Sustainable propagation of the fodder tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”) [Madagascar]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Johanna Goetter
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1677 - Madagascar
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Sustainable propagation of the fodder tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”): 9 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Sustainable propagation of the fodder tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”): 3 de Maio de 2017 (inactive)
- Sustainable propagation of the fodder tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”): 3 de Maio de 2017 (inactive)
- Sustainable propagation of the fodder tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”): 5 de Setembro de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Herinavalona Rabemirinra
University of Antananarivo
Madagascar
Especialista em GST:
Yeddiya Ratovonamana
World Wildlife Fund (WWF Toliara)
Madagascar
Especialista em GST:
Goum O. Antsonantenainarivony
University of Antananarivo
Madagascar
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Sustainable Landmanagement in south-western Madagascar (SuLaMa / GLUES)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Brandenburg Technical University (btu) - AlemanhaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
University of Antananarivo - MadagascarNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Increasing environmental awareness using comic-style illustrations as a … [Madagascar]
Communicating and transferring scientific results and recommendations about sustainable land management to local people
- Compilador/a: Tobias Feldt
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
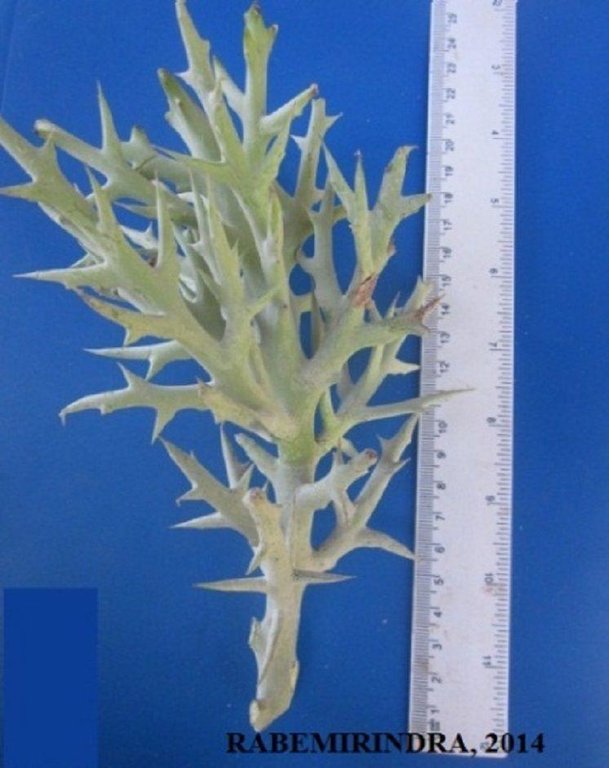
Propagation of “samata” cuttings for long-term provision of supplementary livestock fodder to reduce the pressure on natural vegetation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
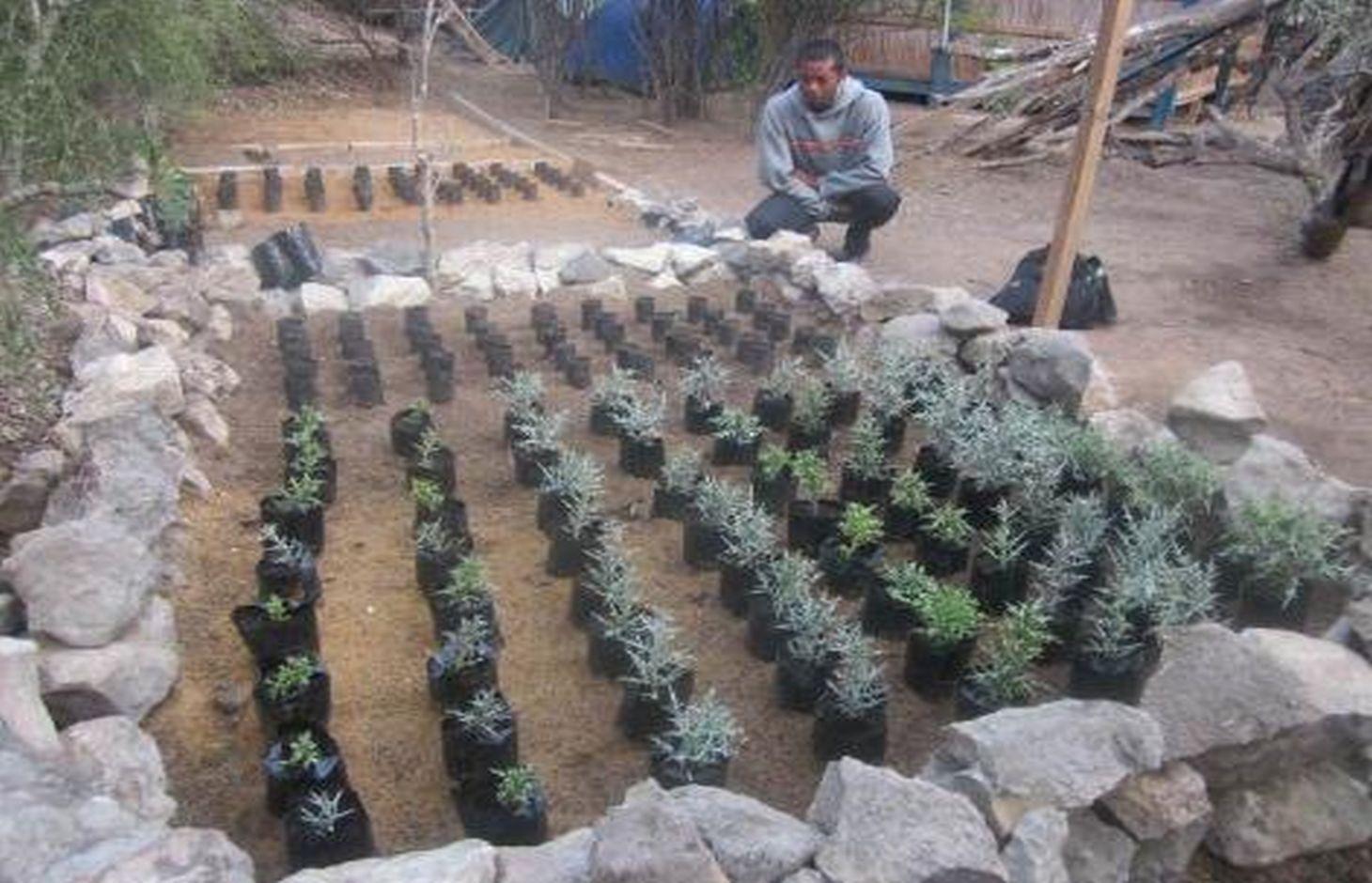
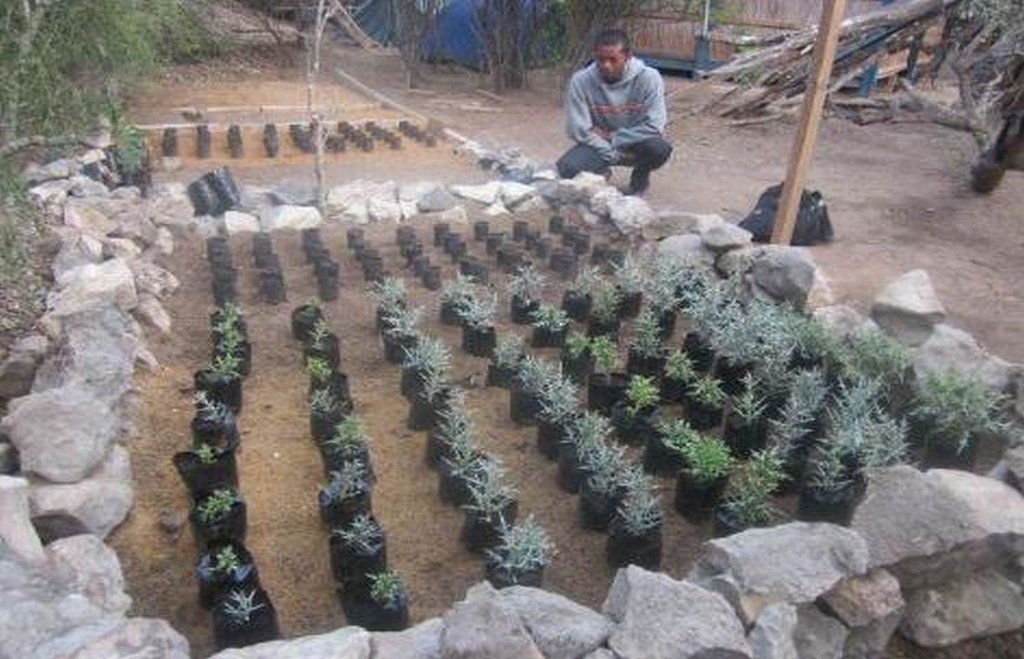
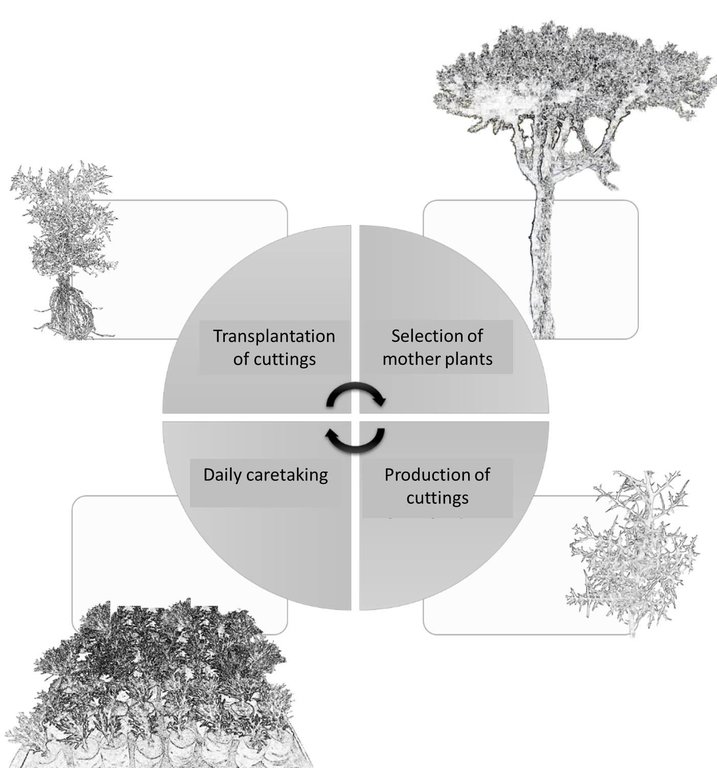
The succulent evergreen tree Euphorbia stenoclada (“samata”) is the most important dry season fodder resource on the coastal plains grazing grounds in the Mahafaly Plateau region. To increase production, samata can be vegetatively propagated with cuttings raised in a nursery. The advantages are: (a) protection against livestock, (b) selection of the most appropriate planting stock to propagate and (c) easy watering. Cuttings should only be taken from mature trees 7-10 years old and 3-4 m high. The mother plants should be healthy, with few spines, and no previous cuttings taken. Cuttings are taken at the upper nodes of the branches, approximately 20-25 cm long and 0.5-1.5 cm diameter. Transport of the cuttings to the nursery should be carried out in the morning to avoid heat. For effective rooting, the cutting is planted 5 cm (1-2 nodes) into a humid substrate in a plastic pot or directly into the ground. Best results are achieved using white sea sand mixed with some organic material. Cuttings should be raised in a sunny location. During the first 15 days, the cuttings need to be watered once every morning. For the next 3-4 months, they need watering every second morning. 24 hours before transplantation from the nursery to the final destination, the cuttings should be abundantly watered. Rooted cuttings are transplanted into pits of 10 cm diameter and 15 cm depth, filled with the same substrate as used in the nursery. For 15 days, the transplants are watered on a daily basis, and afterwards every second day. After 30-45 days, the transplants are ready to survive without further care. If the planting location is open to roaming livestock, the cuttings need protection.
Purpose of the Technology: The samata tree naturally reproduces by seeds as well as by vegetative reproduction. However the German funded SULAMA research project has had most success with multiplication of the local variety with cuttings. This form of propagation is preferable as it is much faster and gives higher survival rates of the individuals: neither does it need much planting material, equipment or technical knowledge. Providing the villagers with the know-how, and assisting them to create local samata-nurseries, makes this technology promising. SuLaMa-WWF started this technique in April 2015, establishing 5 nurseries with 2,000 trees each (3 with village communities, 2 with local schools).
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: On the coastal plain of the Mahafaly plateau region, the climatic and edaphic conditions do not support livestock raising based mainly on grasses. For 6-7 months, the herders are dependent on supplementary fodder plants, especially samata. The tree is fed by cutting its branches and slicing them. However pressure on this resource has led to depletion of stocks around many villages: this results from increasing demand and reduced supply. Higher demand is the result of changed herd movements, especially a shorter transhumance period. Lower supply is attributed to decreased precipitation, overuse of trees leading to poor regeneration or even the death of trees, and reduced samata areas due to the expansion of private crop fields. The overuse of trees is triggered by the overall scarcity of this resource as well as an ongoing privatization of the historically common land resources.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
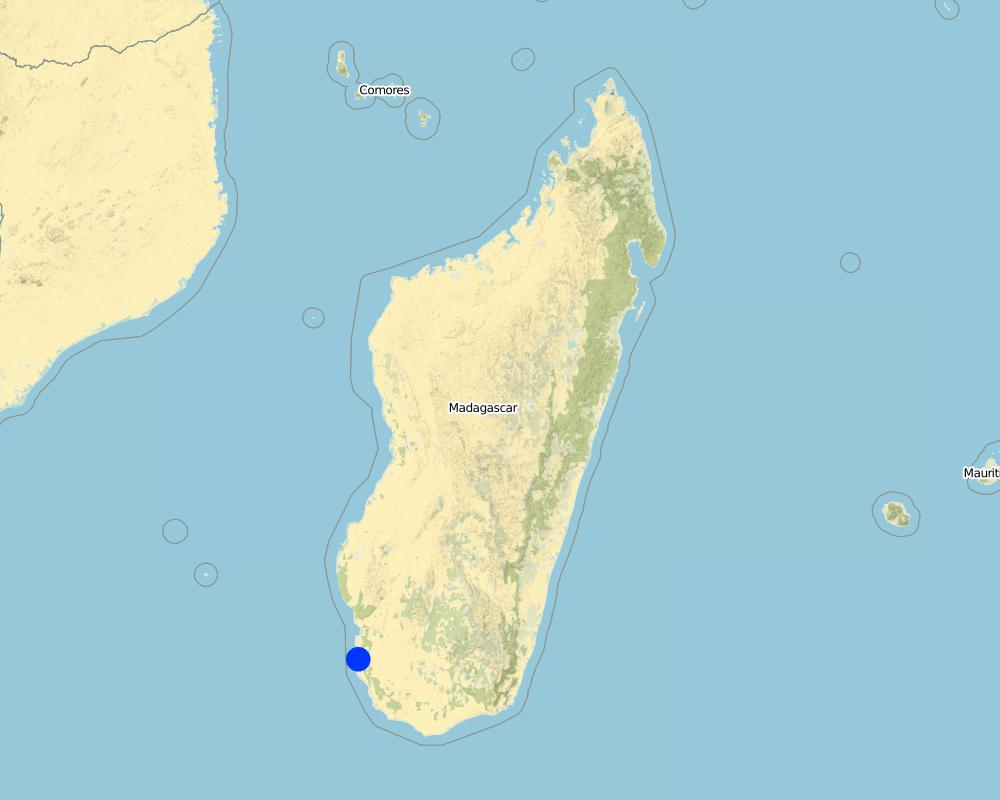
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Madagascar
Região/Estado/Província:
Atsimo-Andrefana, Toliara
Especificação adicional de localização:
Toliara II, Beheloka
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
Application ongoing, the envisaged implementation area might be up to 1,000 km².
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Project started with experimental trials of multiplication by cuttings in February 2014, first capacity development for land users through workshops on propagation technique in May 2015.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- culturas de raízes/tubos - batata doce, inhame, taro/cocoyam, outros
- culturas de raízes/tubérculos- mandioca
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- árvores forrageiras (Calliandra, Leucaena leucocephala, Prosopis, etc.)
- cactus, Euphorbbia stenoclada, samata trees
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period from month to month: June - September

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Pastoralismo semi-nômade
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Comentários:
Major cash crop annual cropping: Maize
Major food crop annual cropping: Cassava
Other crops annual cropping: Sweet potato
Major cash crop tree/shrub cropping: Samata (Euphorbia stenoclada)
Other crops tree/shrub cropping: Cactus
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): : Climatic constraints (especially low and erratic precipitation), deforestation, forest degradation, soil degradation, overgrazing, loss of arable land, fragmentation, low availability of surface and (very saline) ground water, privatization of common pool resources.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Climatic constraints, loss of arable land, low availability of animal fodder, soil degradation, low availability of surface and (very saline) ground water.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: samata trees are both found on the grazing area (naturally), as well as on agricultural fields (naturally, transplanted). Main reason for transplanting to fields however not shade/other positive interaction with crops, but for property rights reasons.
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
- Propagation of fodder plants
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: in blocks
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Slash&burn, charcoal production, overgrazing and grazing in forests), overgrazing (overexploitation of samata-trees), change of seasonal rainfall, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (cyclones), population pressure (ca. 3% / year), poverty / wealth (Extreme poverty, subsistence and low economic development), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited access to improved tecniques for agriculture and livestock keeping)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Non-optimized crops), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Overexploitation of wild plants), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, land tenure (privatization of formerly open access rangeland leading to increased pressure on still open access samata-trees), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …), war and conflicts (armed cattle rustling on neighboring plateau let to new transhumance pattern towards implementation region, thus higher pressure on fodder resources), governance / institutional (limited access to improved tecniques for agriculture and livestock keeping)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Multiplication of samata trees through cuttings preferably in the cold season from June to August: (1) Selection of suitable mother plants: adult trees 7-10 years old, 3-4 m high, good phytosanitary condition, low in spines, without previous cuttings taken (2) Taking cuttings with a sharp knife at the upper nodes of the branches, approximately 20-25 cm long and 0.5-1.5 cm in diameter. To ensure the survival of the mother tree, at least 10 branches should remain uncut. Transportation of the cuttings to the nursery takes place preferably in the early morning to avoid heat. (3) Daily care of cuttings in nurseries till the roots are well-established. The cuttings are planted 5 cm deep (1-2 nodes) into a humid substrate in a plastic bag or pot, filled with a substrate of white ocean sand mixed with some organic material, for example dung (75% sand, 25% dung). During the first 15 days, the cuttings need to be watered once every morning. For the next 3-4 months, they need watering every second morning. Shade has to be avoided. (4) Transplanting cuttings: 24 hours before transplanting, the cuttings need to be abundantly watered. The rooted cuttings are transplanted into holes of 10 cm diameter and 15 cm depth, filled with the same substrate used in
the nursery. For 15 days, the transplants are watered on a daily basis, and afterwards every second day. After 30-45 days, the transplants will be ready to survive without any further human attention.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 300
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Trees/ shrubs species: Euphorbbia stenoclada, planted cuttings (artificial vegetative multiplication)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
Autor:
RATOVONAMANA R. Yeddiya, UNIVERSITE D’ANTANANARIVO FACULTE DES SCIENCES DEPARTEMENT DE BIOLOGIE ET ECOLOGIE VEGETALES
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Madagascar-Ariary
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
3227,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.55
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of cuttings from mother trees | End of wet season |
| 2. | Preparation of substrate and pots/bags | End of wet season |
| 3. | Planting of cuttings in plastic pots/bags | End of wet season |
| 4. | Watering of cuttings during the dry season | First every day, after 15 days every second day during dry season, till transplantion to final destination |
| 5. | Fencing of final destination area for cuttings (hedges of local material), if neccesary | Before transplantation of cuttings |
| 6. | Transplantation of cuttings from plastic pots to final destination | During next wet season |
| 7. | Monitoring | first days after transplantation |
| 8. | Watering of small trees | Every day for first 15 days, then every second day (30-45 days after transplantation) |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 415,0 | 415,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 23,0 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Earth and manure | ha | 1,0 | 7,5 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Transportation, ox chart hire | ha | 1,0 | 9,3 | 9,3 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Plastic pots | ha | 1,0 | 93,0 | 93,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 547,8 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 0,17 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 4.5 month(s)
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: knives, scissors, shovels, watering cans
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The multiplication of samata trees comprise labour costs mainly. The time spent watering the cuttings is the most significant.
There are no maintenance costs, as after transplantation to final destination and watering for some month, there are no yearly recurring activities.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: tropics
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
1% of the land users are rich.
9% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
70% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: business, trade, temporary labour migration, charcoal making
Market orientation cropland production system: Subistence (self-supply) (agriculture with annual food shortages and some off-farm income) and mixed (subsistence and commercial) (livestock mainly used for selling and thus getting some cash in order to buy food or other aims)
Market orientation grazing land production system: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) (samata has become an importan local cash crop, selling of annual harvesting rights to livestock owners )
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
Land devoted by the communities for crop production belong to clans/lineages and their members (individual, untitled), while land devoted to grazing is an open access common pool resource, but currently undergoing an unregulated privatization process.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
more/better fodder --> less loss in animals --> easier to mitigate annual food shortage (subsistance agriculture) by selling animals
Atenuação de conflitos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Still not, as technology still very new, knowledge transfer has just started very recently (May 2015).
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Espécies benéficas
Outros impactos ecológicos
Shade for wild and domestic animals
Pressure on / degradation of wild samata
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Knowledge transfer of new technology has just started recently
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Knowledge transfer of new technology has just started recently
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Knowledge transfer of new technology has just started recently
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Land users are interested in applying this technology, as the samata tree is their main dry season fodder plant and overuse and scarcity today is severe How can they be sustained / enhanced? Providing land users with the technical knowledge and know how about samata propagation. |
| ‘Artificial’ propagation of samata by vegetative multiplication (cuttings) does not require any special equipment or much specific knowledge. |
| Increasing the number of trees on the grazing land, and decreasing the pressure on trees enlarges the crown diameter of trees, thus providing additional shade for wild and domestic animals. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Land users are unaware that ‘artificial’ propagation through cuttings is possible | Spread this knowledge. |
| The cuttings need constant care, as they need to be watered frequently over many weeks. This requires attention and labour | The long-term benefits outweigh the labour invested. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Johanna Goetter and Regina Neudert (2016) New rules are not rules: Privatization of pastoral commons and local attempts at curtailment in southwest Madagascar
Disponível de onde? Custos?
International Journal of the Commons (10:2). DOI: 10.18352/ijc.743
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Johanna Goetter et al. (2015) Degradation of the Important Fodder Tree Euphorbia stenoclada
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Southwest Madagascar and Approaches for Improved Management. Poster presented at the conference Tropentag 2015, September 16 - 18, Berlin, Germany. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.3734.7445
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Antsonantenainarivony O. Goum (2015) Guide pratique pour la bouture de samata (Euphorbia stenoclada Baill.) dans la partie littorale de la région Sud-Ouest de Madagascar.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.sulama.de/index.php/en/literature/reports-english.html
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Antsonantenainarivony O. Goum (2015) Guide pratique pour la bouture de samata (Euphorbia stenoclada Baill.) dans la partie littorale de la région Sud-Ouest de Madagascar.
URL:
http://www.sulama.de/index.php/en/literature/reports-english.html
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Increasing environmental awareness using comic-style illustrations as a … [Madagascar]
Communicating and transferring scientific results and recommendations about sustainable land management to local people
- Compilador/a: Tobias Feldt
Módulos
Não há módulos