Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Таджикистан]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Christian Wirz
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: David Streiff
Dajmardei Kaspi (professional herder)
technologies_1407 - Таджикистан
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - ШвейцарияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Кыргызстан1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
15/08/2008
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (-ы) по Подходам УЗП
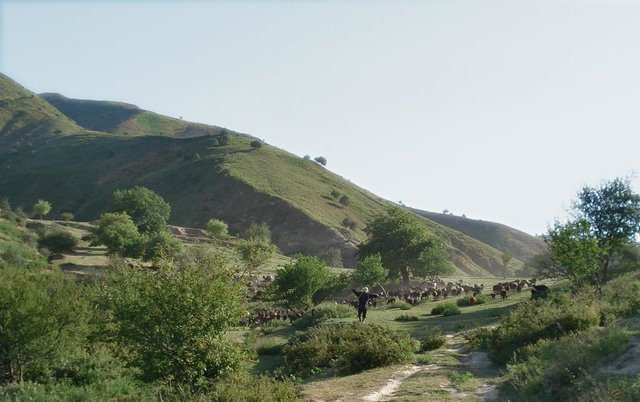

Seminomadic individual herding [Таджикистан]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Составитель: Christian Wirz
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
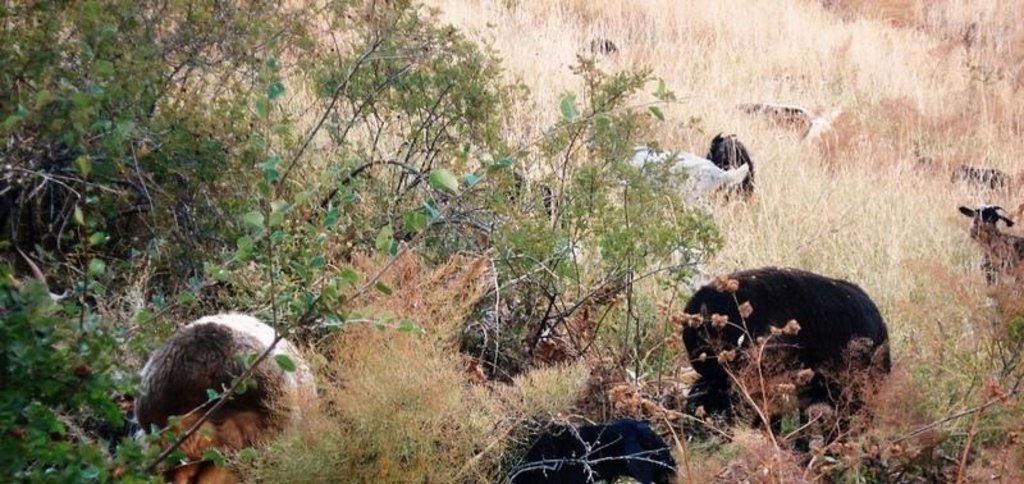
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
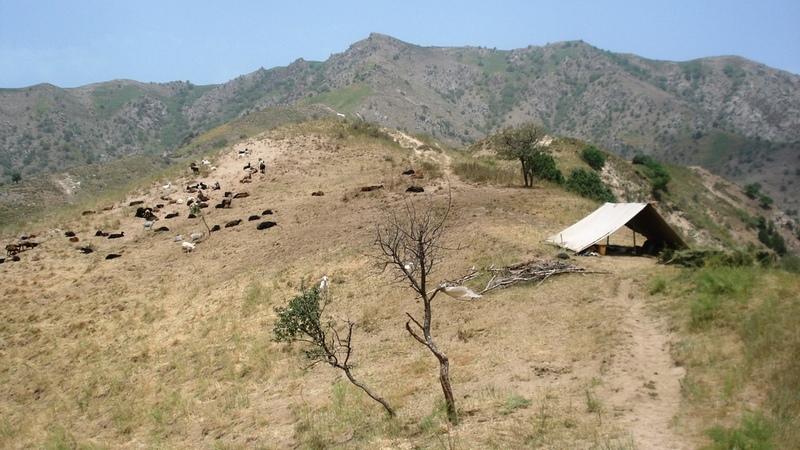
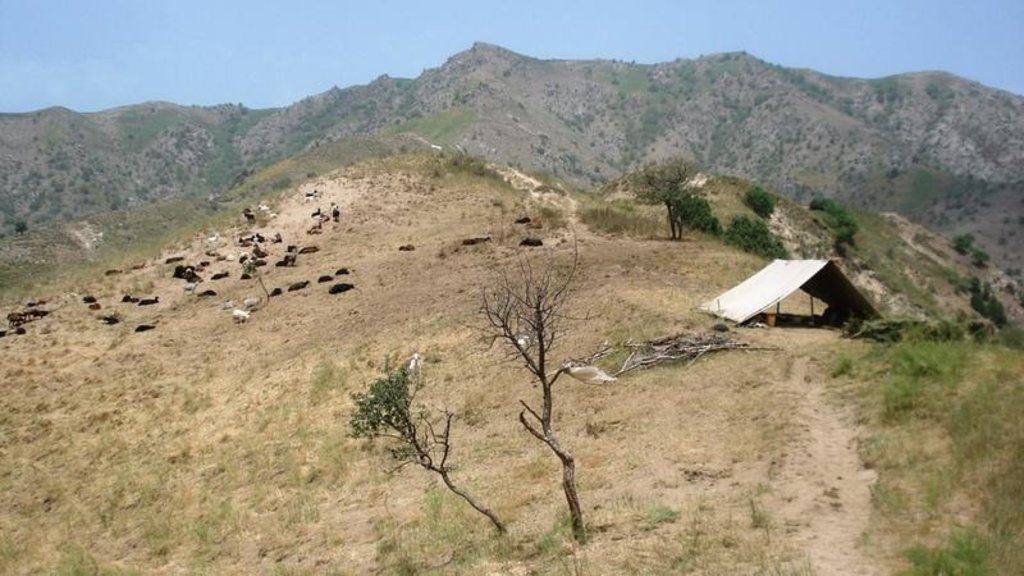
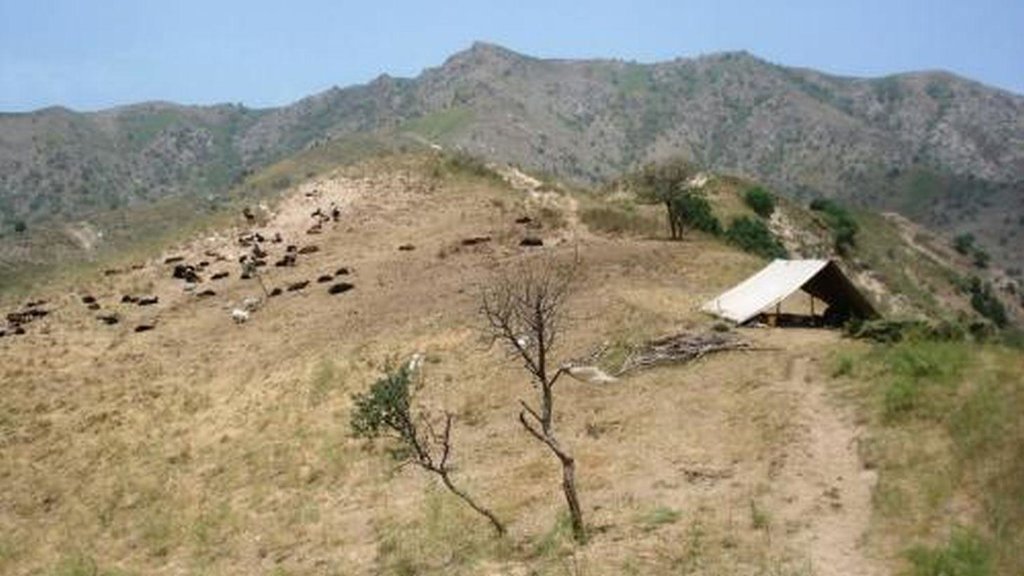
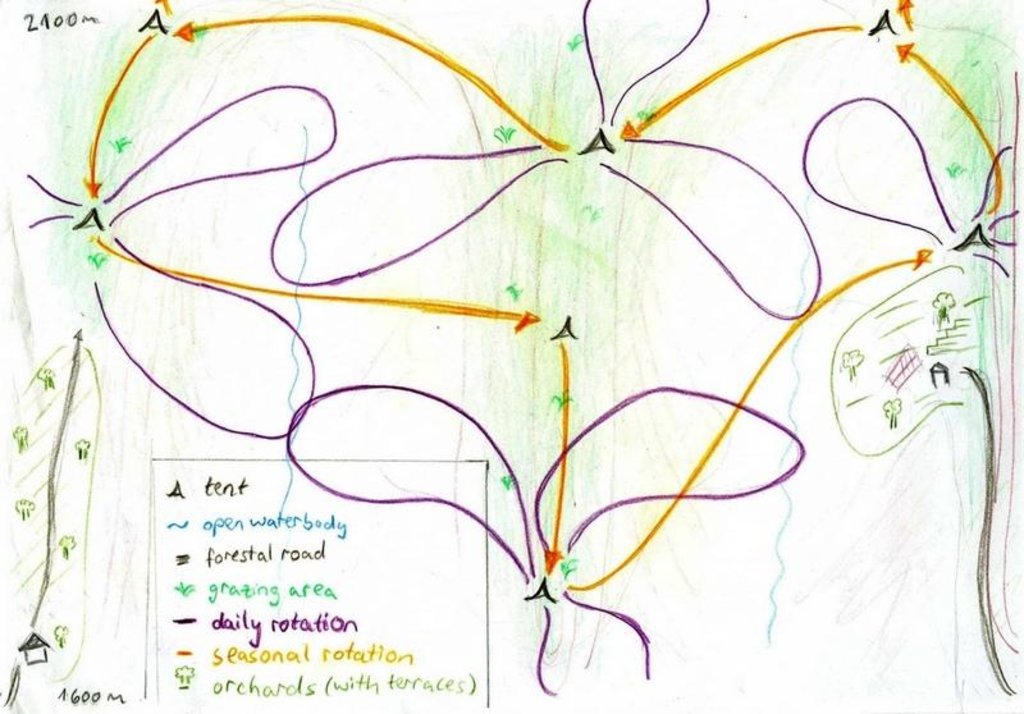
Half-year herding with 500 sheep, goats and cows (very few), with 7-8 different locations of the herder's tent. The herder visits each place twice to thrice per grazing season and stays in one place for one week to maximally one month (during the Ramadan period, due to limited forces). The area is grazed from the higher zone (around 2000m) to the lower zone (around 1600m) twice per season, in a sort of circle. Every day the herder starts in another direction from his tent and leads the animals to the pastures, once in the morning and once in the evening. He passes a stream once (autumn) to twice (summer) a day.
Purpose of the Technology: The grass should not get dusty and dirty, explaining why the herder daily changes the pastures, only revisiting the same places every two to three days.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After accompanying his father as a child and a kind of an apprenticeship (of one year) later on, M. is considered by the villagers as a good herder and they give him their animals for herding. But M. applies for land on the forest department only after working as a guardian and as a tractor driver for 20 years. For the herding profession observing the animals precisely is necessary, in order not to lose any of them. And the maintenance of the pastures is guaranteed by the strict rotational scheme.
Natural / human environment: The pasture-area is in a generally well-conserved state. Moderate to high values of fractional vegetation cover can be observed and only few signs of recent erosion processes (through water) are visible. The area is characterised by steep slopes where still signs of past tree-planting during the USSR period are visible by some trees, many little platforms made for tree-planting and a few terraced areas. Eventhough, many trees have been grazed and do not stand anymore. Besides steep areas there are small, quite flat areas (where the herder installs his tents), that used to be cultivated (wheat) till 1966. These areas generally have low cover-values and signs of rill-erosion, which the herder attributes to the past tilling activity. However, it might also be the trampling and sitting of the animals (staying near the herder's tent at noon-time and during the night) causing this erosion. Nutrient management is provided for by the dung of the animals which is not collected, contrarily to the pastures near the villages.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Таджикистан
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Region of Republican Subordination
Более точная привязка места:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- более 50 лет назад (традиционная)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как часть традиционной системы землепользования (более 50 лет назад)
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
There are traditional herding peoples like Kuagwates, Kaleks, Lakais, Duramanes, Kurtshaliks), not Tajiks. These often move around with their whole families.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пастбищные угодья
Пастбищные земли, экстенсивный выпас:
- Полукочевое/ отгонное животноводство
Основные породы скота и виды продукции:
sheep* / goats* / cows
* if wildlife is major part of the grazing system
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The trampling of the animals near the tent, the feeding on young trees and the daily passage of the herd of a limited number of streams (eutrophication).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): No major land use problems due to good management. Only the first rain that cannot be absorbed by the dry soils is a problem.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: sheep* / goats* / cows
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
Если использование земель изменилось с началом применения Технологии, укажите тип землепользования до применения Технологии:
Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jun
Поголовье скота на единицу площади (если применимо):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- Кочевое животноводство и пастбищное хозяйство
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
The half of the herded area is rented by another person from the village, who gives his animals to the herder. Apart from the interviewed herder there are varying numbers of other semi-nomadic herders with similar management practices, some of them from other regions.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

управленческие мероприятия
- У1: Смена типа землепользования
- У4: Существенные изменения в сроках проведения мероприятий
Пояснения:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)

биологическая деградация
- Бв: потеря природного разнообразия
Пояснения:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Causing Pc, Bc, Wt), droughts (Causing Pk, Pc, Ha), degradation of near-village pastures (The pressure on more distant areas increases)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (passed tilling with impact on Wt), floods (Intensive rains causing Wt), land tenure (Little interest in tree-planting if land can only be rented annually)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Daily and seasonal rotation.
Location: Above Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 05.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Obeying to what the herder says)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is necessary to know how to lead animals, more than in the case of the common pasture-area)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of fires, palatable fodder
Change of land use type: From afforestation and limited use as cropland to extensive grazing
Major change in timing of activities: Introduction of a strict rotational grazing scheme
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
Укажите денежные единицы, использованные для подсчета затрат:
- Доллары США
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
6.10
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a herd | Управленческие | constantly investing |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Другие | Buying a herd | animals | 50,0 | 87,7 | 4385,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 4385,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rent fee for land of forest department | Управленческие | once per year |
| 2. | Salary of an assistant herder (normally, but not in 2008) | Управленческие | at the end of the season |
| 3. | compensation for dead animals | Управленческие | at the end of the season |
| 4. | Animal medecine | Управленческие | if necessary |
| 5. | Salt | Управленческие | daily |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Salary of an assistant herder | Days | 120,0 | 6,1 | 732,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Rent fee for land of forest department | 300ha/d | 180,0 | 0,4888888 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Compensation for dead animals | animals | 2,0 | 44,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Animal medecine | per year | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Salt | kg | 1000,0 | 0,08 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 1076,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
The costs are valid for a herd of 250 animals kept by the herder alone for six months and additional 250 animals kept during summer holidays with the help of additional workforce. The salary indicated was not valid for 2008 (the grandsons helped the herder), but for years when M. hires external workforce. For all costs, including 50 own animal, prices in 2008 are taken.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Buying an own herd and looking for the animals are the most expensive factors, expecially if there are sick or dead animals.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Mainly in spring and also in autumn, with a trend to decrease
Агроклиматическая зона
- полузасушливая
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Altitudinal zone: Pasture area around 1600 to 2000 m
Landforms ridges: Small, not so steep areas where the tent of the herder is installed
Landforms mountain slopes: The pasture area is generally very steep
Slopes on average steep (31-60%): The areas mostly frequented are steep
Slopes on average very steep (>60%): The areas dominating spatially are very steep
Slopes on average hilly (16-30%): Ridge areas
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average shallow: Most grassy areas
Soil fertility is low: on the surface of 300 ha the summed up dung of 500 sheep and goats cannot compensate for the loss of topsoil by wind and water
Soil drainage / infiltration is good: Generally high infiltration capacity enhanced by high vegetation cover values
Soil water storage capacity medium (dominatig the area): Loamy soils and high cover values, but generally little trees and dried vegetation in August
Soil water storage capacity can also be good: Near the streams higher water retention, according to herder
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Доступность поверхностных вод:
недостаточны/ отсутствуют
Качество воды (без обработки):
исключительно для сельскохозяйственного использования (орошение)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Water quality (untreated): Locals drink the water, but are affected by diarrhoea
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- высокое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Diversity higher than near the villages, but not comparable with biodiversity hot-spots
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Осёдлый или кочевой:
- Полукочевой
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- обеспеченный
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Пол:
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Herding is considered as a male profession, inherited from father to son. In nomadic peoples the whole families are mobile and women are responsible for domestic work.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are rich (100).
Off-farm income specification: The herder claims to nourish himself and his wife with the income from herding. But, once he willl not be able to work as a herder anymore, he might depend on off-farm income from his children (remittances)
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
3 households can afford to pay the services of the professional herder (clearly a minority of village population)
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- государственная
Право землепользования:
- аренда
Право водопользования:
- общинное (контролируемое)
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
электроснабжение:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство кормов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Higher vegetation cover and biomass values than for village-pastures
качество кормов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Much less impalatable species' frequency
производство продуктов животноводства
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The animals get much fatter and are sold for around 50% higher price than animals from common pastures
производство древесины
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The herder says that tree density has decreased, due to livestock but also to chopping. Additionally chopping of living trees is generally forbidden (since the 1960s, when the forest department was created as a new land use type), not making possible the
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The use of the land for fruit production is not possible with animals grazing, but this was also the case before, as to the herder's opinion
Доступность и качество воды
качество оросительных вод
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to reduced stocking rates in comparison with village-pastures (and the soviet times), better water quality
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
состояние здоровья
возможности отдыха и рекреации
Livelihoods and human well-being
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Better control of runoff, but steeper land
водный дренаж
Почвы
почвенный покров
Количество до применения УЗП :
40%
Количество после применения УЗП:
80%
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Higher cover than on village-pastures
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
разнообразие флоры
Количество до применения УЗП :
36 species
Количество после применения УЗП:
47 species
Комментарий/ пояснения:
More plant systematical diversity
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
риск пожаров
Комментарий/ пояснения:
According to forest department the area above Karsang, due to ist trees, is more prone to fires than other areas
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | плохо |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | хорошо |
Пояснения:
A possible adaption to dryer conditions would be smaller herds.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
очень позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
4 Years ago a herd of 400 animals had to be sold due to disease. Since then M was able to rebuild a herd of 500 animals. On a short term investing into animals is expensive but pays quickly. The maintenance costs are finally decisive, but quite constant.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
- отдельные случаи/ эксперимент
Если возможно, дайте количественную характеристику (число домохозяйств и/или площадь применения):
1 Household
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 0-10%
Пояснения:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The herder gets paid by the villagers for taking care of their animals
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: According to the herder, young people do not (want to) bear the very physical work.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Grazing stabilises the soils and is thus a prevention against gully erosion in areas with low cover (former cropland). Animals have the same effect as the terraces built years ago. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing activity should continue, once M. is too old for working. |
| The animals provide for soil fertility by their dung, instead of the fertilisers used in Soviet times. This positively influences the share of palatable plants and cover in general and, by this, soil moisture. |
| The area on the forest department is a good alternative to the much too small pasture-area near the village |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Form of land use making it possible to take some pressure from the common pastures without great damages. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It needs to be assured that also poorer families, who depend even more on livestock breeding than richer ones, can give their animals to M. or other professional herders. This could be realised by engaging herder assistants from poor families |
|
The rotational scheme is much more elaborated than in the case of the villages' pastures, which can be explained by more land available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land users like M. should be addressed by forest administration to elaborate legal forms of herding with little damages on natural resources on this land. This will probably require land reforms. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Tree planting is not possible as long as the area is used for grazing. | By giving people land for longer periods (than one year) and with more freedoms in its use, people would gain interest in diversifying use: They would split up "their" land into haymaking, orchard and pasture areas. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| The main problem of this form of grazing is that it doesn't allow the regrowth of trees. | Changing the areas use for grazing, respectively haymaking, every few years. |
| Cover is markedly reduced around the places where tents are installed. | By changing the camping place (but: limited flat areas!) or not keeping the animals in the same place at noon time and during night time, these areas might recover. |
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Seminomadic individual herding [Таджикистан]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Составитель: Christian Wirz
Модули
Нет модулей