Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Christian Rumbaur
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
罗布红麻 and 罗布百麻 (Chinese)
technologies_1721 - China
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 9 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 4 de Abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Apocynum planting to protect and profit from saline soils in the Tarim River Basin, north-west China: 19 de Março de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Rouzi Ahmatjan
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett
Alemanha
Especialista em GST:
Thevs Niels
World Agroforestry Center, University of Central Asia
Quirguizistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Catholic University Ingolstadt-Eichstaett (KU) - AlemanhaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - Quênia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
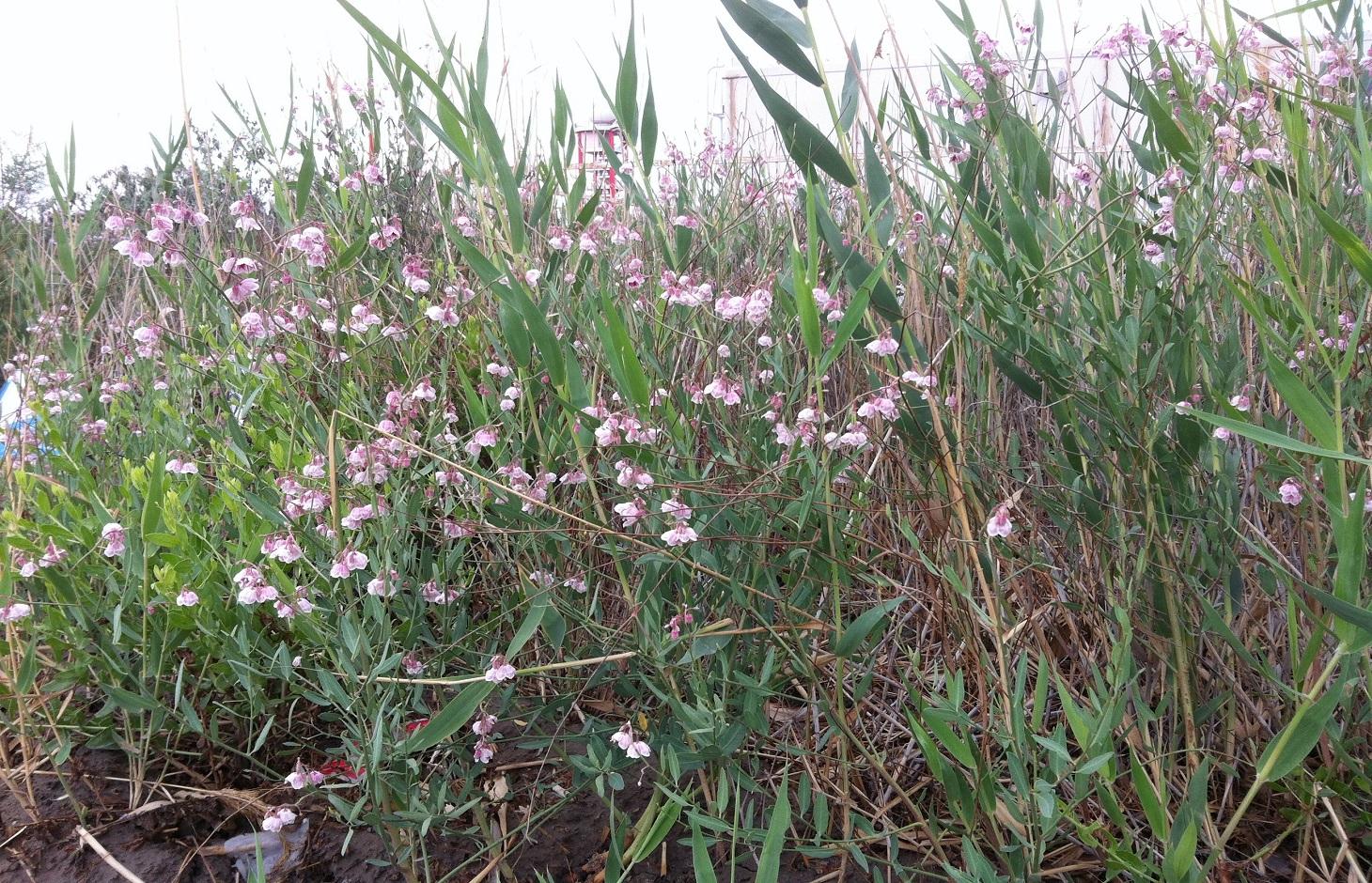
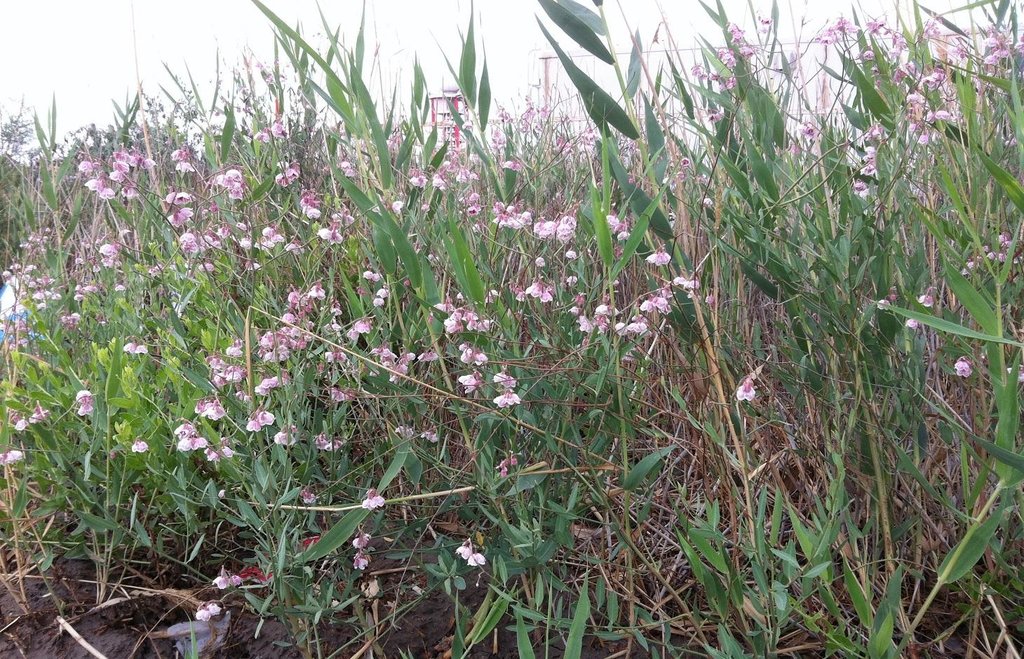
Plantation of Apocynum pictum and Apocynum venetum as protective and profitable indigenous plants - on soils made saline through irrigation of cotton without adequate drainage.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
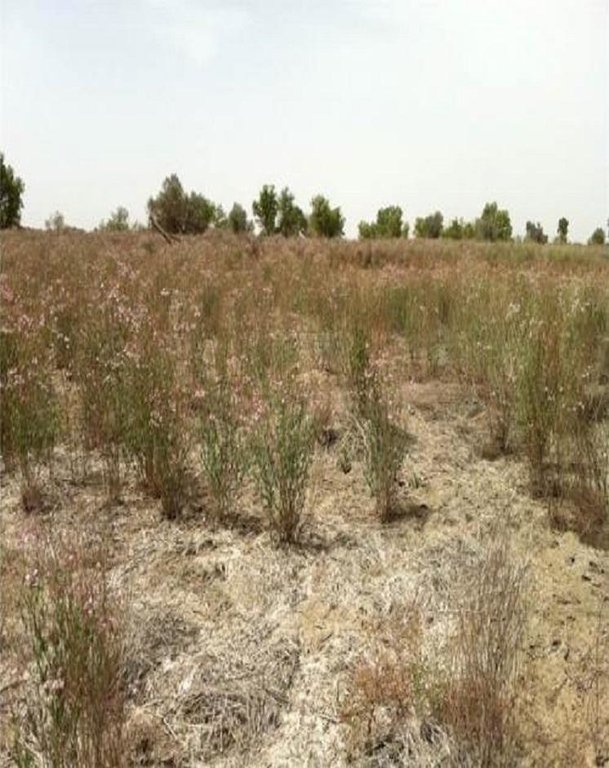
The natural ecosystems in north-west China, especially in Xinjiang Province, are dominated by steppes, semi-deserts and desert. Riparian forests along the Tarim River Basin have been reduced and degraded by the expansion of irrigated agriculture since the 1950s. The main crop planted is cotton. In the arid temperate cold desert climate, precipitation is very low and evaporation high. The only water source for the region is the Tarim River. Xinjiang is being promoted to become the main cotton production area of China, especially in the upper reaches of the Tarim River, and reservoirs with a large irrigation infrastructure have been established. Farmers water their fields with flood and drip irrigation. But most of the fields have no drainage system. With the high evaporation and the capillary rise of the shallow groundwater, salts dissolved in the water accumulate on the soil surface and in the soil. This salinization makes the fields unusable for cotton production and are abandoned as farmers move on. These barren saline soils are prone to wind erosion, as almost no plants can grow on them. Large-scale desertification is the result.
Purpose of the Technology: To halt desertification the barren saline soils need to be protected by vegetation to avoid soil loss by wind. But if this can be done through vegetation that yields an income then the advantage is double: a win-win situation. Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum are indigenous and both are drought and salt tolerant. They are phreatophytes: deep-rooted plants that tap groundwater or the soil layer just above the water table. A.venetum and A. pictum are rhizomatous perennials – and importantly they are cash crops too. Fibre from the stems are used to produce textiles, though the extraction process is time and labor consuming. The advantage of apocynum yarn is that it has antibacterial properties. The leaves and flowers are also sold and used to produce tea which is a Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) that reduces blood pressure. On a per hectare basis, the stem generates a potential income of US$ 3,650, the leaves US$ 1,995, and the flowers US$ 1,815: nevertheless the market for apocynum products is small. In Xinjiang most of the apocynum plantations are under commercial large-scale farmers. They have the capital to deal with the costly establishment of apocynum.
Natural / human environment: Fields on which apocynum is sown should have a groundwater level not deeper than 2m. Nevertheless the soil should be well-drained: best is a sandy loam. Waterlogged, calcareous, clayey soils are not suitable. Apocynum can withstand periods of water inundation; however, prolonged submergence or waterlogging inhibits its growth. The topsoil under apocynum is often saline, reaching salt contents of up to 20%. Apocynum can grow on sites with a pronounced surface salinization, as long as the subsoil and the groundwater are not strongly salinized. There are two methods of planting apocynum: by seed or by vegetative means. While irrigation helps establishment and good yields, this is at a much lower level than for cotton. In conclusion, A.venetum and A. pictum provide profitable options on saline soils, grow with minimal irrigation, and protect the land against wind erosion.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
China / Xinjiang Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Tarim River Basin
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
6000,0
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Location in China between 37°~46°N and 76°~104°E. Location in Tarim River Basin: 41°12'34.94"N and 84°19'28.19"E
In China the area of Apocynum vegetation, natural or artificial, amounts to 1,330,000 ha. One third to half of this area is located in Xinjiang, ie approximately 600,000 ha
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
- naturally
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- culturas de fibras - algodão
- wheat
- Apocynum
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
Comentários:
Apocynum venetum and Apocynum pictum
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Salinization, desertification, mismanagement of cotton monoculture, inadequate drainage under irrigation, abandonment of degraded land.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water scarcity, salinization, land use rights.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: salt crust on the top soil layer and high salt content in the soil
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
Desertification: Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Quebra-vento/cerca de árvores
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Cotton monocultures), wind storms / dust storms (Duststorms, blow ou tof topsoil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (doubling the population during the last thirty years), land tenure (land belongs to the state), education, access to knowledge and support services (poorer farmers have less access to extension services)
Secondary causes of degradation: discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Most fields have no drainage -> Increase of groundwater -> salinisation of soils), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests)), poverty / wealth (family farmers are poorer than city dwellers)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Apocynum planted in a levelled field with strips of 8 to 18 cm height and 30 to 40 cm width with 40 cm space between each strip
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (for regeneration and multiplication)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 20,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3 to 0.4
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 60,000 to 70,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0%
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
-0,42
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manuring (3700 to 5000 kg/ha) and ploughing | Before sowing |
| 2. | Site establishment/ preparation | |
| 3. | Planting of seedlings/ root cuttings/ transplants | most suitable seeding time is mid April to May or transplantation |
| 4. | Irrigation at establishment (10000-12000 m3/ha) | After sowing |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Site establishment/ preparation | ha | 2,0 | 18,7 | 37,4 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 100,0 | 2,5 | 250,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 100,0 | 6,18 | 618,0 | |
| Outros | Manure | ha | 171,1 | 18,7 | 3199,57 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Waterfee | - | 1,0 | 460,0 | 460,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 4564,97 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | -10868,98 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | irrigation and weeding labor | 6 times |
| 2. | Fertilizer | |
| 3. | Harvest labor | at harvest |
| 4. | Transport | after harvest |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | irrigation and weeding labor | ha | 10,0 | 114,0 | 1140,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Harvest labor | ha | 1,0 | 359,0 | 359,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Transport | ton | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer (Phosporus) | kg | 150,0 | 4,12 | 618,0 | |
| Outros | Waterfee | 1,0 | 2280,0 | 2280,0 | ||
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 4408,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | -10495,24 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel, tractor and plough
Costs were calculated for 2015, per hectare. Labour has become more expensive over the last few years. In the beginning (first two years) cultivation of apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 years the plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the products of apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high. Direct seeding as compared to vegetative propagation is the most labour-saving method to cultivate apocynum.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Per year: 90 mm; Jan, Feb, Apr, May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: Altitude between 800 and 1300 m
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium - high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table also < 5 m: Apocynum is a phreatophyte. The most productive sites of Apocynum venetum are found on a groundwater not deeper than 3 m with salt contets between 1g/l and 10g/l.
Ground water table 5-50 m: Apocynum pictum is mainly found on groundwater levels of 4-6m below surface with a maximum groundwater depth of 8 m. Apocynum is restricted to groundwater levels not deeper than 4 m below surface.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the hard work in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The plantation of Apocynum brings a high income to the farmers.
Level of mechanization manual labour: harvesting
Market orientation of production system commercial/ market: Apocynum is planted for fibre, tea and medicinal products
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: field preparation
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
< 0.5 ha: family farms
5-15 ha: state farms
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Comentários:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
market for apocynum fibre
market for TCM
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Atenuação de conflitos
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade de habitat
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
In the beginning (first two years) the plantation of Apocynum is very labour and input intensive. After 1.5 to 2 yearsthe plants can be harvested for the first time. The price for the producst of Apocynum (leafs and stems) are very high.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
No number on households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Most of the plantations are planted by large investing farmers. The farmers sell the products of Apocynum to the pharmaceutical companies for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Both species yield fibres and leaves for fiber production and the leaves for medicinal products or tea on considerable areas under the arid climate of Xinjiang Province, China, without intensive irrigation, because they use the groundwater as for example cotton. Furthermore, both species can withstand higher soil salinization levels than cotton. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The plantations can be enhanced by analyzing the water consumption and the water use efficiency to apply only as much water to the plants as they need Not decreasing the yields. |
|
Both species can provide an income to local people - fibre and leaves for medicinal products or tea - under conditions which are unfavorable to grow crops under irrigation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote apocynum on saline wastelands and subsidize the establishment of the plantations. Explore further markets and promote the products. |
|
Through apocynum plantations wastelands are reclaimed. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Highlight the potential to reduce wind erosion and ‘dust bowls’. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Difficult process to extract fibre from the stems. | New technology needs to be developed. |
| Small market. | New uses need to be explored to expand the market. |
| High investment in the beginning of the plantation. | Planting of apocynum should be subsidized. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
N Thevs et al. (2012) Apocynum venetum L. and Apocynum pictum Schrenk (Apocynaceae) as multi-functional and multi-service plant species in Central Asia: a review on biology, ecology, and utilization.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Journal of Applied Botany and Food Quality 85, 159-167.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos