Integrated watershed management for landslip and stream bank stabilisation [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dileep Kumar Karna
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Pahiro ra nadikinar katan roktham ka lagi ekikrit jaladhar byabasthapan (Nepali)
approaches_2354 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development (G.B. Pant Institute of Himalayan Einvironment & Development) - 印度有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
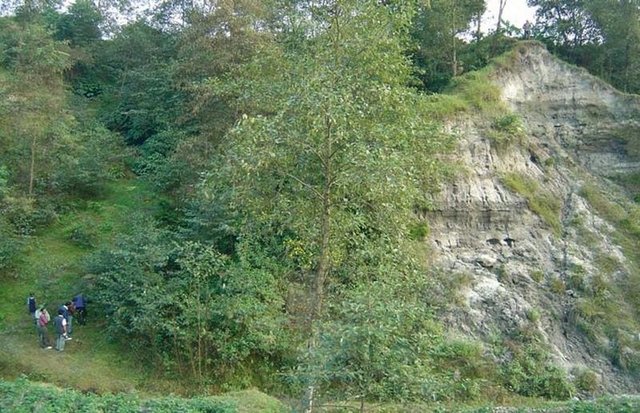

Landslip and stream bank stabilisation [尼泊尔]
Integration of vegetative and structural measures for landslip, stream bank and gully stabilisation on hillsides.
- 编制者: Dileep Kumar Karna
2. SLM方法的描述
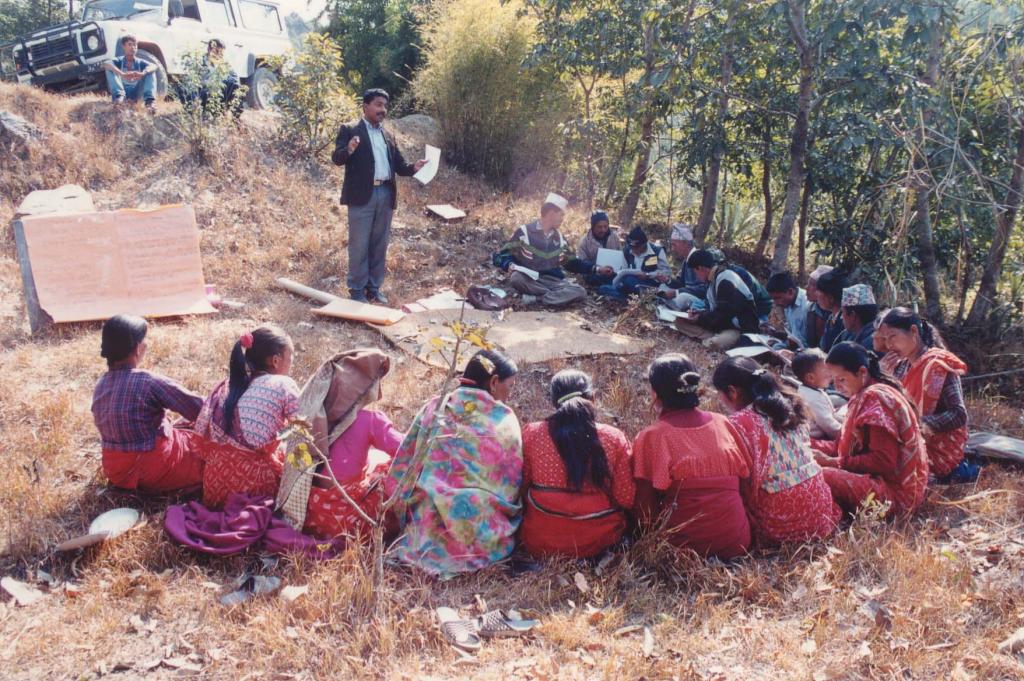
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Integrated watershed management as an example for landslip and stream bank stabilisation based on fostering a partnership between community institutions, line agencies, district authorities and consultants
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
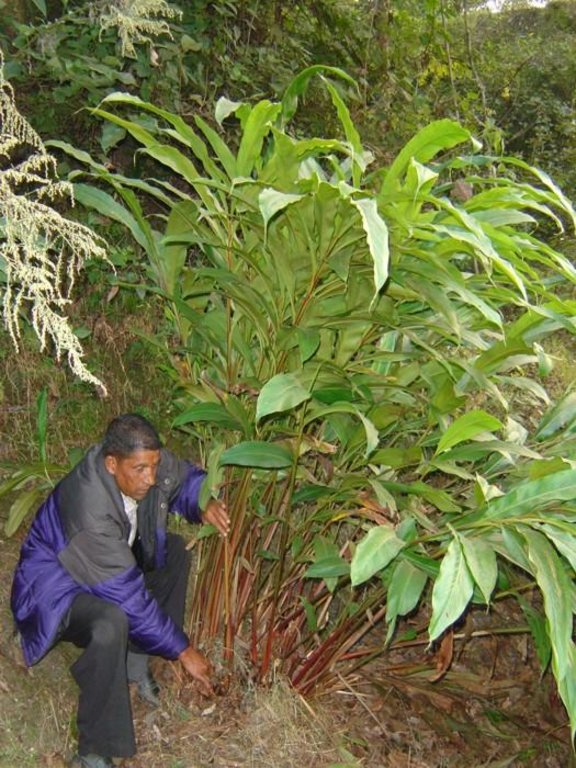
Aims / objectives: The sustainable management of mountain watersheds is a huge challenge for watershed management programmes due to the lack of collaboration between the various institutions involved. Building of synergies between these institutions is crucial for improved management. The Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP) started in 1986, initiated, coordinated, and organised by the Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management with support from the European Commission. The programme aimed to help overcome natural resource degradation and thereby raise the standard of living of the rural population. The main causes of degradation and options to address the related problems were identified through participatory action research. Landslip and stream bank stabilisation was identified as one of the most promising and needed options to conserve soil and water, whilst providing direct livelihood benefits to local people, for example planting of large cardamom, later used as a cash crop, and reestablishment of damaged agricultural terrace above the landslip. The approach was to foster partnership between and among communities, district authorities, line agencies, and consultants. Key priorities were to ensure the equitable involvement of women and socially disadvantaged people and to promote local ownership, institutional capacity building, and sustainability.
Methods: The programme used participatory extension methods such as farmer-to-farmer exchange, training workshops, and onsite demonstrations, with participatory approaches to planning, implementing, and monitoring. The activities were based on villager’s priorities and were implemented by individual households, farmer groups, and village institutions. The local village development committee, local NGOs, community forest user group, and individual households worked together on landslip and stream bank stabilisation. Involving a range of stakeholders was paramount for success.
Stages of implementation: The first phase began in 1986 and focused on developing technical packages which were implemented through user groups. The second phase focused on improvements to implementation procedures, especially community organisation, extension, and income generation activities. The capacity of community groups was developed by establishing communication facilities, building up community networks, and empowering women and disadvantaged groups. BIWMP ended in 2003 with much of its success attributed to the close involvement of all the main stakeholders, and especially the local people, in all the activities. It successfully helped land users to adopt improved livelihood options.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Bagmati Watershed
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
1992
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2003
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (poverty reduction through sustained income generation, infrastructure improvement through equitable involvement of women and the socially disadvantaged.)
To overcome the constraints to effectively implementing a watershed management programme by building synergies between diverse stakeholder institutions. In the case of landslip and stream bank stabilisation work, the specific objective was to come up with a technology that conserved soil and water whilst also providing direct livelihood benefits to local people.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of institutional capacity and collaboration for managing watershed resources
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Following conventional top-down approaches.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Introduction of improved methods with more participation/ involvement of land users.
机构设置
- 阻碍
Lack of inter-institutional collaboration.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Building and ensuring collaboration.
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The fact that the land was communal land (state property, use right with community) greatly helped smooth implementation of the approach as it was not necessary to deal with different land users.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Lack of new options.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training about new technologies.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Men and women worked equally. existing groups of land users; men and women worked equally. BIWMP took a bottom-up approach to planning and implementation and encouraged the equitable involvement of women in its activities. The decisions about implementing the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology were taken jointly by men and women
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 教师/学龄儿童/学生
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
For the landslip and stream bank stabilisation technology, the approach was mainly designed by programme staff of the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office.
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | rapid/participatory rural appraisal |
| 计划 | 互动 | rapid/participatory rural appraisal; Share information from users right from planning period. |
| 实施 | 互动 | responsible for major steps; Users were agreed to conserve soil by using SLM approaches. |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | Mainly: reporting, public meetings, measurements/observations; partly: workshop/seminars; Regular monitoring and evaluation were successfully conducted by DSCO Office for the backstopping of the activities. |
| Research | 互动 | on-farm; This site is used as a Farmers School for extension of the technology on National and International level. |
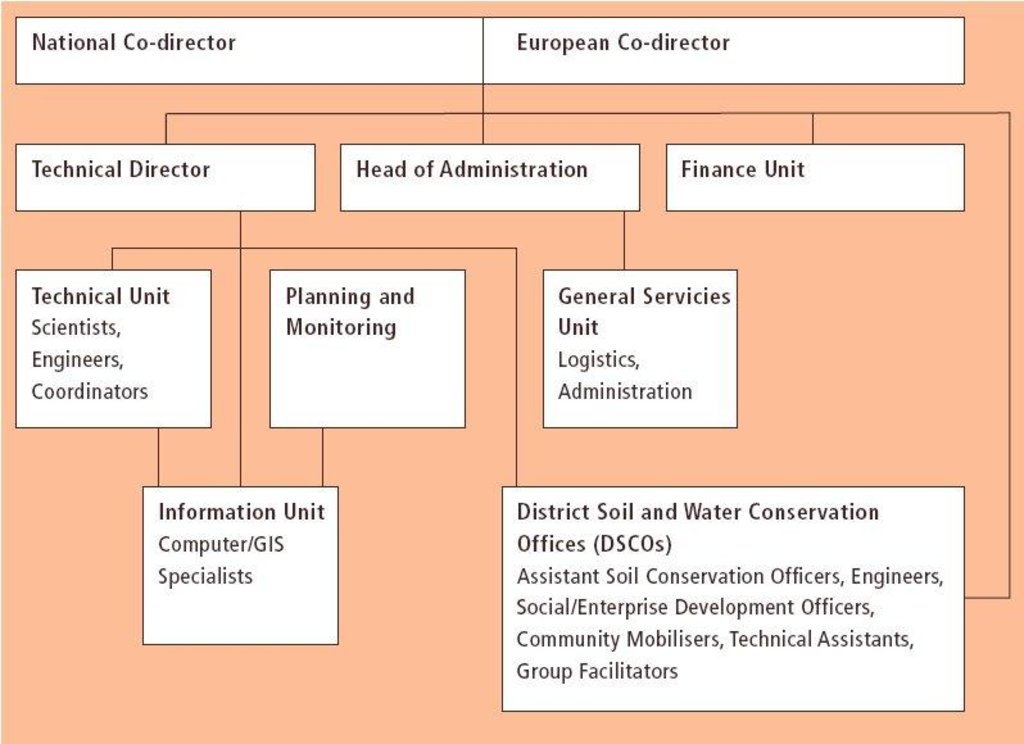
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
Organogram of the Bagmati Integrated Watershed Management Programme (BIWMP). The landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was implemented by the Kathmandu District Soil Conservation Office supervi
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
The land users did not know about the technologies
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. As measures required technical know-how
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
涵盖的主题:
On soil and water conservation
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Integrated Watershed Management Programme; Key elements: Participatory Rural Appraisal, Trainings, Farmer to farmer exchange, workshops, seminars, On site Demnostration; 1) Advisory service was carried out through: government's existing extension system; Extension staff: mainly government employees 2) Target groups for extension: land users; Activities: Planning,Training, Awareness about SLM approaches
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; An extension workers is able to cover the areas where activities are implemented in small scale (i.e. subwatreshed or Micro subwatershed level programme).
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored through observations
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored through observations
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through observations
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored through observations
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored through observations
There were many changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach described was designed on the basis of the results shown through monitoring and evaluating the first phase of BIWMP (1986-1992). In the second phase from 1992, more attention was focused on building up the capacity of community groups to plan, implement, and continue development activities. Capacity was built through (1) community-level training; (2) supporting the installation of com
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 生态学
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
see also further reading
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- > 1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (European Commission): 81.0%; government (national - His Majesty's Government (Nepal)): 4.0%; local community / land user(s) (Bagmati watershed): 15.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | ||
| Seedlings and samples | 部分融资 | |
- 建筑
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| community infrastructure (cement, bricks, stones) | 充分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
About 75% of the labour for the landslip and stream bank stabilisation work was voluntar. The remainder was paid
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The approach helped to improve soil and water management by promoting many activities related to agroforestry, water harvesting, landslip stabilisation, and community forestry. Many local land users adopted these technologies.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
By influencing the forest department ot allocate forest to the people as community forest.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
It is not known whether this approach has been taken to address landslip and stream bank erosion problems in other areas by other projects.
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
The land users were keen on maintaining the implemented technologies due to the benefits they could get from it. There has to be a strong driving force within the land users and the community to continue this approach.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Helped land users improve their livelihoods. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Similar approaches should be implemented by government and community programmes.) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Involves all key actors in watershed management. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Institutionalise the approach.) |
| The approach encourages land users communities and local institutions to get involved in planning and decision making (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Involve them more in planning and decision making) |
| The implementation of technologies through this approach is cost-effective and socio-culturally acceptable. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Take into account local resources and knowledge) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| No opinion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Some activities with high input requirements may not be spontaneously adopted by poor land users | Further research on how to reduce inputs or provide specifi c incentives for such disadvantaged groups. |
| The approach is 'project focussed' | Institutionalise the approach |
| The approach does not focus on landless families. | Implement watershed management activities that involve and benefit landless people |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Mallik, D.B. (2000) 'Working with Community'. In Jaladhar-QuarterlyBIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
BIWMPBIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
BIWM (1998 to 2001) Annual Workplans for Project Years 1998 to 2002, prepared for Government of Nepal,MOFS,DSCWM and EU; Kathmandu, Nepal
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
BIWMP email: biwmp@mos.com.np
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Landslip and stream bank stabilisation [尼泊尔]
Integration of vegetative and structural measures for landslip, stream bank and gully stabilisation on hillsides.
- 编制者: Dileep Kumar Karna
模块
无模块