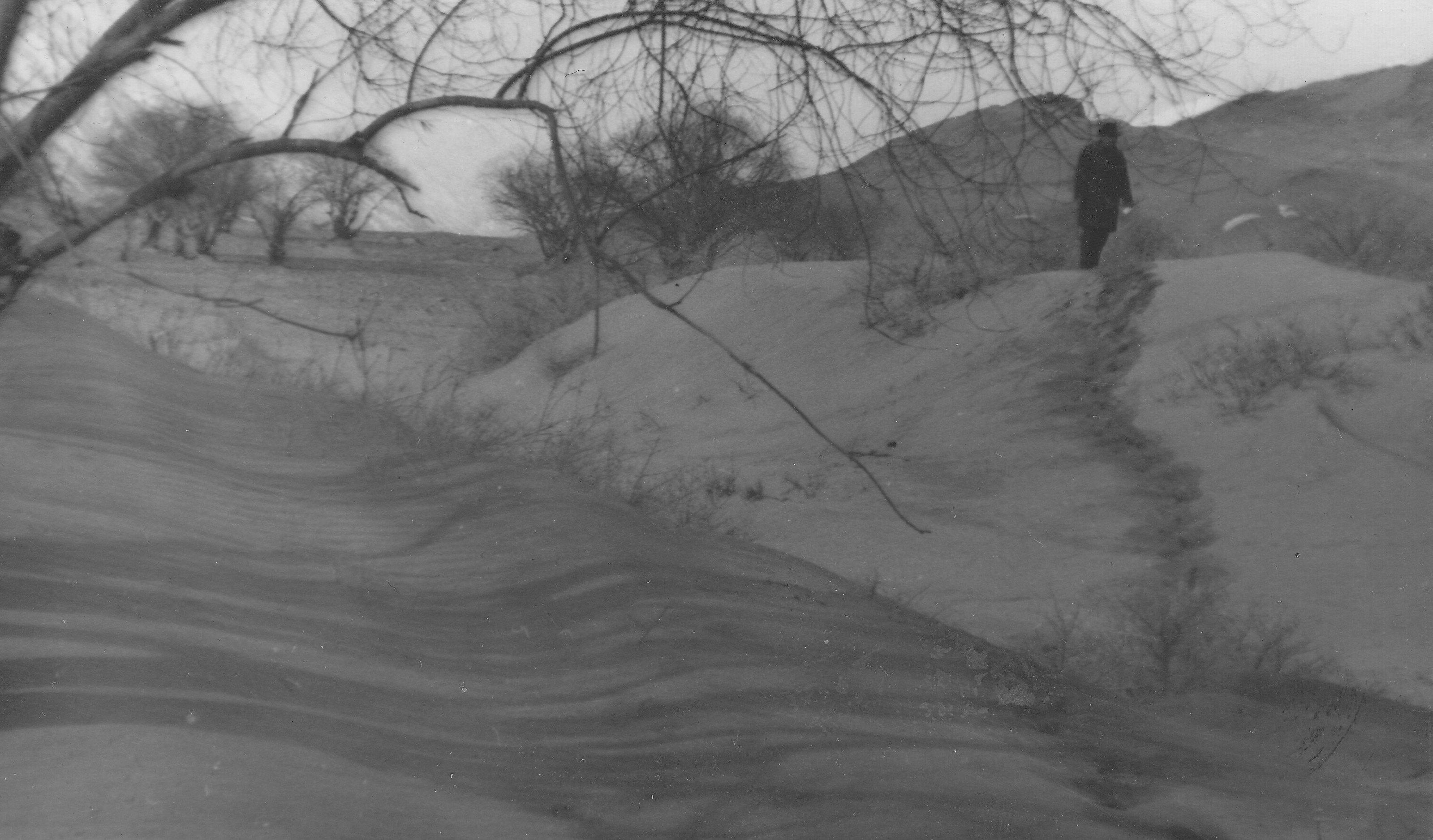
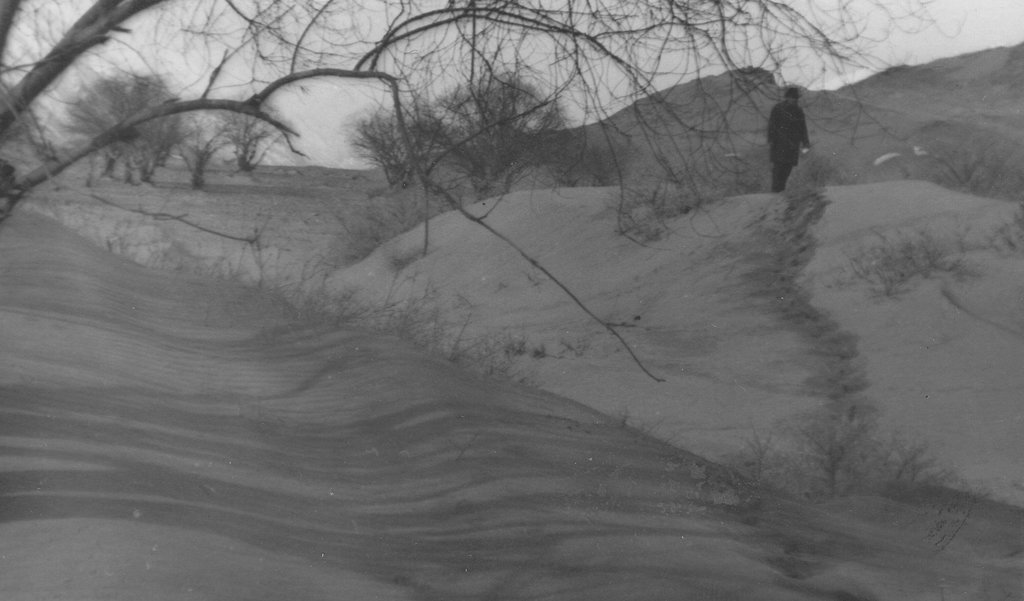
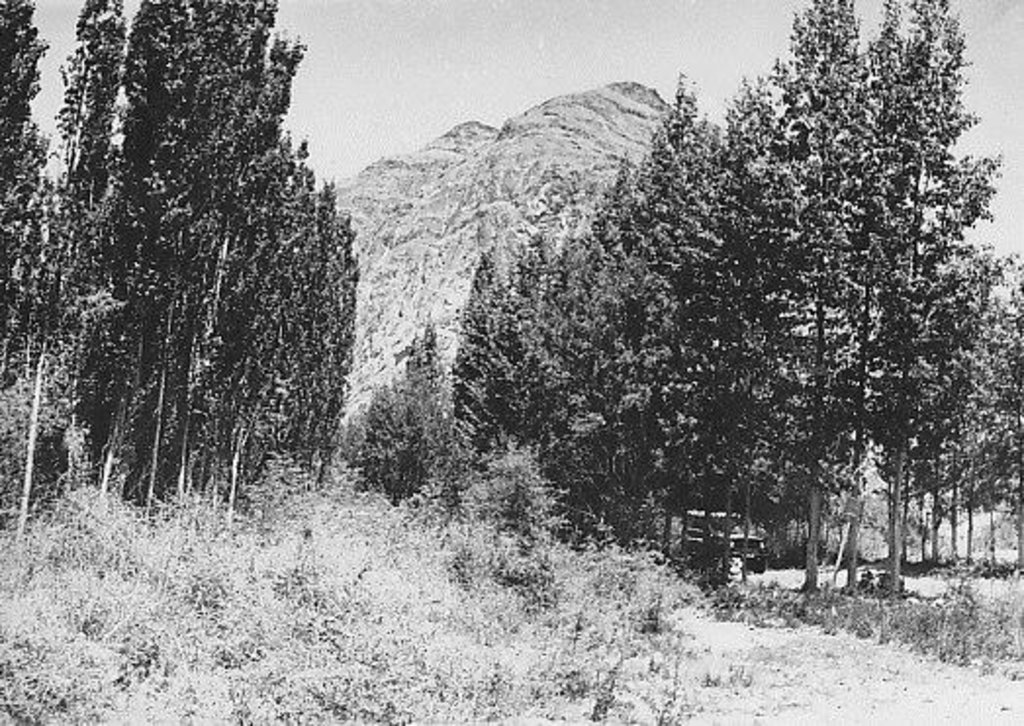
Wind forest strips for land protection against wind erosion on sandy soils [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Aslam Qadamov
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1451 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Wind forest strips for land protection against wind erosion on sandy soils: 14 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Wind forest strips for land protection against wind erosion on sandy soils: 19 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Wind forest strips for land protection against wind erosion on sandy soils: 21 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Wind forest strips for land protection against wind erosion on sandy soils: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Kosumbekov Ahoyatbek
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Forestry Department of GBAO - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Pamir Biological Institute (Pamir Biological Institute) - Tajiquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
09/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
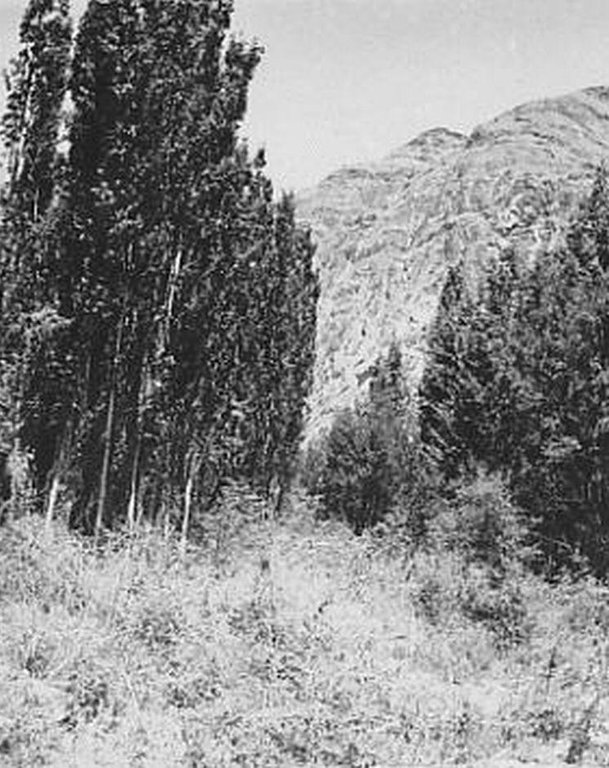
Establishment of an 8-row shelterbelt consisting of different varieties of willow, poplar and sea-buckthorn to protect irrigated cropland with poor quality soil in the high Pamir region from wind erosion.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The 24m wide shelterbelt consists of eight rows of trees. Three plots, 50m wide and 350m long were left in-between the trees to intercrop with lucerne and other perennial herbs. Thus, the total area which includes the shelterbelts, meadows and irrigation ditches makes up nearly 10 ha. The shelterbelt was established perpendicular to the direction of the strong winds. Past trials have shown that under the harsh climatic conditions of the Pamir region, shelterbelts in sandy and pebbly areas should include at least eight rows of trees and shrubs.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology was to intercrop the shelterbelts with lucerne in order to help protect crops from wind erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Shelterbelts were planted by hand, not using any machinery. Trees and shrubs were planted in accordance with their physiological characteristics and their tolerance to deflation. The eight rows were planted in the following order: 1st row: sea-buckthorn, 2nd: Shugnan willows, 3rd: Thuran willows, 4th: Pamir poplars, 5th: Bolle's poplars, 6th: Wilhelm’s willows, 7th: Shugnan willows and 8th: Sea Buckthorn. The distance between trees in each row was 4m. Willows and poplars were planted as cuttings, around 1.5–3m in length cut off at the point at which the diameter of the base was around 6cm. Sea buckthorn was planted as seeds at a depth of 4-6cm. Horizontal planting, which increases the growth by 25%, was used instead of vertical planting. The trees were planted between late March and early April. Furrow irrigation ditches were dug before the actual planting of the trees. The irrigation ditches were 0.3m deep and 0.5m wide. The plot was then watered before the actual planting of the trees and the Lucerne, to increase the soil moisture and improve the subsequent growth of the trees. Further watering of the area was carried out every 4-7 days depending on the weather conditions and levels of moisture in the soil. These willow and poplar trees can be pruned 5-6 years after the initial planting. At this stage the branches will be 1-3 m long and can be used by the local population.
Natural / human environment: The plot is located in an arid zone which has sandy and pebbly soil with low fertility. Initially this area was covered by Tugai forest and used as grazing land as well as for timber production. However, as a result of deforestation, the land in this area has become highly unstable and poses a threat to the irrigated lands upslope. 80% of the soil consists of stones and sand. Vegetation cover is mainly composed of sagebrush deserts. These shelterbelts were established during Soviet times and when the civil war broke out after independence, many of the poplar trees were cut down by the local population for construction- and firewood. Therefore only parts of the original shelterbelts are still in place today.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
GBAO
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ishkashim
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: 36.40.46 - 71.47.28 36.40.37 - 71.47.26 36.4051 - 71.47.01 36.40.36 - 71.47.02
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
58 years ago
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: potato, alfa alfa, poplar
major food crop: potato, alfa alfa, poplar
other: carrot, onion, cabbage and willow

Floresta/bosques
Produtos e serviços:
- Lenha
- Frutas e nozes
- Pastagem/Alimentação de folhas e brotos
- Conservação/proteção da natureza
- Proteção contra desastres naturais
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): land loss, soil fertility decrease, desertification of the area, poverty,
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): land degradation, land fertility decrease, deforestation, poverty
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection, protection against natural hazards
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: from May to September
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.1 m2.
about 10 ha
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Ed: deflação e deposição
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ed: deflation and deposition
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (excessive cutting of natural trees and shrubs), wind storms / dust storms (during the wind storm sand covers the cultivated lands), land tenure (more of the forests destroyed in transition period), poverty / wealth (shortage of electricity was the main reason of forest degradation)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (grass was used for livestock), overgrazing (overgrazing of the natural forests by livestock)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
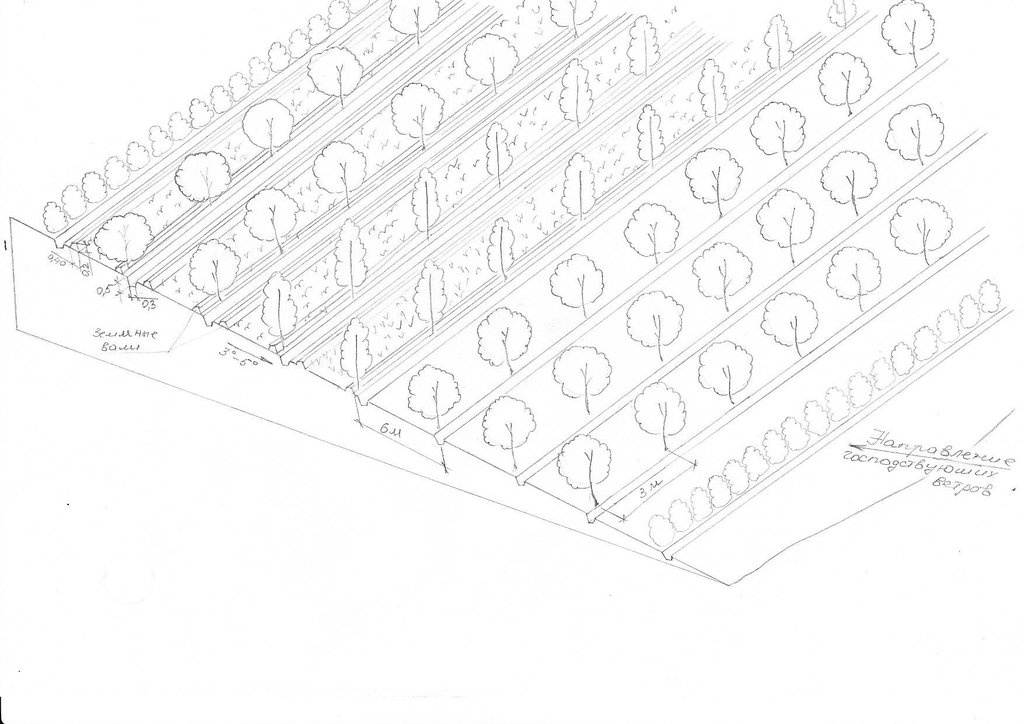
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Восьмирядная лесополоса из тополей, ивы и облепихи устраиваеться против направления господствуюших ветров. Первый ряд состоит из облепихи которая очень устойчива к воздействии пыльных бур. В междурядья в тыльной части высеиыается люцерна.
Location: GBAO. Ishkashim
Date: 20.04.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (All the works are simple for implementaton)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (All the works are simple for implementaton)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 390
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 20 kg seeds
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 4
Trees/ shrubs species: sea-buckthorns, willows and poplars
Perennial crops species: alfa alfa
Grass species: alfa alfa
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 0.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.20%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging of pits for tree planting | Vegetativo | first year |
| 2. | planting of trees | Vegetativo | first year |
| 3. | sowing of the alfa-alfa in drills | Vegetativo | every 5 years |
| 4. | construction of irrigation canals | Vegetativo |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Digging of pits for tree | Persons/day | 10,0 | 18,0 | 180,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting of trees | Persons/day | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing of the alfa-alfa in drills | Persons/day | 8,0 | 3,125 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of irrigation canals | Persons/day | 15,0 | 15,0 | 225,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Shovels and other tools | pieces | 30,0 | 1,0 | 30,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedling | pieces | 400,0 | 0,11 | 44,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Alfalfa sees | kg | 20,0 | 0,65 | 13,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 45,0 | 2,244444 | 101,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 718,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | sanitary cutting and pruning | Vegetativo | every year |
| 2. | cutting of alfa alfa | Vegetativo | three times per year |
| 3. | maintenance of the irrigation system | Vegetativo | every year |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Sanitary cutting and pruning | Persons/day | 3,0 | 3,333 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cutting of alfa alfa | Persons/day | 5,0 | 12,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Maintenance of the irrigation system | Persons/day | 2,0 | 22,5 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Scissors | pieces | 3,0 | 10,0 | 30,0 | |
| Equipamento | Tools | pieces | 7,0 | 1,0 | 7,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 152,0 | |||||
Comentários:
wind breakes and grass strips
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
seeds and seedlings cost
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
average annual rainfall - 110 mm, during winter - spring times, 5 - 6 month of dry time
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Thermal climate class: boreal. 3 months below 5°C and 6 months above 5°C
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone is 2600 m
Slopes on average are 10 - 14°
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture consists of about 70% of sand and 30% of clay
Soil fertility is low, with humus about 0.2 - 0.3 %
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium and during the summer time soil waters rise up to 1m from top soil
Soil water storage capacity is low because of the sandy soil
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water also medium, but good water availibility during vegetation time
Water quality (untreated) is good because water comes from glaciers
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 5% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 70% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Products are for subsistence needs mainly but for sale as well
Level of mechanization: Animal traction is available fro most landusers, but machines only for some landusers.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
< 0.5 ha for forests.
Average land size is 1.5 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
irrigation canals are protected and therefore don't have to be cleaned from sediments every year
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
80%
Comentários/especificar:
technology increases yield from croplands
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50%
Comentários/especificar:
during field work farmers acquire knowledges about erosion and methods to prevent it
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50%
Comentários/especificar:
poor farmers get opportunity to use more croplands
Livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Because of increased knowledge of the local farmers about erosion, reduce wind storm related diseases
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50%
Solo
Umidade do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20%
Comentários/especificar:
windbreak rows conserve soil moisture
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Quantidade anterior à GST:
100%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20%
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Quantidade anterior à GST:
100%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20%
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
No, drought is only a problem if it lasts longterm (for a year or more)
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
81 Households
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
81 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: unfortunately, after the collapse of the Soviet Union and during the civil war people cut down all the shelterbelts for fuelwood, some people have starte to rehabilitate the shelterbelts as they understand their importance, but it is difficult because there is no material support
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Low cost of the technology as compared to other technologies |
| The use of local sorts of trees and shrubs allows to apply this technology in any climatic zone of the Pamir |
| High tolerance of selected sorts of trees and shrubs to sand storms, which has been confirmed by multiple practical surveys |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Willows and poplar trees are prone to various diseases | use herbicides |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Forest strips need irrigation | construction of irrigation system |
| Willows and poplar trees are prone to various diseases | use herbicides |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos