implement conservation activities, involving farmers in all stages of planning, implementation and evaluation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Aims / objectives: The Local Level Participatory Planning Approach (LLPPA) starts with the selection of communities based on needs and problem assessment. Then development committees are formed, consisting of one or two technical staff and seven to eight farmers. They are elected by the community through a general assembly of land users.
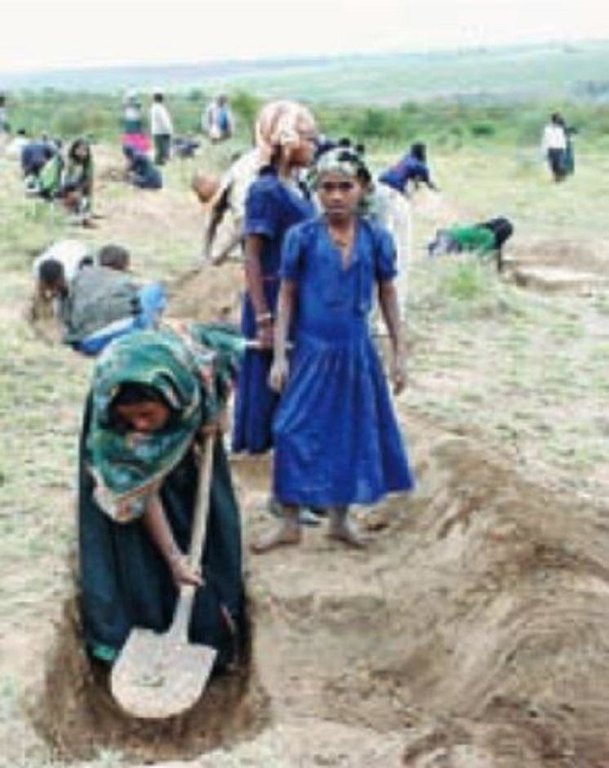
Stages of implementation: The development committees plan and coordinate development activities. They first conduct a survey of the biophysical and socio-economic conditions of the area. Then problems are identified and prioritised with the community members through participatory rural appraisal (PRA). Land use analysis, followed by the definition of objectives, identification of development options and selection of appropriate SWC interventions, is carried out on a consultative basis. Targets for achievements are established, and resources and inputs are determined. Finally the development committee prepares a work plan. The plan for SWC activities is then submitted to the community leaders, and the approval of the plan is made by the general assembly of land users, in consultation with the technical field staff. The development committee is given the responsibility for organising implementation. The beneficiaries actively participate in this implementation, in maintenance and in utilisation of the assets created, by contributing their labour and resources. Whenever required technical field staff give technical advice during implementation of development activities - area closure for rehabilitation in this case. Participatory monitoring and evaluation of activities is another important element of the approach.
Role of stakeholders: The main purpose of LLPPA is to enhance farmers’ involvement in all steps of the development process, from the initial stages of planning, to implementation of the activities, and in the evaluation of the achievements. A good relationship between land users and field workers, and acceptance as well as support of the development activities by the land users are fundamental prerequisites for fruitful implementation and maintenance of SWC measures.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Alaba
Especificação adicional de localização:
South Ethiopia, Ethiopia
Map
×2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
- encourage the involvement of the beneficiary population and the technical personnel in the whole development process (ie initial planning, implementation, monitoring/evaluation) so that sustainable development, leading to improved living conditions is attained, - reduce land degradation (gully formation and landslides, sediment flow into downstream water harvesting and storage tanks) and enhance natural regeneration and fertility of soils in order to increase the productivity of degraded areas: provide livestock feed, fuel and construction wood, and higher crop yields
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Difficulties in attaining sustainable development through area closures for rehabilitation are due to: - lacking sense of ownership: land users feel that development attained in enclosures belongs to the government, - lack of awareness about land degradation problems, and the values of conservation measures, - reluctance to maintain activities and protect assets created, - shortage of livestock feed, fuelwood and construction material, - increasing land degradation problems (on- and off-site) due to improper land use and poor farming practices, - food insecurity and poverty
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Inibitivo
Lack of financial resources: >90% of the community members are poor.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Provision of hand tools by the project. Provide training to raise awareness about benefits.
Quadro jurídico (posse de terra, direitos de uso da terra e da água)
- Inibitivo
Land tenure (land is state and public property)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Assure land user rights and provide certificates
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation Area closures would provide better opportunities and advantages to the beneficiaries if hillsides were distributed to individual farmers, and if they were provided with user right certificates for the plots developed by them. In that case each farmer would give more attention to the protection and maintenance of assets developed.
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Inibitivo
1) Cultivating steep slopes due to overpopulation and land subdivision (holdings of 0.25-0.5 ha/household).
2) Deforestation: illegal cutting of trees due to lack of fuel/construction wood, letting livestock into closed areas. Lack of management plans for planted trees.
3) Overgrazing of sloping lands resultng in severe gullies (on >50% of the land) and landslides. No controlled grazing
Treatment through the SLM Approach: 1) Apply appropriate land use practices according to land potential and apply SWC practices. Alternative income generation.
2) Training and awareness raising on how to assume responsibilities to protect the assets developed. Plant trees in woodlots and provide alternative energy sources (e.g. kerosene)
3) practise zero grazing, cut-and-carry and/or controlled grazing
Outro
- Inibitivo
Lack of awareness: Lack of awareness about soil degradation and appropriate management practices.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness raising through training and awareness creation seminars.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
In the approach area women's participation is more than 50% (and this is increasing) in the implementation of SWC measures. However, women are still not playing a sufficient role in decision making, due to cultural norms/values.
- Especialistas em GST/ consultor agrícola
- Governo nacional (planejadores, responsáveis pelas decisões)
- Organização internacional
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Participativo | self-motivation: few farmers take the initiative |
| Planejamento | Participativo | initiated by technical staff, motivated by the development committee: identify problems, prioritise them and seek solutions |
| Implementação | Participativo | community is responsible for implementation, some incentives are given for motivation: farmers are organised into working teams |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Passivo | initiated by extension agents, annual evaluation during community meeting |
| Research | Nenhum | none |
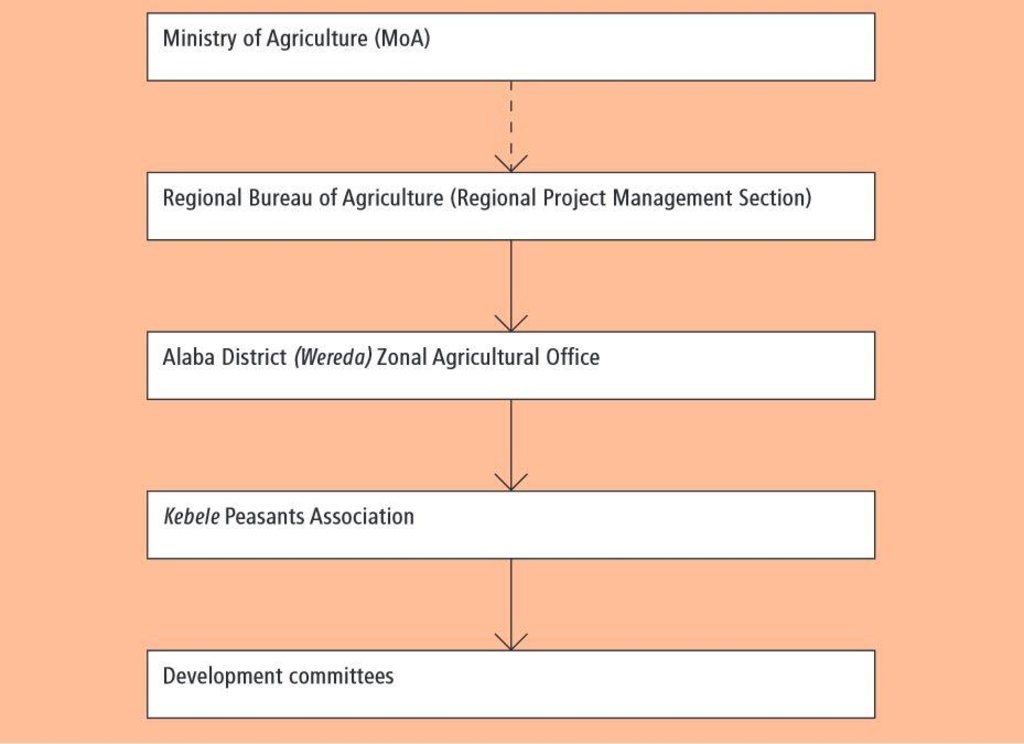
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
Descrição:
The Regional Bureau of Agriculture provides the technical support and coordinates the programme at the regional level. It is linked but not directly accountable to MoA. The Zonal office participates in the monitoring and evaluation of the activities and also provides technical advice. Kebele is the lowest administrative unit formed of different villages. Several Kebeles make a Wereda. Development committees are assigned by the general assembly and comprise members from farmers/community and the development agents working in the area.
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente usuários da terra, apoiados por especialistas em GST
Explique:
Made by the community/land users in consultation with SWC specialists/extension workers.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Made by the community members based on the plan of action prepared by the development committee (comprising farmers and technical staff).
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Tipo de formação:
- Cursos
Assuntos abordados:
Extension workers and Wereda district SWC specialists are given regular training on LLPPA and area closure management. Community leaders and the development committee are trained every year on the various techniques of soil conservation. Two to three day awareness creation seminars are held for the community in general. The awareness creation programme played a significant role.
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
Descreva/comentários:
Key elements: training, demonstration of the technology, provision of the necessary inputs for application
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; The extension service has been adequate, due to support by MoA and donor agencies such as the World Food Programme.
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, significativamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Local
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Financeiro
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: chane in slope, sediment trapped in ditch, soil depth, ground cover, amount of biomass, rate of regeneration of trees and shrubs, productivity of livestock, spring water discharge, soil loss, runoff
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: quality of structural measures, survival rate of planted trees
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: community participation in planning and implementation, trends in the participation of poor and rich farmers, womens' participation and decision making between men and women
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: amount of grass produced, household income from enclosures, availability and production of wood for fuel, increas in soil fertility
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: area treated by structural and vegetative measures
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: land users participating in planning, implementation and decision making
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: number of land users participating in the implementation, land users participating in maintenance activities, type of activities undertaken on voluntary basis
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: As a result of monitoring and evaluation improvements in quality of micro-basins and/or trenches, for example, led to better attaining the standards of technology design initially proposed.
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
Very little work is done with regard to research in area closure and LLPPA.
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 10.0%; international non-government ((World Food Programme, WFP)): 40.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 50.0%
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique tipo(s) de apoio, condições e fornecedor(es):
There is considerable support to local institutions: they get more money through selling trees and grass from enclosures, which in turn strengthens the institutions financially and socially. The development committee continues to exist after the project phases out. The same committee could take up other development issues.
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Agrícola
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Sementes | Totalmente financiado | |
| Seedlings | Totalmente financiado | |
Se a mão-de-obra pelos usuários da terra foi uma entrada substancial, isso foi:
- Comida por trabalho
Comentários:
Because of poor farmers and the labour intensive activities, they are given 3 kg grain/person day, voluntary labour contribution by the community for activities such as planting, weeding and other management activities is more than 50%.
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Applied conservation measures in areas under closure considerably improve soil and water management, resulting in an increase in soil depth, ground cover, biomass, and in survival rates of planted trees and forage shrubs.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
There has been a high adoption rate (both with and without project support) of the approach as well as the technology - as can be observed in nearby communities.
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
Land users can continue without support - and are actually doing so where the support for area closure has already stopped.
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Involvement of land users in decision making (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More work on empowerment/land use rights.) |
| Encourages working in a team (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Further strengthen team organisation.) |
| Application of appropriate land use practices contributing to sustainable development (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Further improvement of productivity by encouraging land users to make maximum use of development achievements.) |
| Rapid benefits obtained: provision of livestock fodder (through cut-andcarry), fuel wood and construction material (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Expand use of improved planting materials.) |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Dependence on incentives | Improve the methods of using incentives: incentives should be understood as a means for promoting participation rather than as a payment. |
| Low sense of ownership | Distribute the enclosures to individual land users. |
| The involvement of rich members of the community in the development committee is low | Development committee needs to be represented by different target groups. |
| Site guards are given incentives by the project | The community will have to assume this responsibility in future. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Escobedo et al (1990) The minimum planning procedures for soil and water conservation in Ethiopia. Assistance to Soil
Disponível de onde? Custos?
FAO
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Voli C et al (1999) The Local Level Participatory Planning Approach for the soil and water conservation
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos