Contour Grass Hedgerows on Steep Slopes [Butão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ONGPO LEPCHA
- Editor: Kuenzang Nima
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Tsayi Gaytshig (ཙྭའི་རྒད་ཚིག།)
technologies_6854 - Butão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Daza Khemo
Boucholing village
Butão
usuário de terra:
Dorji Ugyen
Boucholing village
Butão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
National Soil Services Centre, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Livestock (NSSC) - Butão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
The technology described is not problematic with regard to land degradation.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
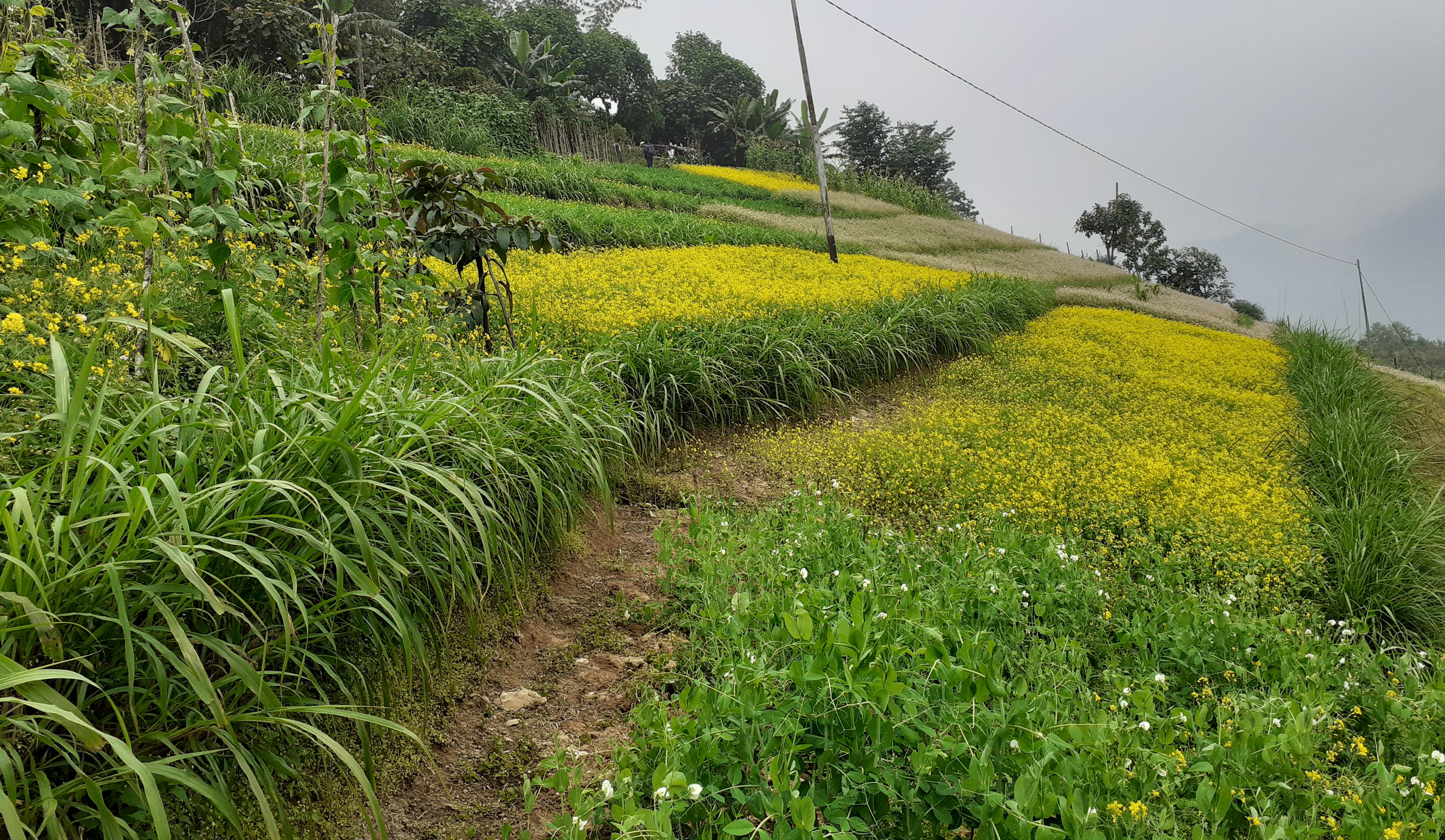
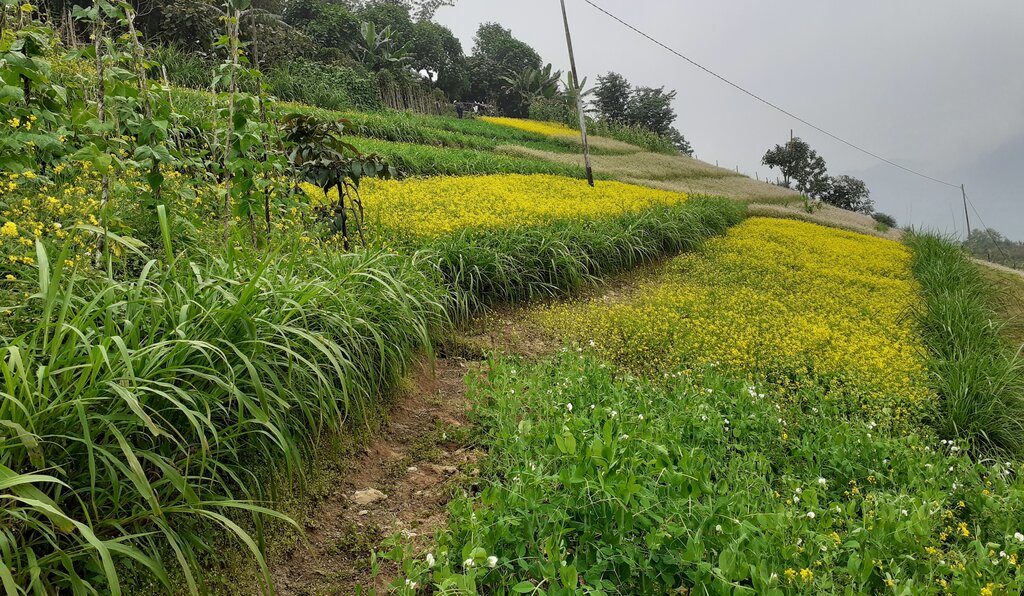
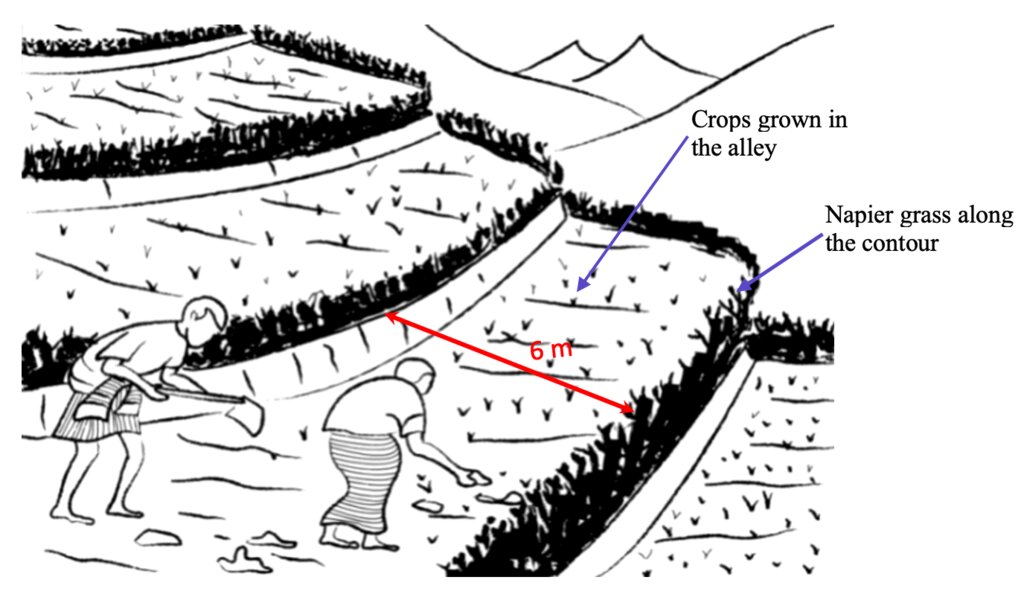
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involve planting of Napier grass cuttings along contour lines on the slope at a horizontal distance of 6 m. The area between the contour hedgerows is used for crop cultivation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involves planting Napier stem cuttings along contour lines on slopes. They are planted at a horizontal distance of 6 meters between rows and 15-20 centimeters between cuttings within lines. On average it requires 3500-4000 Napier slips to cover one acre (0.4 ha). Hedgerows form living barriers that trap sediment and reduce surface runoff. With time, as the sediment builds up behind the hedges, the area between the hedgerows develops into flat alleys or “terrace beds”. This technology is effective in reducing soil erosion and conserving water. The hedgerows also boost crop productivity. The contour hedgerow system is widely used in hilly terrain in Bhutan and elsewhere.
The main purposes of the technology are to 1) serve as a barrier to check the movement of soil and water down the slope, 2) effectively utilize sloping areas for agricultural purposes, and 3) increase crop and fodder production.
The major activities/ inputs needed to establish/ maintain contour hedgerows are: 1) surveying of the area by an SLM specialist (planning and site assessment), 2) selecting suitable hedgerow planting materials, 3) registration of interested farmers, 4) training of farmers, 5) layout of contour lines using A-frames, 6) distribution of planting materials and establishment of hedgerows in farmland, 7) monitoring and evaluation of hedgerows, and 8) maintenance of hedgerows. Maintenance includes replacement of cuttings in gaps - either damaged by cattle or natural mortality and trimming of grass back to 15 centimeters after reaching 1 meter. Inputs required include: 1) planting materials (Napier grass), 2) A-Frame for contour lines, 3) spades, pickaxes, shovels, crowbars, etc., and 4) human resource input by SLM specialists.
Contour hedgerows have many benefits/ impacts on the livelihood of the land users including 1) soil and water conservation, 2) use of the sloping areas for crop or fodder production, 3) effective conservation through using local materials with a 90% survival rate, 4) habitat for natural predators, pollinators, insect-eating birds, and rodent predators, 5) groundwater recharge, and 6) they beautify the overall agricultural landscape. Another important benefit of the hedgerows is the availability of fodder grass for livestock, which otherwise would have to be collected from the forest. The disadvantages include the need for regular maintenance and gapping up. At times, conflicts arise within the community due to grazing of hedges by neighbors’ cattle.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Butão
Região/Estado/Província:
Mongar
Especificação adicional de localização:
Boucholing village, Thangrong gewog (block), Mongar Dzongkhag (district)
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2014
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The project was funded by UNDP and technical support was provided by the SLM Specialists from the National Soil Service Center and the agriculture extension agent of Thangrong gewog.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - milho
- culturas de raízes/tubos - batata doce, inhame, taro/cocoyam, outros
- vegetais - vegetais de folhas (saladas, couve, espinafre, outros)
- chilli
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Vegetables are grown for two times in a year but the cereal crops are grown for only one time.
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Sim
Em caso afirmativo, especifique quais são as culturas intercultivadas:
Maize and legumes
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Maize followed by vegetables
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water is a major constraint and land users mostly depend on rain for irrigation.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
Comentários:
Napier grass were planted on the bunds if the already constructed terrace.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
The technology addresses the issue of soil erosion through rain and prevented the degradation the top soil.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
The main goal of the technology is to combat farm land degradation and prevent soil erosion.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Technical drawing as per the specification given in the SLM Guidelines 2021. See steps for the establishment of hedgerows below:
a)Determine the hedgerow interval for each landform based on the gradient (but based on farmers feedback, the interval is generally set at 6 meters) and then lay out the contour lines. Along the contours, prepare a strip of land with a width of about 40-50cm wide to plant the grass slips or broadcast fodder grass seeds. Napier (Pennisetum spp.) and Pakchong grass spp. is recommended as hedgerow plants for areas that are below 1600 m. However, for areas above 1600 m, temperate grass mixture should be considered;
b)A row of fodder grass slips or seedlings should be planted with a spacing of 15-20 cm. If grass slips are used, at least two nodes should be inserted into the soil for proper establishment/rooting. On the other hand, if grass seeds are used, the seed rate should be 25g per square metre;
c)Mulching should be done right after the grass slip planting or grass seeding to reduce surface erosion, conserve soil moisture, and aid proper germination;
d)Gap filling and trimming of hedgerows should be done as and when required. The trimmed materials can either be used as fodder or mulching materials; and
e)If desired, improved fruit trees suitable at the proposed site can be planted along the hedges at 5 x 5 m spacing. Fruit trees in two adjacent hedgerows should be planted in staggered position to avoid competition for sunlight, water, and soil nutrients.
Autor:
NSSC
Data:
10/09/2021
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
Ha
Se utilizar uma unidade de área local, indicar fator de conversão para um hectare (por exemplo, 1 ha = 2,47 acres): 1 ha =:
0.4
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ngultrum
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
82,08
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
250
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planning | done between the stakeholders several times |
| 2. | Community meeting and member agreement | twice |
| 3. | Training and workshop | for almost a week |
| 4. | Demonstration | once |
| 5. | Implementation (Planting of napier in the field in groups) | based on the land users convenience and season of plantation |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labours | person-days | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Napier | bundle | 35,0 | 200,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Outros | Payment for resource persons | No of days | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 15500,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 188,84 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
The funding was provided by UNDP, with technical support from the National Soil Services Center and the Dzongkhag.
Comentários:
The cost breakdown of the technology establishment was for one acre of land.
The total grant amount was Nu. 2,834,416, however, the total budget for Boucholing specifically was not available.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting, cutting of napier and maintaining the height of the plant | when the napier reaches a height of one meter |
| 2. | Replacing of missing and damaged hills | whenever possible |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | person-days | 2,0 | 250,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Napier slips | Bundle | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2500,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 30,46 | |||||
Comentários:
Minimal cost go into the maintenance of the hedgerows.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour cost and cost of the planting materials.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The data used was from the nearest weather station of the National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology (NCHM).
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
https://www.nchm.gov.bt/home/pageMenu/906
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Dry subtropical zone
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Contour hedgerows can be applied in both concave and convex situations, so not relevant
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
água de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
The flooding of the area occurs mostly due to heavy rainfall and some surface water.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Diversidade de habitat:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Higher diversity because Napier grass adds to diversity to already existing crops.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
There are a total of 130 acres of land with an average area of around 2.3 acres for each household.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
The traditional legal system in our country is as per the land act and rules and regulations which dictate the land use in the country.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Crop production is higher than in the past since the contour hedgerows have helped control soil erosion and allowed for proper land utilization. The land user reported about a 25% increase compared to the past.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
The crop quality is also relatively better now compared to the past when the technology was not applied. The land users reported that crops near the hedgerows were found more greener.
Produção de forragens
Quantidade anterior à GST:
No fodder was produced
Quantidade posterior à GST:
After napier plantation, napier are harvested as fodder for cattle.
Comentários/especificar:
Napier grass was not planted in the past. It was introduced by the National Soil Services Center as part of this technology. The Napier grass planted along the contour has helped not only with soil erosion control but also provided fodder grass for the cattle. The land user reported that there was a 100% increase in fodder because unlike in the past now they don't have to send their cow for grazing in the forest.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Compared to normal grass that the cattle would graze on, napier is nutrient-rich and of better quality than the normal grass.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The napier plantation has helped prevent soil erosion that would normally occur in the farm lands thereby preventing crop failure due to soil fertility and moisture conservation.
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
With the help of the project, the land users were able to utilise the sloping land. This enabled land users to grow crops other than maize.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
The contour hedgerows have allowed for the sloping and degraded lands to be revitalised into usable cultivable lands.
Gestão de terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
Hard manual land management
Quantidade posterior à GST:
mechanization of the agriculture in the community
Comentários/especificar:
With the help of the project, farm lands in the community were made into terraces and made land management easier compared to the past.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
The expenses on agricultural inputs have stayed relatively the same, however, has made working on the farm land easier.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
With fodder availability, land users can now focus more on agriculture instead of herding cattle for grazing. The project has also allowed for land users to diversify their products.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Workload has decreased due to farm mechanization through use of power tillers, which was not possible prior to the SLM intervention.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Prior to hedgerow establishemt, there was serious surface erosion, which is not the case now.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
primarily maize was cultivated
Quantidade posterior à GST:
maize, cole crops, tubers and chilies are cultivated
Comentários/especificar:
In the past, the community members would normally cultivate maize and small amounts of vegetables for self consumption, but now a diverse variety of crops are cultivated.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Deslizamentos de terra/fluxos de escombros
Quantidade anterior à GST:
More prominent in the summer season
Quantidade posterior à GST:
occurrence is very minimal
Comentários/especificar:
The presence of a terrace and hedgerows in the bunds of the terrace has prevented the erosion of the soil in the farm lands of the farmers.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Downstream flooding is relatively less, since the hedgerows has prevented or reduced surface eorsion which would otherwise impact the downstream settlements and water bodies.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Trovoada local | muito bem |
| Tempestade de granizo local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Deslizamento de terra | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Since the project was fully funded and minimal cost went into its establishment by the land users, the benefits are higher.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
40 households
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
Since the program was supported by project, the labor were contributed by the land user while the inputs in all sites were provided by the project at every household level.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Hedgerow requires less management |
| Napier are also used as fodder for livestock |
| Prevents the land from erosion due to heavy rain |
| Helps in build up of terraces and facilitates in mechanization of farm |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Additional income opportunities through the production of marketable products from hedgerow vegetation. |
| Improved livelihoods for communities through long-term agricultural productivity. |
| Support for sustainable agricultural practices and resilient farming systems. |
| Preservation of fertile land and protection of agricultural resources. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Grazing of hedges by free cattle in absence of fences in farm land | Establish community byelaws not to let their cattle free in the fields or install fencing aroung the field. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Shading and potential competition with crops for soil nutrients by hedges | Maintaining height and width of hedges |
| The establishment and maintenance of contour hedgerows require time, effort, and financial resources | The funding for the establishment of technology has already been provided and for maintenance, the expenditure is minimal. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
1 household
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
2 individuals
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
ICIMOD. (1999). Manual on Contour Hedgerow Inter-cropping Technology. ICIMOD.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://lib.icimod.org/record/31840/files/manual_on_contour_hedgerow_inter-cropping_technology.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Pellek, R. (1992). Contour hedgerows and other soil conservation interventions for hilly terrain. Agroforestry Systems, 17, 135-152.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00053118
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kaushal, R., Mandal, D., Panwar, P., Rajkumar, Kumar, P., Tomar, J. M. S. & Mehta, H. (2021). Chapter 20 - Soil and water conservation benefits of agroforestry.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128229316000204
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Sustainable Land Management for improved land productivity and community livelihood in Thangrong, Mongar
URL:
https://sgp.undp.org/spacial-itemid-projects-landing-page/spacial-itemid-project-search-results/spacial-itemid-project-detailpage.html?view=projectdetail&id=27647
Título/ descrição:
Soil erosion control with contour planting
URL:
https://apps.worldagroforestry.org/Units/Library/Books/Book%2082/imperata%20grassland/html/4.1_soil.htm?n=20
Título/ descrição:
Sustainable Land Management: Guidelines and Best Practices 2021
URL:
https://www.nssc.gov.bt
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos