Daily and seasonal rotation on grassland [Tadjikistan]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : David Streiff
Dajmardei Kaspi (professional herder)
technologies_1407 - Tadjikistan
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuisseNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirghizistan1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Quand les données ont-elles été compilées (sur le terrain)?
15/08/2008
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
1.5 Référence au(x) questionnaire(s) sur les Approches de GDT
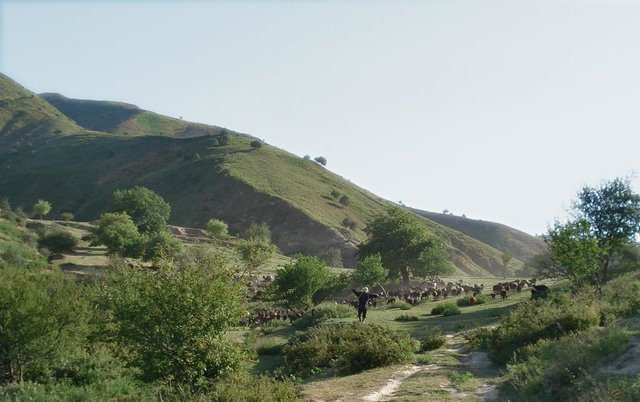

Seminomadic individual herding [Tadjikistan]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
Extensive grazing of sheep and goats by the means of a precise rotational scheme
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
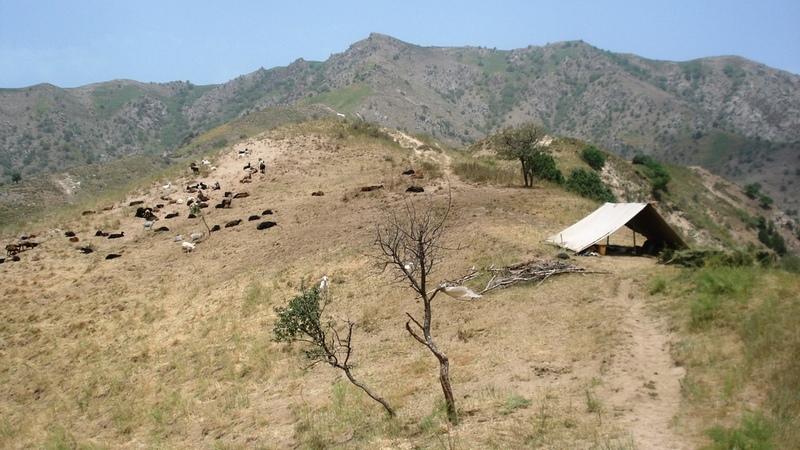
Half-year herding with 500 sheep, goats and cows (very few), with 7-8 different locations of the herder's tent. The herder visits each place twice to thrice per grazing season and stays in one place for one week to maximally one month (during the Ramadan period, due to limited forces). The area is grazed from the higher zone (around 2000m) to the lower zone (around 1600m) twice per season, in a sort of circle. Every day the herder starts in another direction from his tent and leads the animals to the pastures, once in the morning and once in the evening. He passes a stream once (autumn) to twice (summer) a day.
Purpose of the Technology: The grass should not get dusty and dirty, explaining why the herder daily changes the pastures, only revisiting the same places every two to three days.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: After accompanying his father as a child and a kind of an apprenticeship (of one year) later on, M. is considered by the villagers as a good herder and they give him their animals for herding. But M. applies for land on the forest department only after working as a guardian and as a tractor driver for 20 years. For the herding profession observing the animals precisely is necessary, in order not to lose any of them. And the maintenance of the pastures is guaranteed by the strict rotational scheme.
Natural / human environment: The pasture-area is in a generally well-conserved state. Moderate to high values of fractional vegetation cover can be observed and only few signs of recent erosion processes (through water) are visible. The area is characterised by steep slopes where still signs of past tree-planting during the USSR period are visible by some trees, many little platforms made for tree-planting and a few terraced areas. Eventhough, many trees have been grazed and do not stand anymore. Besides steep areas there are small, quite flat areas (where the herder installs his tents), that used to be cultivated (wheat) till 1966. These areas generally have low cover-values and signs of rill-erosion, which the herder attributes to the past tilling activity. However, it might also be the trampling and sitting of the animals (staying near the herder's tent at noon-time and during the night) causing this erosion. Nutrient management is provided for by the dung of the animals which is not collected, contrarily to the pastures near the villages.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tadjikistan
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Region of Republican Subordination
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Faizabad
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a plus de 50 ans (technologie traditionnelle)
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- dans le cadre d'un système traditionnel (> 50 ans)
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
There are traditional herding peoples like Kuagwates, Kaleks, Lakais, Duramanes, Kurtshaliks), not Tajiks. These often move around with their whole families.
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Pâturages
Pâturage extensif:
- Semi-nomadisme/ pastoralisme
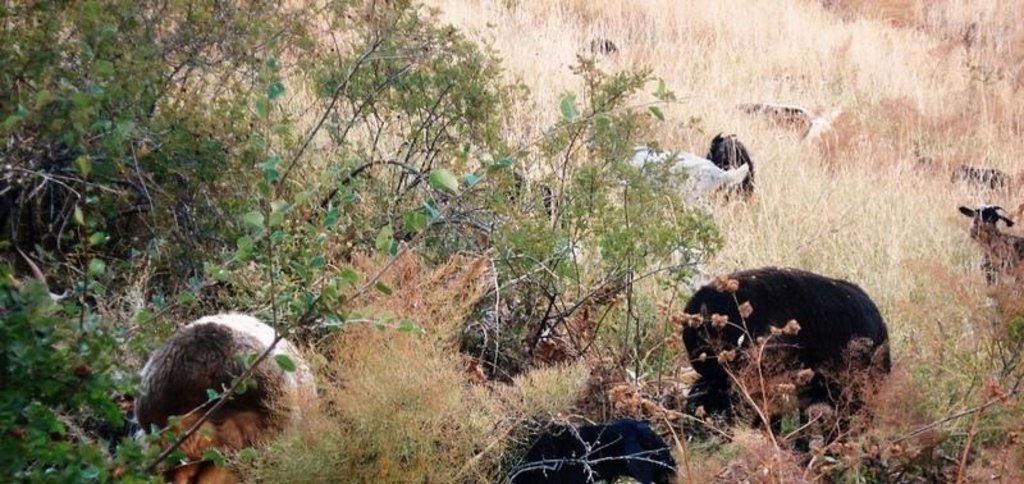
Principales espèces animales et principaux produits:
sheep* / goats* / cows
* if wildlife is major part of the grazing system
Commentaires:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The trampling of the animals near the tent, the feeding on young trees and the daily passage of the herd of a limited number of streams (eutrophication).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): No major land use problems due to good management. Only the first rain that cannot be absorbed by the dry soils is a problem.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: sheep* / goats* / cows
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
Si l'utilisation des terres a changé en raison de la mise en œuvre de la Technologie, indiquez l'utilisation des terres avant la mise en œuvre de la Technologie:
Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 Informations complémentaires sur l'utilisation des terres
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 1
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Jun
Densité d'élevage/ chargement (si pertinent):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Groupe de GDT auquel appartient la Technologie
- pastoralisme et gestion des pâturages
3.5 Diffusion de la Technologie
Commentaires:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3 km2.
The half of the herded area is rented by another person from the village, who gives his animals to the herder. Apart from the interviewed herder there are varying numbers of other semi-nomadic herders with similar management practices, some of them from other regions.
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

modes de gestion
- M1: Changement du type d’utilisation des terres
- M4: Changement majeur dans le calendrier des activités
Commentaires:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bs: baisse de la qualité et de la composition/ diversité des espèces
Commentaires:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Causing Pc, Bc, Wt), droughts (Causing Pk, Pc, Ha), degradation of near-village pastures (The pressure on more distant areas increases)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (passed tilling with impact on Wt), floods (Intensive rains causing Wt), land tenure (Little interest in tree-planting if land can only be rented annually)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
Commentaires:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
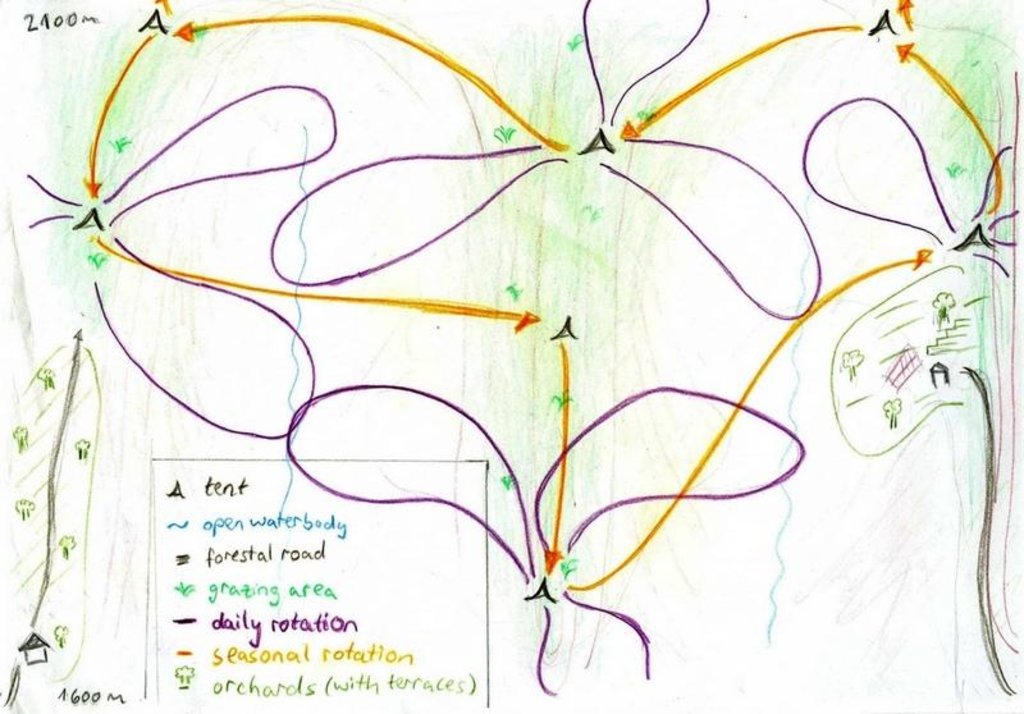
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
4.2 Spécification/ explications techniques du dessin technique
Daily and seasonal rotation.
Location: Above Karsang. Faizabad / Tajikistan
Date: 05.08.09
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (Obeying to what the herder says)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is necessary to know how to lead animals, more than in the case of the common pasture-area)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, control of fires, palatable fodder
Change of land use type: From afforestation and limited use as cropland to extensive grazing
Major change in timing of activities: Introduction of a strict rotational grazing scheme
4.3 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
Indiquez la monnaie utilisée pour le calcul des coûts:
- dollars US
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
6.10
4.4 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a herd | Modes de gestion | constantly investing |
4.5 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autre | Buying a herd | animals | 50,0 | 87,7 | 4385,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 4385,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Type de mesures | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rent fee for land of forest department | Modes de gestion | once per year |
| 2. | Salary of an assistant herder (normally, but not in 2008) | Modes de gestion | at the end of the season |
| 3. | compensation for dead animals | Modes de gestion | at the end of the season |
| 4. | Animal medecine | Modes de gestion | if necessary |
| 5. | Salt | Modes de gestion | daily |
4.7 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % des coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | Salary of an assistant herder | Days | 120,0 | 6,1 | 732,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Rent fee for land of forest department | 300ha/d | 180,0 | 0,4888888 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Compensation for dead animals | animals | 2,0 | 44,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Animal medecine | per year | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Autre | Salt | kg | 1000,0 | 0,08 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 1076,0 | |||||
Commentaires:
The costs are valid for a herd of 250 animals kept by the herder alone for six months and additional 250 animals kept during summer holidays with the help of additional workforce. The salary indicated was not valid for 2008 (the grandsons helped the herder), but for years when M. hires external workforce. For all costs, including 50 own animal, prices in 2008 are taken.
4.8 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Buying an own herd and looking for the animals are the most expensive factors, expecially if there are sick or dead animals.
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Spécifications/ commentaires sur les précipitations:
Mainly in spring and also in autumn, with a trend to decrease
Zone agro-climatique
- semi-aride
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la topographie:
Altitudinal zone: Pasture area around 1600 to 2000 m
Landforms ridges: Small, not so steep areas where the tent of the herder is installed
Landforms mountain slopes: The pasture area is generally very steep
Slopes on average steep (31-60%): The areas mostly frequented are steep
Slopes on average very steep (>60%): The areas dominating spatially are very steep
Slopes on average hilly (16-30%): Ridge areas
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- moyen (limoneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- faible (<1%)
Si disponible, joignez une description complète du sol ou précisez les informations disponibles, par ex., type de sol, pH/ acidité du sol, capacité d'échange cationique, azote, salinité, etc.
Soil depth on average shallow: Most grassy areas
Soil fertility is low: on the surface of 300 ha the summed up dung of 500 sheep and goats cannot compensate for the loss of topsoil by wind and water
Soil drainage / infiltration is good: Generally high infiltration capacity enhanced by high vegetation cover values
Soil water storage capacity medium (dominatig the area): Loamy soils and high cover values, but generally little trees and dried vegetation in August
Soil water storage capacity can also be good: Near the streams higher water retention, according to herder
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
faible/ absente
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
uniquement pour usage agricole (irrigation)
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la qualité et la quantité d'eau:
Water quality (untreated): Locals drink the water, but are affected by diarrhoea
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- élevé
Commentaires et précisions supplémentaires sur la biodiversité:
Diversity higher than near the villages, but not comparable with biodiversity hot-spots
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Sédentaire ou nomade:
- Semi-nomade
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- riche
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Herding is considered as a male profession, inherited from father to son. In nomadic peoples the whole families are mobile and women are responsible for domestic work.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are rich (100).
Off-farm income specification: The herder claims to nourish himself and his wife with the income from herding. But, once he willl not be able to work as a herder anymore, he might depend on off-farm income from his children (remittances)
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres détenues ou louées par les exploitants appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
Commentaires:
3 households can afford to pay the services of the professional herder (clearly a minority of village population)
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- état
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- loué
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production fourragère
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Higher vegetation cover and biomass values than for village-pastures
qualité des fourrages
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Much less impalatable species' frequency
production animale
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The animals get much fatter and are sold for around 50% higher price than animals from common pastures
production de bois
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The herder says that tree density has decreased, due to livestock but also to chopping. Additionally chopping of living trees is generally forbidden (since the 1960s, when the forest department was created as a new land use type), not making possible the
surface de production
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
The use of the land for fruit production is not possible with animals grazing, but this was also the case before, as to the herder's opinion
Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
qualité de l'eau d'irrigation
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Due to reduced stocking rates in comparison with village-pastures (and the soviet times), better water quality
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
situation sanitaire
possibilités de loisirs
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
ruissellement de surface
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Better control of runoff, but steeper land
drainage de l'excès d'eau
Sols
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
40%
Quantité après la GDT:
80%
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
Higher cover than on village-pastures
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
diversité végétale
Quantité avant la GDT:
36 species
Quantité après la GDT:
47 species
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
More plant systematical diversity
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
Commentaires/ spécifiez:
According to forest department the area above Karsang, due to ist trees, is more prone to fires than other areas
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | pas bien |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | bien |
Commentaires:
A possible adaption to dryer conditions would be smaller herds.
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
neutre / équilibrée
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
légèrement positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
positive
Commentaires:
4 Years ago a herd of 400 animals had to be sold due to disease. Since then M was able to rebuild a herd of 500 animals. On a short term investing into animals is expensive but pays quickly. The maintenance costs are finally decisive, but quite constant.
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
- cas isolés/ expérimentaux
Si disponible, quantifiez (nombre de ménages et/ou superficie couverte):
1 Household
Parmi tous ceux qui ont adopté la Technologie, combien d'entre eux l'ont fait spontanément, à savoir sans recevoir aucune incitation matérielle ou aucun paiement?
- 0-10%
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The herder gets paid by the villagers for taking care of their animals
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: According to the herder, young people do not (want to) bear the very physical work.
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Grazing stabilises the soils and is thus a prevention against gully erosion in areas with low cover (former cropland). Animals have the same effect as the terraces built years ago. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Grazing activity should continue, once M. is too old for working. |
| The animals provide for soil fertility by their dung, instead of the fertilisers used in Soviet times. This positively influences the share of palatable plants and cover in general and, by this, soil moisture. |
| The area on the forest department is a good alternative to the much too small pasture-area near the village |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
Form of land use making it possible to take some pressure from the common pastures without great damages. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It needs to be assured that also poorer families, who depend even more on livestock breeding than richer ones, can give their animals to M. or other professional herders. This could be realised by engaging herder assistants from poor families |
|
The rotational scheme is much more elaborated than in the case of the villages' pastures, which can be explained by more land available How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land users like M. should be addressed by forest administration to elaborate legal forms of herding with little damages on natural resources on this land. This will probably require land reforms. |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Tree planting is not possible as long as the area is used for grazing. | By giving people land for longer periods (than one year) and with more freedoms in its use, people would gain interest in diversifying use: They would split up "their" land into haymaking, orchard and pasture areas. |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| The main problem of this form of grazing is that it doesn't allow the regrowth of trees. | Changing the areas use for grazing, respectively haymaking, every few years. |
| Cover is markedly reduced around the places where tents are installed. | By changing the camping place (but: limited flat areas!) or not keeping the animals in the same place at noon time and during night time, these areas might recover. |
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens

Seminomadic individual herding [Tadjikistan]
Pasture management by a single herder, assisted either by an employee or by his own grandchildren, in collaboration with the habitants of the nearby village Karsang.
- Compilateur : Christian Wirz
Modules
Aucun module trouvé