Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank [ทาจิกิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff
Чамоварии оби борон
technologies_1460 - ทาจิกิสถาน
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปแบบของ PDF เพื่อพิมพ์
- บทสรุปทั้งหมดในรูปหน้าเว็บ
- บทสรุปทั้งหมด (ไม่มีการจัดเรียง)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 สิงหาคม 2019 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 2 พฤศจิกายน 2021 (public)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 4 เมษายน 2018 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 21 กรกฎาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 6 พฤษภาคม 2017 (inactive)
- Roof Top Rain Water Harvesting - Concrete Tank: 16 มีนาคม 2017 (inactive)
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - สวิตเซอร์แลนด์ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership (CAMP - Central Asian Mountain Partnership) - คีร์กีซสถานชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - คีร์กีซสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
27/04/2011
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
The roof top rain water harvesting system using a concrete tank was designed to improve household access to water for irrigation of kitchen garden plots during the hot and dry summer months.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
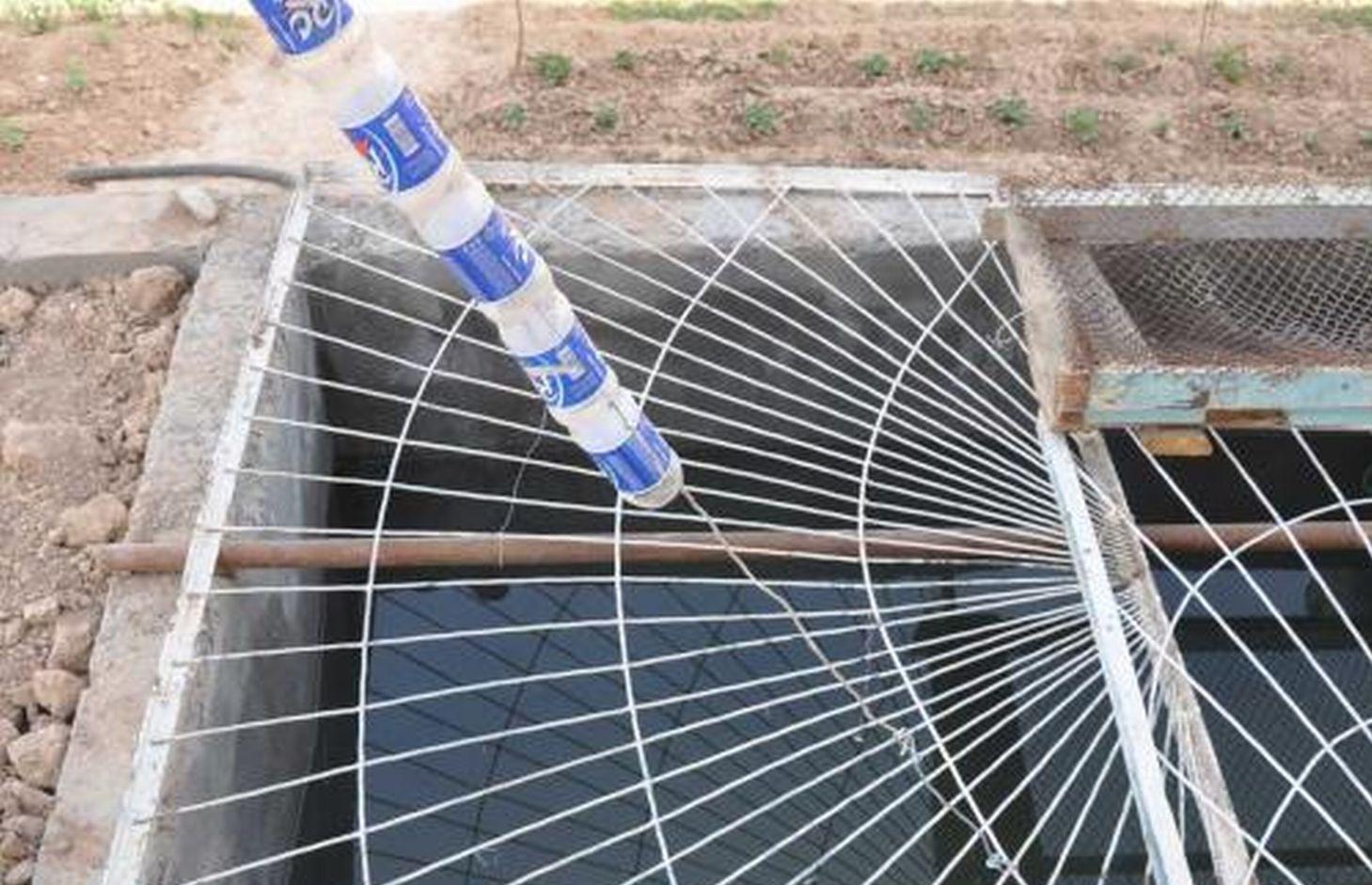
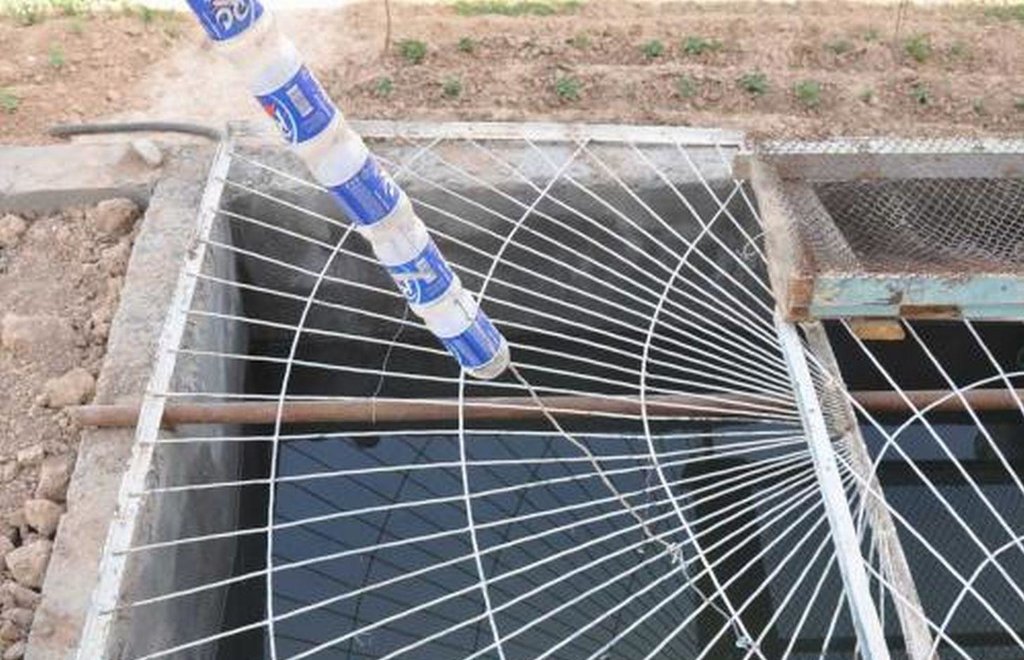
A 16 cubic metre concrete tank situated in the shadow of the house constructed to retain rainwater that collects in the roof guttering.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the tank is to retain water to be used for drinking, sanitation and irrigation during the hot and dry summer months. The retained water allows for the irrigation of kitchen garden plots and more diverse crops, and hence should improve the livelihoods of households involved.
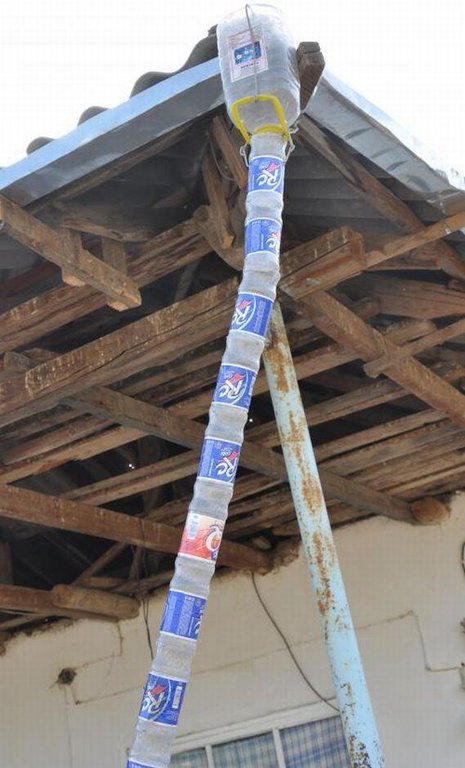
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There are three main elements to the construction of the rainwater harvesting system. The first is the construction of a metal gutter on wooden supports around the perimeter of the roof; second, the construction of a concrete pool in the shadow of the house; and finally the provision of a connection pipe between the gutter and the pool. The pool needs to be cleaned periodically to prevent contamination and build up of algae around the edge the pool.
Natural / human environment: During the Soviet period the water supply for the village was supplied through a concrete storage tank located at the foot of the hills above the village. After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and its associated infrastructure fell into disrepair. As a result the inhabitants were faced with water shortages, especially during the hot dry summers. In response to this issue the residents invested time, finance and resources into constructing rainwater collection systems.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
ทาจิกิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Tajikistan
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Rudaki, Boshkengash
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- 10-50 ปี
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The land owner built the concrete tank in 2010, however numerous other tanks have been constructed during the last 10 years.
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- access to water
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
พืชหลัก (พืชเศรษฐกิจและพืชอาหาร):
Major food crop: Legumes, fruit trees

การตั้งถิ่นฐาน โครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
- การตั้งถิ่นฐาน ตึกอาคาร
ข้อสังเกต:
Urban areas with small kitchen gardens.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The village has 600mm/yr of precipitation, but it only falls during two months of the year. The land within the village is becoming increasingly dry and thus more denuded and unsuitable for cultivation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water at critical times of the year.
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: It is household garden plots that benefits from the water supply. These plots tend to be fruit trees intercropped mainly with onions, potatoes, carrots.
Constraints of settlement / urban: Use of land for concrete tank could be used to grow crops.
ถ้าการใช้ที่ดินมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงเนื่องมาจากการนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้ ให้ระบุการใช้ที่ดินก่อนนำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้:
Forests / woodlands: Fo: Other
3.3 ข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้ที่ดิน
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเก็บเกี่ยวน้ำ
3.5 กระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
A roof top rainwater harvesting system that channels water into a concrete collecting tank has been replicated in numerous houses within the village.
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A6: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S5: เขื่อน ชั้นดินที่แน่นแข็งบ่อน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (The domestic plots were over used due to poor water supply.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (This occured previously and the trees were not replaced.), other human induced causes (specify) (After the collapse of the Soviet Union the concrete tank and it's associated infrastructure fell into disrepair.), change of seasonal rainfall (Less rainfall at critical times impacted on cultivation activity.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Lack of vegetation results in higher losses of soil erosion during heavy rainfall events.), droughts (Longer dry periods in the summer months.), population pressure (The population and number of houses in the village is increasing.)
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
4.2 ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิคและการอธิบายแบบแปลนทางเทคนิค
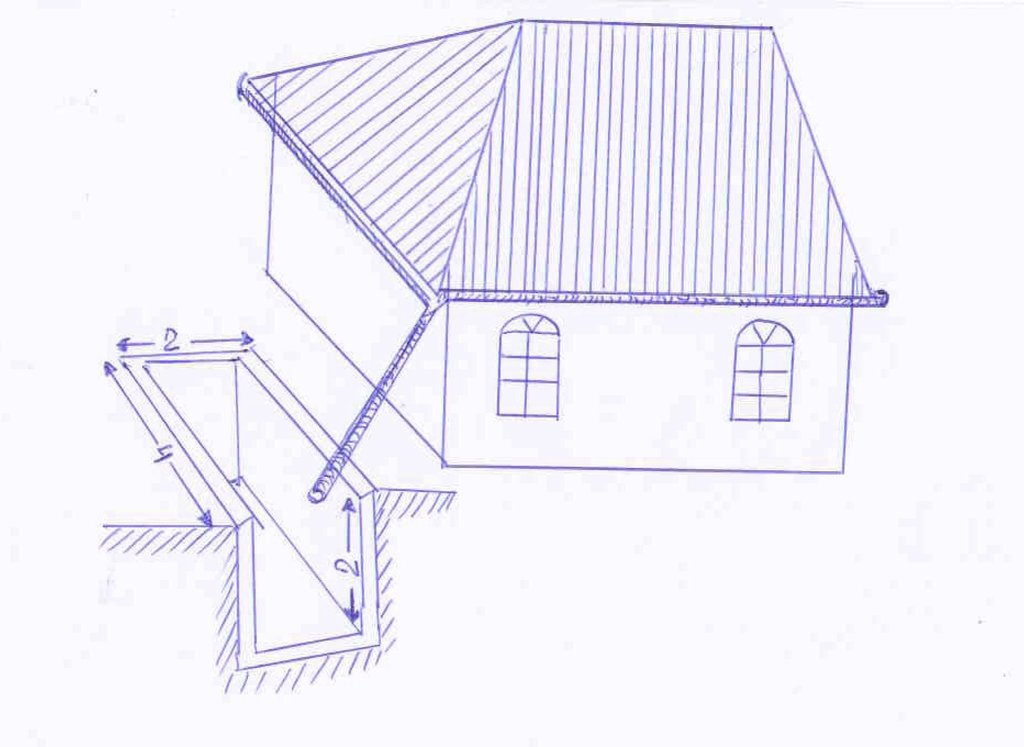
The drawing shows the metal guttering (0.15m) wide around the perimeter of the roof top. The guttering collects the rainwater run off from the roof, and through a plastic pipe made of old plastic bottles stitched together by thin wire it drains into a concrete tank. In this example the tank is 4m long, 2 wide and 2 metres deep and is located within the shadow of the house to reduce evaporation rates. In this example the tank is located on a slope and is partially buried on the upslope. The tank is covered for safety reasons and to prevent external contamination.
Location: Boshkengash.. Rudaki, Tajikistan
Date: 20011-05-06
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Some technical knowledge is required or else the structure will collapse.)
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 16m3
Catchment area: 20 m sqm2
Beneficial area: 0.2 h.am2
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Material: Other
Slope of dam wall inside: 0%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 0%
Dimensions of spillways: 0m
Other specifications: tank size 2*2*4m
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
Somoni
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
10.00
4.4 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงเวลาดำเนินการ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of concrete tank and guttering | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | spring |
| 2. | None | None |
4.5 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Construction of concrete tank and guttering | Persons/day | 20.0 | 22.5 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tools | pieces | 6.0 | 11.1666666 | 67.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Concrete sand, stone | tons | 2.0 | 337.5 | 675.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Metal guttering | tons | 0.5 | 900.0 | 450.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Wood | tons | 0.5 | 240.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Plastic pipes | pieces | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1772.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ประเภทของมาตรการ | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning | ด้วยโครงสร้าง | annually |
4.7 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Cleaning | Person/day | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 25.0 | |||||
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The costs were calculated based on 2010 prices per tank.
4.8 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Labour, tools and piping can be provided by the land user and stone for the foundation is locally available, however, there is an initial outlay of $300 for the cement, wood and metal guttering. In this example the money for the initial outlay was collected by family members working in Russia and from local salaries.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
Estimated to be at the lower end of the range
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
Altitudinal zone = 800m
Slopes on average: The village is located on a flat plain at the foothill of a slope.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil texture: Loess soils.
Soil fertility has a potential to be high when cultivated under good conditions.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium but can be reduced under dry conditions. i.e crusts.
Soil water storage capacity is low-medium since loess material does contain some clay soils.
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Availability of surface water is good during spring rains and poor/none in the summer months.
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water during winter and spring (snow and rainfall), but poor during summer.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Mixture of vegetables and orchards being grown.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- เพื่อการยังชีพ (หาเลี้ยงตนเอง)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- หญิง
- ชาย
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
15% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy (for the land user used for this example).
15% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The residents do not have a significant income from their garden plots.
Market orientation of production system: The water is for personal use.
Level of mechanization: All work is done by hand.
5.7 พื้นที่เฉลี่ยของที่ดินที่เป็นเจ้าของหรือเช่าโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- รายบุคคล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In regards to the water in the tank, household plots are allocated by the local government. All land is owned by the state.
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Due to access to water in the summer months
การผลิตไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
From the increased number of fruit trees.
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
ความหลากหลายของผลิตภัณฑ์
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำดื่มไว้ให้ใช้
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Readily available especially in the summer months.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้ปศุสัตว์
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Dramatically increased, in the summer months.
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
During the drought periods.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
In some households water had to be purchased.
ภาระงาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
No collection of water from distant sources.
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคมอื่น ๆ
Potential debt issues if finance is borrowed for the initial outlay
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Initial outlay in the region of $400
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Able to grow more and of a better quality.
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Previously residents had to wait at water points.
Hygiene and sanitation
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Constant access to water dramatically improves sanitation levels in the village.
Livelihood and human well-being
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Permanent access to water has dramatically improved the sanitation and hygiene levels, and increased crop quality and diversification. It has also improved the quality of and access to drinking water, and therefore has significant health benefits.
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Readily available water supply.
คุณภาพน้ำ
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
หลังจาก SLM:
16 cub m
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The technology concentrates on harvesting water.
การระเหย
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Tank is built in the shadow of the house.
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Able to grow crops at different times of the year.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | ประเภทของการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
ผลลัพธ์ตามมาที่เกี่ยวข้องกับภูมิอากาศอื่น ๆ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| ช่วงการปลูกพืชที่ลดลงมา | ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
In times of heavy rainfall and prolonged summer drought the size of the tank could be increased.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
If it is constructed to a reasonable standard then it will not need any significant maintenance.
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- มากกว่า 50%
ถ้ามีข้อมูลให้บอกปริมาณด้วย (จำนวนของครัวเรือนหรือครอบคลุมพื้นที่):
900 household (70 percent of the area covered)
จากทั้งหมดที่ได้รับเทคโนโลยีเข้ามามีจำนวนเท่าใดที่ทำแบบทันที โดยไม่ได้รับการจูงใจด้านวัสดุหรือการเงินใด ๆ:
- 90-100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The urban roof top rainwater harvesting has been replicated by many members of the community without external support.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People observed, and experienced the benefits, and decided that it was worth the initial investment.
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Improved the standard of living, and the increased access to water allowed the households to have more automony over what that grow and eat. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
|
Improves the provision of irrigated water for the hot dry summer periods. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further dissemination to other households. |
|
Allowed for the improvement and expansion of kitchen gardens. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training on keeping a kitchen garden. |
| Improved the quality and quantity of fruit yields |
|
Improved the access of water for sanitation and drinking water purposes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Education on sanitation methods. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| The perception was that the water was not clean in the concrete pool. | However, it was tested and proved to be safe to use. This provided reassurance to the household members. It would be a major benefit if the water tank remains covered and is cleaned periodically. |
| The initial outlay may be considered expensive for some families. | Many families have adopted this, possibly if many were built at once the material costs would be reduced. The technology could be tied in with micro finance activities. |
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล