Conservation agriculture to restore abandoned cropland [Mongolie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Otgontsetseg Davaanyam
- Rédacteur : Mandakh Nyamtseren
- Examinateur : Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Khurs Khamgaalliin gazar tarialan
technologies_6938 - Mongolie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Personne(s)-ressource(s) clé(s)
exploitant des terres:
Batdeleg Batnaran
Khentiin Tarialan LLC
Mongolie
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
Mongolian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Geography and Geoecology (IGG) - Mongolie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.4 Déclaration sur la durabilité de la Technologie décrite
Est-ce que la Technologie décrite ici pose problème par rapport à la dégradation des terres, de telle sorte qu'elle ne peut pas être déclarée comme étant une technologie de gestion durable des terres?
Non
Commentaires:
This technology is a SLM technology, because it returned abandoned land to productive agricultural land while building up soil health.
1.5 Référence au(x) Questionnaires sur les Approches de GDT (documentées au moyen de WOCAT)
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
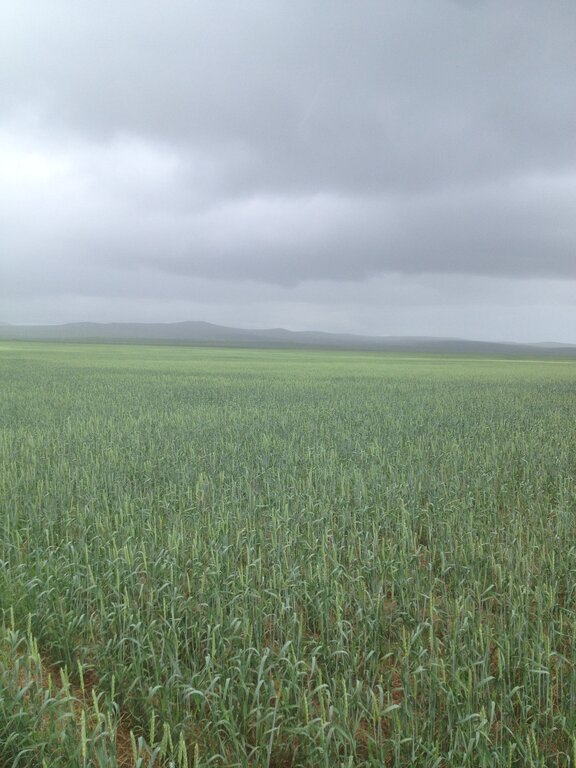
This technology aimed to restore abandoned cropland which was used for crop and fodder production during the 1970s-1980s. Since 2016, the farmer applied conservation agriculture and mixed cropping to reduce land degradation, revive cropping practices, increase land productivity for agriculture and enhance soil health.
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
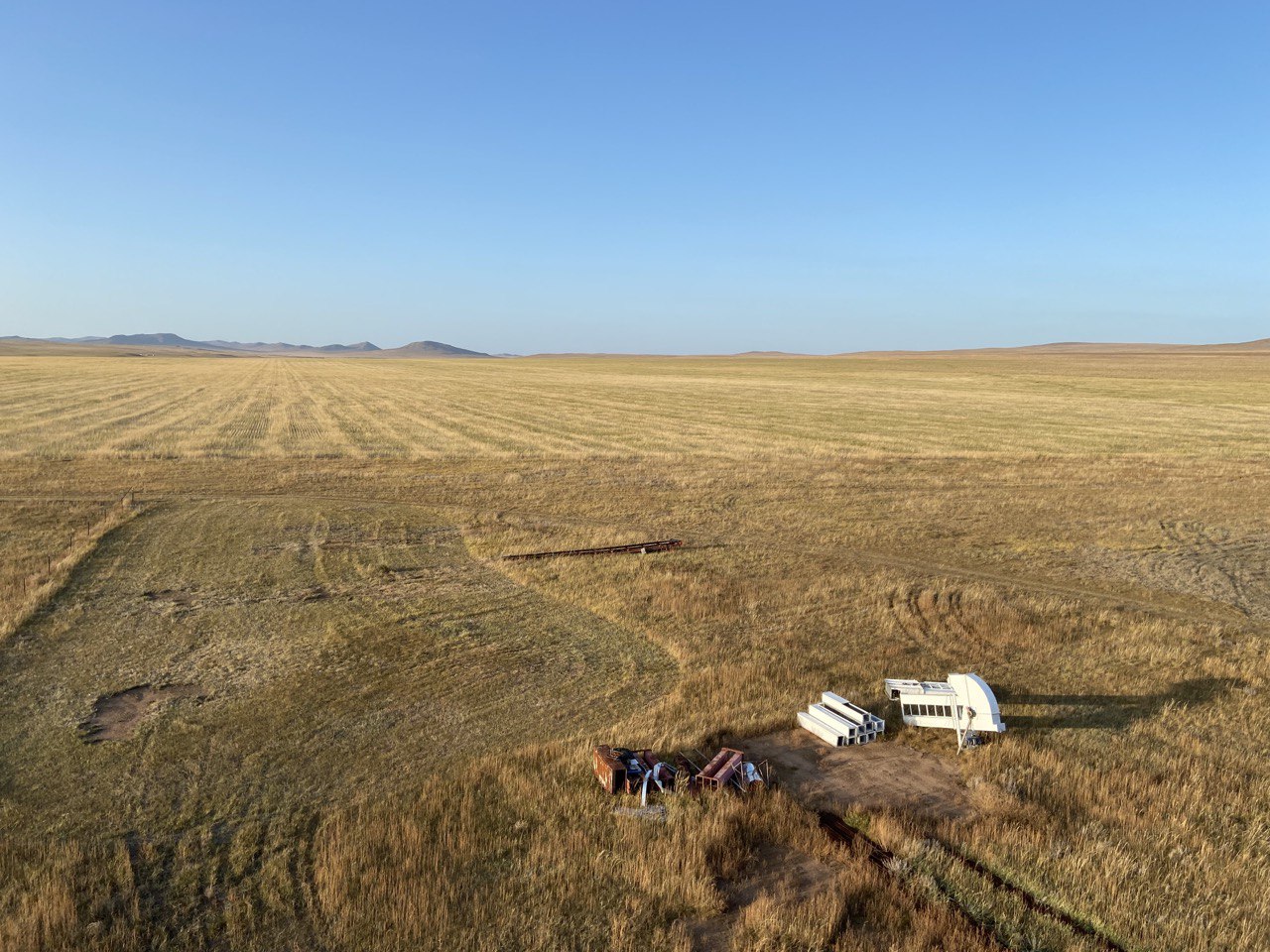
The land in Kherlen soum, Khentii province, spanning 500 hectares, was used for crop production and later for producing fodder for livestock. However, since 1984, it has been left abandoned. To rehabilitate the area and revive cropland, conservation agriculture combined with mixed cropping was introduced in 2014.
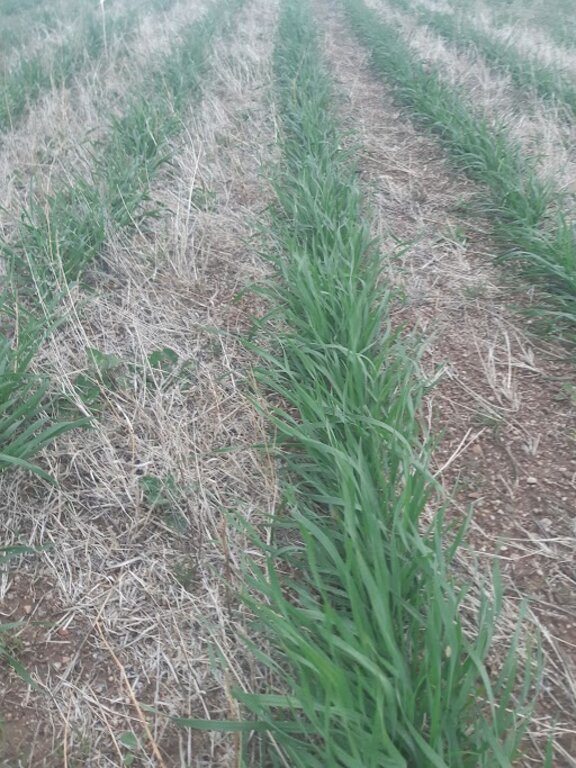
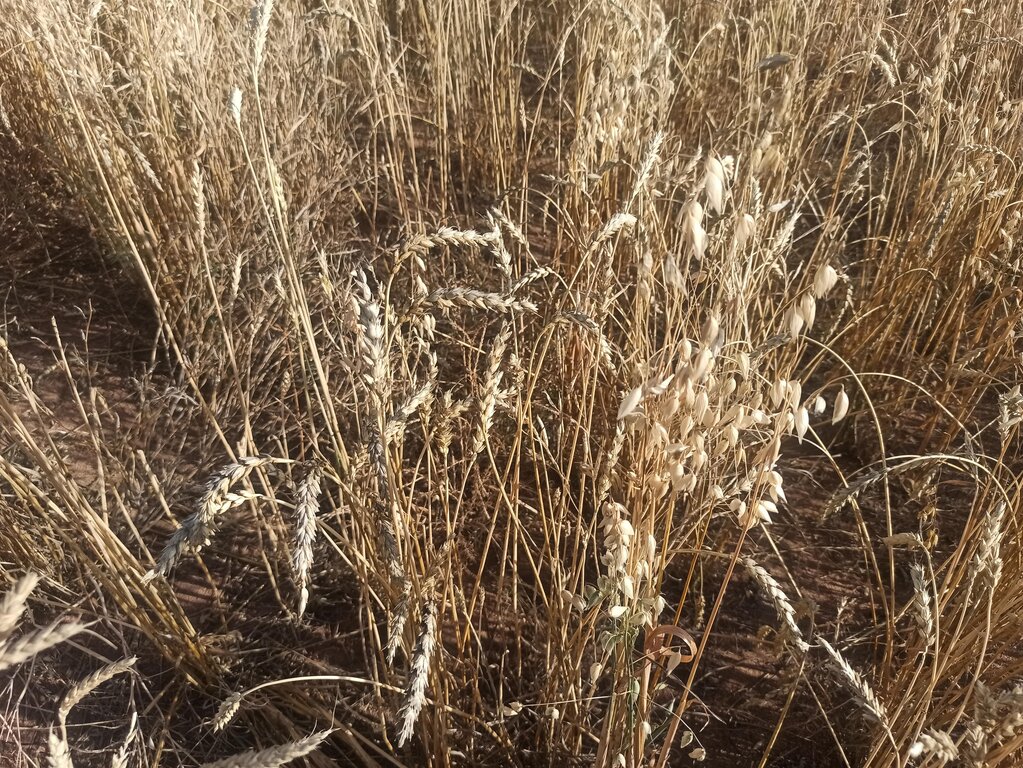
Mixed cropping encompasses various agrotechnical practices that involve the cultivation of different crops together, making use of their ability to interact with each other. The aim is to sustain crop yield in regions with limited moisture, protect the soil surface, regulate soil moisture levels, and enhance the availability of micro and macro-nutrients. In Kherlen soum, Khentii province, mixed cropping was implemented by planting seed mixtures of different proportions, taking into consideration the specific requirements and differences among various crops. Presently, annual crops such as mustard, peas, Cape rice, and wheat, rye along with rapeseeds, are successfully cultivated mixed and/or in rotation in the area.
Conservation agriculture in soil protection agriculture offers several advantages, including the enhancement of soil, its resilience to external factors such as erosion by wind, regulation of soil fertility and microorganism populations, avoidance of highly toxic substances in agriculture, and increased productivity. One significant aspect of conservation agriculture is using no-till and direct sowing techniques to minimize soil disturbance. During harvesting, only the crop heads are collected, while the remaining rootsystems and stems are left in and above the soil contributing to increasing soil organic matter. Other residues and parts of plants, such as straw/ stalks and leaves, are shredded and spread across the field to reduce soil moisture evaporation and protect it from the sun and wind. Soil erosion by wind can be mitigated by covering the soil as much and long as possible either by leaving the crop residues on the soil and/or including cover crops into crop rotations. Furthermore, this technology improves the soil health and microenvironment/ microclimate.
To initiate and implement this technology, the land user leased most of his land through a proposal, aimed at improving the soil quality of abandoned land, to the local government, and also purchased a certain amount of land through a land auction announced on the government website. Initial preparation of land for sowing consisted of removing stones from the field and spraying herbicides to get rid of weeds and their seeds. A minimal dose of herbicides with low toxicity is used to control the growth and spread of weed plants commonly found in abandoned fields. Later on mustard was incorporated into mixed cropping and rotations suppressing the growth of weed.
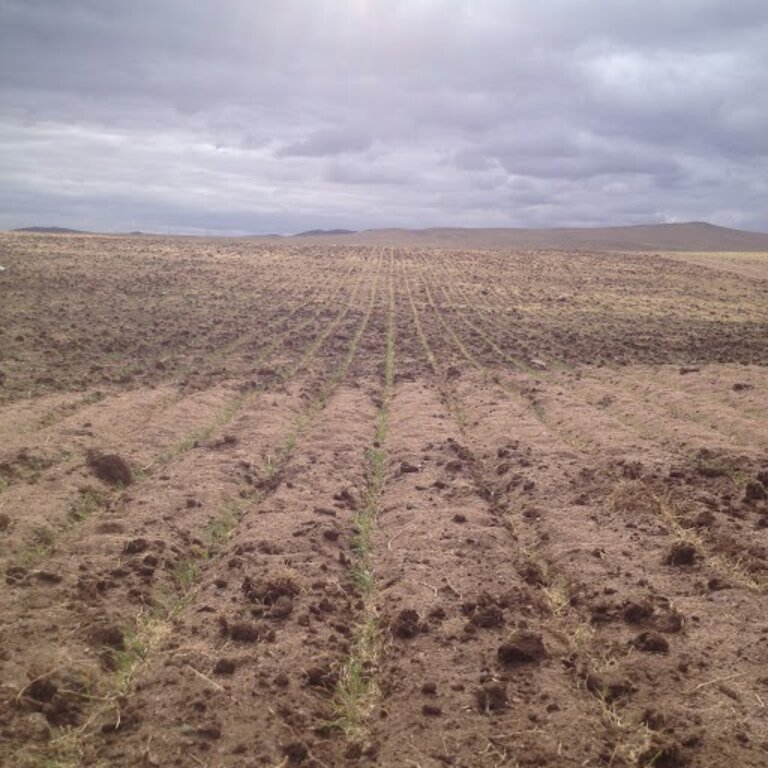
In the first year, the farmer planted a mixture of mustard, oilseed rape and lucerne to enhance soil penetration and break up compacted soil, as well as wheat in a 40 cm strip on stony soil with low fertility. First few years 2014-2018), the farmer didn’t harvest all the yields to keep the soil covered and improve the soil quality.
In 2019 the farmer built a fence to protect against grazing and yields significantly improved. Moreover, various equipment such as direct seeder for no till or minimum tillage crop cultivation, combine harvester, tractor, herbicide spraying machine and seed sorting machines to improve the quality of produce for the market (clean and separate seeds of different sizes and different types of crops) were bought with a bank loan.
A comprehensive knowledge of the interactions and symbiotic relationships between different crops is also essential to plan for crop mixtures and rotations. Crop morphology such as root system, competition for nutrients and water should be considered. Mustard-pea mixture facilitates harvesting as pea is difficult to harvest in monoculture and mustard can provide biological weed control.
He divided the land / field into 12 plots, which were planted with different crop mixtures and in rotation, maintaining soil fertility, limiting pests and diseases, and increasing crop yields. Legumes can improve soil fertility by adding nitrogen to the soil. The farmer practiced five-field rotation in his cropland using legumes including pea, bean, lentils and alfalfa. The rotation plan depends on climate conditions.
The levels of potassium and phosphorous in the soil were monitored and regularly measured. Only when a deficit occurred the land user used mineral fertilizers.
According to farmers who practice conservation agriculture and mixed farming, these technologies effectively maintains soil stability, ensuring its long-term sustainability.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Mongolie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Khentii province
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Kherlen soum, Takhilgat bag
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
Si la Technologie est uniformément répartie sur une zone, précisez la superficie couverte (en km2):
8,0
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- 1-10 km2
Est-ce que les sites dans lesquels la Technologie est appliquée sont situés dans des zones protégées en permanence?
Non
Commentaires:
The area is not a part of the permanently protected area.
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Indiquez l'année de mise en œuvre:
2014
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a moins de 10 ans (récemment)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- grâce à l'innovation d'exploitants des terres
- au cours d'expérimentations / de recherches
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The farmer planted mustard, rapeseed, and alfalfa in rotation and mixture based on national and international experiences and research on conservation agriculture. These plants have taproot systems that penetrate the soil, enhance water uptake from lower soil depth and make the hardpan soil more porous. After implementing this technology, the land user observed and monitored the field himself. He observed that the retention of soil moisture has increased, soil erosion has significantly decreased, and biological diversity, including microorganisms, insects, and birds, has also increased due to the presence of cover plants.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.1 Principal(aux) objectif(s) de la Technologie
- améliorer la production
- réduire, prévenir, restaurer les terres dégradées
- conserver/ améliorer la biodiversité
- s'adapter au changement et aux extrêmes climatiques et à leurs impacts
- créer un impact économique positif
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres cultivées
- Cultures annuelles
Cultures annuelles - Précisez les cultures:
- céréales - orge
- céréales - avoine
- céréales - blé de printemps
- cultures de plantes à fibres - lin, chanvre, autres
- cultures fourragères - luzerne
- legumes and pulses - lentils
- légumineuses et légumes secs - pois
- cultures oléagineuses - tournesol, colza, autres
- cultures de semences - sésame, moutarde, pavot, autres
Système de cultures annuelles :
Blé ou rotation similaire de foin/pâturage
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Plant seeds are sown in April and harvested in August to September.
Est-ce que les cultures intercalaires sont pratiquées?
Non
Est-ce que la rotation des cultures est appliquée?
Oui
Si oui, veuillez préciser:
Entire field/ area was divided into 5 main sections, allowing to practice crop rotation. In general, a rotation consists of cereal crops follow by broad leaved crops. Within one plot, the land user decides the mixture of crop depending on the weather condition in the year. If a mixture of mustard-wheat was planted in this year, another crop mixture should be planted in the next year.
3.3 Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
Est-ce que l’utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie ?
- Oui (Veuillez remplir les questions ci-après au regard de l’utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie)
Les divers types d'utilisation des terres au sein du même unité de terrain: :
Non

Terres improductives
Précisez:
Abandoned land
Remarques:
Monoculture crops were planted in the area during the socialist period, and it was left unused and abandoned since 1986. Therefore, the productivity and fertility of the land decreased.
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Commentaires:
Irrigation systems are not used throughout the field.
3.5 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- système de rotation (rotation des cultures, jachères, agriculture itinérante)
- Amélioration de la couverture végétale/ du sol
- perturbation minimale du sol
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
- A5: Gestion des semences, amélioration des variétés
- A6: Gestion des résidus des cultures
A3: Différenciez les systèmes de travail du sol:
A 3.1: Systèmes de culture sans travail du sol
A6: Précisez la gestion des résidus des cultures:
A 6.5: Résidus retenus

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
Commentaires:
Abandoned land had been converted into annual cropland. According to the classification of Mongolian Land Unified Fund, land was classified as abandoned land and changed into agricultural land after starting to use it.
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion éolienne des sols
- Et: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)
- Eo: effets hors site de la dégradation

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
- Bq: baisse de la quantité/ biomasse
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
The soil in the abandoned land became infertile due to water and wind erosion, and thus, there had been a decrease in biodiversity in the soil as well as in plant diversity and productivity.
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- restaurer/ réhabiliter des terres sévèrement dégradées
Commentaires:
The technology aims to revive the agricultural practice in abandoned cropland, protect the soil from erosion, enhance its moisture and organic matter, and improve biological diversity by planting a variety of plants, thereby allowing opportunities for long-term sustainable use.
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
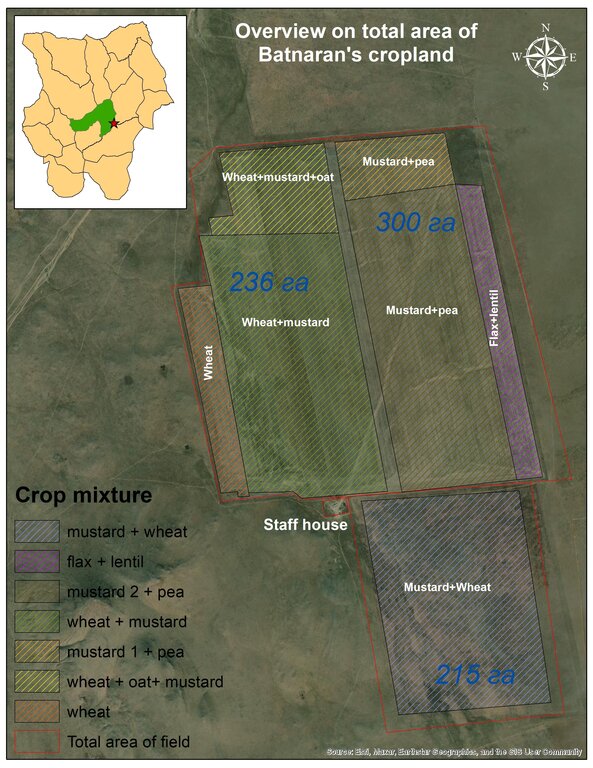
This diagram shows how the crop mix was distributed across the field in 2023 (on different plots). Entire field was divided into 5 main sections which are intended for crop rotation and also several small sections which are for ensuring seed source. More than 20 types of crops were planted in the whole field. A five-field rotation is practiced in this cropland with a sequence of cereal grains (wheat, barley, oats, etc.) followed by leafy plants (flax, lentils, peas, mustard, etc.), depending on the climatic conditions of the year. In dry years, the land user prefers to grow cereals and flax, which are more resistant to drought, and then rotate cereals with a mixture of leafy plants the following year. In years with good humidity, on the other hand, a mixture of mustard + peas + oats + lentils is suitable. The advantages of this mixture is to improve soil fertility and to control diseases and pest. In addition, soil remains covered against soil erosion. Inclusion of different crops means also increase in agrobiodiversity.
Auteur:
Ankhbayar N., Gereltuya G.
Date:
02/10/2023
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Spécifiez la manière dont les coûts et les intrants ont été calculés:
- par superficie de la Technologie
Indiquez la taille et l'unité de surface:
800 ha
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tugrik
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
3453,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
50000 - 100000 Tugrik
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Build fence | before sowing |
| 2. | Prepare (picking stones) and plough land | before sowing |
| 3. | Buy and spray herbicide | before sowing |
| 4. | Purchase tractor | before sowing |
| 5. | Purchase direct seeder | before sowing |
| 6. | Purchase combine harvester | before sowing |
| 7. | Purchase spray machine | before sowing |
| 8. | Purchase seed cleaning machine | before sowing |
| 9. | Purchase stone picker machine | before sowing |
| 10. | Purchase or rent pile machine for fencing | before sowing |
| 11. | Purchase silos | before harvesting |
| 12. | Storage shed | before harvesting |
Commentaires:
Establishing a fence before the technology is an essential activity to protect from grazing and retain cover plants. The farmer empahsized that it is important to choose materials with good quality for building fence. He used imported fencing material from Canada of which the price was higher than average local market price.
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Build fence | person | 2,0 | 15000000,0 | 30000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Spray herbicide | person | 2,0 | 350000,0 | 700000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Sowing | person | 1,0 | 4000000,0 | 4000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Stone picking | person | 1,0 | 4800000,0 | 4800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Tractor | piece | 1,0 | 220000000,0 | 220000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Direct seeder | piece | 1,0 | 224000000,0 | 224000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Combine harvester | piece | 2,0 | 397000000,0 | 794000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Agriculture spray machine | piece | 1,0 | 170000000,0 | 170000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Stone picker machine | piece | 1,0 | 15000000,0 | 15000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Seed cleaning machine | piece | 3,0 | 35000000,0 | 105000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Pile machine for fencing | piece | 1,0 | 6900000,0 | 6900000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Silos | tonnes (holding capacity) | 700,0 | 714285,72 | 500000004,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds first year | tonnes | 70,5 | 4400000,0 | 310200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Herbicide | l | 2400,0 | 8000,0 | 19200000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériaux de construction | Poles and net for fence | km | 25,0 | 10800000,0 | 270000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Land lease | ha | 800,0 | 500000,0 | 400000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 3073800004,0 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 890182,45 | |||||
Commentaires:
The implementation of conservation agriculture and mixed cropping was self-funded by land user. For certain initial investments he took a loan from the bank. The fence materials were imported from Canada, for its good quality.
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Sowing/ direct seeding | April to May per year |
| 2. | Harvesting and separating harvested seeds | once in August to September |
| 3. | Reproducing seed for own use and sowing | after harvest |
| 4. | Spray herbicide | if necessary, once in 2-3 year |
| 5. | Monitoring on plant development (e.g. germination, flowering, maturity) | at each plant development stage |
| 6. | Monitoring soil fertility | once a year, in August |
Commentaires:
Soil samples are taken and sent to a specialized laboratory for analysis.
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Spray herbicide | person | 2,0 | 1400000,0 | 2800000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Harvesting | person | 4,0 | 1500000,0 | 6000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Separating seeds | person | 2,0 | 1000000,0 | 2000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Main d'œuvre | Sowing seeds | person | 2,0 | 1500000,0 | 3000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spare parts and maintenance of machines | ha | 800,0 | 10500,0 | 8400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Spraying machine (fuel) | l/year | 400,0 | 2400,0 | 960000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Sowing machine (fuel) | l/year | 4000,0 | 2400,0 | 9600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipements | Combine harvesting machine (fuel) | l/year | 4000,0 | 2400,0 | 9600000,0 | 100,0 |
| Matériel végétal | Seeds | tonne/year | 13,7 | 4400000,0 | 60280000,0 | 100,0 |
| Engrais et biocides | Herbicide (different types) | l | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Land use tax | MNT/year | 1,0 | 1900000,0 | 1900000,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Soil sampling and testing | MNT/year | 1,0 | 830000,0 | 830000,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 105400000,0 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 30524,18 | |||||
Commentaires:
The amount of herbicide used in a given year depends on the type of weed and its distribution. Initially, the land user spent 19 million (2400 litres) on herbicide to prepare the field for cultivation, and the price was relatively low compared to today (8000 MNT on average). But, in 2022, different types of herbicides were bought for different types of weeds distributed in the field and 120 million MNT (1800 litres) were spent because the price became high compared to other years due to the border closure (COVID). But in 2023, only 30 000 MNT (1 litre) was spent on herbicides in the whole field.
The land user and a permanent help receive a monthly salary.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Factors that mainly affect the cost are inflation and the MNT exchange rate (mainly relevant when purchasing imported products). In addition, in the event of extreme weather and disastrous conditions, extra labor may be required to mitigate damage.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifiez la pluviométrie moyenne annuelle (si connue), en mm:
150,00
Indiquez le nom de la station météorologique de référence considérée:
Undurkhaan
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
This region includes a region with harsh cold winters and dry summers. The average annual air temperature is -0.2 celsius, and the difference between day and night temperature ranges from 13 to 15 degrees.
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Indiquez si la Technologie est spécifiquement appliquée dans des:
- situations concaves
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Texture du sol (> 20 cm sous la surface):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
5-50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
La qualité de l'eau fait référence à:
à la fois les eaux souterraines et de surface
La salinité de l'eau est-elle un problème? :
Non
La zone est-elle inondée?
Oui
Régularité:
épisodiquement
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
It depends on intensity of rainfall.
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
Diversité des habitats:
- faible
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Based on an animal and plant richness research study, biodiversity in this region is classified as moderate. After the implementation of the technology, more species of insects and birds were found in the fields due to the increase in agrobiodiversity.
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Sédentaire
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- employé (entreprise, gouvernement)
Niveau de mécanisation:
- mécanisé/ motorisé
Genre:
- hommes
Age des exploitants des terres:
- personnes d'âge moyen
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Khentiin Tarialan LLC is a company with theland user and an aid are employed and with seasonally hired labour.
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- moyenne dimension
Commentaires:
Based on standards, the area used by the land user is considered to be a medium-scale.
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- individuel
Est-ce que les droits d'utilisation des terres sont fondés sur un système juridique traditionnel?
Non
Commentaires:
Land is rented for a period of 15 years and when duration is over, the contract can be extended. Land users pay land use tax every year. Land use rights for agricultural production was leased by auction.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
0
Quantité après la GDT:
25 centner/ha
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is important to note that crop production is highly dependent on weather conditions. In 2021, when there was enough precipitation, a yield of 25 centner/ha was achieved. However, in 2014-2016, when technology implementation was just starting in severely degraded land and coincided with drought, there were occasions where all yield was lost.
qualité des cultures
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Specific weight, indicating seed quality, of grain reached 900 g/l and, gluten content of wheat always meets the requirements of first grade of food.
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Comparisons between 2018 and 2022 indicate that the average length of the wheat grain head increased and reached 10 - 12 centimeters by 1st July, resulting in a higher yield. Oats and wheat are harvested for fodder production while peas are supplied to chicken farms.
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
In terms of wheat quality, it is classified into first grade. The protein content of Bayalag variety of peas is 18-20%, starch content is 26-35%.
risque d'échec de la production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
We concluded that this technology can overcome any risks related to labor and expenses, because sowing time is different for many types of crops, reducing the amount of expenses and labor load.
diversité des produits
Quantité avant la GDT:
1
Quantité après la GDT:
20
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
About 20 species of plants are being cultivated.
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
9 centner
Quantité après la GDT:
3 centner
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The amount of seeds used for planting is lower, the seeds can be used for the next year cultivation: The spread of plant diseases / pests and use of pesticides is relatively low. Herbizides and fertilizers are not applied in this technology. Thus, there is no expense on that.
revenus agricoles
Quantité après la GDT:
5 centner
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The yield is dependent on the climatic conditions of the year. In wheat yield, 3 centners were spent on sowing and 5 centners were obtained for each hectare when the weather was not favorable and precipitation was relatively low. Therefore, the net income is 2 centners in this case.
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
4
Quantité après la GDT:
2
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Sowing time is different for many types of crops, so it does not requires a high number of labor. 2 persons typically work on the entire area throughout the year and, 2 more persons are employed during harvesting.
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mentorship program for other farmers is organized.
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
évaporation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to cover crops and residue left on the soil, it reduces the amount of water evaporation from the soil and keeps the soil moisture .
Sols
humidité du sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Cover crops and plant residues left on the soil surface protect against wind erosion, reduces soil water evaporation and improves soil moisture content.
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
0 cm
Quantité après la GDT:
2 cm
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before the technology was introduced, the field was barely covered with plants and the topsoil had been severely eroded by the wind, resulting in a loss of fertility and covered with gravel.
perte en sol
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Snow cover in winter, has an important effect on protecting the soil from wind erosion in the spring.
cycle/ recharge des éléments nutritifs
matière organique du sol/ au dessous du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
It is believed that when the content of organic matter in the soil increases by 1 percent, the water holding capacity of the soil increases by 4 percent. From this point of view, it can be concluded that the content of organic matter has improved.
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
Couverture végétale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Before the technology, vegetation cover was sparse and there were only 2-3 species of weeds in a square of 1m x 1m.
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Aboveground biomass increased. Prairie sagebrush is predominating in natural vegetation community.
diversité végétale
diversité animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
According to the results of soil sampling, the ratio of microorganisms in the soil has increased. It is also clearly observed that the variety of insects and the birds that feed on them have increased due to the rise in plant species.
espèces bénéfiques
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
From 2019, mushrooms started growing in the field. Flaxes, forming symbioses with fungus, are planted in order to enhance distribution of fungus in soil. Fungus has a positive effect on soil quality.
contrôle des animaux nuisibles/ maladies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Mustard and peas have been observed to limit the growth of weeds such as hogweed. Additionally, mustard releases two powerful substances that can help limit the spread of diseases.
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
impacts des inondations
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Sown stands and plant cover can mitigate heavy flooding, then, the risk of washing away the fertile layer of the soil can be reduced. In addition, the stands will retain plant residues and other objects carried by the flood water. It can also be composted into the soil.
impacts de la sécheresse
Quantité avant la GDT:
high
Quantité après la GDT:
low
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Because the soil moisture content is good compared to other areas, the yield is higher in drought years and soil erosion is less.
vitesse du vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Wind velocity is high in this region. We are thinking about establishing windbreak in the field.
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts sur site (sous forme de mesures):
In winter, vertical stems of plants hold snow well. It has an important effect on soil protection and increasing soil moisture in spring.
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
sédiments (indésirables) transportés par le vent
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Improves wind cleanliness by catching organic material and other residues carried by the wind.
dommages sur les champs voisins
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The technology can reduce the risk of flooding
Précisez l'évaluation des impacts extérieurs (sous forme de mesures):
The land user, implementing the technology, made a conclusion based on his own observations.
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien | |
| températures saisonnières | été | augmente | modérément |
| températures saisonnières | hiver | décroît | pas bien |
| précipitations saisonnières | été | décroît | pas bien |
| précipitations saisonnières | printemps | décroît | modérément |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| tempête de neige locale | modérément |
| tempête de sable/ de poussière locale | pas bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| canicule | très bien |
| sécheresse | très bien |
Catastrophes biologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| maladies épidémiques | bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas bien |
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
négative
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
Establishment cost for 800 hectare of agricultural farm was approximately 3.6 billion MNT and there is no income in first several years. In long term, annual cost have decreased and, annual income became 320 million MNT, net income 128 million MNT. Thus, income can be positive in long term.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1 household
De tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle, ou aucune rémunération? :
- 91-100%
Commentaires:
All expenses were paid by own.
6.6 Adaptation
La Technologie a-t-elle été récemment modifiée pour s'adapter à l'évolution des conditions?
Oui
Si oui, indiquez à quel changement la Technologie s'est adaptée:
- changements/ extrêmes climatiques
Spécifiez l'adaptation de la Technologie (conception, matériaux/ espèces, etc.):
Crop rotation decisions are made based on spring weather conditions and soil moisture of the planting year. In some years, the crop rotation and mixture is not changed.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
| The technology provides higher yields than traditional monoculture in climate condition in Mongolia. |
| The technology allows to plant crops early in spring, because soil moisture absorbed from winter snow provide convenient condition. |
| Soil erosion and sand accumulation have been significantly reduced. |
| Conservation agricuture can significantly improve the physical properties of soil, providing sustainable and ecological rehabilitation of abandoned land. |
| Over time, soil fertility should improve as a result of increased soil organic matter. |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
| Abandoned land can be restored at the lowest cost. |
| Soil conservation technology was used without reducing the soil fertility as well as returning of abandoned land into use. |
| The use of machinery in medium-scale farming is advantageous because it reduces labor costs. |
| Planting with low seed rates increases the economic efficiency in the long term. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Due to climate change and aridity, in some years, crop loss occurs during the planting and growing period. | Install irrigation system for seasonal irrigation or irrigation when needed. |
| When harvesting, it is necessary to leave a plant cover as high as possible, which requires particular harvesting machine. | A combine harvester or a machine (head stripper) that collects only heads of the crop is required. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The use of imported seeds increases the cost. | To cultivate crop seeds in small isolated areas. |
| With climate change, the lack of irrigation facilities increases risk of production failure. | More water harvesting techniiques and soil moisture conservation/accumulation technologies to be identified and implemented. Installation of an irrigation system for supplementary irrigation or irrigation when needed. |
| It is difficult to separate the seeds after harvesting due to the lack of techniques and appropriate equipement. Sorted seeds will increase market value. | Improve seed sorting mechanism. |
| Due to the lack of appriopriate harvesting equipment, the crop cannot be harvested completely. | Buy a new type of combine harvester or rent from others. |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
- interviews/entretiens avec les exploitants des terres
The information was acquired from land users who adopted the technology.
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
02/10/2023
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Guidelines for Intercropping. Charles L. Mohler, Sue Ellen Johnson. 2009. ISBN 978-1-933395-21-0
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.sare.org/wp-content/uploads/Crop-Rotation-on-Organic-Farms.pdf
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, Reference Work. Second Edition. 2013. ISBN 978-0123847195
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
https://www.amazon.com/Encyclopedia-Biodiversity-2nd-Set/dp/0123847192
7.3 Liens vers les informations pertinentes en ligne
Titre/ description:
Intercropping: benefits and types
URL:
https://geopard.tech/blog/what-is-intercropping-and-how-does-it-work/
Titre/ description:
Intercropping: Ergonomic And Efficient Farming
URL:
https://eos.com/blog/intercropping/
Titre/ description:
INTERCROPPING
URL:
http://nwrm.eu/measure/intercropping
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé