Conservation agriculture to restore abandoned cropland [Mongólia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Otgontsetseg Davaanyam
- Editor: Mandakh Nyamtseren
- Revisor: Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Khurs Khamgaalliin gazar tarialan
technologies_6938 - Mongólia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Batdeleg Batnaran
Khentiin Tarialan LLC
Mongólia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Geography and Geoecology (IGG) - Mongólia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O compilador e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através do WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
This technology is a SLM technology, because it returned abandoned land to productive agricultural land while building up soil health.
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
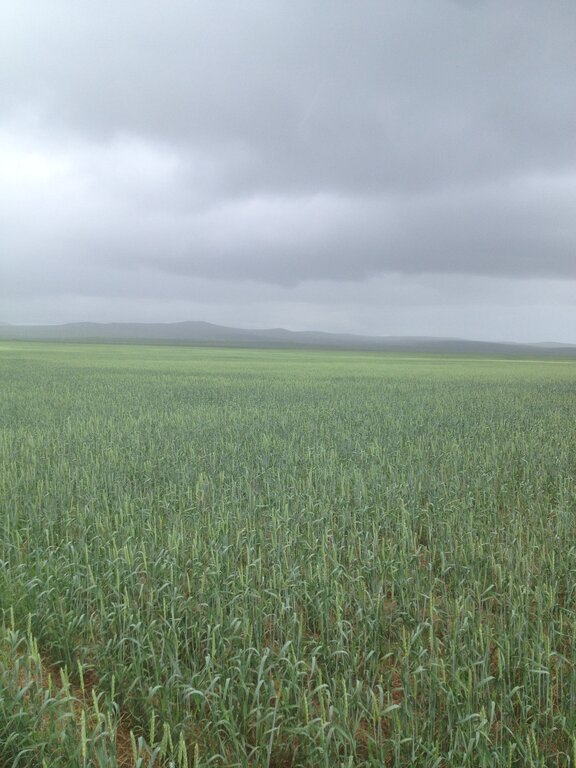
This technology aimed to restore abandoned cropland which was used for crop and fodder production during the 1970s-1980s. Since 2016, the farmer applied conservation agriculture and mixed cropping to reduce land degradation, revive cropping practices, increase land productivity for agriculture and enhance soil health.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
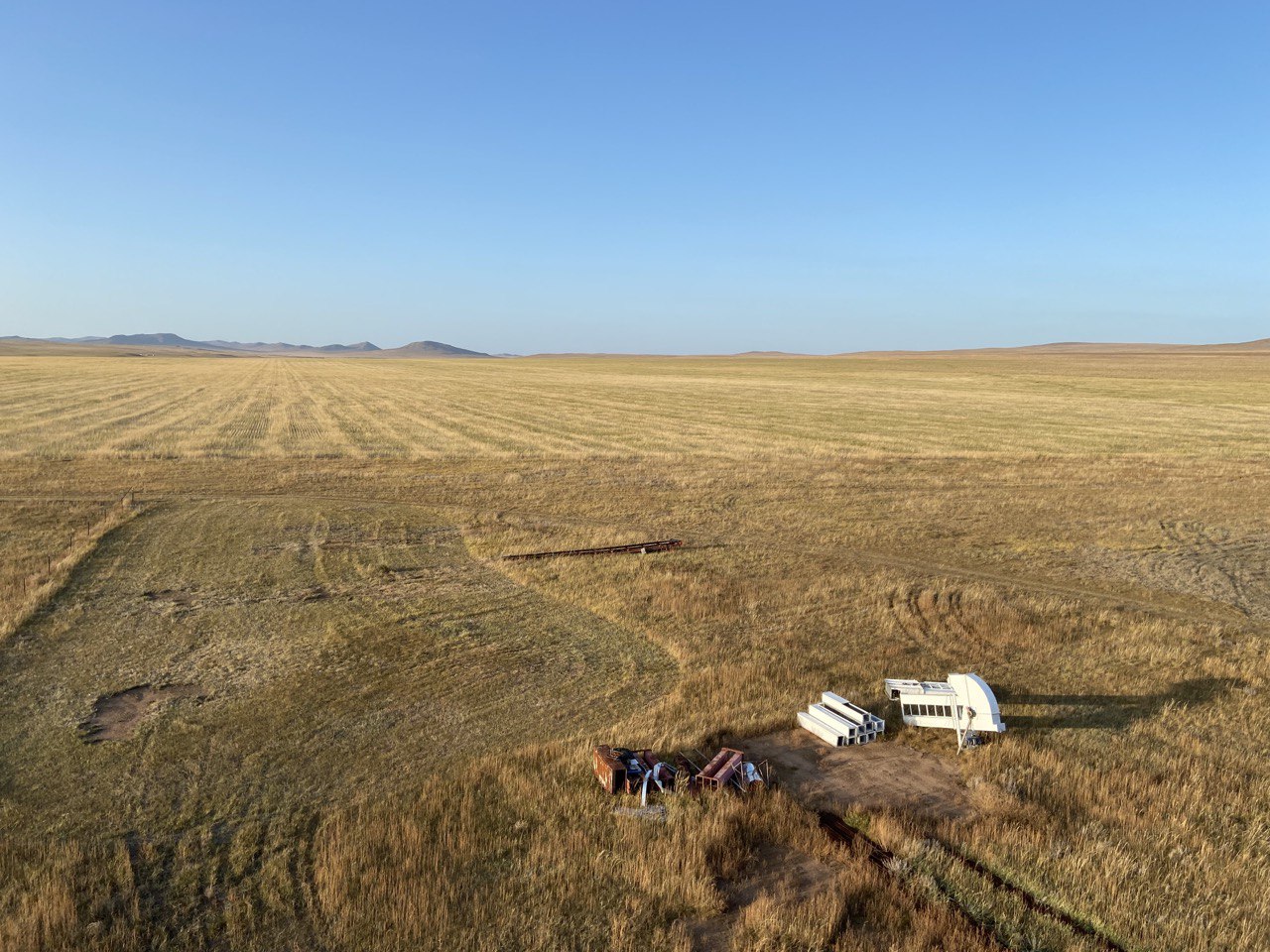
The land in Kherlen soum, Khentii province, spanning 500 hectares, was used for crop production and later for producing fodder for livestock. However, since 1984, it has been left abandoned. To rehabilitate the area and revive cropland, conservation agriculture combined with mixed cropping was introduced in 2014.
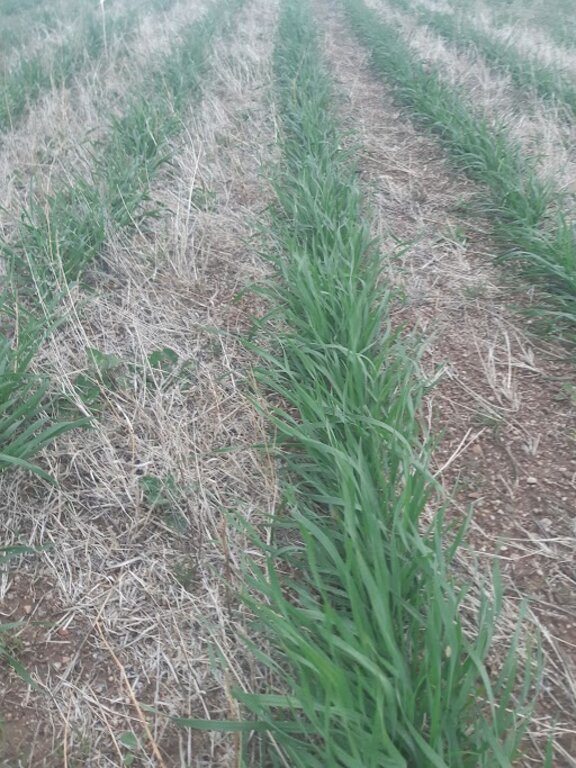
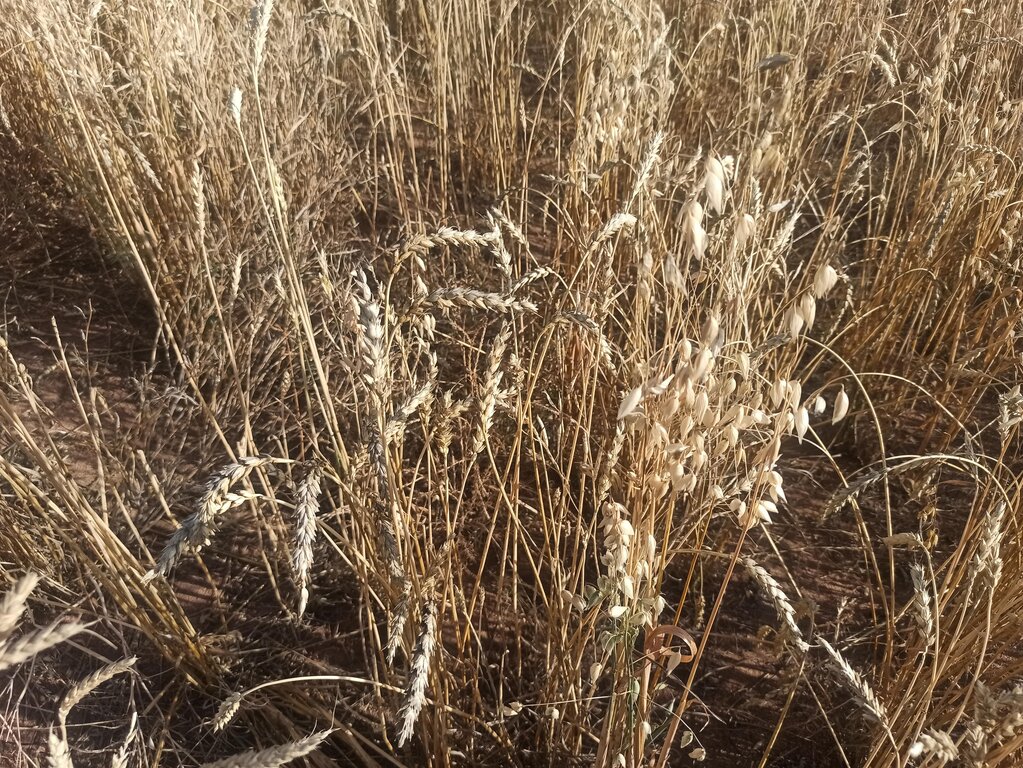
Mixed cropping encompasses various agrotechnical practices that involve the cultivation of different crops together, making use of their ability to interact with each other. The aim is to sustain crop yield in regions with limited moisture, protect the soil surface, regulate soil moisture levels, and enhance the availability of micro and macro-nutrients. In Kherlen soum, Khentii province, mixed cropping was implemented by planting seed mixtures of different proportions, taking into consideration the specific requirements and differences among various crops. Presently, annual crops such as mustard, peas, Cape rice, and wheat, rye along with rapeseeds, are successfully cultivated mixed and/or in rotation in the area.
Conservation agriculture in soil protection agriculture offers several advantages, including the enhancement of soil, its resilience to external factors such as erosion by wind, regulation of soil fertility and microorganism populations, avoidance of highly toxic substances in agriculture, and increased productivity. One significant aspect of conservation agriculture is using no-till and direct sowing techniques to minimize soil disturbance. During harvesting, only the crop heads are collected, while the remaining rootsystems and stems are left in and above the soil contributing to increasing soil organic matter. Other residues and parts of plants, such as straw/ stalks and leaves, are shredded and spread across the field to reduce soil moisture evaporation and protect it from the sun and wind. Soil erosion by wind can be mitigated by covering the soil as much and long as possible either by leaving the crop residues on the soil and/or including cover crops into crop rotations. Furthermore, this technology improves the soil health and microenvironment/ microclimate.
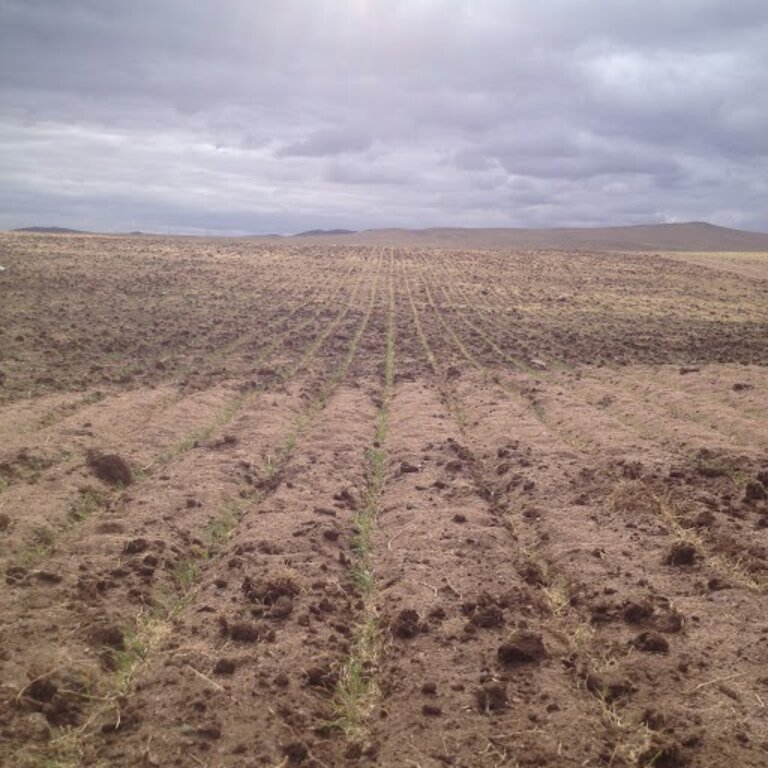
To initiate and implement this technology, the land user leased most of his land through a proposal, aimed at improving the soil quality of abandoned land, to the local government, and also purchased a certain amount of land through a land auction announced on the government website. Initial preparation of land for sowing consisted of removing stones from the field and spraying herbicides to get rid of weeds and their seeds. A minimal dose of herbicides with low toxicity is used to control the growth and spread of weed plants commonly found in abandoned fields. Later on mustard was incorporated into mixed cropping and rotations suppressing the growth of weed.
In the first year, the farmer planted a mixture of mustard, oilseed rape and lucerne to enhance soil penetration and break up compacted soil, as well as wheat in a 40 cm strip on stony soil with low fertility. First few years 2014-2018), the farmer didn’t harvest all the yields to keep the soil covered and improve the soil quality.
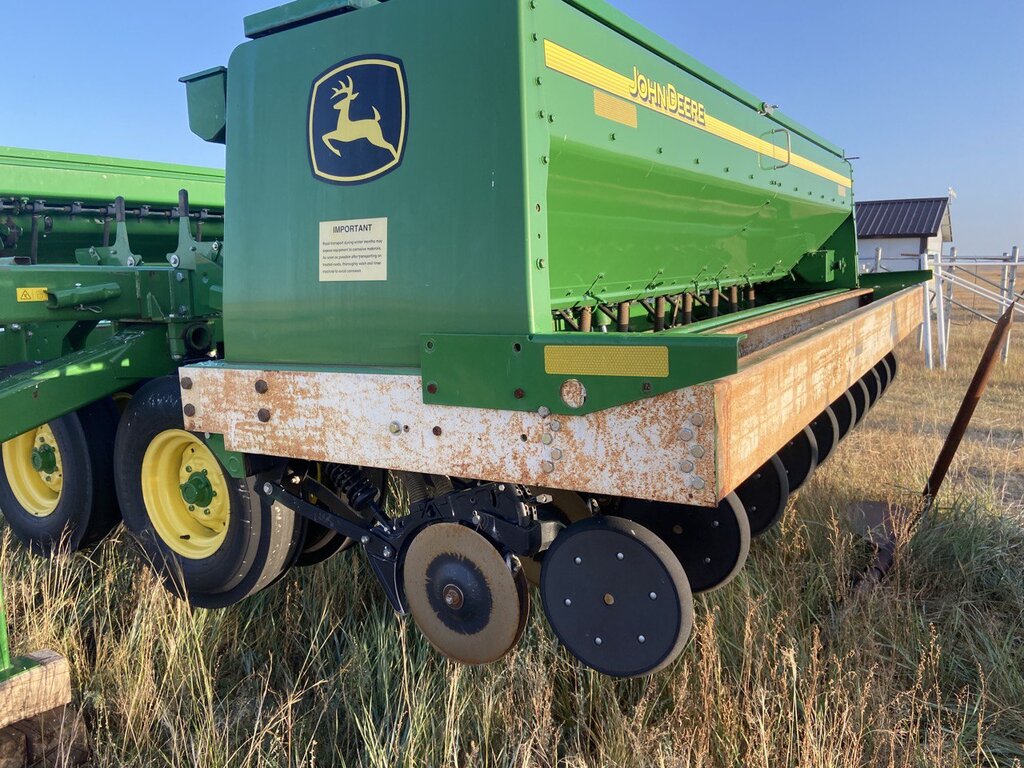
In 2019 the farmer built a fence to protect against grazing and yields significantly improved. Moreover, various equipment such as direct seeder for no till or minimum tillage crop cultivation, combine harvester, tractor, herbicide spraying machine and seed sorting machines to improve the quality of produce for the market (clean and separate seeds of different sizes and different types of crops) were bought with a bank loan.
A comprehensive knowledge of the interactions and symbiotic relationships between different crops is also essential to plan for crop mixtures and rotations. Crop morphology such as root system, competition for nutrients and water should be considered. Mustard-pea mixture facilitates harvesting as pea is difficult to harvest in monoculture and mustard can provide biological weed control.
He divided the land / field into 12 plots, which were planted with different crop mixtures and in rotation, maintaining soil fertility, limiting pests and diseases, and increasing crop yields. Legumes can improve soil fertility by adding nitrogen to the soil. The farmer practiced five-field rotation in his cropland using legumes including pea, bean, lentils and alfalfa. The rotation plan depends on climate conditions.
The levels of potassium and phosphorous in the soil were monitored and regularly measured. Only when a deficit occurred the land user used mineral fertilizers.
According to farmers who practice conservation agriculture and mixed farming, these technologies effectively maintains soil stability, ensuring its long-term sustainability.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Mongólia
Região/Estado/Província:
Khentii province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kherlen soum, Takhilgat bag
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
8,0
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The area is not a part of the permanently protected area.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
2014
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The farmer planted mustard, rapeseed, and alfalfa in rotation and mixture based on national and international experiences and research on conservation agriculture. These plants have taproot systems that penetrate the soil, enhance water uptake from lower soil depth and make the hardpan soil more porous. After implementing this technology, the land user observed and monitored the field himself. He observed that the retention of soil moisture has increased, soil erosion has significantly decreased, and biological diversity, including microorganisms, insects, and birds, has also increased due to the presence of cover plants.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preservar/melhorar a biodiversidade
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - cevada
- cereais - aveia
- cereais - trigo (primavera)
- culturas de fibras - linho, cânhamo, outros
- culturas forrageiras - alfalfa
- leguminosas e pulses - lentilhas
- legumes e leguminosas - ervilhas
- culturas oleaginosas - girassol, colza, outros
- culturas de sementes - sésamo, papoula, mostarda, outros
Sistema de cultivo anual:
Trigo ou rotação similar com feno/pasto
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Plant seeds are sown in April and harvested in August to September.
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Entire field/ area was divided into 5 main sections, allowing to practice crop rotation. In general, a rotation consists of cereal crops follow by broad leaved crops. Within one plot, the land user decides the mixture of crop depending on the weather condition in the year. If a mixture of mustard-wheat was planted in this year, another crop mixture should be planted in the next year.
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Sim (Por favor, preencha as perguntas abaixo com relação ao uso do solo antes da implementação da Tecnologia)
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra improdutiva
Especifique:
Abandoned land
Observações:
Monoculture crops were planted in the area during the socialist period, and it was left unused and abandoned since 1986. Therefore, the productivity and fertility of the land decreased.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Irrigation systems are not used throughout the field.
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo
- A5: Gestão de sementes, variedades melhoradas
- A6: Gerenciamento de resíduos
A3: Diferenciar os sistemas de lavoura:
A 3.1: Sem lavoura
A6: Especificar o gerenciamento de resíduos:
A 6.4: retido

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
Comentários:
Abandoned land had been converted into annual cropland. According to the classification of Mongolian Land Unified Fund, land was classified as abandoned land and changed into agricultural land after starting to use it.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
- Eo: efeitos de degradação externa

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Comentários:
The soil in the abandoned land became infertile due to water and wind erosion, and thus, there had been a decrease in biodiversity in the soil as well as in plant diversity and productivity.
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
The technology aims to revive the agricultural practice in abandoned cropland, protect the soil from erosion, enhance its moisture and organic matter, and improve biological diversity by planting a variety of plants, thereby allowing opportunities for long-term sustainable use.
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
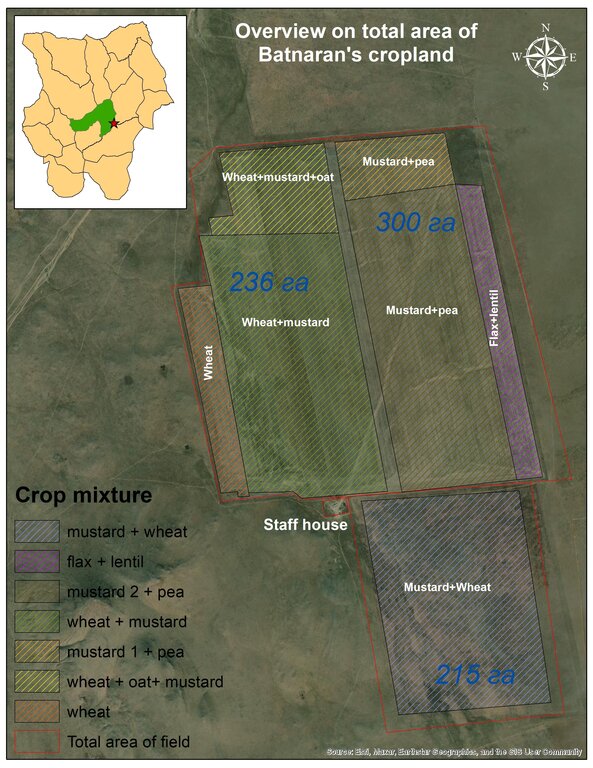
This diagram shows how the crop mix was distributed across the field in 2023 (on different plots). Entire field was divided into 5 main sections which are intended for crop rotation and also several small sections which are for ensuring seed source. More than 20 types of crops were planted in the whole field. A five-field rotation is practiced in this cropland with a sequence of cereal grains (wheat, barley, oats, etc.) followed by leafy plants (flax, lentils, peas, mustard, etc.), depending on the climatic conditions of the year. In dry years, the land user prefers to grow cereals and flax, which are more resistant to drought, and then rotate cereals with a mixture of leafy plants the following year. In years with good humidity, on the other hand, a mixture of mustard + peas + oats + lentils is suitable. The advantages of this mixture is to improve soil fertility and to control diseases and pest. In addition, soil remains covered against soil erosion. Inclusion of different crops means also increase in agrobiodiversity.
Autor:
Ankhbayar N., Gereltuya G.
Data:
02/10/2023
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
800 ha
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tugrik
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
3453,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
50000 - 100000 Tugrik
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Build fence | before sowing |
| 2. | Prepare (picking stones) and plough land | before sowing |
| 3. | Buy and spray herbicide | before sowing |
| 4. | Purchase tractor | before sowing |
| 5. | Purchase direct seeder | before sowing |
| 6. | Purchase combine harvester | before sowing |
| 7. | Purchase spray machine | before sowing |
| 8. | Purchase seed cleaning machine | before sowing |
| 9. | Purchase stone picker machine | before sowing |
| 10. | Purchase or rent pile machine for fencing | before sowing |
| 11. | Purchase silos | before harvesting |
| 12. | Storage shed | before harvesting |
Comentários:
Establishing a fence before the technology is an essential activity to protect from grazing and retain cover plants. The farmer empahsized that it is important to choose materials with good quality for building fence. He used imported fencing material from Canada of which the price was higher than average local market price.
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Build fence | person | 2,0 | 15000000,0 | 30000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Spray herbicide | person | 2,0 | 350000,0 | 700000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing | person | 1,0 | 4000000,0 | 4000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Stone picking | person | 1,0 | 4800000,0 | 4800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tractor | piece | 1,0 | 220000000,0 | 220000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Direct seeder | piece | 1,0 | 224000000,0 | 224000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Combine harvester | piece | 2,0 | 397000000,0 | 794000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Agriculture spray machine | piece | 1,0 | 170000000,0 | 170000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Stone picker machine | piece | 1,0 | 15000000,0 | 15000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Seed cleaning machine | piece | 3,0 | 35000000,0 | 105000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Pile machine for fencing | piece | 1,0 | 6900000,0 | 6900000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Silos | tonnes (holding capacity) | 700,0 | 714285,72 | 500000004,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds first year | tonnes | 70,5 | 4400000,0 | 310200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicide | l | 2400,0 | 8000,0 | 19200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Poles and net for fence | km | 25,0 | 10800000,0 | 270000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Land lease | ha | 800,0 | 500000,0 | 400000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 3073800004,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 890182,45 | |||||
Comentários:
The implementation of conservation agriculture and mixed cropping was self-funded by land user. For certain initial investments he took a loan from the bank. The fence materials were imported from Canada, for its good quality.
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing/ direct seeding | April to May per year |
| 2. | Harvesting and separating harvested seeds | once in August to September |
| 3. | Reproducing seed for own use and sowing | after harvest |
| 4. | Spray herbicide | if necessary, once in 2-3 year |
| 5. | Monitoring on plant development (e.g. germination, flowering, maturity) | at each plant development stage |
| 6. | Monitoring soil fertility | once a year, in August |
Comentários:
Soil samples are taken and sent to a specialized laboratory for analysis.
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Spray herbicide | person | 2,0 | 1400000,0 | 2800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Harvesting | person | 4,0 | 1500000,0 | 6000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Separating seeds | person | 2,0 | 1000000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing seeds | person | 2,0 | 1500000,0 | 3000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Spare parts and maintenance of machines | ha | 800,0 | 10500,0 | 8400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Spraying machine (fuel) | l/year | 400,0 | 2400,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Sowing machine (fuel) | l/year | 4000,0 | 2400,0 | 9600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Combine harvesting machine (fuel) | l/year | 4000,0 | 2400,0 | 9600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | tonne/year | 13,7 | 4400000,0 | 60280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicide (different types) | l | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Land use tax | MNT/year | 1,0 | 1900000,0 | 1900000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Soil sampling and testing | MNT/year | 1,0 | 830000,0 | 830000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 105400000,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 30524,18 | |||||
Comentários:
The amount of herbicide used in a given year depends on the type of weed and its distribution. Initially, the land user spent 19 million (2400 litres) on herbicide to prepare the field for cultivation, and the price was relatively low compared to today (8000 MNT on average). But, in 2022, different types of herbicides were bought for different types of weeds distributed in the field and 120 million MNT (1800 litres) were spent because the price became high compared to other years due to the border closure (COVID). But in 2023, only 30 000 MNT (1 litre) was spent on herbicides in the whole field.
The land user and a permanent help receive a monthly salary.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Factors that mainly affect the cost are inflation and the MNT exchange rate (mainly relevant when purchasing imported products). In addition, in the event of extreme weather and disastrous conditions, extra labor may be required to mitigate damage.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
150,00
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Undurkhaan
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
This region includes a region with harsh cold winters and dry summers. The average annual air temperature is -0.2 celsius, and the difference between day and night temperature ranges from 13 to 15 degrees.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
tanto de águas subterrâneas quanto de superfície
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
Regularidade:
Esporadicamente
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
It depends on intensity of rainfall.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Based on an animal and plant richness research study, biodiversity in this region is classified as moderate. After the implementation of the technology, more species of insects and birds were found in the fields due to the increase in agrobiodiversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Khentiin Tarialan LLC is a company with theland user and an aid are employed and with seasonally hired labour.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Based on standards, the area used by the land user is considered to be a medium-scale.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Não
Comentários:
Land is rented for a period of 15 years and when duration is over, the contract can be extended. Land users pay land use tax every year. Land use rights for agricultural production was leased by auction.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25 centner/ha
Comentários/especificar:
It is important to note that crop production is highly dependent on weather conditions. In 2021, when there was enough precipitation, a yield of 25 centner/ha was achieved. However, in 2014-2016, when technology implementation was just starting in severely degraded land and coincided with drought, there were occasions where all yield was lost.
Qualidade da safra
Comentários/especificar:
Specific weight, indicating seed quality, of grain reached 900 g/l and, gluten content of wheat always meets the requirements of first grade of food.
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Comparisons between 2018 and 2022 indicate that the average length of the wheat grain head increased and reached 10 - 12 centimeters by 1st July, resulting in a higher yield. Oats and wheat are harvested for fodder production while peas are supplied to chicken farms.
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
In terms of wheat quality, it is classified into first grade. The protein content of Bayalag variety of peas is 18-20%, starch content is 26-35%.
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
We concluded that this technology can overcome any risks related to labor and expenses, because sowing time is different for many types of crops, reducing the amount of expenses and labor load.
Diversidade de produtos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1
Quantidade posterior à GST:
20
Comentários/especificar:
About 20 species of plants are being cultivated.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
9 centner
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3 centner
Comentários/especificar:
The amount of seeds used for planting is lower, the seeds can be used for the next year cultivation: The spread of plant diseases / pests and use of pesticides is relatively low. Herbizides and fertilizers are not applied in this technology. Thus, there is no expense on that.
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5 centner
Comentários/especificar:
The yield is dependent on the climatic conditions of the year. In wheat yield, 3 centners were spent on sowing and 5 centners were obtained for each hectare when the weather was not favorable and precipitation was relatively low. Therefore, the net income is 2 centners in this case.
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
4
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2
Comentários/especificar:
Sowing time is different for many types of crops, so it does not requires a high number of labor. 2 persons typically work on the entire area throughout the year and, 2 more persons are employed during harvesting.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Mentorship program for other farmers is organized.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Due to cover crops and residue left on the soil, it reduces the amount of water evaporation from the soil and keeps the soil moisture .
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Cover crops and plant residues left on the soil surface protect against wind erosion, reduces soil water evaporation and improves soil moisture content.
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0 cm
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2 cm
Comentários/especificar:
Before the technology was introduced, the field was barely covered with plants and the topsoil had been severely eroded by the wind, resulting in a loss of fertility and covered with gravel.
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Snow cover in winter, has an important effect on protecting the soil from wind erosion in the spring.
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
It is believed that when the content of organic matter in the soil increases by 1 percent, the water holding capacity of the soil increases by 4 percent. From this point of view, it can be concluded that the content of organic matter has improved.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Before the technology, vegetation cover was sparse and there were only 2-3 species of weeds in a square of 1m x 1m.
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Aboveground biomass increased. Prairie sagebrush is predominating in natural vegetation community.
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
According to the results of soil sampling, the ratio of microorganisms in the soil has increased. It is also clearly observed that the variety of insects and the birds that feed on them have increased due to the rise in plant species.
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
From 2019, mushrooms started growing in the field. Flaxes, forming symbioses with fungus, are planted in order to enhance distribution of fungus in soil. Fungus has a positive effect on soil quality.
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Mustard and peas have been observed to limit the growth of weeds such as hogweed. Additionally, mustard releases two powerful substances that can help limit the spread of diseases.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Sown stands and plant cover can mitigate heavy flooding, then, the risk of washing away the fertile layer of the soil can be reduced. In addition, the stands will retain plant residues and other objects carried by the flood water. It can also be composted into the soil.
Impactos da seca
Quantidade anterior à GST:
high
Quantidade posterior à GST:
low
Comentários/especificar:
Because the soil moisture content is good compared to other areas, the yield is higher in drought years and soil erosion is less.
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
Wind velocity is high in this region. We are thinking about establishing windbreak in the field.
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos no local (medidas):
In winter, vertical stems of plants hold snow well. It has an important effect on soil protection and increasing soil moisture in spring.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
Improves wind cleanliness by catching organic material and other residues carried by the wind.
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
The technology can reduce the risk of flooding
Especificar a avaliação dos impactos fora do local (medidas):
The land user, implementing the technology, made a conclusion based on his own observations.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | verão | aumento | moderadamente |
| Temperatura sazonal | inverno | redução/diminuição | não bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | não bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | primavera | redução/diminuição | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tempestade de neve local | moderadamente |
| Tempestade de areia/tempestade de poeira | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Onde de calor | muito bem |
| Seca | muito bem |
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Establishment cost for 800 hectare of agricultural farm was approximately 3.6 billion MNT and there is no income in first several years. In long term, annual cost have decreased and, annual income became 320 million MNT, net income 128 million MNT. Thus, income can be positive in long term.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
1 household
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
All expenses were paid by own.
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mudança climática/extremo
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Crop rotation decisions are made based on spring weather conditions and soil moisture of the planting year. In some years, the crop rotation and mixture is not changed.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The technology provides higher yields than traditional monoculture in climate condition in Mongolia. |
| The technology allows to plant crops early in spring, because soil moisture absorbed from winter snow provide convenient condition. |
| Soil erosion and sand accumulation have been significantly reduced. |
| Conservation agricuture can significantly improve the physical properties of soil, providing sustainable and ecological rehabilitation of abandoned land. |
| Over time, soil fertility should improve as a result of increased soil organic matter. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Abandoned land can be restored at the lowest cost. |
| Soil conservation technology was used without reducing the soil fertility as well as returning of abandoned land into use. |
| The use of machinery in medium-scale farming is advantageous because it reduces labor costs. |
| Planting with low seed rates increases the economic efficiency in the long term. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Due to climate change and aridity, in some years, crop loss occurs during the planting and growing period. | Install irrigation system for seasonal irrigation or irrigation when needed. |
| When harvesting, it is necessary to leave a plant cover as high as possible, which requires particular harvesting machine. | A combine harvester or a machine (head stripper) that collects only heads of the crop is required. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do compilador ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The use of imported seeds increases the cost. | To cultivate crop seeds in small isolated areas. |
| With climate change, the lack of irrigation facilities increases risk of production failure. | More water harvesting techniiques and soil moisture conservation/accumulation technologies to be identified and implemented. Installation of an irrigation system for supplementary irrigation or irrigation when needed. |
| It is difficult to separate the seeds after harvesting due to the lack of techniques and appropriate equipement. Sorted seeds will increase market value. | Improve seed sorting mechanism. |
| Due to the lack of appriopriate harvesting equipment, the crop cannot be harvested completely. | Buy a new type of combine harvester or rent from others. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
The information was acquired from land users who adopted the technology.
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
02/10/2023
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Guidelines for Intercropping. Charles L. Mohler, Sue Ellen Johnson. 2009. ISBN 978-1-933395-21-0
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.sare.org/wp-content/uploads/Crop-Rotation-on-Organic-Farms.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, Reference Work. Second Edition. 2013. ISBN 978-0123847195
Disponível de onde? Custos?
https://www.amazon.com/Encyclopedia-Biodiversity-2nd-Set/dp/0123847192
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Intercropping: benefits and types
URL:
https://geopard.tech/blog/what-is-intercropping-and-how-does-it-work/
Título/ descrição:
Intercropping: Ergonomic And Efficient Farming
URL:
https://eos.com/blog/intercropping/
Título/ descrição:
INTERCROPPING
URL:
http://nwrm.eu/measure/intercropping
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos