Intercropping of grass and corn to increase soil organic matter [Países Baixos]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Jason Stuka
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Gras onderzaai bij mais (NL)
technologies_1248 - Países Baixos
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
Países Baixos
Especialista em GST:
Leever Henk
HOEDuurzaam
Países Baixos
Especialista em GST:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
Países Baixos
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Provincie Gelderland - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Hoe Duurzaam - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Ministerie van Economische Zaken - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - Países Baixos1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Regional process, social innovation [Países Baixos]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilador/a: Simone Verzandvoort
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Grass intercropping on corn fields
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
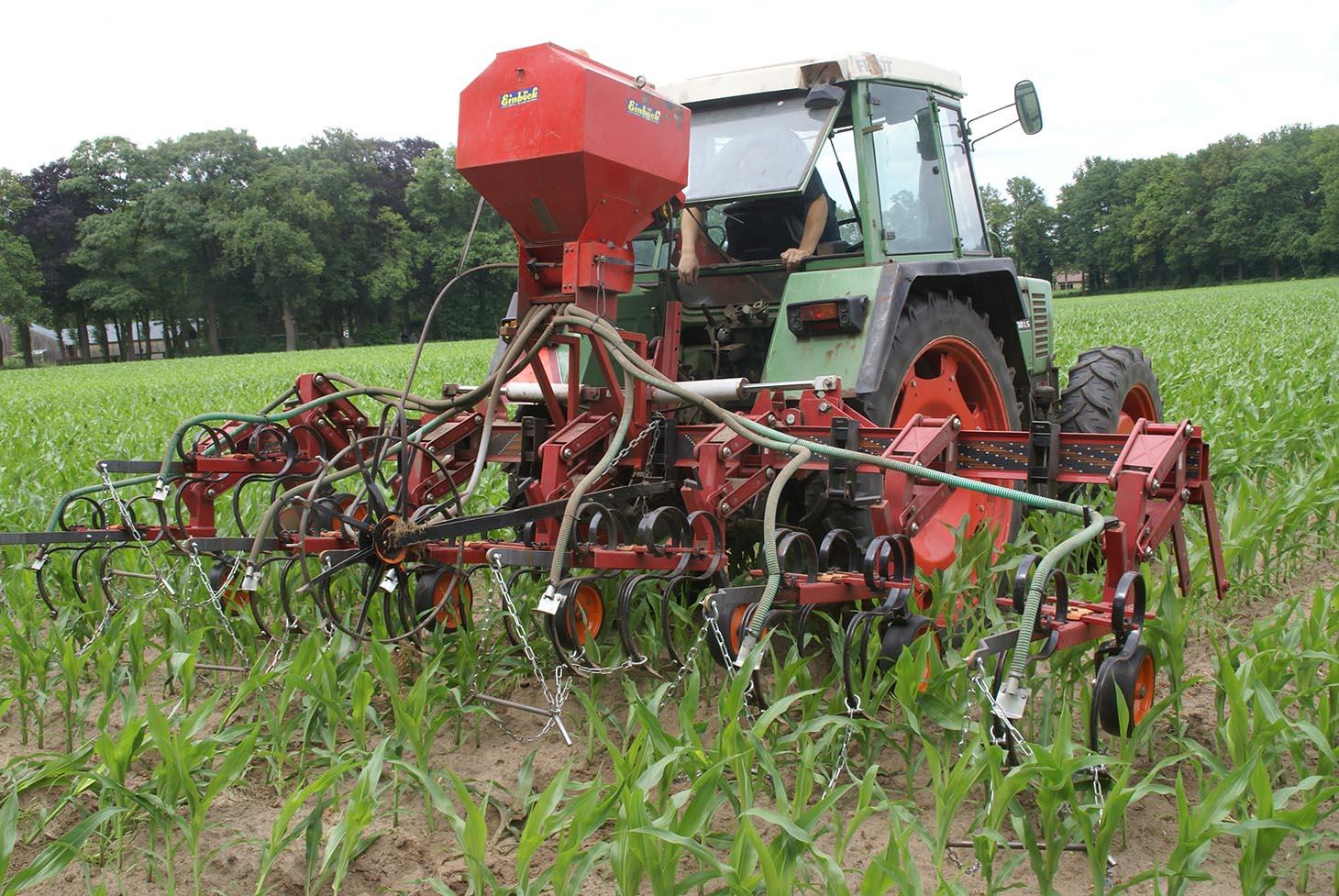
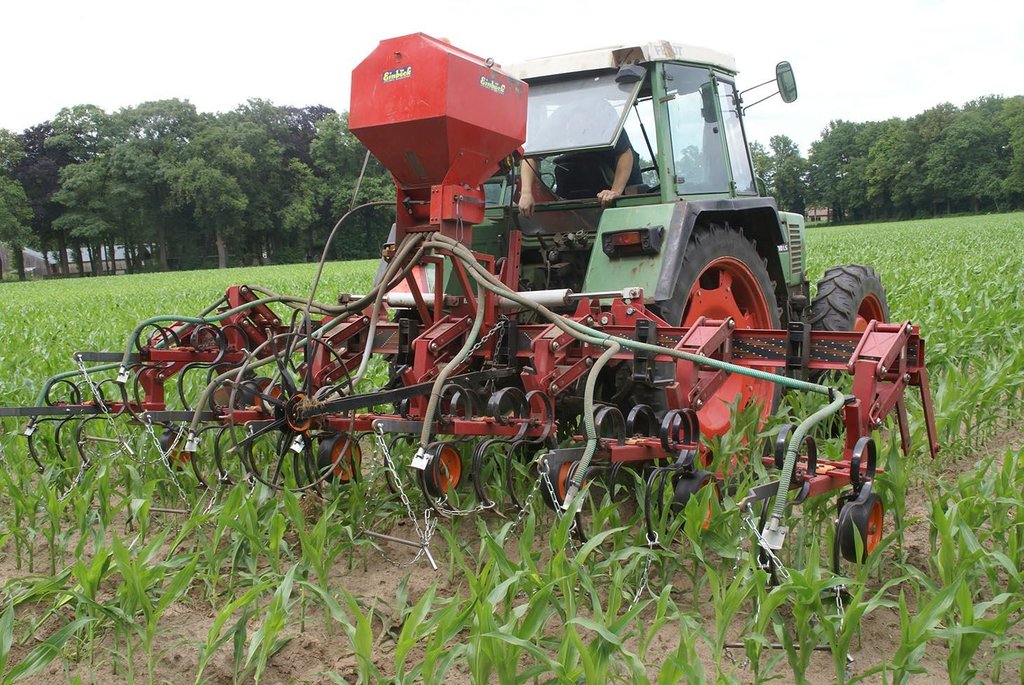
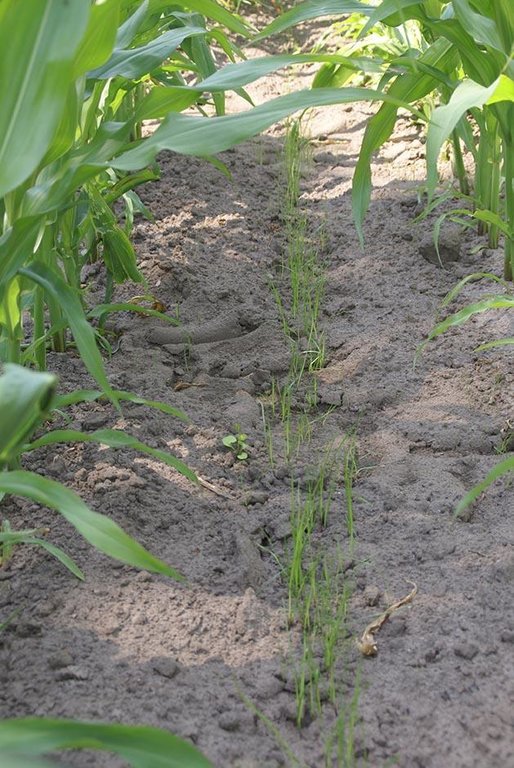
Italian rye grass is sown when the corn has grown to knee height, and has not yet developed a closed cover. The grass is plowed into the soil several months after the harvest of the corn crop.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to enable a good growth of the catch crop (the grass) and to increase root biomass production after the corn is harvested. This will contribute to the organic mater content of the soil, and reduce the leaching of nitrogen and potassium. After underplowing of the grass, the nitrogen and potassium will be released to the soil and become available for the next crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: When corn is well established (between 30-60 cm height), grass is seeded between rows. A special seeder is required. Tractor must have tires that fit between corn rows. Grass germinates, but growth is reduced as corn matures and creates shade. When corn is harvested, grass continues to grow as a winter catch-crop. Some years, grass is sprayed with fertiliser to increase mineralisation. Grass is cultivated into the soil in early spring.
Natural / human environment: Multi-functional rural area with land use for agriculture, recreation, residence and nature. Dairy agriculture in small farms for Dutch standards combined with arable cropping. High livestock density.
Undulating landscape with cover sands and clayey and loamy sediments. Podzols and cambisols developed in sandy substrate. The area also has patches of anthroposols, soils enriched in Medieval times with manure and organic residues. Phosphate and nitrogen levels in these soils are in general high.
Mean monthly temperature varies between 2 and 17°C. The long-term mean annual precipitation is between 800 and 825 mm, with the lowest amounts in spring, and the highest in autumn. The long-term average annual precipitation deficit is between 200 and 240 mm.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Países Baixos
Região/Estado/Província:
Gelderland
Especificação adicional de localização:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
0,94
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Left: 52.098865, 6.563182
Right: 52.095031, 6.634282
Top: 52.111764, 6.589390
Bottom: 52.081761, 6.620607
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.94 km2.
94 ha over 32 fields. 20 farmers applied this technology.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The land users's initiative was through the application for the project Healthy Sand by a group of farmers. During the Gezond Zand Project the group organised themselves in the Foundation HOEDuurzaam. The project ran from 2012-2014 and is followed by the new project BodemRijk.
The external initiative was from the drinking water company Vitens and the Province of Gelderland in the same period.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- cereais - outros
- culturas forrageiras - gramíneas
- culturas de raiz/tubérculos- batatas
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 250Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Intercropping of grass and corn to increase soil organic matter
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main soil threat in the Olden-Eibergen Case Study area is the gradual decline of soil organic matter stocks. On average, agricultural fields have lost up till 5.4% of organic matter in the last 10 years according to farmers. This threatens the agricultural potential of the soil as well as its water holding capacity, and its potential to buffer leaching of nutrients and pesticides. In the long term, agricultural productivity will fall, costs of agricultural inputs such as manure, fertilizers, pesticides and irrigation will increase and the additional costs for cleaning drinking water withdrawn from ground water will rise.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience declining crop production, problems with too dry and too wet soils, and decreasing organic matter content in soil due to long-term monocultures of maize, the use of pig manure and legislation forcing farmers to process or export manure from their farms.
Grazingland comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
Type of grazing system comments: Nothing filled in in this section, since the technology applies specifically to maize cropping.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Comentários:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Intercropping
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, green manure, rotations / fallows
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação da água
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (ploughing for renewal of grassland or rotation to arable cropping), governance / institutional (Stricter manure legislation since January 2014 deriving from the EU Nitrates Directive has forced farmers to process part of the manure from their farms on-farm, or to export it from their farms.)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (long-term monoculture of maize and intensive cropping of seed potatoes)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
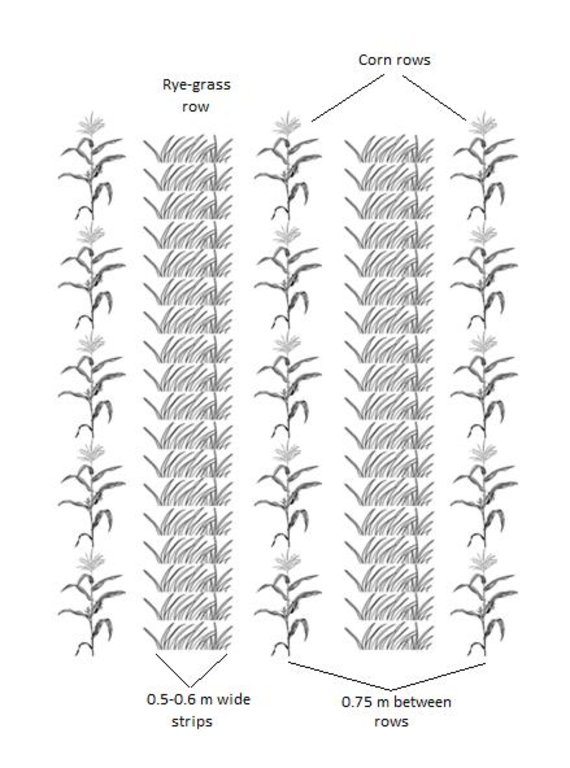
After the corn crop is growing, a tractor with a seeder sows Italian Rye-grass seeds between the rows of corn. The grass seeds are sown in strips parallel to the corn rows. The corn rows are 0.75 metres apart. The grass strips are usually between 0.50 and 0.60 metres wide, but this is according to the farmer's preference. this means that a spacing of between 0.075 and 0.125 metres remains bare on each side of the grass strip, between the grass and the corn.
Location: Haarlo - Oude Eibergen. Gelderland
Date: April 8 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Technical knowledge required for agricultural contractor: high (technical skills are required from an agricultural contractor with a special machine to sow the grass in the already standing maize crop.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Green manure
Material/ species: Italian rye-grass
Quantity/ density: 25 kg/ha
Remarks: Between corn rows width 0.075-0.125 m bare space.
Rotations / fallows
Remarks: The Italian rye grass is worked into the soil ca 5 months after the harvest of the maize.
Aligned: -linear
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): not applicable
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.75-1.25
Grass species: Italian rye grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): not applic%
Autor:
Jason Stuka, Niemeijerstraat 26-II, 6701 CT, Wageningen, The Netherlands
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Euro
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
0,94
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
255.70
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buy a seeder |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Seeder | Machine | 1,0 | 5327,05 | 5327,05 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 5327,05 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 5667,07 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0 month(s)
Life span of the seeder: 6 years
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Seeding | After corn is established |
| 2. | Fertilizer | Every other year |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 117,2 | 117,2 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 42,62 | 42,62 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer Hired(machine+fert) | ha | 1,0 | 9,06 | 9,06 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 168,88 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 179,66 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Specific tractor to perform grass undersowing (seeder), tractor, sprayer/applicator
To seed the Rye-grass strips between the corn rows. Done a few months after the corn is seeded.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
New equipment (Seeder) - The seeding and fertilizer applications are hired from a company. The company purchases the new equipment to seed between the corn rows.
The greatest determinate factor to the land users are then the cost of hired machine hours.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
182 days of precipitation annually
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
Slopes on average: Flat and gentle (Only incidental)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Deep (A and B horizons up till 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area) Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm) and very deep (Deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture is coarse/light (Most soils have a sandy texture due to the substrate consisting of cover sands) and medium (Soils in former creek valleys contain loam (Umbric Gleysols))
Soil fertility is low (most soils have a low fertility due to the sandy substrate (specifically the Gleyic Podzols, ca 40% of the area)) or very high (in Fimic Anthrosols originated due to application of farmyard manure since medieval times (12% of the area))
Topsoil organic matter is medium-high (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water table (H > 40-80 cm; L>120 cm) in the sandy soils on thick substrate of cover sands (in 65% of the area)) and medium (shallow groundwater tables in the Umbric Gleysols (35% of the area))
Soil water storage capacity is very high (in the Fimic Anthrosols with high SOM in the topsoil) and medium (in the other soils, varying with the soil organic matter content)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table is <5m (in all soil types the highest level of the groundwater table during the year is <140 cm below the soil surface. The lowest level can be lower than 120 cm)
Availability of surface water is medium (from small rivers (De Berkel) and creeks)
Water quality (untreated) is poor drinking water (treatement required - levels of the pesticides Bentazon, and MCPP in the groundwater have incidentally exceeded the norms for drinking water production between 1985 and 2009.)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Soil biodiversity is high in the Fimic Anthrosols.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm operations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers are contractual workers. Wives of farmers often have a job, e.g. at the municipality, craft work. No B&B activities or educational services.
Market orientation: Mixed (Maize is completely used to feed cows (max 20% of the area is allowed under maize); other arable crops are sold to the market. Dairy production is commercial.)
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
15-50 ha 6 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
50-100 15 land owners (source: geoinformation from the project gezpnd Zand)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
All agriculture land is owned or rented by individual farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. Leased land is less well managed, resulting in lower organic matter contents. Investments in SLM would lead to a higher renting fee, or the land owner taking the land back in exploitation.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Expected increase of maize production: to 6-7 tonnes/ha. Not proven yet.
Possible competition between crop and grass. Not shown yet.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Only for farmers with fields at higher elevations and drier soils.
Renda e custos
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Saves seeding winter crop in autumn.
Added planning, but work is hired.
Undersowing of grass in the standing maize crops requires specific skills.
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Created farmer's foundation.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts of farming practices and organic matter in soils.
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Farmers collaborating with water company.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Dairy farmers have learned more about the importance of soil organic matter for their production systems, and about the consequences of soil management on soil organic matter and other aspects of soil health. This learning was brought by the exchange of knowledge between farmers and experts, and between farmers themselves. Farmers also profited from services provided to them by the farmers' foundations: shared investments (e.g. in the manure separator) and support in the application for subsidies to finance the SLM measure.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet. Little to no slope.
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
Insignificantly more water transpiration.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet. Claimed by some farmers already.
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Not measured but observed on photographs.
Diversidade vegetal
Espécies benéficas
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Possibly. Not proven.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
No modifications to the technology in response to climate change.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Comentários:
Farmers are subsidized for seeding rye-grass between corn rows. If not subsidized, they are unlikely to invest. Few farmers have seen short-term benefits. Their willingness to invest is based on their understanding of the long-term benefits, brought about by the Approach developed in the Project Gezond Zand (and in RECARE).
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
20
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
|
increases maize crop yield in the long term How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
increases soil organic matter How can they be sustained / enhanced? annual application of the measure; subsidy to execute the measure |
| increases available soil moisture |
| reduces leaching of nitrogen, potassium and pesticides to the groundwater |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Uncertainty of the success or positive effect of the measure. | |
| Uncertainty of negative effects to the crop. | |
| Uncertainty of competition between grass and crop for nutrients and moisture. | |
| Concerns about cost and labour | |
| Uncertainty of hindrance from legislation. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| technology requires hiring of skilled labour and machinery, which is not viable without subsidy in the short term | provide subsidy in the first 3-5 years of implementation |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort2014
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Freeannemieke.smit@wur.nl
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden EibergenBy Willem Rienks and Henk Leever2014
URL:
Freehttp://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdf
Título/ descrição:
Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The NetherlandsArjan Reijneveld2013
URL:
Wageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Regional process, social innovation [Países Baixos]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- Compilador/a: Simone Verzandvoort
Módulos
Não há módulos