Strip Tillage Conservation Farming [Zâmbia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Silenga Wamunyima
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1187 - Zâmbia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Ndandula Sharon
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zâmbia
Especialista em GST:
Katoweji Alfred
Golden Valley Agricultural Research Trust
Zâmbia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Golden Valley agricultural research trust (Golden Valley agricultural research trust) - Zâmbia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Participatory Research and Development [Zâmbia]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilador/a: Arthur Chomba
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
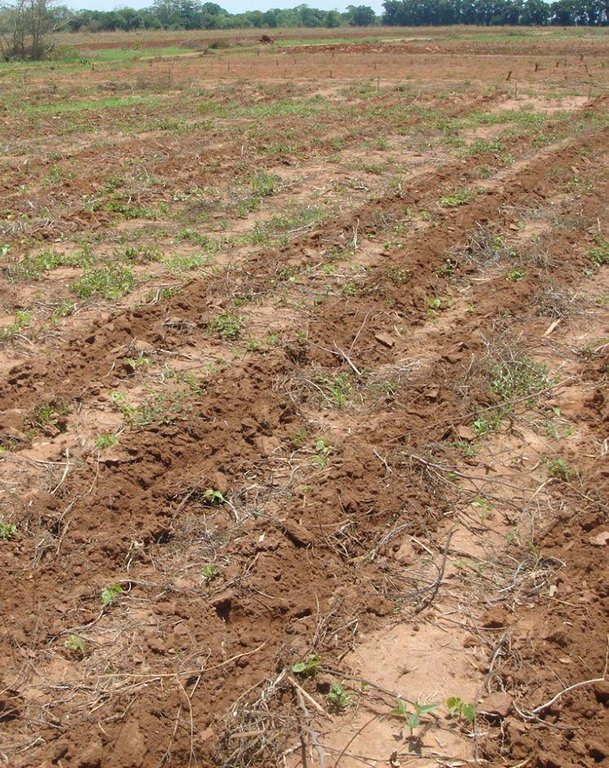
Strip Tillage Conservation Farming is an animal draft reduced tillage method that involves loosening a strip of soil with a strip tillage tool so as to reduce soil disturbance and improve soil and water conservation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
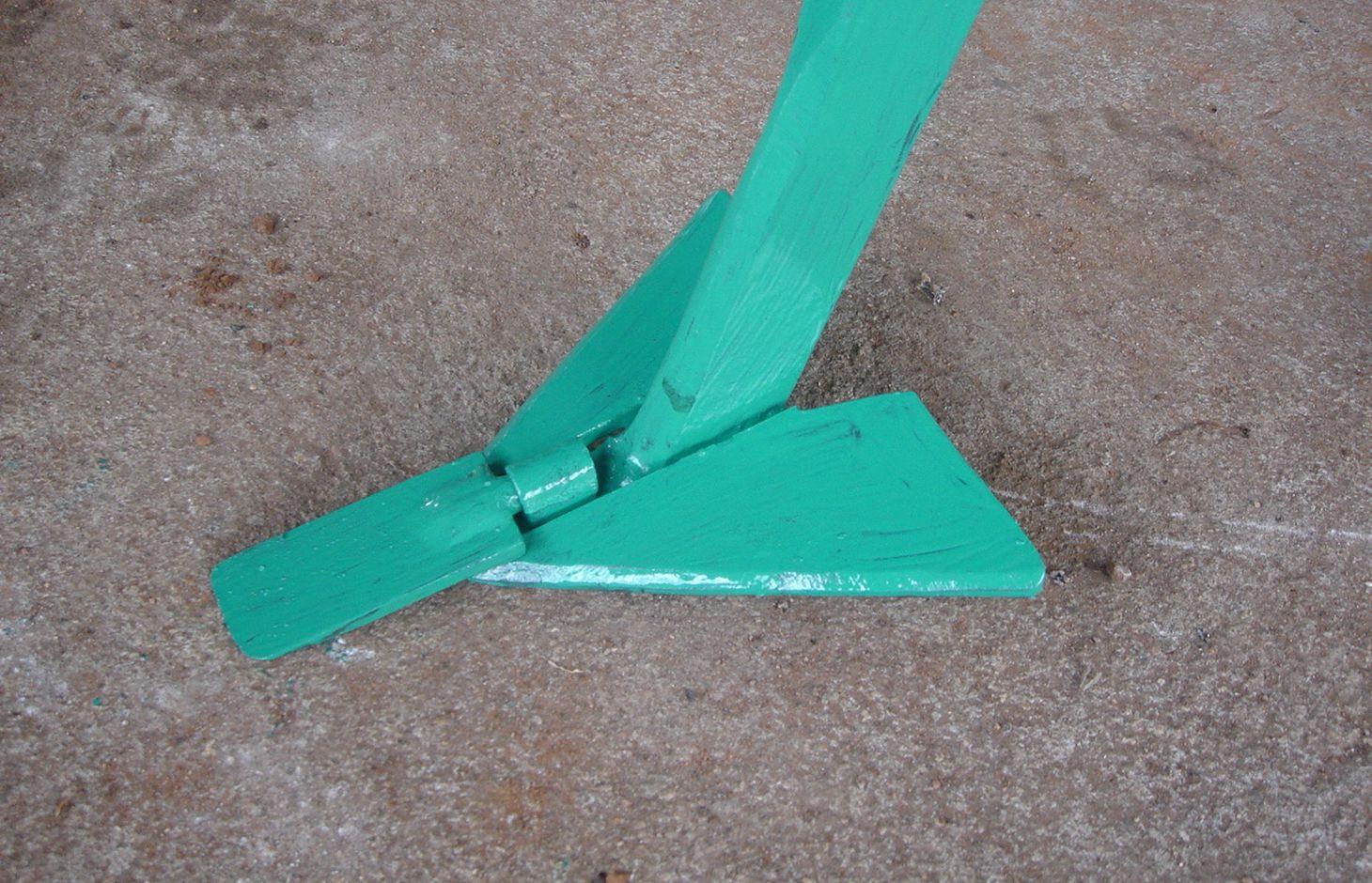
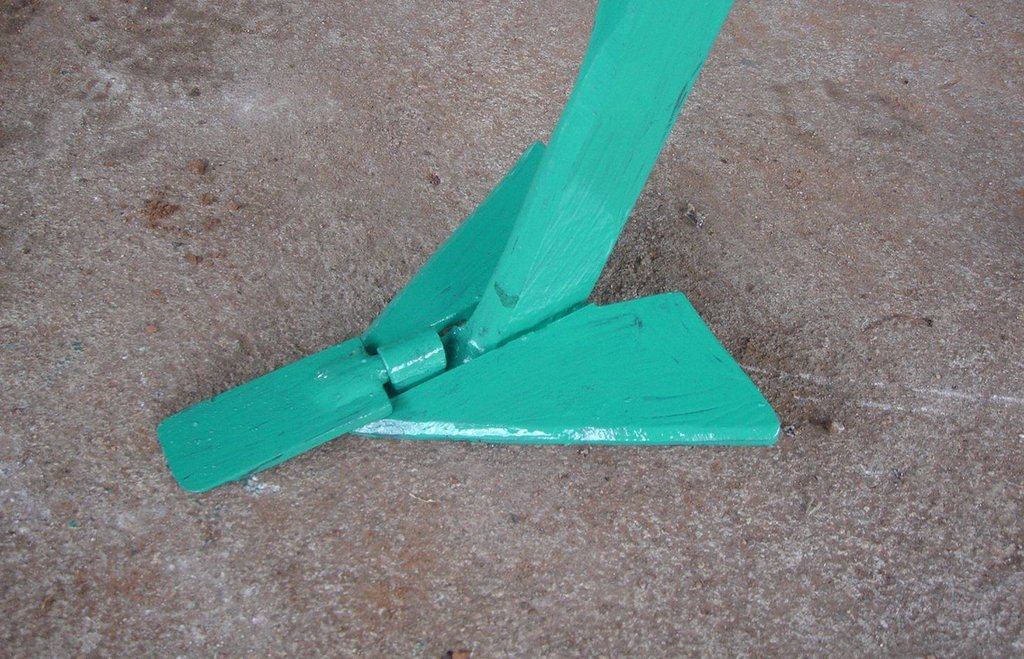
The strip tillage tool is an adaptation of a Magoye Ripper but is meant to be used in moist soil. In the strip tillage tool, sub-surface wings are attached to the ripper tine to increase the width of soil disruption which the ripper will be unable to achieve in moist soil. The sub-surface wings loosen the soil by lifting it slightly and letting it fall in place without inverting it. In this way, a strip of soil with a width of around 20cm is tilled up to 20cm deep and this is where the crop will be planted. The region between the strips is maintained as a no-till region for soil and water conservation.
Purpose of the Technology: The strip tillage tool is meant to be a transitional technology for farmers intending to adopt Conservation Agriculture (CA) in degraded soils. These soils will need routine loosening while the biological activities allow the soil structure to recover sufficiently until tillage is no longer required. Strip tillage is able to achieve deeper soil loosening with much less draft force, wear of tines and soil disturbance than ripping. The untilled region between the strips enables the benefits of soil cover such as improved infiltration, soil water storage and increased soil organic matter. Soil loosening by strip tillage does not produce large clods like ripping does but instead produces a fine seedbed that enables uniform emergence of the crop, and this together with the deep penetration results in early plant vigour. The strip tillage implement is also designed to allow the attachment of a planter unit to enable tillage and planting in one operation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of strip tillage based conservation agriculture mainly involves the purchase of the strip tillage implement and the replaceable tines. Liming acidic soils (low pH soils) followed by a final ploughing will be required to correct the soil PH which otherwise will be difficult to correct once conservation tillage has been established. Maintenance activities include strip-tilling the soil which may or may not include planting and fertilizing in the same operation. Weeding should preferably include the use of herbicides, implying that the major operations will include spraying. In addition to the normal conventional inputs, herbicides will also become a major input and cost.
Natural / human environment: The strip tillage technology is most suited to the bigger small-scale farmers with a capacity of 5ha to about 20ha. The strip tillage tool together with the planter will require a relatively substantial investment and only the bigger farmers will fully utilize its capacity. The strip tillage action will not be very effective in wet soils especially in the heavier soils, soil disruption is best achieved when the soil is slightly moist but not too dry as to require to high draft forces. Strip tillage is useful in soil with poor structure that will require routine loosening to maintain yields while the soil is being rehabilitated.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Zâmbia
Região/Estado/Província:
Zambia/Southern Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mazabuka/Magoye
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
The strip tillage technology is only in its second year of promotion and 7 farmers had adopted the technology in the 2011/12 season. The field sizes range from 1ha to 30ha.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Development of the strip tillage technology began in 2008 in response to farmers’ feedback from the promotion of another conservation agricultural technology, the Magoye Ripper. The technology was introduced to the farmers in 2011.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Sim
Especificar o uso misto da terra (culturas/ pastoreio/ árvores):
- Agropecuária (incl. agricultura e pecuária)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- culturas de fibras - algodão
- culturas de oleaginosas - amendoim
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 135; Longest growing period from month to month: Mid November to end of March

Pastagem
Tipo de animal:
- gado - lácteo
- caprinos
- aves

Floresta/bosques
Comentários:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des sols (opinion du compilateur): perte de structure du sol et perte de fertilité du sol
Principaux problèmes d'utilisation des terres (perception des utilisateurs fonciers): sécheresses et périodes de sécheresse
L'élevage pèche sur les résidus de récoltes
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
- A6: Gerenciamento de resíduos
- A7: Outros
A3: Diferenciar os sistemas de lavoura:
A 3.1: Sem lavoura
A6: Especificar o gerenciamento de resíduos:
A 6.1: queimado
Comentários:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Zero till, Crop Residue
Type of agronomic measures: early planting, mulching, manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum), rotations / fallows, breaking compacted topsoil, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage, breaking compacted subsoil
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
- Pi: selagem do solo

Degradação biológica
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: soil management (over ploughing, soil nutrient mining), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping of Maize), overgrazing (overgrazing of crop residues), poverty / wealth (Charcoal burning, under application of fertilizer)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (charcoal burning, openning up new land for agriculture), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (high intensity storms resulting in soil erosion and leaching), land tenure (over-exploitation of communal land), governance / institutional (lack of credit facilities)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
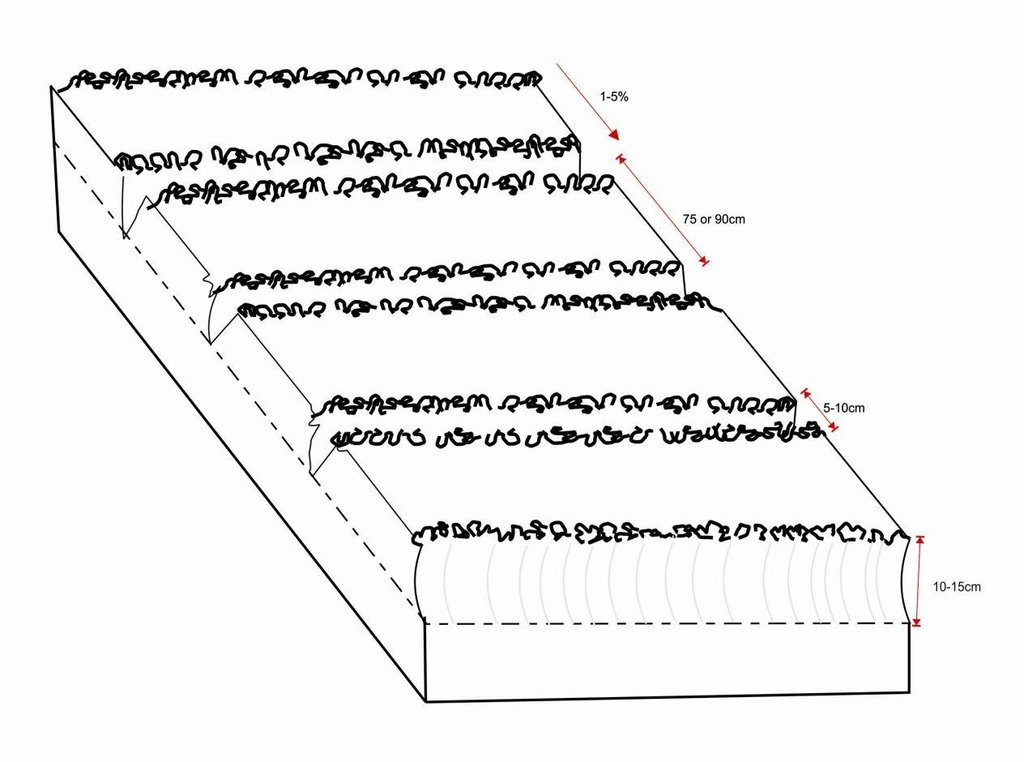
Planting lines are done at a depth of 15-20cm with inter row of 75 or 90cm. The width of the open furrow is 5-10cm wide. Planting rows are done across the slope to reduce runoff, these planting rows may be made in the dry season or during the rainy season when the soil is moist.
Location: Magoye. Mazabuka/Southern Province/Zambia
Date: 2014-06-29
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (must be able to troubleshoot and advise the farmers on how to adapt the technology to fit into their production systems.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (knowledge of soil health management required when adopting the practice)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply
Early planting
Material/ species: Maize, Cotton
Quantity/ density: 44,000 pla
Remarks: 25cm intra row x 75cm
Mulching
Material/ species: Crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: Uniformly spread
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues
Quantity/ density: 3ton/ha
Remarks: uniformly spread
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: basal and top dressing
Quantity/ density: 800kg/ha
Remarks: spot application
Soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
Material/ species: lime
Quantity/ density: 1ton/ha
Remarks: every 2-3 years
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: rotations of maize, cotton, cowpeas
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Quantity/ density: 20cm deep
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: strip tillage
Breaking compacted subsoil
Material/ species: strip tillage
Autor:
Silenga Wamunyima, Box 670577, Mazabuka, Zambia
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.40
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strip Tillage implement | |
| 2. | Knapsack Sprayer |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Strip Tillage implement | pieces | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Knapsack Sprayer | pieces | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 580,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 580,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Slashing and spreading crop residues | May-June yearly after harvest |
| 2. | Liming soil | Nov-Dec every 3 years |
| 3. | strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | Nov-Dec at onset of rain |
| 4. | Chemical weeding | 3 times per season |
| 5. | Harvesting | April-May |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Slashing and spreading crop residues | persons/day/ha | 8,0 | 2,5 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Liming soil | persons/day/ha | 2,0 | 2,5 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Strip tillage, planting and fertilizing | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 2,5 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | kg/ha | 20,0 | 2,5 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | kg/ha | 400,0 | 0,8 | 320,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicides | l/ha | 5,0 | 6,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Lime | kg | 1000,0 | 0,042 | 42,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Chemical weeding (sprayers) | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Harvesting | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 4,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 621,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 621,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Strip tillage planter
Calculations are for 1 ha of maize under strip tillage based conservation tillage and costs are for the Zambia situation in Magoye as of August 2012.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The weed control method employed is the main determinate factor depending on whether the farmer uses hand hoe or herbicides for weeding. Weed densities are higher in unploughed fields increasing the labour requirements/costs by a factor of about 5 if hand weeding is used instead of herbicides. Another major recurrent cost is that of fertilizer which makes up about half the cost hence the total cost will vary significantly depending on fertilizer cost.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Summer rains from November to March
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics. 3 distinct seasons – summer, winter and one rainy season
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is low - medium and low fertility caused mainly by poor soil management practices, otherwise soils are inherently fertile.
Topsoil organic matter: Due to excessive ploughing and under fertilization
Soil drainage / infiltration is good - medium. Soils are naturally well drained but become less so after compaction due to ploughing
Soil water storage capacity is medium. Soils mostly loam to sandy loam with medium storage capacity
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: Hand wells are <20m but reliable boreholes are > 50m
Availability of surface water: Mostly seasonal streams and dams
Water quality (untreated):Good when from communal hand-pumps and poor when from hand-dug wells.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The technology is applied mostly by men since most households are headed males and animal traction operation are reserved for men. Planting and weeding operations are the domain of women and children
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
8% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land (own more than 10 cattle).
8% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (own 5 - 10 cattle).
16% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (less than 5 cattle).
68% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (do not own cattle).
Off-farm income specification: sale of rainfed crops makes up about half of their income, the remainder coming from sale of livestock, petty trading, hiring out labour and remittances
Market orientation of production system: Livestock, maize and legumes for home consumption/subsistence and sale of excess maize and cotton, dairy products (mixed).
Level of mechanization: Manual labour only for small backyard fields. Families without cattle borrow or hire
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Cropland: 1-2 ha (families without oxen), 2-5 ha (families with one pair of oxen), 5-15 ha (families with over five oxen)
Grazing land: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Apportioned by traditional rulers
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3tons/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5tons/ha
Comentários/especificar:
Due to early planting
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Residues needed for soil cover
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Better resistance
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2-3ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
>10ha
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Due to increased production area and improved yield
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
More time and labour freed for other activities
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Due to mechanised planting and herbicide use
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Due to incresed yields
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Improved nutrition due to crop diversification
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
Less time spent on farm operations
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers trained through cooperatives
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Due to incresed soil Carbon, crop residues to reduce run off, and capacity building
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Due to competition with neighbours cattle for crop residues
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The technology was only introduced recently and not yet widely adopted to make an impact. However the few farmers that have adopted have been able to multiply their production capacities and incomes.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil cover
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil cover
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Improved soil structure
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
Due to good drainage
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil cover
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to better soil cover
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to non-inversion tillage
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to deep tillage
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Salinidade
Comentários/especificar:
Due to good drainage
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to minimum soil disturbance, soil cover
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Due to soil organic matter (SOM) buildup
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Resistance to chemical weed control
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Due to Carbon (C) sequestration
Outros impactos ecológicos
Ground water contamination
Comentários/especificar:
Some chemicals get carried down the profile
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Only if applied over an extensive area
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Comentários/especificar:
Only if applied over an extensive area
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Only if applied over an extensive area
Sedimentação a jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Only if applied over an extensive area
Danos em áreas vizinhas
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Timely and quicker planting enables larger areas to be planted and with less labour in the short term. Improved soil structure and soil fertility leads to higher yields and better resilience to droughts in the long term.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
7 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2 (field size 1 ha - 30 ha)
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
7 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: These farmers heard of the technology by word of mouth and solicited for the technology even before it could be officially promoted
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even before promotion, inquiries to purchase the strip planter have been overwhelming. This is most likely due to the ability to till, plant and fertilizer in one operation.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? acquire more than one strip tillage implement |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant the seed and apply the fertilizer in one opperation |
|
Lighter to pull enabling deeper penetration of the tillage tool increasing the rooting depth How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use in moist soils |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Enables early planting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Plant with the first heavy rain in November |
|
Quicker planting enables planting of larger areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use herbicides because without them, the capacity to weed will limit the production capacity |
|
Preserves soil cover and reduces soil disturbance How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training in residue management (No Burning) and use of zero tillage implement |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price of the strip tillage planter | subsidizing the strip tillage implement |
| Excessive weeds and lack of information on herbicide use | More training on herbicide use |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The purchase price is high making it affordable only to the larger small-scale farmers | It is already by far the cheapest planter available but mass production can lead to significant reduction in purchase price |
| Benefits are more evident on a scale larger than many farmers capacity especially when used in combination with herbicides | Support farmers to increase capacity |
| Difficult to control weeds in the absence of herbicides | make herbicides more available at a lower cost |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Social-economic analysis of conservation agriculture in southern Africa, FAO, 2011
Disponível de onde? Custos?
FAO
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Steven Haggblade, Gelson Tembo, October 2003
Disponível de onde? Custos?
INDABA project, Michigan State University
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Conservation farming in Zambia, Conservation farming unit (CFU), 2011
URL:
cfu@zamnet.zm
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory Research and Development [Zâmbia]
This is a collaborative process between researchers and farmers for developing and adapting new technologies that focus on incorporating the perspectives and inputs from the farmers into the development process.
- Compilador/a: Arthur Chomba
Módulos
Não há módulos