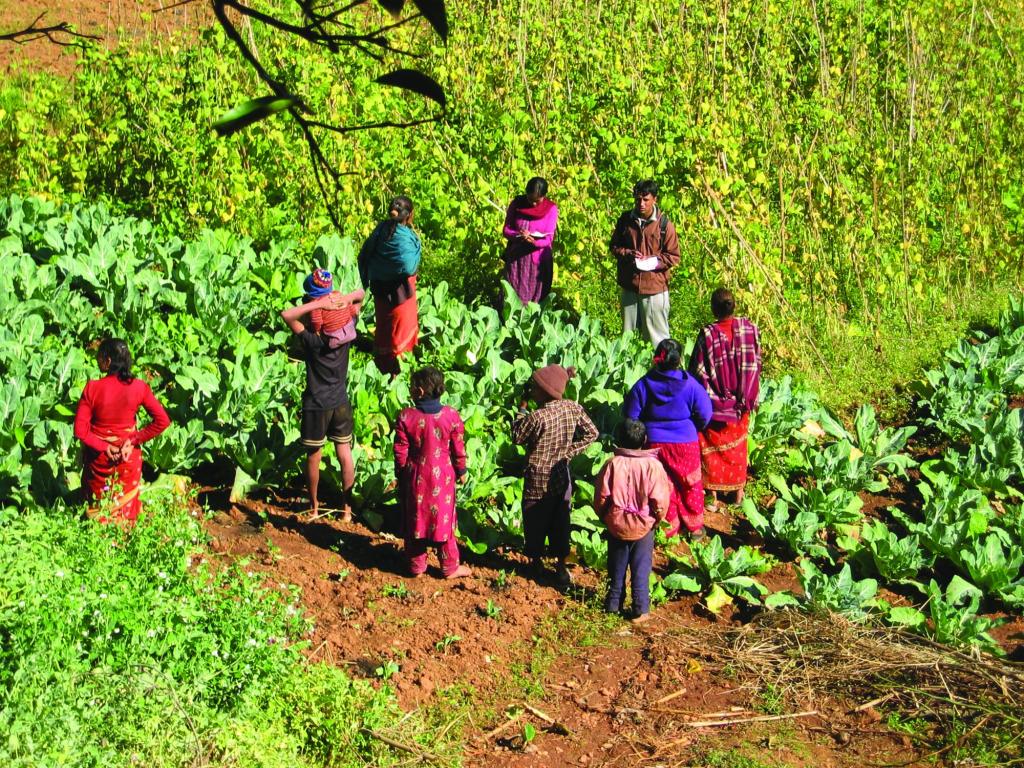
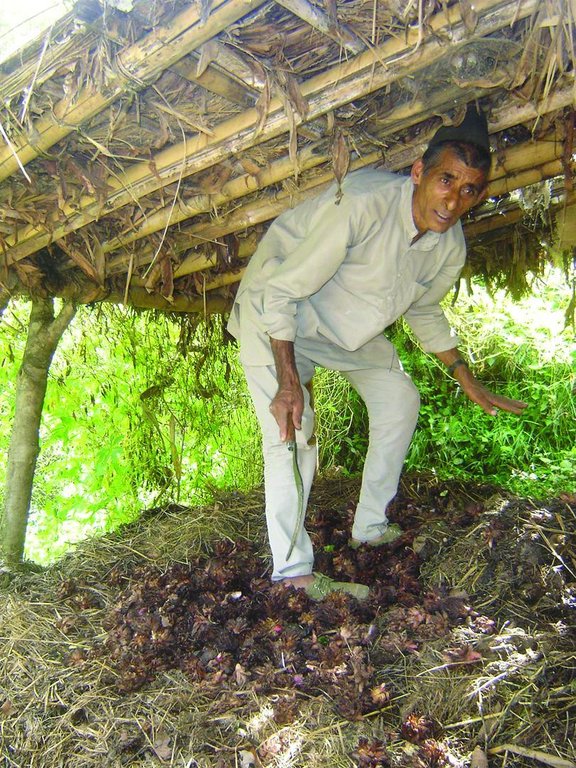
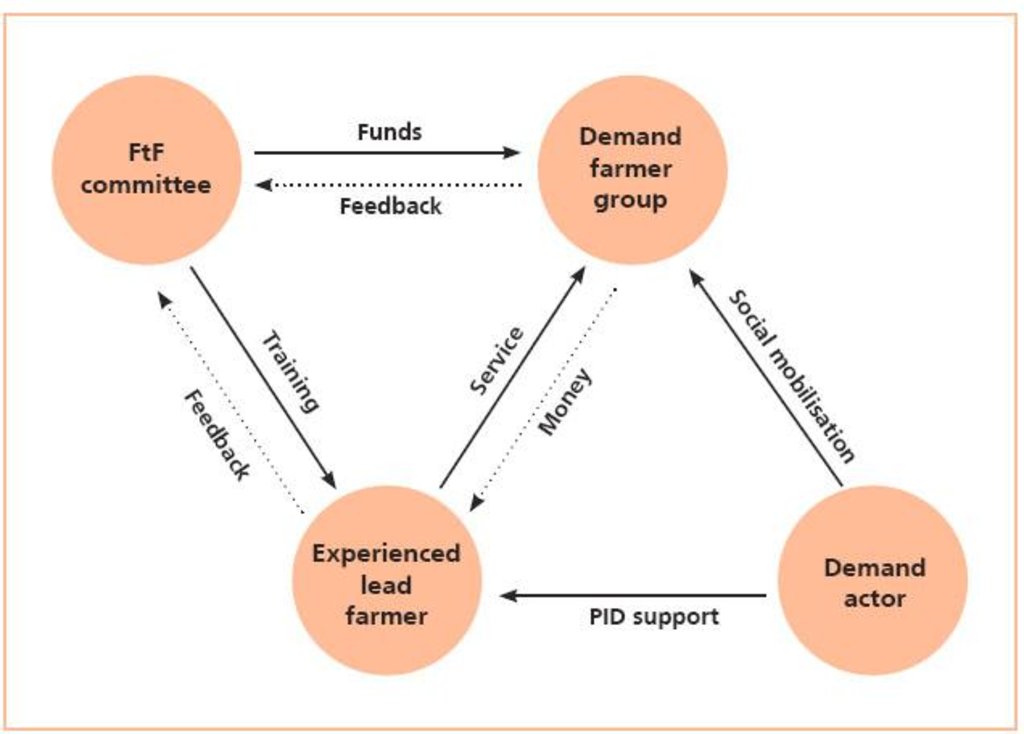
Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [Непал]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Richard Allen
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Laura Ebneter
Kisan-kisan krishi prasar (Nepali)
approaches_2558 - Непал
1. Общая информация
2. Описание Подхода УЗП
3. Участие и распределение ролей заинтересованных сторон
4. Техническая поддержка, повышение компетенций и управление знаниями
5. Финансирование и внешняя материальная поддержка
6. Анализ влияния и заключительные положения
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
Ссылки и модули
Свернуть всеСсылки
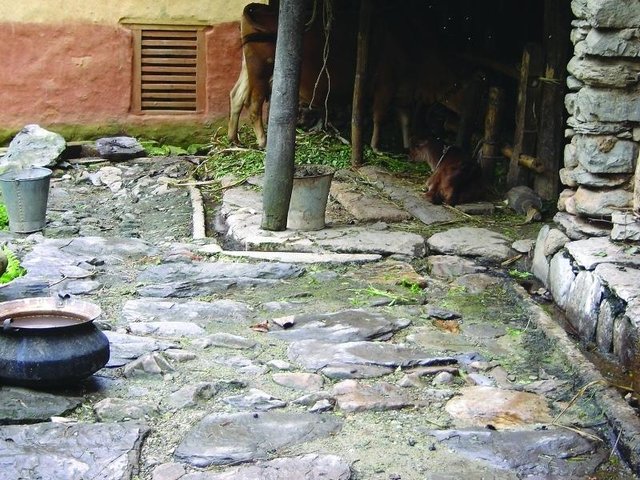

Improved cattleshed for urine collection [Непал]
Collection of cattle urine in improved cattle sheds for use as liquid manure and organic pesticide
- Составитель: Richard Allen
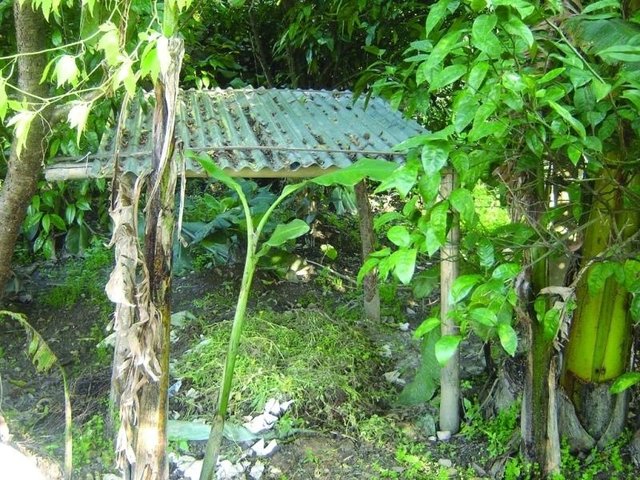

Improved compost preparation [Непал]
Improved compost preparation using a range of biomass and waste to produce high value fertiliser
- Составитель: Richard Allen
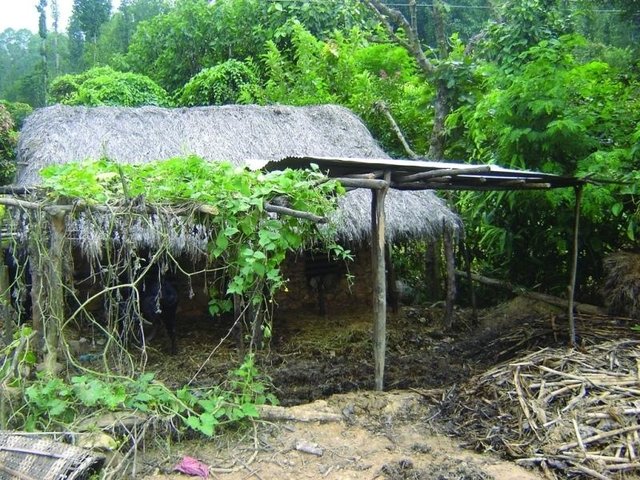

Improved farmyard manure through sunlight, rain and runoff … [Непал]
Improving farmyard manure by protecting it from direct sunlight, rainfall, and runoff to reduce volatilisation and leaching
- Составитель: Richard Allen
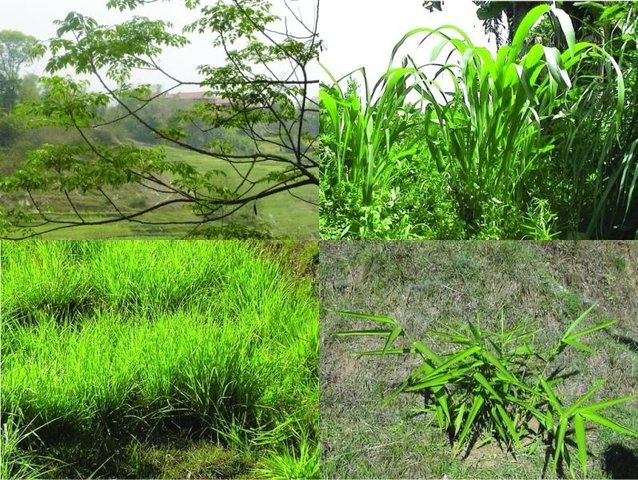

Cultivation of fodder and grasses [Непал]
Cultivation of fodder crops on marginal lands and terrace risers
- Составитель: Richard Allen

Urine application through drip irrigation for bitter gourd … [Непал]
Application of cattle urine through drip irrigation technology to provide constant flow of fertiliser to bitter gourd
- Составитель: Richard Allen
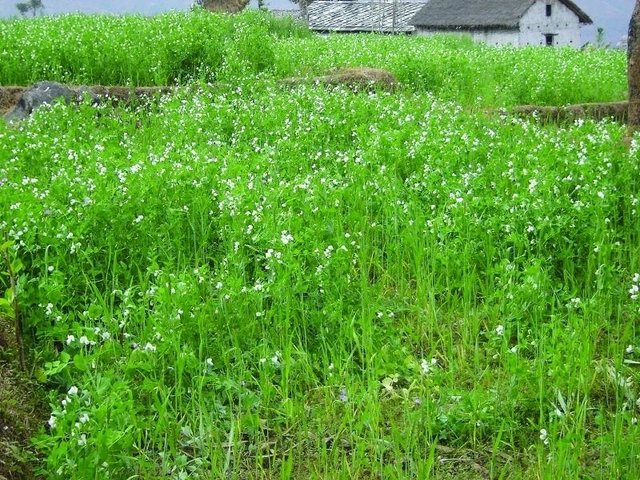

Legume integration [Непал]
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
- Составитель: Richard Allen

Organic pest management [Непал]
Promotion of botanical pesticides for organic pest management and liquid manure
- Составитель: Richard Allen
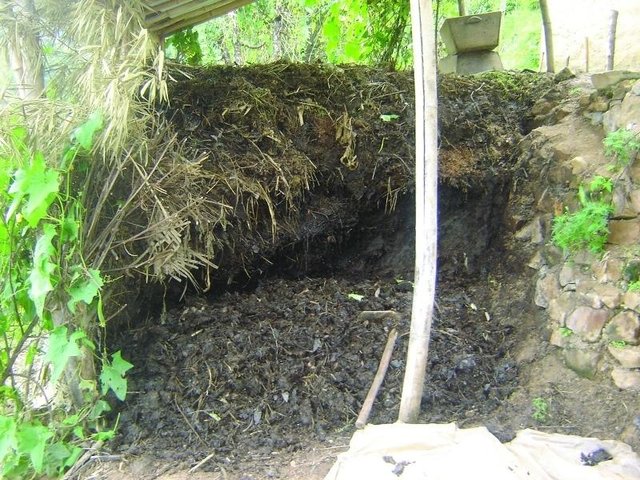

Better quality farmyard manure through improved decomposition [Непал]
Collection and proper storage of farmyard manure in heaps or pits
- Составитель: Richard Allen
Модули
Нет модулей