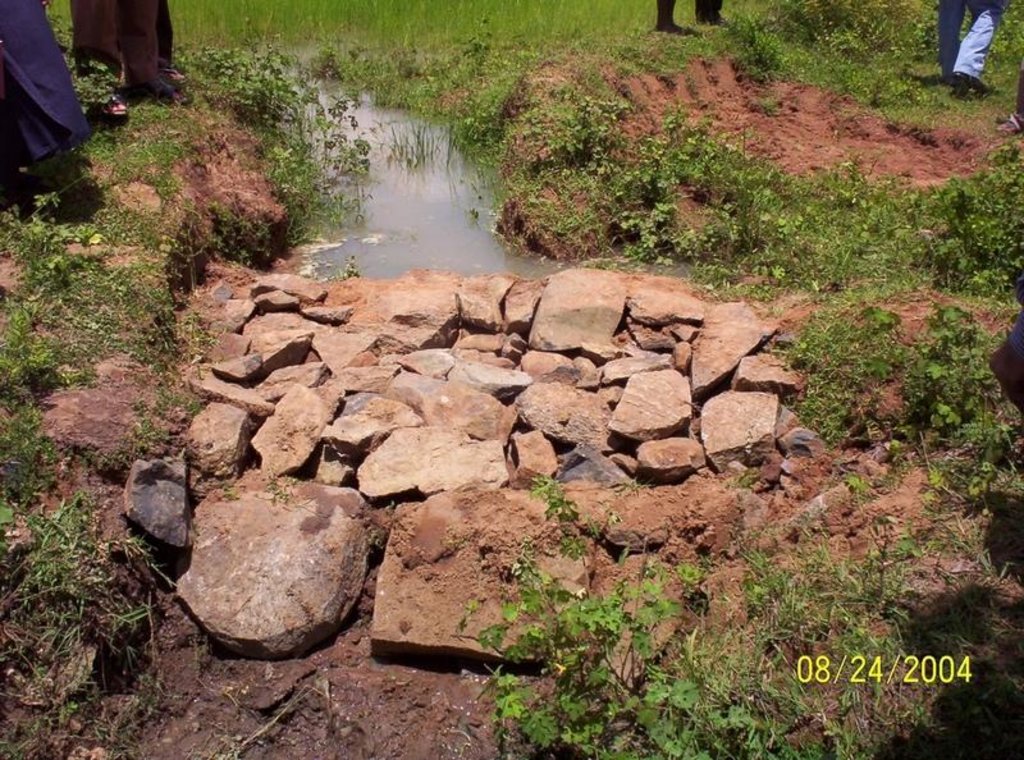
Dugout Sunken Pond with Catchment Treatment [Индия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Unknown User
- Редактор: –
- Рецензент: Fabian Ottiger
Bandha/ Pokhari (Oriya)
technologies_1475 - Индия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Ответственный (-ые) специалист (-ы)
Специалист по УЗП:
Patnaik Kishore Chandra
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Pradhan Gandhi
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Tripathy Dasarathi
MALKANGIRI (ORISSA) INDIA
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Panda R.K
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute
Semiliguda, Koraput, Orissa, India
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Mohanty K.C
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society
Malkangiri Orissa India
Индия
Специалист по УЗП:
Mishra BIJAYALAXMI
IDCWDP
Koraput
Индия
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Central Soil & Water Conservation Research & Training Institute - ИндияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Sahid Laxman Naik Development Society - ИндияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
IDCWDP (IDCWDP) - Индия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
20/08/2004
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (-ы) по Подходам УЗП
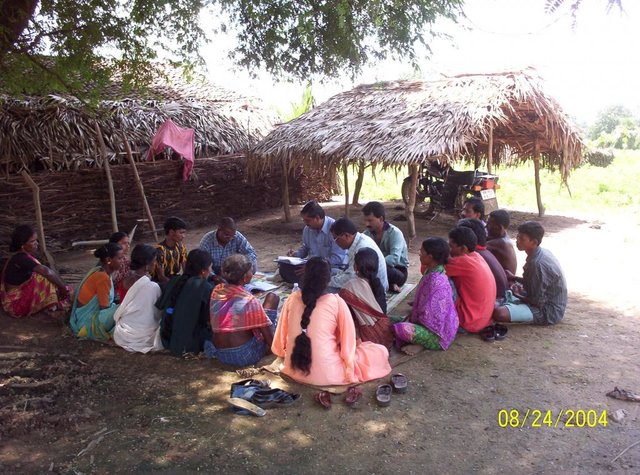

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Индия]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Составитель: Srikanta Kumar Parida
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
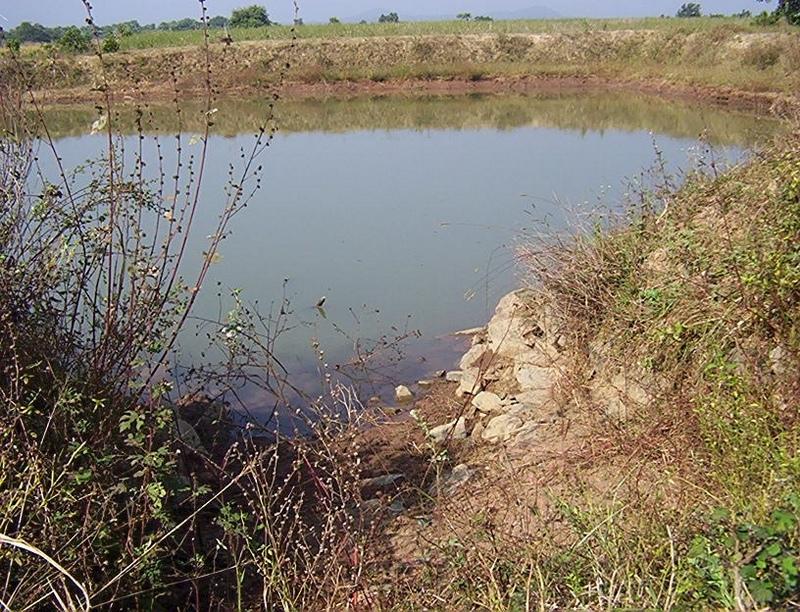
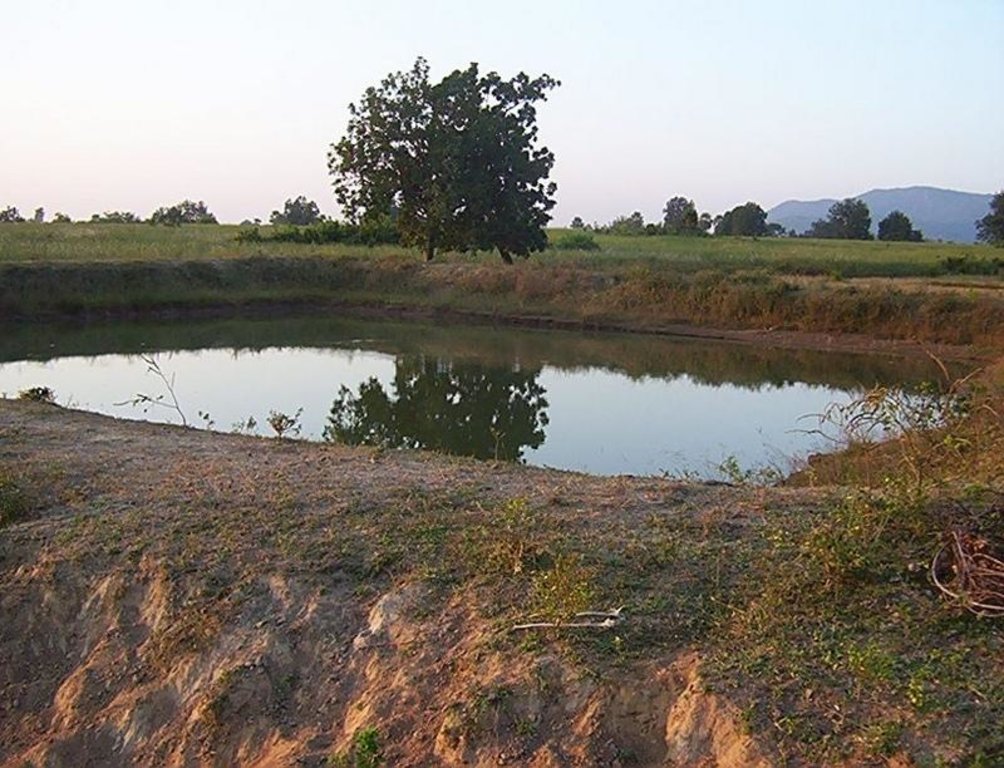
Dugout sunken pond with catchment treatment.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
(1) Total size of the project area = 4.75 Ha.
(2) Different structures taken up in the project area are
(i) Brushwood check dam- 6 Nos.
(ii) Drop structure- 8 Nos.
(iii) Dugout sunken pond - 1 No.
(3) All the above structures were positioned to ridge to valley treatment
(Ref.QT-6/2.1.2/a)
Purpose of the Technology: 1) Storage of runoff for cattle and human use.
2) Construction of structures to check soil erosion and sand casting.
3) Pisciculture.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment :-
1) SWC specialist selected sites for dugout sunken pond, layout the design.
2) SWC specialist also selected sites for drop structures, brushwood check
dams in gullied portion of project area with reference to vertical interval
of slope gradient and space between structures.
3) The execution of work were done by concerned villagers on payment basis.
4) During execution, 20% of the total cost of the dugout sunken pond was
contributed by the villagers in shape of labour.
5) Training on technical know how imparted to the villagrs during execution
of pond, bund, drop structure and brush wood check dam.
Maintenance:-
1) The dugout sunken pond requires (a) Desiltation once in two years (b)
Repair of earthern bund around inlet and outlet every year.
2) The drop structure & brushwood check dams requires little maintenance when
ever requires.
3) One management group has formed in the same village & funds has been
raised by doing pisciculture in the pond.
4) The management group is taking major reponsibility for its maintenance.
Natural / human environment: (1) Drainage line stablilized (2) Adjuscant area cultivated (3) Users group
formed and pisciculture taken up for the Ist time in the village.
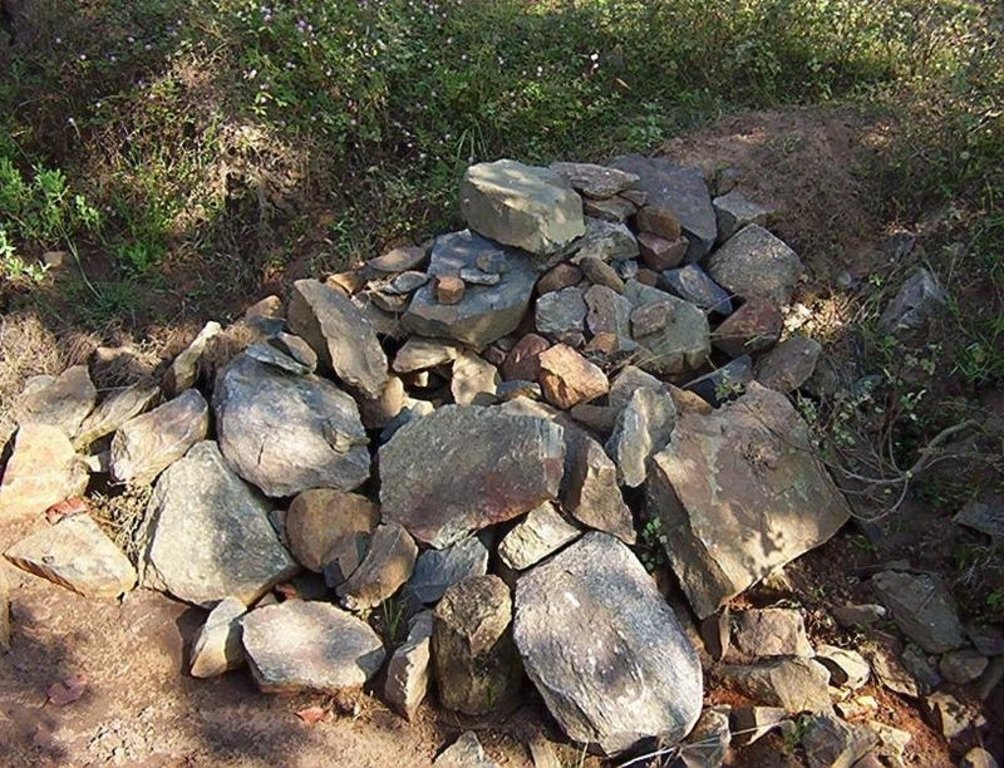
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Индия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Orissa
Более точная привязка места:
Orissa/ Malkangiri
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
National Watershed Development Project for Rainfed Area (NWDPRA)
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- повышение производства
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
Основные сельскохозяйственные культуры (товарные и продовольственные):
Major food crop: Paddy

Пастбищные угодья
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion):
1) A fellow, undulating, gullied piece of land.
2) Acute sand casting at the down stream cropland.
3) About 40% of the project area were practicing local paddy which suffers from erratic rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): A piece of land which depends upon the mercy of the Rain God for annual production.
3.3 Дополнительная информация о землепользовании
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
Число урожаев за год:
- 1
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jul - Nov
3.4 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- сбор атмосферных осадков
- Пчеловодство, аквакультура, птицеводство, разведение кроликов, разведение шелкопряда и т.д.
3.5 Распределение Технологии по площади
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если Технология равномерно применяется на той или иной территории, укажите ее приблизительную общую площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0475 km2.
A fellow, understanding, gullied piece ofland selected for the technology which suffers from sand casting and uncertainity of rain.
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Coordination of traditional method of agricultural practices like along the slope, use of long term local varieity of seeds etc.), poverty / wealth (lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Erosion problem), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge), Common social practices
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
4.2 Спецификация / пояснения к техническому рисунку
Aerial view of dugout sunken pond
Location: Siadimal, Korkonda. Malkangiri/Orissa/ India
Date: 15.3.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, water harvesting / increase water supply, Control of sand casting
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.45
Vegetative measure: In earthern bund slope
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): Compact
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3.7
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Vertivera and local grass slods
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/brushwood check dam
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.6
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Sediment/Sand/Trap/ drop structure
Vertical interval between structures (m): 9
Spacing between structures (m): 15
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.05
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 5.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Structural measure: Dam/Pan/Dugout sunken pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 28/26/24/22
Structural measure: Bund/Trapizoidal
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.85
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.50+8.9/2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 157
Construction material (earth): Soil excavated from pond is used to built bund around pond.
Construction material (stone): Inlet and outlet of pond and drop structure are made up of stone
Construction material (wood): Brush wood check dams are made up of wooden poles and bush wood.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 3%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:41
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Rupee
Укажите обменный курс между долларом США и местной валютой (если уместно): 1 доллар США =:
45,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
0.89
4.4 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection grass sods and vertivera slips | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Transporting grass sods on established banks | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Watering | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | When dry in Ist. Season |
| 4. | Dugout sunken pond-Surveying | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 5. | Dugout sunken pond- soil excavated from pondage area used in trapizodical bund around leaving inlet & outlet portion. | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 6. | Dugout sunken pond- Collection and transporting stone to inlet & outlet site | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 7. | Dugout sunken pond- construction of inlet & outlet with stone | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 8. | Dugout sunken pond- collection of local grass sods & vertiver slops | Инженерные | Onset of rain |
| 9. | Dugout sunken pond- turfing the bund slopes and planting of vertiver slips in rows at up stream and down steam side of inlet and outlet | Инженерные | On set of rain |
| 10. | Brushwood check dam- surveying | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 11. | Brushwood check dam- collection of wooden poles and brush wood | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 12. | Brushwood check dam- collection of picked up stones | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 13. | Brushwood check dam- fixing of wooden pole, weiving with brush wood, filling up the gaps with picked up stones | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 14. | Brushwood check dam- collection of vertiver slips and planting in upstream and downstream of each structure | Инженерные | On set of rain |
| 15. | Drop structure- surveying | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 16. | Drop structure- collection & transportation of stones to work spot | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 17. | Drop structure- construction of drop structure with stones | Инженерные | Summer season |
| 18. | Drop structure- collection of vertiver slips and planting at up stream and down stream of structure | Инженерные | On set of rain |
4.5 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 225,0 | 225,0 | 14,0 |
| Оборудование | Animal traction | ha | 1,0 | 49,0 | 49,0 | |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 4,0 | 4,0 | |
| Другие | Royalty charges for stones | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | |
| Другие | Fishery and feed | ha | 1,0 | 9,0 | 9,0 | |
| Другие | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 73,0 | 73,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 372,0 | |||||
4.6 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Тип мероприятия | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collecting vertiver slips & grass sods for gap filling | Мероприятия с использованием растительности | Onset of rain /annual |
| 2. | Collection of grass sods and gap fillling to bund layers | Инженерные | On set of rain/Annualy |
| 3. | Desiltation | Инженерные | Before on set of rain/Biannualy |
4.7 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 18,0 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Field bunding | ha | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Другие | Water way | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 21,0 | |||||
Пояснения:
The above calculation is based on the total establishment/ recurring cost both born by the project and land users is devided by the total project area i.e 4.75 ha. To get average hect. cost.
4.8 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Availability of stone affects the cost from implementing SWC
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Укажите среднегодовое количество осадков (если известно), мм:
1760,00
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
South Eastern Ghat Agro Climatic Zone
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (423 m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Plateau/plains (2-7% slope)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- плохой
- средний
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
70% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Land users from SWC technology area proctise contour plough, line sowing and using HYV paddy have increased their income significantly.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour and aniaml traction (bullock plough, both ranked 1)
Market orientation of production system: Pisciculture (Selling at village level)
5.7 Средний размер земельных участков, арендуемых или находящихся в собственности землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- общинная/ поселковая
Право землепользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
разнообразие продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Fish add to their income
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Closure of land by pondage area
Доступность и качество воды
доступность воды для скота
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Pisciculture support to live stock, dirnking water for cattle
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Management group formed and strengthened due to continurous income from pisciculture.
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Training conducted
Linkage with other institutions
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to different activities in the pond linkage to other institution has increased like Horticulture, Fishery etc.
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
поверхностный сток
Количество до применения УЗП :
90
Количество после применения УЗП:
40
водный дренаж
Почвы
влажность почв
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Due to water storage
утрата почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
87
Количество после применения УЗП:
45
Другие экологические последствия
Biodiversity
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
отложение наносов ниже по течению
Soil moisture regime
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
влияние незаметно
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Среди применяющих Технологию землепользователей, какова доля лиц, применяющих её по собственной инициативе, т.е. без какого-либо материального стимулирования со стороны?
- 90-100%
Пояснения:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
19 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If the community find the technology is low cost to teke up and gets eye catching benefits, then the treand of adoption is good.
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
|
Water problem for human and cattle solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular maintenance of pond needed |
|
Damage of crops reduced by construction of series of structures How can they be sustained / enhanced? More field bunding, vegetative cover should be imparted. |
|
Users group brings villagers closure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Manageent group to be reorganised annuly |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
|
Water scarcity of the area partly solved How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular desilting shound be done. |
|
Heavy sand casting and soil loss controled How can they be sustained / enhanced? More vegetative cover required for catchement area |
|
Crop production increased in the project area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Should be replicated by the people. |
|
Pisciculture added extra income to the villagers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Hybrid fingerlings to be adopted |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Sand casting could not be checked fully | By full vegetative cover and more structural measures it can be checked. |
| Sediment deposit in down stream area decreased | The loss can be over come by increasing crop yield. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.2 Ссылки на опубликованные материалы
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Watershed Survey Report
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
Director of Soil Conservation, Orissa, Bhubaneswar
Название, автор, год публикации, ISBN:
Plan and Estimate
Где опубликовано? Стоимость?
-do-
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

PARTICIPATORY APPROACH IN IDCWDP, DANIDA [Индия]
Participatory approach for holistic and intigrated development of the defined area on watershed basis involving all level of stake holders.
- Составитель: Srikanta Kumar Parida
Модули
Нет модулей