Participatory technology development [República Árabe da Síria]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Francis Turkelboom
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2631 - República Árabe da Síria
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Especialista em GST:
Tubeileh Ashraf
A.Tubeileh@cgiar.org
República Árabe da Síria
Especialista em GST:
Bruggeman Adriana
The Cyprus Institute (CyI)
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
The Cyprus Institute (The Cyprus Institute) - Chipre1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre tecnologias da GST
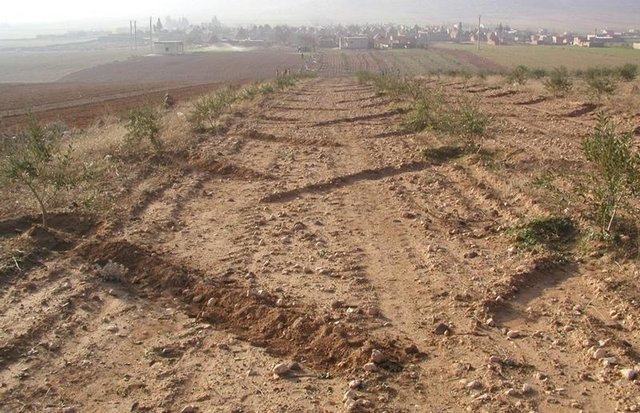

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [República Árabe da Síria]
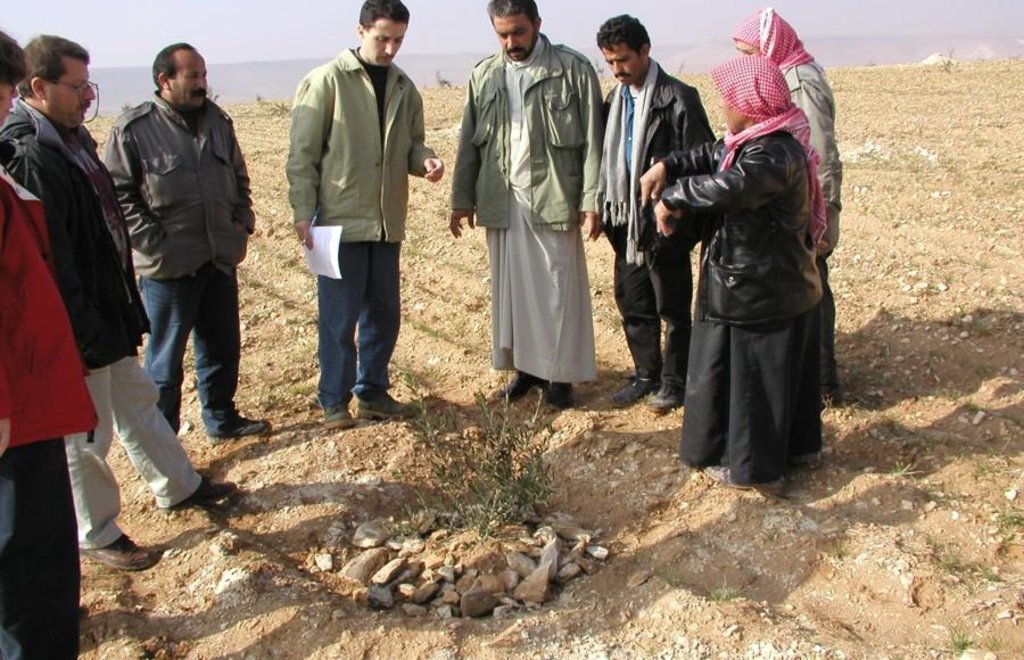
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- Compilador/a: Francis Turkelboom
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
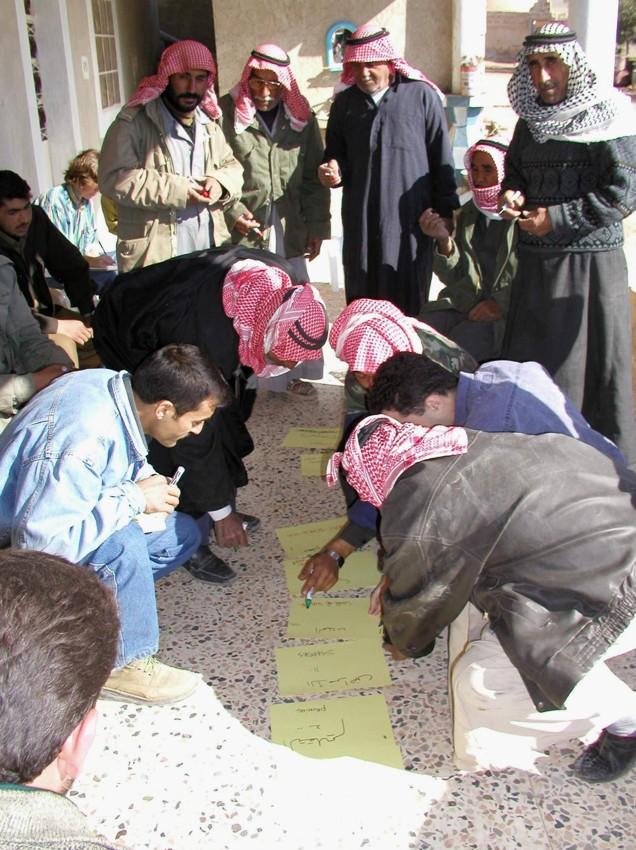
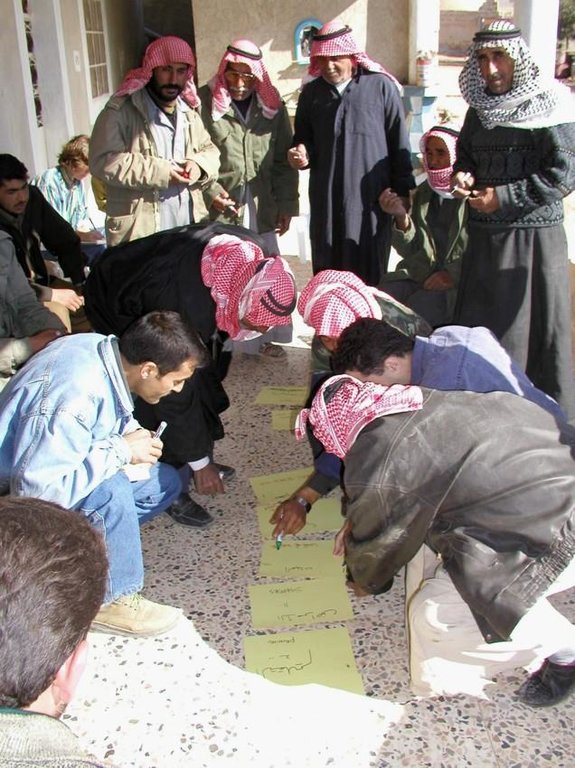
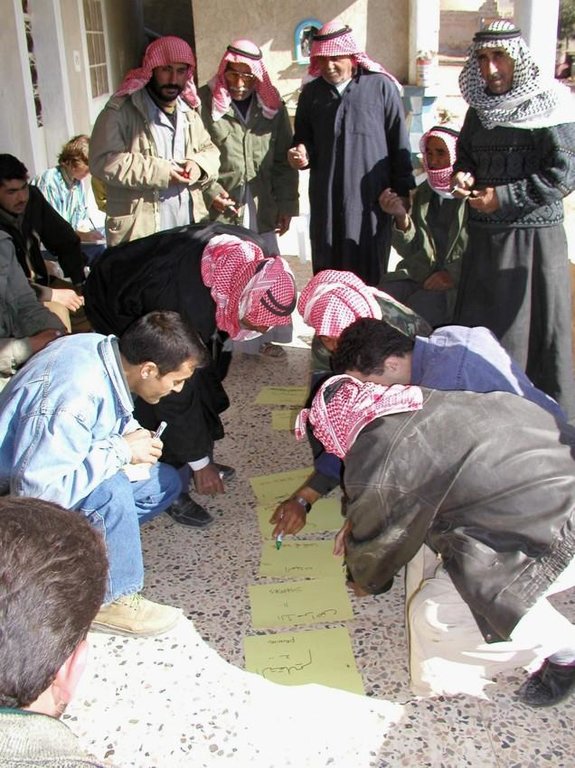
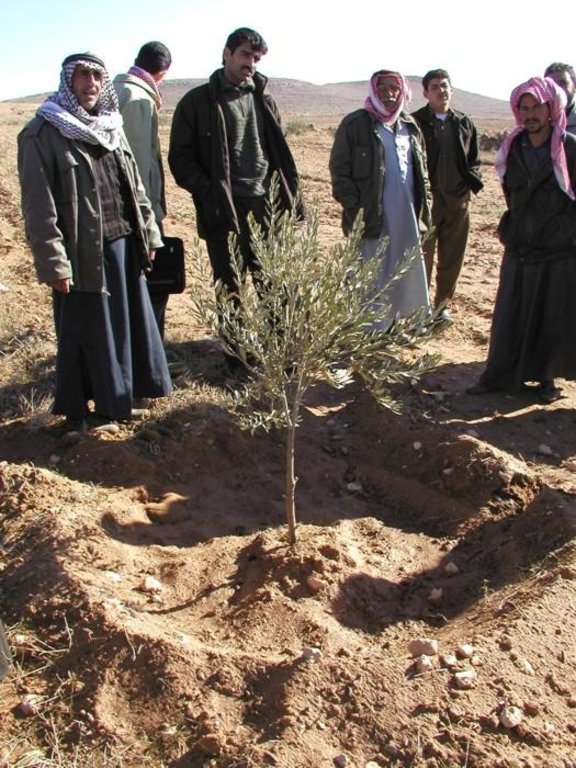
Participatory technology development, through close researcher-farmer interaction, for sustainable land management of olive orchards in dry marginal areas.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
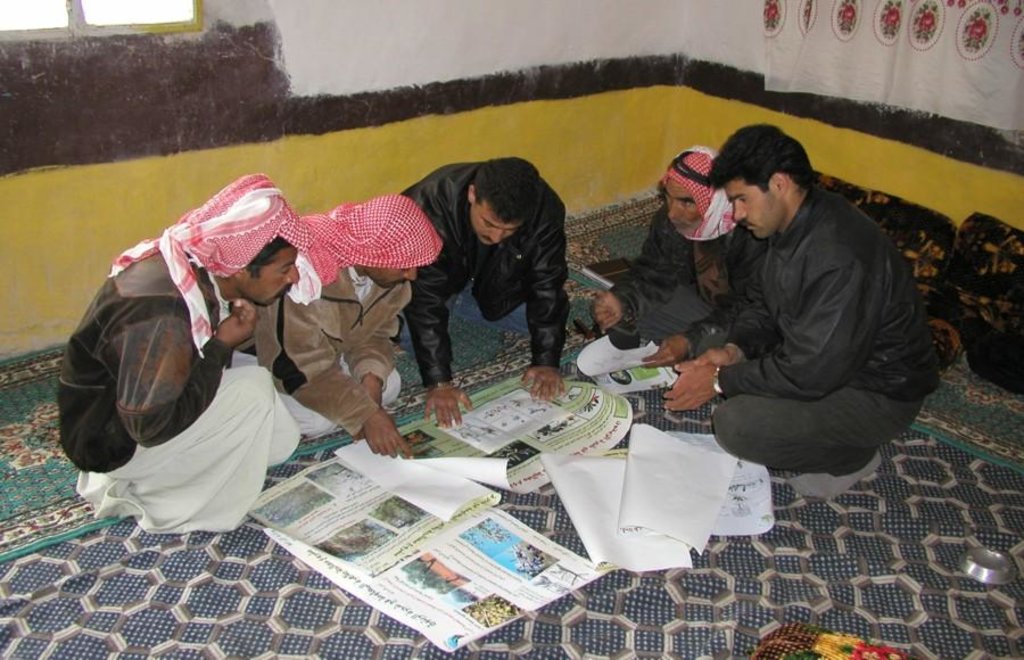
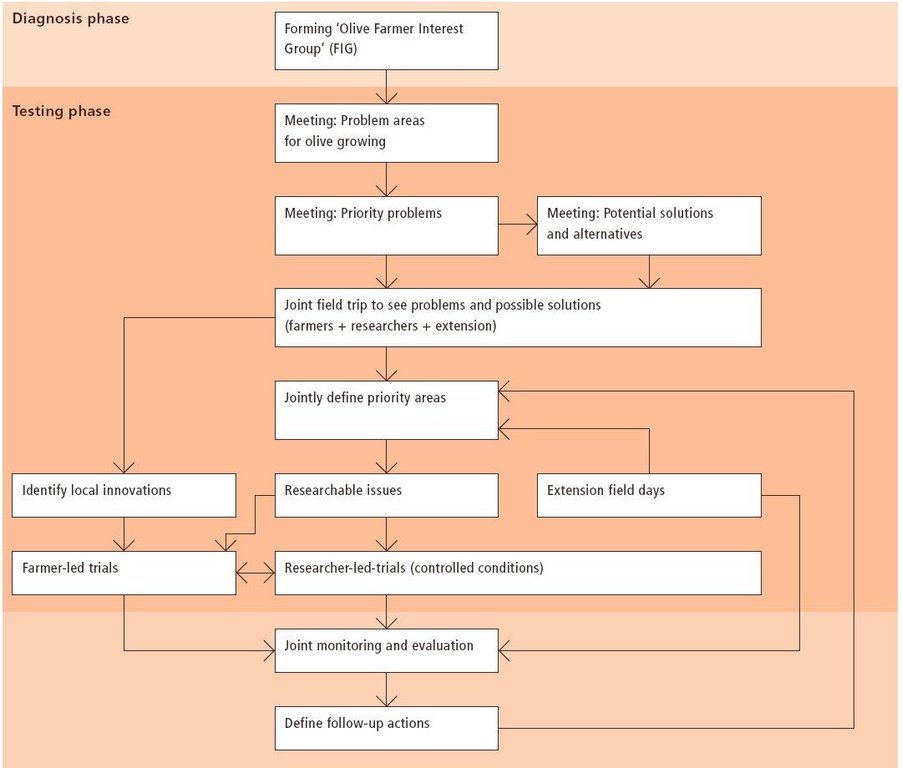
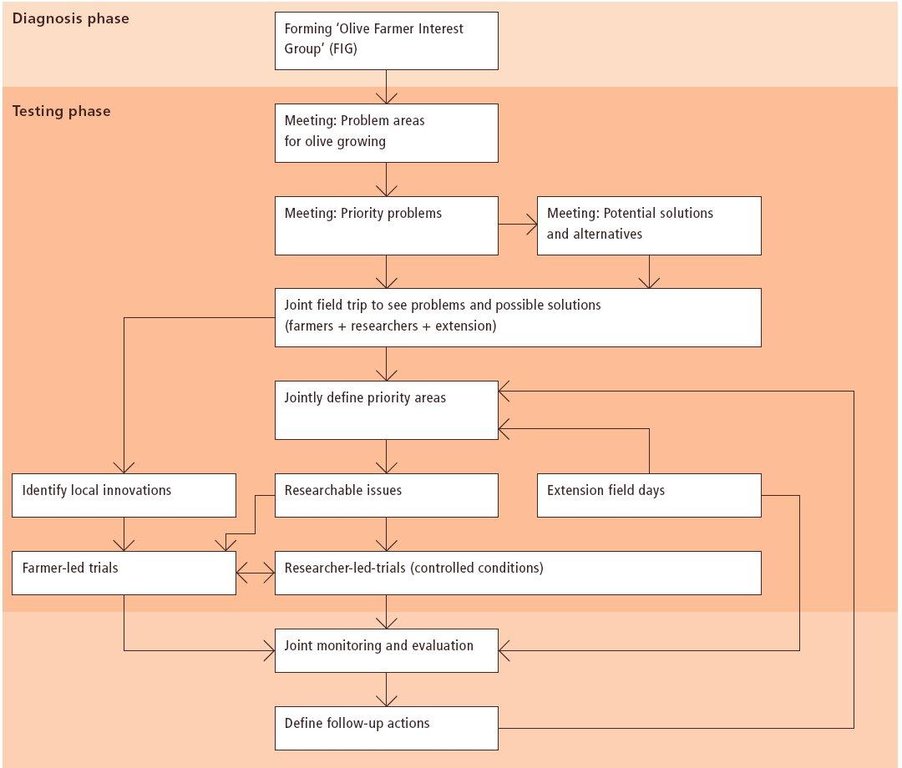
Aims / objectives: The purpose of participatory technology development is to gain from the synergy between indigenous knowledge and scientific expertise. The specific objective in this case was to develop and test water and land management techniques in order to sustainably improve olive production in a semi-arid area, while ensuring that the techniques were well adapted to local farming practices. The approach consists of group meetings, joint field trips, identification of local innovations, extension days, monitoring of farmer practices, and researcher-controlled experiments. The approach consists of a cycle with three major stages: a diagnostic phase, a testing phase, followed by monitoring and evaluation. In this case study, farmers were invited based on their interest in growing olives. Participation throughout the learning cycle was completely voluntary: no material or financial incentives were used (although they expected them in the beginning of the process). The role of farmers was to identify priority problems and potential solutions, to test new technologies on their farms, and to evaluate their suitability. Farmers observed the research experiment with water harvesting, and then adapted the technology to their needs. As shown, they built V-shaped bunds around their olive trees to capture rainwater runoff, but - contrary to the researchers??? suggestion - they continued to plough the olive orchards, as this is their standard weed control practice. Weeds attract sheep, lead to fires and compete for water with the olives. This simple runoff harvesting system is well adapted to farmers??? objectives, and their modification -the up-and-down slope furrows created through ploughing - actually serves to increase the efficiency of the water harvesting. The system is now being monitored by researchers to assess its technical and economic efficiency.
Methods: Improved farmer-researcher interaction helps farmers learn about a useful basic technique from researchers, while researchers learn in turn about potential improvements to the technology from local innovators. A community facilitator of ICARDA (International Centre for Agricultural Research in Dry Areas) facilitated the group discussions, and the researchers were asked to be open-minded to new approaches while conducting and monitoring field trials. The approach was tested by an interdisciplinary team of ICARDA as part of the ???Khanasser Valley Integrated Research Site???. This project aimed to develop local-adapted options for agriculture in dry marginal areas alongside a generally applicable integrated approach for sustainable land management in these zones.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
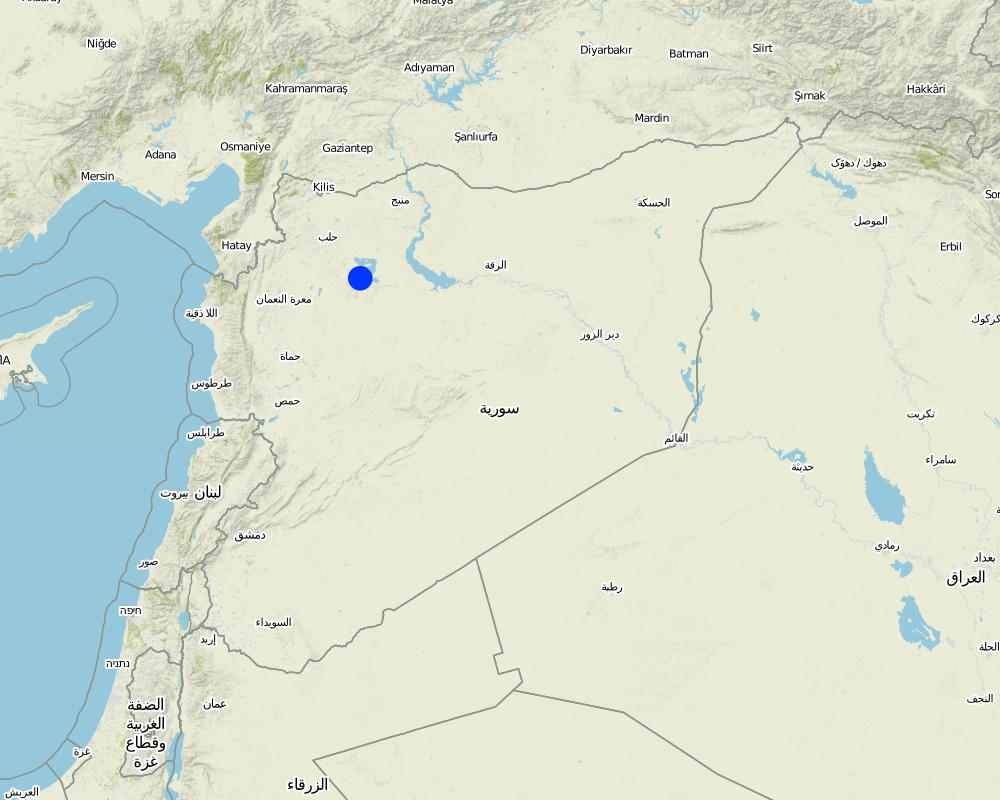
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
República Árabe da Síria
Região/Estado/Província:
Khanasser Valley
Especificação adicional de localização:
NW Syria
Map
×2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
- design, test and disseminate alternative technologies adapted to local conditions - strengthen local knowledge of SWC measures - strengthen joint learning by farmers and researchers
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The lack of appropriate ways to develop sustainable technologies to remedy loss of runoff water and poor olive growth -in the context of low-input agriculture on gentle undulating land in water scarce areas with an absence of soil conservation measures.
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Inibitivo
Water harvesting is considered expensive due to labour cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Identification of a low-cost water harvesting measure, which can be implemented during the off-season. Cost-benefit analysis.
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Inibitivo
Difficulty in tilling the land when water harvesting structures are in place.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Integrating local innovations into the water harvesting system.
Outro
- Inibitivo
Uncertainty about appropriate size of micro-catchment area. Uncertainty about the amount of water harvested. Lack of technical expertise for olive crop husbandry in dry areas.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Researcher-controlled research and carry out farmer field days, desseminate and elaborate extension leaflets as a help.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
Mainly men were involved, as most activities in olive orchards are managed by men. In addition, culturally bound gender segregation in public makes it difficult to organise gender-mixed meetings. Therefore, separate meetings were organised for women. In the case of one household, the de facto partner was a woman who takes most of the orchard-related decisions and does the work herself.
- researchers
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Passivo | public meetings |
| Planejamento | Participativo | public meetings |
| Implementação | Participativo | completely conducted by land-users |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Participativo | interviews/questionnaires, public meetings; |
| Research | Participativo | on-farm; farmer experiments and controlled on-farm experiments |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente usuários da terra, apoiados por especialistas em GST
Explique:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Tipo de formação:
- Em exercício
- Agricultor para agricultor
- Reuniões públicas
Assuntos abordados:
Demand-driven training of olive husbandry techniques (eg pruning, grafting, pest management)
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
Descreva/comentários:
Farmer-to-farmer extension; Key elements: innovative farmers showed their technique to other olive farmers during farm visits
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Não
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Comentários:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: soil moisture
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: water harvesting structures and management measures
technical aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: perceptions of the technology
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: cost and benefits
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual field survey using GPS
area treated aspects were regular monitored by None through measurements; indicators: annual farmer interview
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: There were few changes: interest in the farmers??? orchards and questions about the technology stimulated some other farmers to apply water harvesting.
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Especifique os tópicos:
- Sociologia
- Economia/Marketing
- Tecnologia
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
Research was an important part of this approach. Technical and socio-economic topics were treated as follows: (1) Researcher-controlled on-farm experiments: this helped evaluate the impact of water harvesting design on the amount of water harvested and the olive crop response. (2) Monitoring of farmer-managed trials: to evaluate the performance of water harvesting under on-farm conditions. (3) Cos
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national - ICARDA, Atomic Energy Commission Syria): 10.0%; international non-government (BMZ (Germany)): 50.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 40.0%
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
Se a mão-de-obra pelos usuários da terra foi uma entrada substancial, isso foi:
- Voluntário
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
Adoption of the furrow-enhanced runoff-water harvesting technique resulted in a concentration of scarce rainwater and nutrients in the basins around the olive trees. The consequence is a significant reduction of soil loss and runoff at the field level.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
This approach is now being applied in other ICARDA-coordinated projects in the region.
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
The complete PTD process/learning cycle needs outsider facilitation, but lack of outsiders will not stop farmers experimenting further by themselves. In terms of the technology itself, farmers can continue independently with water harvesting structures, as the system is very simple and relatively cheap.
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Engagement of researchers with local innovators and thus interaction between scientific and indigenous knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: This approach can only be sustained if it is mainstreamed into national research and extension services.) |
| Attitude changes by researchers about farmers??? knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Building on local knowledge (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Capacity building of both land users and researchers (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
| Demand-driven technologies (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Ditto.) |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Time demanding | Less time needed after the first experience. |
| Appropriate facilitating skills required | Mainstreaming facilitation skills. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Tubeileh A and Turkelboom F (2004) Participatory research on water and soil management with olive growers in the Khanasservan Veldhuizen L, Waters-Bayer A, Abd de Zeeuw H (1997) Developing technology with farmers:
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Furrow-enhanced runoff harvesting for olives [República Árabe da Síria]
Runoff harvesting through annually constructed V-shaped microcatchments, enhanced by downslope ploughing.
- Compilador/a: Francis Turkelboom
Módulos
Não há módulos