Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Чамоварии оби борон
technologies_1460 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 4 de Abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 6 de Maio de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 16 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - QuirguizistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Quirguizistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
27/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
The roof top rain water harvesting system using a concrete tank was designed to improve household access to water for irrigation of kitchen garden plots during the hot and dry summer months.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
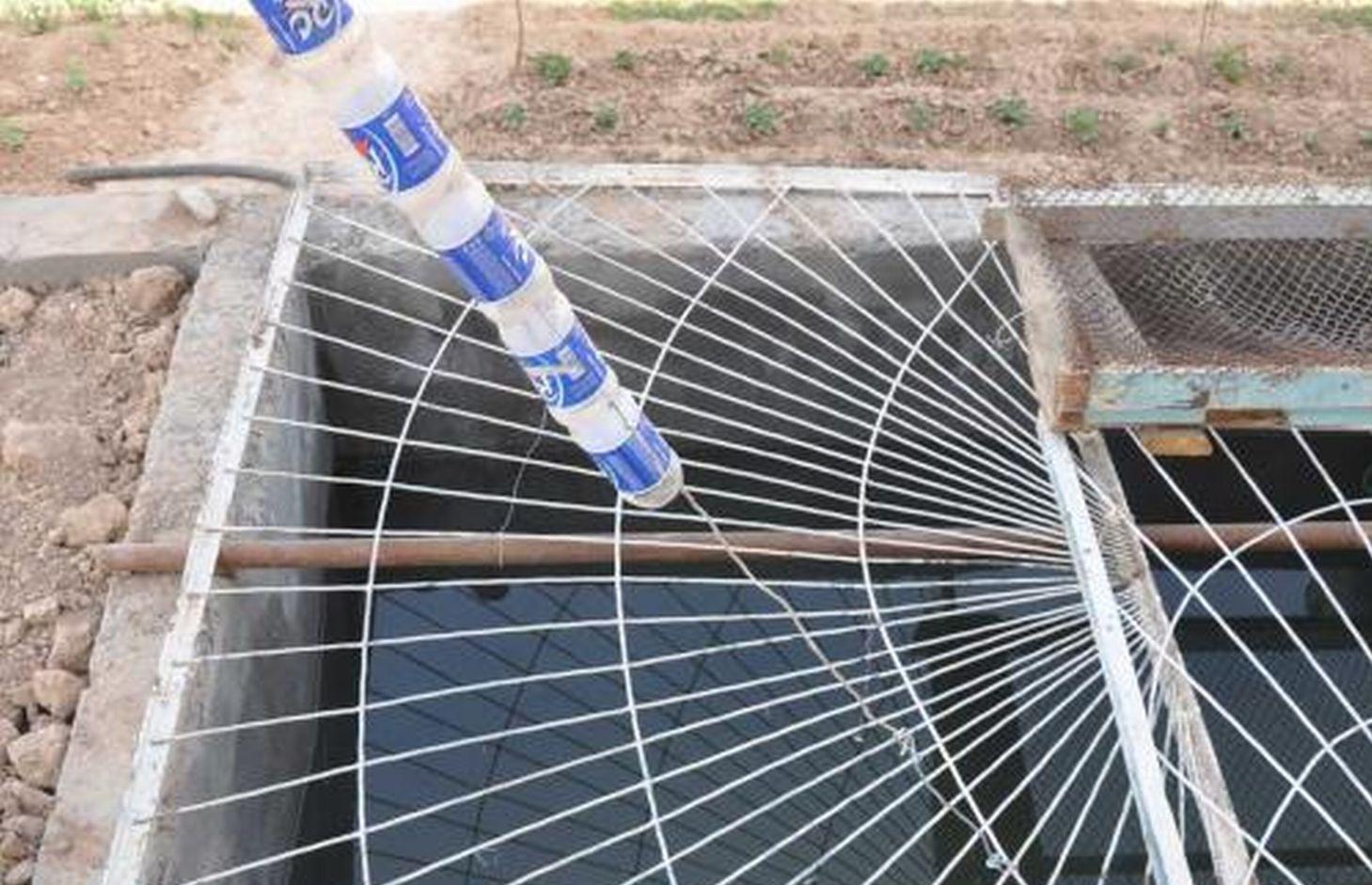
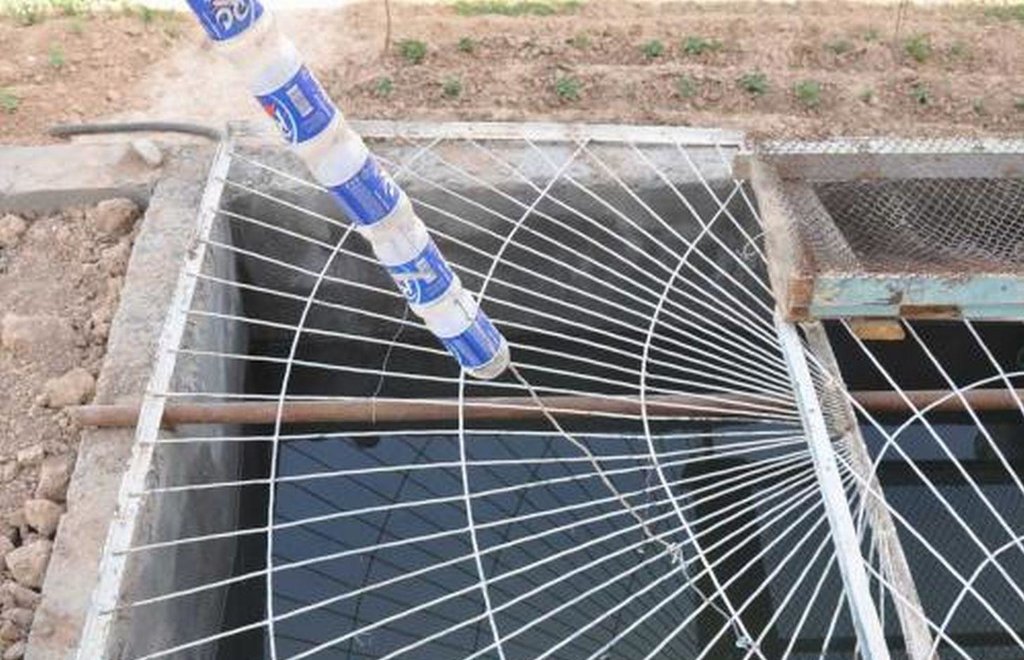
A 16 cubic metre concrete tank situated in the shadow of the house constructed to retain rainwater that collects in the roof guttering.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the tank is to retain water to be used for drinking, sanitation and irrigation during the hot and dry summer months. The retained water allows for the irrigation of kitchen garden plots and more diverse crops, and hence should improve the livelihoods of households involved.
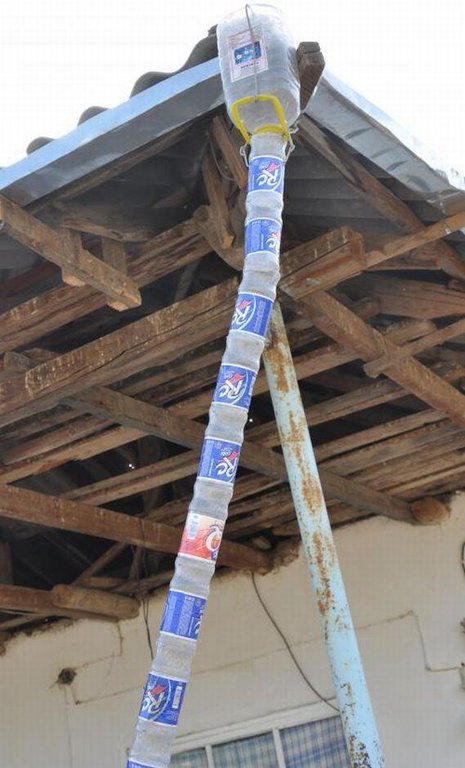
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are three main elements to the construction of the rainwater harvesting system. The first is the construction of a metal gutter on wooden supports around the perimeter of the roof; second, the construction of a concrete pool in the shadow of the house; and finally the provision of a connection pipe between the gutter and the pool. The pool needs to be cleaned periodically to prevent contamination and build up of algae around the edge the pool.
Natural / human environment: During the Soviet period the water supply for the village was supplied through a concrete storage tank located at the foot of the hills above the village. After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and its associated infrastructure fell into disrepair. As a result the inhabitants were faced with water shortages, especially during the hot dry summers. In response to this issue the residents invested time, finance and resources into constructing rainwater collection systems.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Rudaki, Boshkengash
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The land owner built the concrete tank in 2010, however numerous other tanks have been constructed during the last 10 years.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major food crop: Legumes, fruit trees

Assentamentos, infraestrutura
- Assentamentos, edificações
Observações:
Urban areas with small kitchen gardens.
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The village has 600mm/yr of precipitation, but it only falls during two months of the year. The land within the village is becoming increasingly dry and thus more denuded and unsuitable for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water at critical times of the year.
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: It is household garden plots that benefits from the water supply. These plots tend to be fruit trees intercropped mainly with onions, potatoes, carrots.
Constraints of settlement / urban: Use of land for concrete tank could be used to grow crops.
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Forests / woodlands: Fo: Other
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
A roof top rainwater harvesting system that channels water into a concrete collecting tank has been replicated in numerous houses within the village.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A6: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (The domestic plots were over used due to poor water supply.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (This occured previously and the trees were not replaced.), other human induced causes (specify) (After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and it's associated infrastructure fell into disrepair.), change of seasonal rainfall (Less rainfall at critical times impacted on cultivation activity.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Lack of vegetation results in higher losses of soil erosion during heavy rainfall events.), droughts (Longer dry periods in the summer months.), population pressure (The population and number of houses in the village is increasing.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
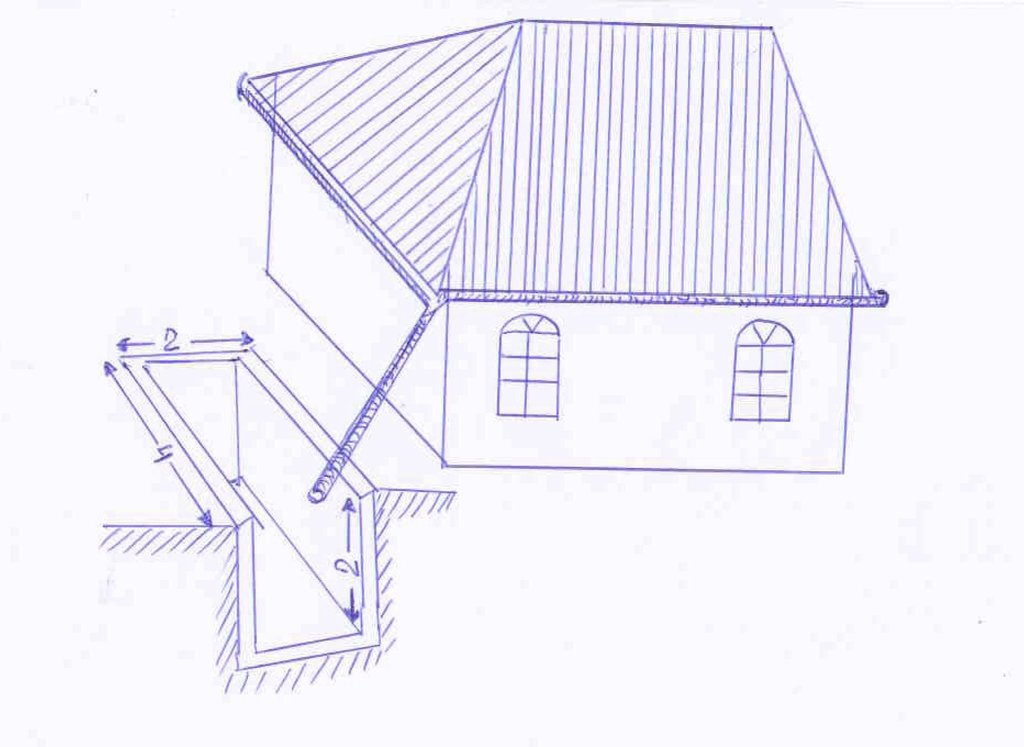
The drawing shows the metal guttering (0.15m) wide around the perimeter of the roof top. The guttering collects the rainwater run off from the roof, and through a plastic pipe made of old plastic bottles stitched together by thin wire it drains into a concrete tank. In this example the tank is 4m long, 2 wide and 2 metres deep and is located within the shadow of the house to reduce evaporation rates. In this example the tank is located on a slope and is partially buried on the upslope. The tank is covered for safety reasons and to prevent external contamination.
Location: Boshkengash.. Rudaki, Tajikistan
Date: 20011-05-06
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Some technical knowledge is required or else the structure will collapse.)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 16m3
Catchment area: 20 m sqm2
Beneficial area: 0.2 h.am2
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Material: Other
Slope of dam wall inside: 0%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 0%
Dimensions of spillways: 0m
Other specifications: tank size 2*2*4m
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
10.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of concrete tank and guttering | Estrutural | spring |
| 2. | None | None |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of concrete tank and guttering | Persons/day | 20,0 | 22,5 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | pieces | 6,0 | 11,1666666 | 67,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Concrete sand, stone | tons | 2,0 | 337,5 | 675,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Metal guttering | tons | 0,5 | 900,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wood | tons | 0,5 | 240,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Plastic pipes | pieces | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1772,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning | Estrutural | annually |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning | Person/day | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 25,0 | |||||
Comentários:
The costs were calculated based on 2010 prices per tank.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour, tools and piping can be provided by the land user and stone for the foundation is locally available, however, there is an initial outlay of $300 for the cement, wood and metal guttering. In this example the money for the initial outlay was collected by family members working in Russia and from local salaries.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Estimated to be at the lower end of the range
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone = 800m
Slopes on average: The village is located on a flat plain at the foothill of a slope.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture: Loess soils.
Soil fertility has a potential to be high when cultivated under good conditions.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium but can be reduced under dry conditions. i.e crusts.
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium since loess material does contain some clay soils.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water is good during spring rains and poor/none in the summer months.
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water during winter and spring (snow and rainfall), but poor during summer.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Mixture of vegetables and orchards being grown.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
15% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy (for the land user used for this example).
15% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The residents do not have a significant income from their garden plots.
Market orientation of production system: The water is for personal use.
Level of mechanization: All work is done by hand.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
In regards to the water in the tank, household plots are allocated by the local government. All land is owned by the state.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Due to access to water in the summer months
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
From the increased number of fruit trees.
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Comentários/especificar:
Readily available especially in the summer months.
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Comentários/especificar:
Dramatically increased, in the summer months.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Comentários/especificar:
During the drought periods.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
In some households water had to be purchased.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
No collection of water from distant sources.
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Potential debt issues if finance is borrowed for the initial outlay
Comentários/especificar:
Initial outlay in the region of $400
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Able to grow more and of a better quality.
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Previously residents had to wait at water points.
Hygiene and sanitation
Comentários/especificar:
Constant access to water dramatically improves sanitation levels in the village.
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Permanent access to water has dramatically improved the sanitation and hygiene levels, and increased crop quality and diversification. It has also improved the quality of and access to drinking water, and therefore has significant health benefits.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Comentários/especificar:
Readily available water supply.
Qualidade de água
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Quantidade posterior à GST:
16 cub m
Comentários/especificar:
The technology concentrates on harvesting water.
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Tank is built in the shadow of the house.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Able to grow crops at different times of the year.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
In times of heavy rainfall and prolonged summer drought the size of the tank could be increased.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
If it is constructed to a reasonable standard then it will not need any significant maintenance.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
900 household (70 percent of the area covered)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The urban roof top rainwater harvesting has been replicated by many members of the community without external support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People observed, and experienced the benefits, and decided that it was worth the initial investment.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Improved the standard of living, and the increased access to water allowed the households to have more automony over what that grow and eat. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Improves the provision of irrigated water for the hot dry summer periods. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further dissemination to other households. |
|
Allowed for the improvement and expansion of kitchen gardens. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training on keeping a kitchen garden. |
| Improved the quality and quantity of fruit yields |
|
Improved the access of water for sanitation and drinking water purposes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Education on sanitation methods. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The perception was that the water was not clean in the concrete pool. | However, it was tested and proved to be safe to use. This provided reassurance to the household members. It would be a major benefit if the water tank remains covered and is cleaned periodically. |
| The initial outlay may be considered expensive for some families. | Many families have adopted this, possibly if many were built at once the material costs would be reduced. The technology could be tied in with micro finance activities. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos