Integrated watershed management for landslip and stream bank stabilisation [Непал]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Dileep Kumar Karna
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Pahiro ra nadikinar katan roktham ka lagi ekikrit jaladhar byabasthapan (Nepali)
approaches_2354 - Непал
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Подхода
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Специалист по УЗП:
Название проекта, содействовавшего документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development (G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development) - ИндияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - НепалНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Подхода (если применимо)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Швейцария1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование собранных ВОКАТ данных
Составитель и ответственный/-ые специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Ссылка (-и) на Анкету (-ы) по Технологиям УЗП
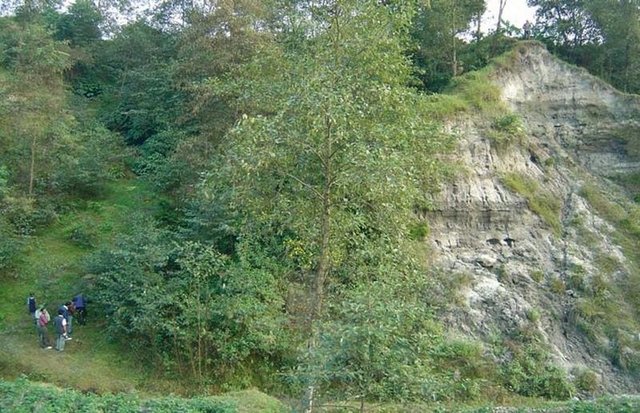

Landslip and stream bank stabilisation [Непал]
Integration of vegetative and structural measures for landslip, stream bank and gully stabilisation on hillsides.
- Составитель: Dileep Kumar Karna
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Подхода
Integrated watershed management as an example for landslip and stream bank stabilisation based on fostering a partnership between community institutions, line agencies, district authorities and consultants
2.2 Подробное описание Подхода
Подробное описание Подхода:
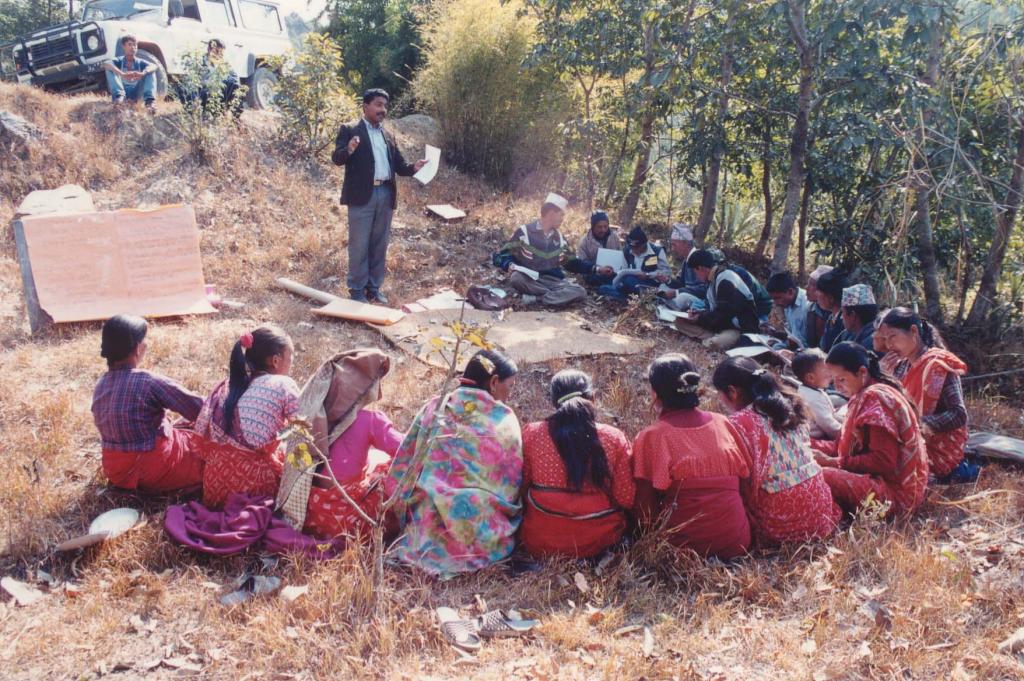
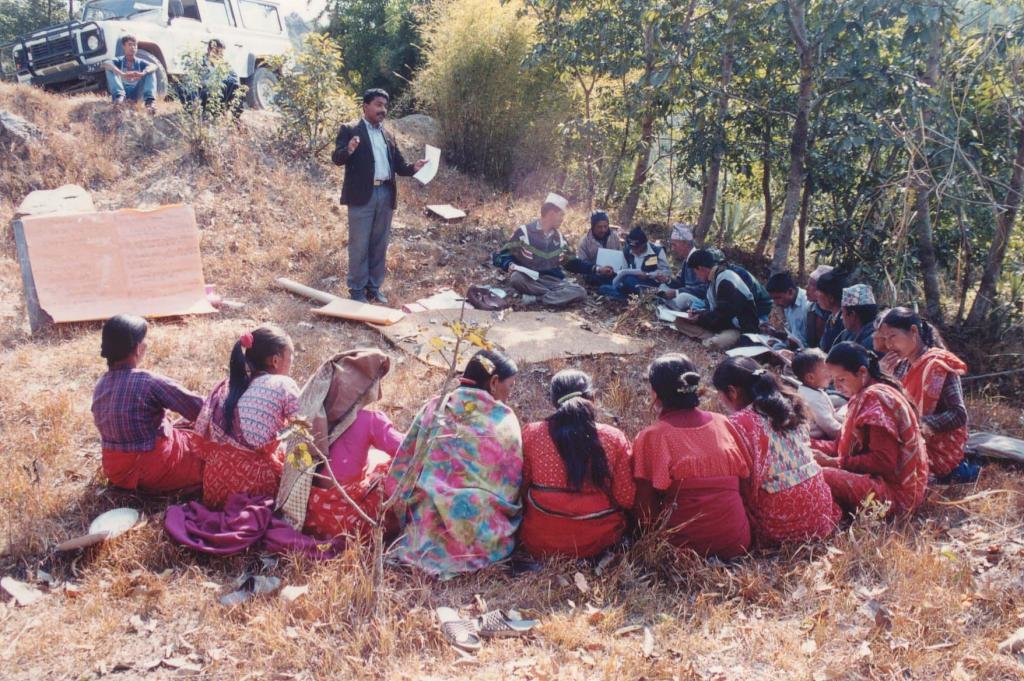
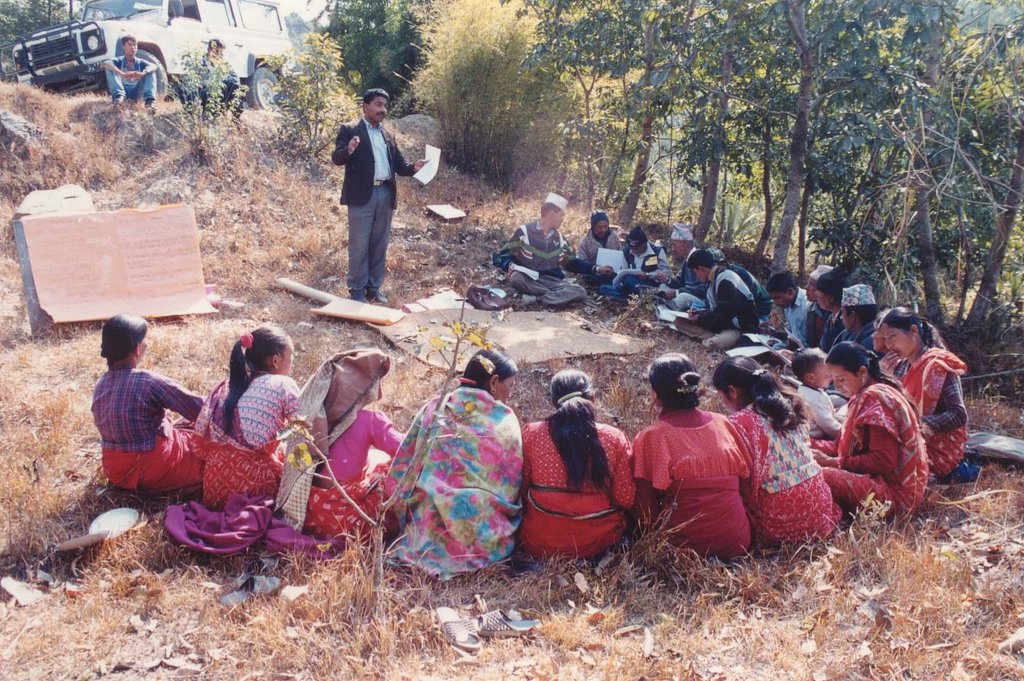
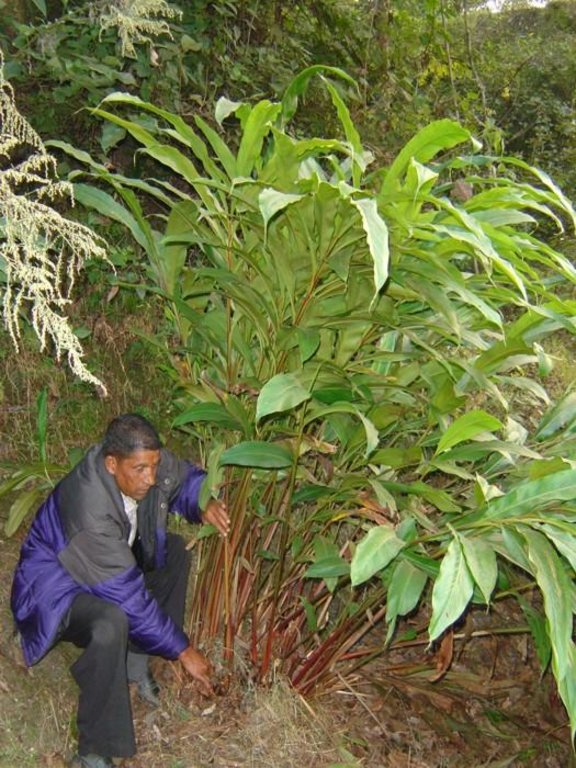
Aims / objectives: The sustainable management of mountain watersheds is a huge challenge for watershed management programmes due to the lack of collaboration between the various institutions involved. Building of synergies between these institutions is crucial for improved management. The Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP) started in 1986, initiated, coordinated, and organised by the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management with support from the European Commission. The programme aimed to help overcome natural resource degradation and thereby raise the standard of living of the rural population. The main causes of degradation and options to address the related problems were identified through participatory action research. Landslip and stream bank stabilisation was identified as one of the most promising and needed options to conserve soil and water, whilst providing direct livelihood benefits to local people, for example planting of large cardamom, later used as a cash crop, and reestablishment of damaged agricultural terrace above the landslip. The approach was to foster partnership between and among communities, district authorities, line agencies, and consultants. Key priorities were to ensure the equitable involvement of women and socially disadvantaged people and to promote local ownership, institutional capacity building, and sustainability.
Methods: The programme used participatory extension methods such as farmer-to-farmer exchange, training workshops, and onsite demonstrations, with participatory approaches to planning, implementing, and monitoring. The activities were based on villager’s priorities and were implemented by individual households, farmer groups, and village institutions. The local village development committee, local NGOs, community forest user group, and individual households worked together on landslip and stream bank stabilisation. Involving a range of stakeholders was paramount for success.
Stages of implementation: The first phase began in 1986 and focused on developing technical packages which were implemented through user groups. The second phase focused on improvements to implementation procedures, especially community organisation, extension, and income generation activities. The capacity of community groups was developed by establishing communication facilities, building up community networks, and empowering women and disadvantaged groups. BIWMP ended in 2003 with much of its success attributed to the close involvement of all the main stakeholders, and especially the local people, in all the activities. It successfully helped land users to adopt improved livelihood options.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Подход
2.5 Страна/ регион/ место, где применялся Подход
Страна:
Непал
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Bagmati Watershed
Map
×2.6 Даты начала и окончания реализации Подхода
Год начала реализации:
1992
Год окончания (Если Подход больше не применяется):
2003
2.7 Тип Подхода
- в рамках проекта/ программы
2.8 Каковы цели/ задачи Подхода
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (poverty reduction through sustained income generation, infrastructure improvement through equitable involvement of women and the socially disadvantaged.)
To overcome the constraints to effectively implementing a watershed management programme by building synergies between diverse stakeholder institutions. In the case of landslip and stream bank stabilisation work, the specific objective was to come up with a technology that conserved soil and water whilst also providing direct livelihood benefits to local people.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of institutional capacity and collaboration for managing watershed resources
2.9 Условия содействующие применению Технологии/ Технологий в рамках Подхода или затрудняющие его
Социальные/ культурные/ религиозные нормы и ценности
- затрудняют
Following conventional top-down approaches.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Introduction of improved methods with more participation/ involvement of land users.
Институциональные условия
- затрудняют
Lack of inter-institutional collaboration.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Building and ensuring collaboration.
Нормативно-правовая база (землевладение, права на земле- и водопользование)
- содействуют
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The fact that the land was communal land (state property, use right with community) greatly helped smooth implementation of the approach as it was not necessary to deal with different land users.
Осведомленность в области УЗП, доступность технической поддержки
- затрудняют
Lack of new options.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training about new technologies.
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
3.1 Заинтересованные стороны, участвующие в реализации Подхода и их роли
- местные землепользователи/ местные сообщества
Men and women worked equally. existing groups of land users; men and women worked equally. BIWMP took a bottom-up approach to planning and implementation and encouraged the equitable involvement of women in its activities. The decisions about implementing the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology were taken jointly by men and women
- эксперты по УЗП/ сельскому хозяйству
- учителя/ преподаватели/ школьники / студенты
- государственные власти (отвечающие за планирование или принятие решений)
- международные организации
Если участвовало несколько заинтересованных сторон, назовите ведущую организацию:
For the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology, the approach was mainly designed by programme staff of the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office.
3.2 Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ на разных стадиях реализации Подхода
| Участие местных землепользователей/ местных сообществ | Перечислите участников и опишите их вовлеченность | |
|---|---|---|
| инициирование/ мотивация | интерактивное | rapid/participatory rural appraisal |
| планирование | интерактивное | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; Share information from users right from planning period. |
| выполнение | интерактивное | responsible for major steps; Users were agreed to conserve soil by using SLM approaches. |
| мониторинг/ оценка | интерактивное | Mainly: reporting, public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; Regular monitoring and evaluation were successfully conducted by DSCO Office for the backstopping of the activities. |
| Research | интерактивное | on-farm; This site is used as a Farmers School for extension of the technology on National and International level. |
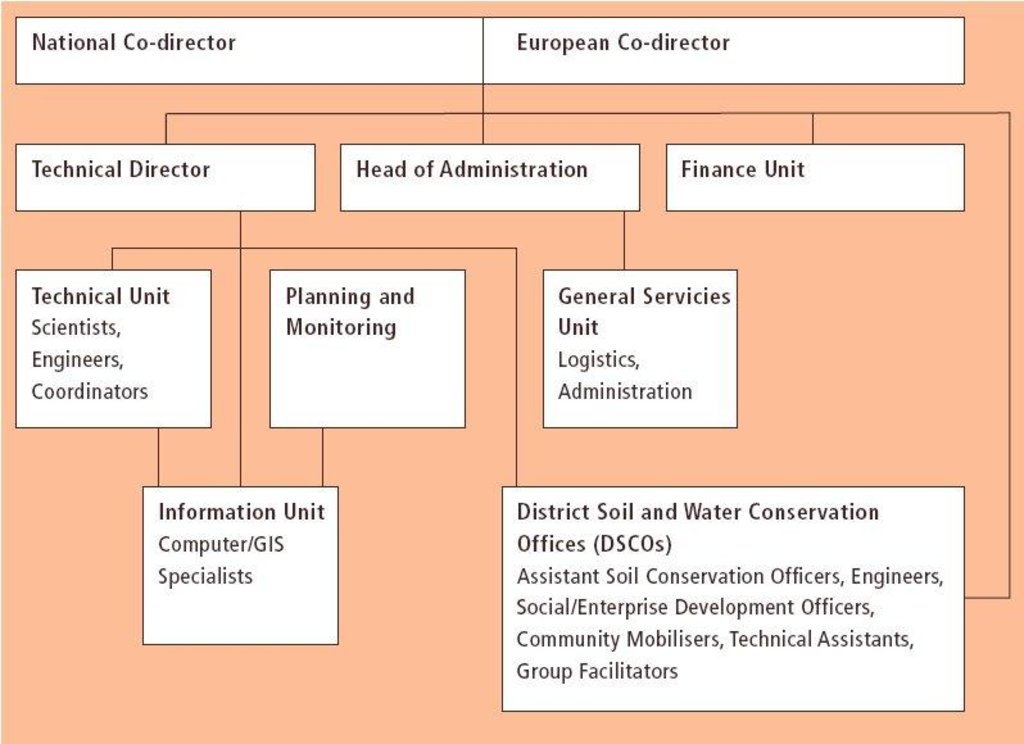
3.3 Схема реализации (если имеется)
Описание:
Organogram of the Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP). The landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was implemented by the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office supervi
3.4 Принятие решений по выбору Технологии/ Технологий УЗП
Укажите, кто принимал решение по выбору применяемой Технологии/ Технологий:
- преимущественно специалисты по УЗП после консультаций с землепользователями
Поясните:
The land users did not know about the technologies
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. As measures required technical know-how
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
4.1 Повышение компетенций/ обучение
Проводилось ли обучение землепользователей/ других заинтересованных лиц?
Да
Укажите, кто проходил обучение:
- землепользователи
Тип обучения:
- обмен опытом между фермерами
- опытные участки
- общие собрания
Рассматриваемые темы:
On soil and water conservation
4.2 Консультационные услуги
Есть ли у землепользователей возможность получать консультации?
Да
Укажите, где именно оказываются консультационные услуги:
- на полях землепользователей
Описание/ комментарий:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated Watershed Management Programme; Key elements: Participatory Rural Appraisal, Trainings, Farmer to farmer exchange, workshops, seminars, On site Demnostration; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Planning,Training, Awareness about SLM approaches
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; An extension workers is able to cover the areas where activities are implemented in small scale (i.e. subwatreshed or Micro subwatershed level programme).
4.3 Институциональная (организационная) поддержка
В ходе реализации Подхода были ли организованы новые институциональные структуры или поддержаны уже существующие?
- да, существенно
Укажите уровень, на котором структуры были укреплены или вновь созданы:
- местные
Укажите тип поддержки:
- повышение компетенций/ обучение
- оборудование
4.4 Мониторинг и оценка
Являются ли мониторинг и оценка частью Подхода?
Да
Комментарии:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored through observations
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach described was designed on the basis of the results shown through monitoring and evaluating the first phase of BIWMP (1986-1992). In the second phase from 1992, more attention was focused on building up the capacity of community groups to plan, implement, and continue development activities. Capacity was built through (1) community-level training; (2) supporting the installation of com
4.5 Научные исследования
Были ли научные исследования частью Подхода?
Да
Укажите темы исследований:
- социология
- экономика / маркетинг
- экология
- технология
Напишите подробнее и назовите тех, кто выполнял исследования:
see also further reading
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
5.1 Годовой бюджет мероприятий по УЗП в рамках Подхода
Если точный годовой бюжет неизвестен, укажите примерный диапазон затрат:
- > 1 000 000
Комментарий (например, основные источники финансирования/ ключевые доноры):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (European Commission): 81.0%; government (national - His Majesty's Government (Nepal)): 4.0%; local community / land user(s) (Bagmati watershed): 15.0%
5.2 Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка, предоставляемая землепользователям
Предоставлялась ли землепользователям финансовая/ материальная поддержка для применения Технологии /Технологий?
Да
5.3 Субсидии на отдельные затраты (включая оплату труда)
- сельскохозяйственные
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| семена | ||
| Seedlings and samples | профинансированы частично | |
- строительные материалы
| Укажите, какие ресурсы были субсидированы | В какой степени | Опишите субсидии подробнее |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure (cement, bricks, stones) | профинансированы полностью | |
Если труд землепользователя был существенным вкладом, укажите, был ли этот вклад:
- добровольный
Комментарии:
About 75% of the labour for the landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was voluntar. The remainder was paid
5.4 Кредитование
Предоставлялись ли в рамках Подхода кредиты на мероприятия УЗП?
Нет
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Подхода
Сумел ли Подход помочь землепользователям внедрить и поддерживать технологии УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
The approach helped to improve soil and water management by promoting many activities related to agroforestry, water harvesting, landslip stabilisation, and community forestry. Many local land users adopted these technologies.
Сумел ли Подход разрешить правовые проблемы землевладения/ землепользования, препятствующие использованию технологий УЗП?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
By influencing the forest department ot allocate forest to the people as community forest.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Нет
- Да, немного
- Да, умеренно
- Да, существенно
It is not known whether this approach has been taken to address landslip and stream bank erosion problems in other areas by other projects.
6.3 Долгосрочная устойчивость мероприятий в рамках Подхода
Могут ли землепользователи самостоятельно (без внешней поддержки) продолжать применение того, что было реализовано в рамках Подхода?
- нет уверенности
Если нет или нет уверенности, объясните почему:
The land users were keen on maintaining the implemented technologies due to the benefits they could get from it. There has to be a strong driving force within the land users and the community to continue this approach.
6.4 Сильные стороны/ преимущества Подхода
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| Helped land users improve their livelihoods. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Similar approaches should be implemented by government and community programmes.) |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Involves all key actors in watershed management. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Institutionalise the approach.) |
| The approach encourages land users communities and local institutions to get involved in planning and decision making (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Involve them more in planning and decision making) |
| The implementation of technologies through this approach is cost-effective and socio-culturally acceptable. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Take into account local resources and knowledge) |
6.5 Слабые стороны/ недостатки Подхода и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| No opinion. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Some activities with high input requirements may not be spontaneously adopted by poor land users | Further research on how to reduce inputs or provide specifi c incentives for such disadvantaged groups. |
| The approach is 'project focussed' | Institutionalise the approach |
| The approach does not focus on landless families. | Implement watershed management activities that involve and benefit landless people |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Mallik, D.B. (2000) 'Working with Community'. In Jaladhar-QuarterlyBIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
BIWMPBIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
BIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
BIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Landslip and stream bank stabilisation [Непал]
Integration of vegetative and structural measures for landslip, stream bank and gully stabilisation on hillsides.
- Составитель: Dileep Kumar Karna
Модули
Нет модулей