Earth checks for Gully reclamation [Эфиопия]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: Daniel Danano
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1069 - Эфиопия
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Estifanos Zena
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development
Эфиопия
Специалист по УЗП:
Desta Hiwot
Boditi, Department of Agriculture and Rural Development
Эфиопия
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ИталияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of Ethiopia (Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development) - Эфиопия1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
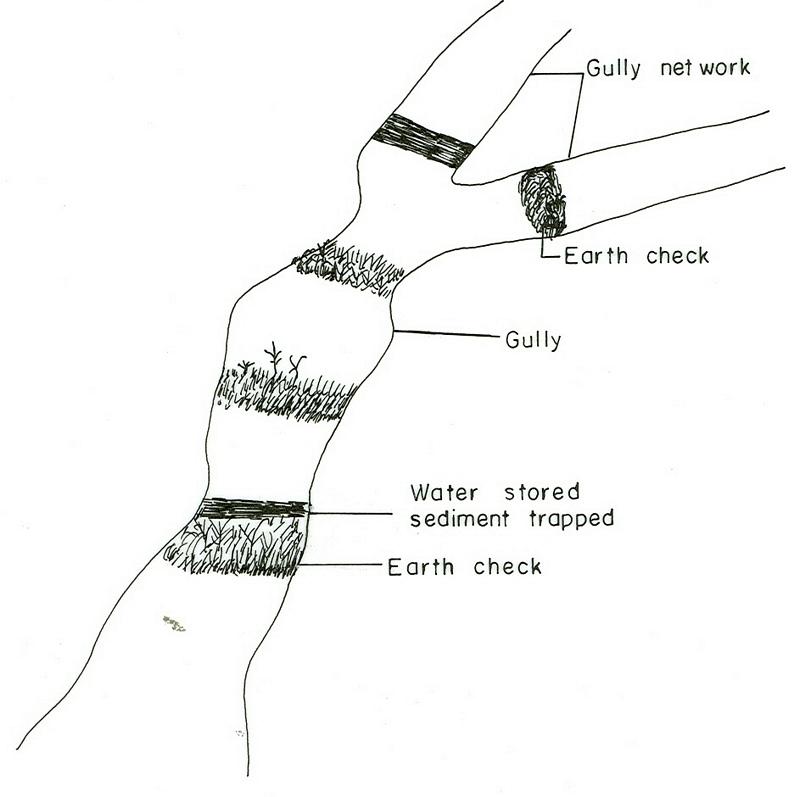
Earh-checks are constructed of earth embankment put across in a deep gully in such a way to trap sediment and store water passing by it.
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Active deep gullies are plugged by digging earth from the bottom as well as gully sides and embanked forming a barrier to runoff passing through it. The embankment is reinforced by planting useful plants such as banana, sesbania, gravillea, gesho, etc., The purpose is to rehabilitate gullies having depth and expand along sides and towards the head. By constructing earth checks the water is stored in the checks. The water percolates down the ground enriching the ground water. The soil is trapped in the checks and later brings up the gully gradient higher. As a result, a cultivable/cropable strip is formed. Weeding and cultivation done to plants established.The gully fence and breaks are repaired. The technology is seen to be suitable to humid highlands where land loss by gully is a serious problem and land under cultivation and grazing is getting here and there. In brief it is suitable in areas where land degradation problem is increasing with currently cultivated and grazed lands are encroched by gully expansion.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
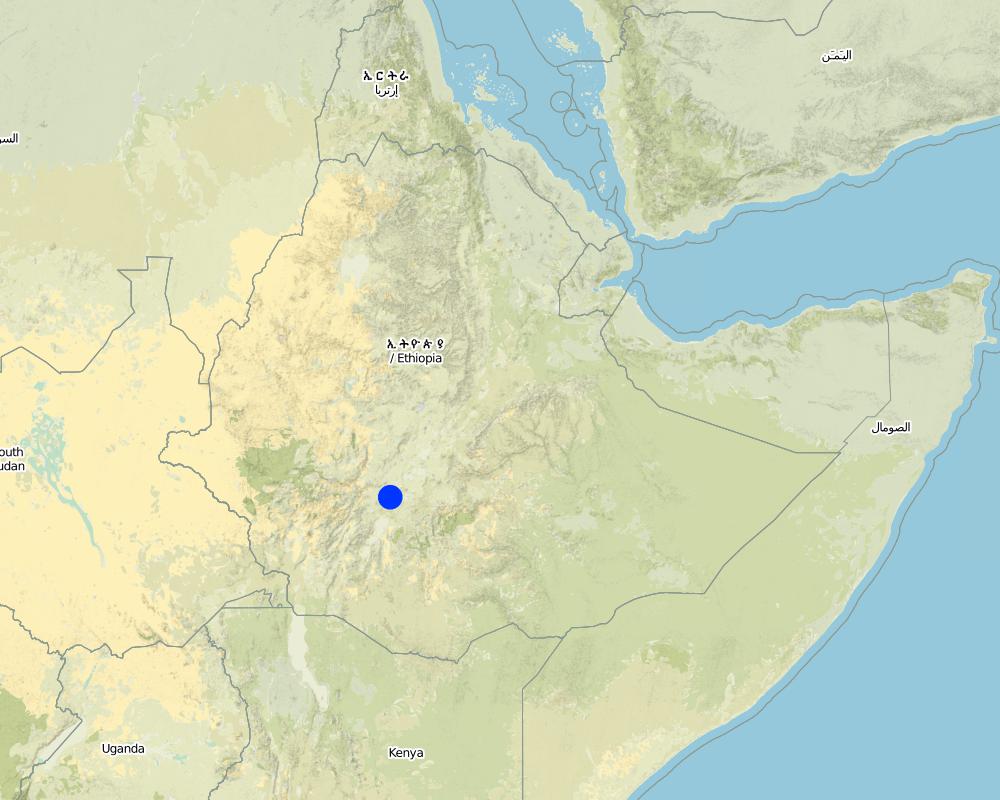
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Эфиопия
Административная единица (Район/Область):
SNNPR
Более точная привязка места:
SNNPR/Damot Galle/Bilate
Пояснения:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 51.2 km2.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The technology is introduced but highly modified by adjesting design, layout and by increasing use of locally available materials for construction.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Агро-лесо-пастбищное хозяйство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
- Однолетние культуры
- Многолетние (недревесные) культуры
- Древесные и кустарниковые культуры
Ежегодный урожай - Уточните культуры:
- зерновые культуры - кукуруза
- зерновые культуры - сорго
- корневые / клубнеплодные культуры - сладкий картофель, ямс, таро / кокоям, другие
- корневые / клубнеплодные культуры - маниока
- корневые / клубнеплодные культуры - картофель
Древесные и кустарниковые культуры - Уточните культуры:
- авокадо
- другие фрукты
- манго, мангостан, гуава
- папайя
- enset, taro, sugar cane, Leucaena, Sesbania, Grevillea
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 180 Second longest growing period from month to month: Aug - Jun
Применяются ли посевы в междурядьях?
Да
Если да, укажите, какие посевы применяются:
maize-sweet potato/haricot bean
Применяется ли севооборот?
Да
Если да, укажите:
maize-tarro-sorghum

Пастбищные угодья
Вид животных:
- крупный рогатый скот - молочный
- лошади
- donkeys, oxen

Леса/ лесистая местность
Продукции и услуги:
- Древесина
- Дрова
- Выпас/ ощипывание молодых побегов и листьев
Пояснения:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Monocropping, soil erosion, fertility mining, overgrazing, improper runoff management.
Grazingland comments: Livestock such as cows, oxen, donkeys and horse are thethered at a very small piece of land left infront of houses usually meant for social purposes. Some farmers thether their animals in a piece of land left uncropped in the field. The most part of livestock feed comes from crop residue which is collected from crop fields. Maize stalk, teff straw and enset leaves are fed stall.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, grazing / browsing
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize-sweet potato-Teff-potato-sorghum
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- мероприятия по влагозадержанию и снижению эрозии почв на склонах
- сбор атмосферных осадков
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭп: поверхностная эрозия/смыв верхних почвенных горизонтов
- ВЭл: овражная эрозия / оврагообразование

ухудшение химических свойств почв
- Хп: Снижение плодородия и уменьшение содержания органического вещества (вызванное не эрозией, а другими причинами)
Пояснения:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- предотвращение деградации земель
- снижение деградации земель
Пояснения:
Main goals: Also rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
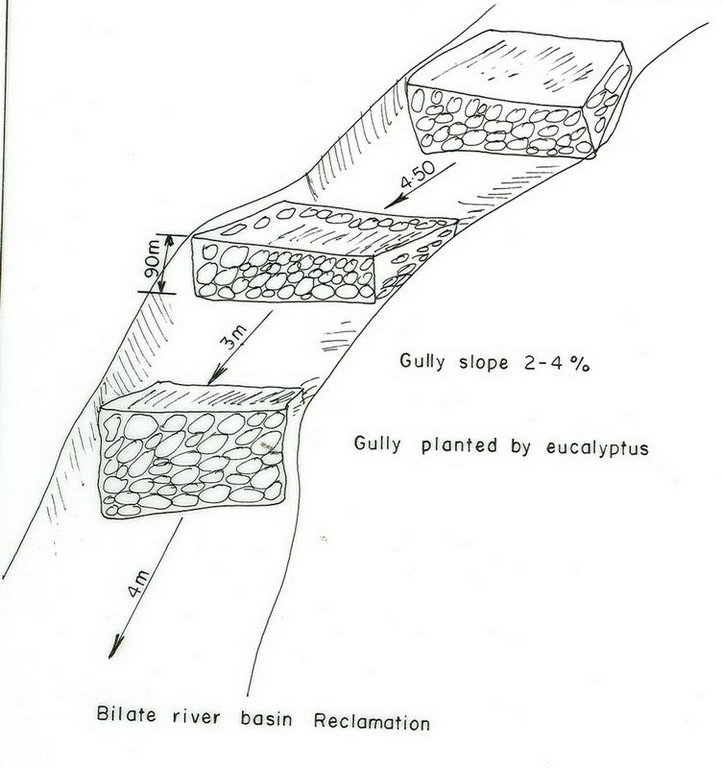
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
SNNPR
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Early planting
Material/ species: maize
Quantity/ density: 85000/ha
Remarks: sawn in lines
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: maize-sweet potato/haricot bean
Remarks: inter cropped & strip cropped
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: maize-taro-enset
Mulching
Material/ species: enset
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: maize, potato, sweet potato, traro
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Teff, maize, sorghum
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: maize-tarro-sorghum
Remarks: only rotations
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: primary and secondary oxen tillage
Contour tillage
Remarks: tillage done following contour
Agronomic measure: harrowing
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: O : other
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2-0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2-4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5-1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 4000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5x1.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2x2
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Trees/ shrubs species: Leucaena, Sesbania, Grevillea
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Mango, papaya, Avocado
Perennial crops species: Casava
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 8.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Terrace: backward sloping
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 12
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.9
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-75
Bund/ bank: level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.2
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Construction material (earth): Most of the structural measures are made by earth involving excavation and embankment.
Construction material (stone): Stone is mainly used for demonstration.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: The land after treatment is closed
Control / change of species composition: Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
Other type of management: change of management / intensity level - Grazing land changed to plantation and cropping
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Birr
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
8,5
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
0.60
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | September, october |
| 2. | Sugar cane planting | November |
| 3. | Sugar cane cultivation | January/August |
| 4. | Casava planting | April |
| 5. | Casava cultivation | June |
| 6. | Maize planting | January-1st plough, April 2nd plough |
| 7. | Maize cultivation | June |
| 8. | Sweet potato planting | September |
| 9. | Sweet potato cultivation | October |
| 10. | Fruite trees | June |
| 11. | Digging foundation | November-February |
| 12. | Forming embankment | November-February |
| 13. | Side wall shaping | November-February |
| 14. | Planting trees and shrubs | March-1st planting & June 2nd planting |
| 15. | Excluding animals by fencing and guarding | all year |
| 16. | Construct cutoff drain | dry season |
| 17. | Establish buffer zone between Area enclosure and crop land by strip of plantation | June/July |
| 18. | Construct earth checks and trenches in the gully | dry season |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 282,3 | 282,3 | 100,0 |
| Оборудование | Tools | ha | 1,0 | 270,6 | 270,6 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,6 | 117,6 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 670,5 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 78,88 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | september, october / 2 times |
| 2. | Sweet potato planting | September / each cropping season |
| 3. | Sweet potato cultivation | October / each cropping season |
| 4. | Maize planting | January/April / each cropping season |
| 5. | Maize cultivation | June / each cropping season |
| 6. | Teff sawing | |
| 7. | Teff weeding | |
| 8. | Prunning | october /once |
| 9. | Mulching | october /once |
| 10. | Thining | october /once |
| 11. | Fencing | any time /once |
| 12. | Weeding | June/each cropping season |
| 13. | Cultivation | March/each cropping season |
| 14. | Replanting | June/each cropping season |
| 15. | Repair in breaks | November-February/each cropping season |
| 16. | Fence | each cropping season |
| 17. | Repair breaks on cutoff drain and earth checks | dry season / 2 years |
| 18. | Prunning, weeding and cultivation | end of rains / each cropping season |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: spade, hoe
Length and width of structure
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
Factors affecting costs in this technology are the depth and width of gully, steepness of slope, planting and replanting of vegetative materials.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Slopes on average: Moderate (ranked 1, about 70%), gentle and rolling (both ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- средние фракции (суглинистый, супесчаный)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- среднее (1-3%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Deep (Soils are very deep (75%))
Soil texture: Medium (fertile loam soils)
Soil fertility is medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Medium (ranked 1, in the crop lands), low (ranked 2, degraded areas) and high (ranked 3, around the homestead)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1, on crop land) and high (ranked 2, on flat plateau land)
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- натуральное хозяйство (самообеспечение)
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- 10-50% всех доходов
Относительный уровень достатка:
- средний
Уровень механизации:
- ручной труд
- тягловая сила
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich.
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
40% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have SWC measures on their land produce more and hence have better financial income, which could allow them get involved in petty trade and other activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked 1, crop lands) and manual work ( ranked 2, homstead and gully lands)
Market orientation of cropland production system: subsistence (self-supply, maize) and mixed (subsistence/ commercial, sweet potato, teff, coffee)
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Пояснения:
Cropland: 0.5-1 ha (more than 80% of farmers) and 1-2 ha
grazing land: 0.5-1 ha (communal grazing lands are severly degraded)
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
производство кормов
качество кормов
площадь, используемая для производства продукции
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Shortage of grazing land: Animals are thethered in a small plots
Доходы и затраты
доходы хозяйства
Социальное и культурное воздействие
местное самоуправление
Комментарий/ пояснения:
teams are formed
институты госуправления
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
смягчение конфликтов
Комментарий/ пояснения:
many wants to be beneficiaries but only the poor given the opportunities
Экологическое воздействие
Почвы
влажность почв
почвенный покров
утрата почв
Другие экологические последствия
Biodiversity enhancement
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
подтопление ниже по течению
Комментарий/ пояснения:
all runoff retained
отложение наносов ниже по течению
Комментарий/ пояснения:
all soil trapped
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Пояснения:
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки
Нет ссылок
Модули
Нет модулей