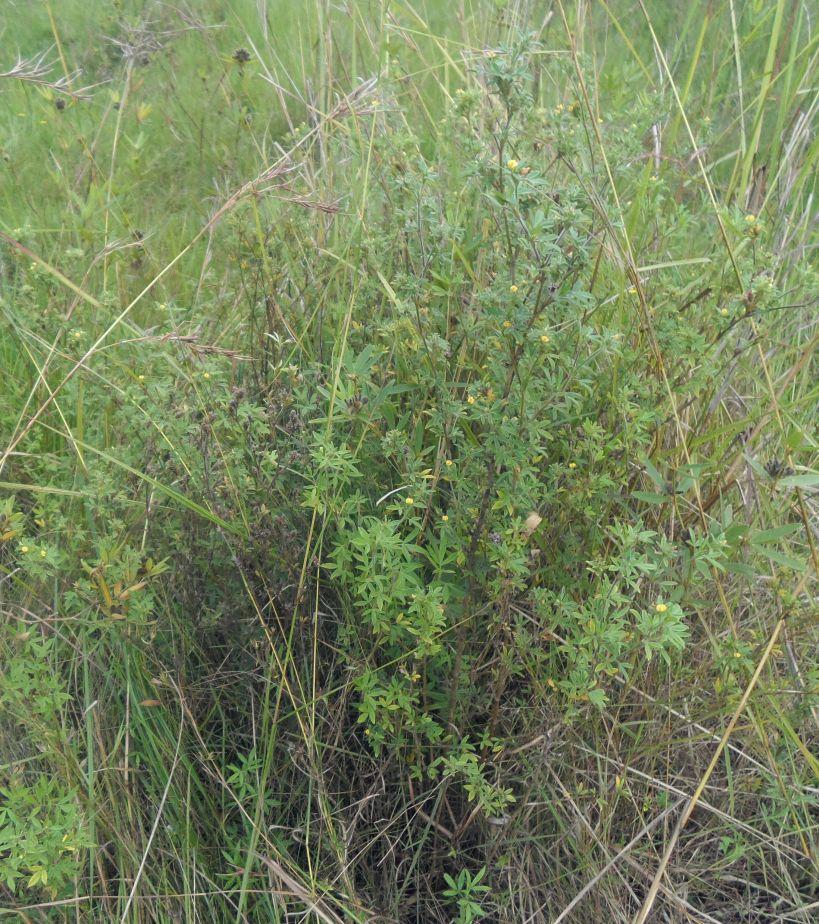
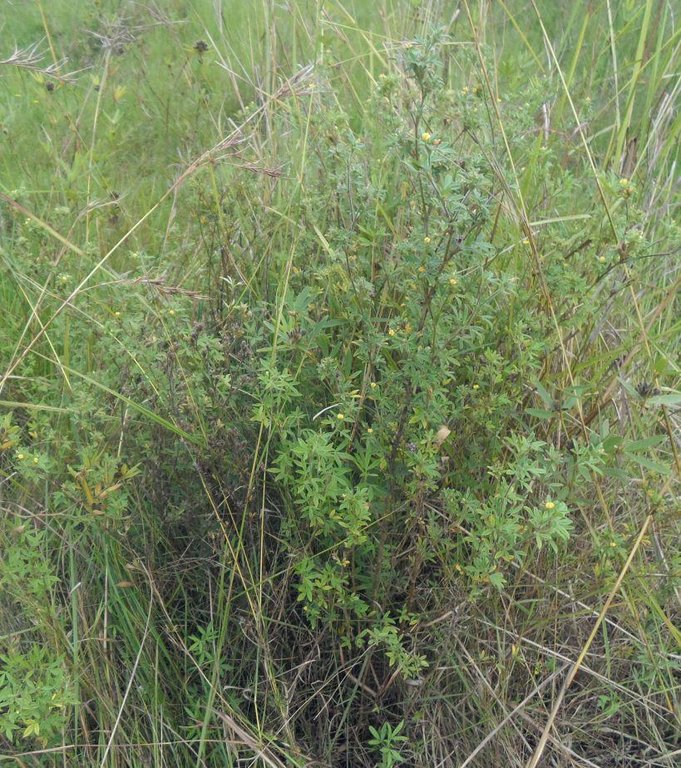
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [Танзания]
- Создание:
- Обновить:
- Составитель: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Редактор: –
- Рецензенты: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - Танзания
Просмотреть разделы
Развернуть все Свернуть все1. Общая информация
1.2 Контактные данные специалистов и организаций, участвующих в описании и оценке Технологии
Специалист по УЗП:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
Танзания
Название организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - ТанзанияНазвание организации (-ий), содействовавших документированию/оценке Технологии (если применимо)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Танзания1.3 Условия, регламентирующие использование данных, собранных ВОКАТ
Составитель и ответственный(-ые) специалист(-ы) согласны с условиями, регламентирующими использование собранных ВОКАТ данных:
Да
1.4 Декларация по устойчивости описываемой Технологии
Вызывает ли описанная здесь Технология проблемы деградации земель настолько, что ее нельзя назвать природосберегающей?
Нет
1.5 Ссылка на Анкету (ы) по Подходам УЗП (документируется с использованием ВОКАТ)
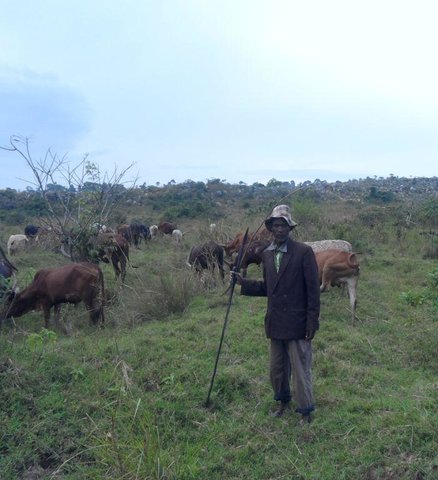

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Танзания]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Составитель: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. Описание Технологии УЗП
2.1 Краткое описание Технологии
Определение Технологии:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 Подробное описание Технологии
Описание:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 Фотографии, иллюстрирующие Технологию
2.5 Страна/ регион/ места, где применяется Технология, информация о которых собрана в данной Анкете
Страна:
Танзания
Административная единица (Район/Область):
Tanzania/Kagera
Более точная привязка места:
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
Охарактеризуйте пространственное распространение Технологии :
- равномерно-однородное применение на определенной площади
Если точная область неизвестна, укажите приблизительную площадь:
- < 0,1 км2 (10 га)
Пояснения:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
Map
×2.6 Сколько лет применяется данная Технология
Если год начала применения Технологии достоверно неизвестен, дайте примерную оценку:
- менее 10 лет назад (недавняя)
2.7 Внедрение Технологии
Укажите, как именно Технология УЗП была внедрена:
- как инновация (инициатива) землепользователей
- через проекты/ внешнее вмешательство
Пояснения (тип проекта и т.д.):
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. Классификация Технологии УЗП
3.1 Основные цели и задачи реализации Технологии
- снижение или предотвращение деградации земель, восстановление нарушенных земель
- сохранение экосистем
- сохранение/ повышение биоразнообразия
3.2 Текущий(-ие) тип(-ы) землепользования на территории, где применяется Технология
Комбинированное землепользование в пределах одной и той же земельной единицы:
Да
Укажите сочетания типов землепользования (посевы / пастбища / деревья):
- Лесо-пастбищное хозяйство

Пахотные угодья и плантации
Число урожаев за год:
- 2
Поясните:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

Пастбищные угодья
Экстенсивный выпас:
- Кочевое животноводство
- Полукочевое скотоводство
Интенсивный выпас/ выращивание кормов:
- Стойловое содержание/ нулевой выпас
Вид животных:
- козы
- овца

Леса/ лесистая местность
- Ficus thonigii
Пояснения:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.4 Водоснабжение
Обеспеченность водой участков, где реализуется Технология :
- богарные земли
3.5 Категория УЗП, к которой относится Технология
- прекращение хозяйственного использования (прекращение доступа к территории, поддержка восстановления)
3.6 Мероприятия УЗП, выполняемые в рамках Технологии

Мероприятия с использованием растительности
- Р2: Злаковые и многолетние травянистые растения

управленческие мероприятия
- У7: Другие
Пояснения:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Основные проблемы деградации земель, на решение которых направлена Технология

водная эрозия почв
- ВЭрб: эрозия речных берегов

ухудшение физических свойств почв
- Фу: уплотнение

биологическая деградация
- Бр: сокращение растительного покрова

деградация водных ресурсов
- Вуп: изменение объема поверхностного стока
Пояснения:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 Предотвращение и снижение деградации земель, или восстановление нарушенных земель
Укажите цель Технологии по отношению к деградации земель :
- снижение деградации земель
- восстановление/ реабилитация нарушенных земель
4. Технические характеристики, мероприятия по практической реализации, вложения и стоимость
4.1 Технический рисунок, иллюстрирующий Технологию
Спецификация (пояснения к техническому рисунку):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.2 Общая информация по необходимым вложениям и стоимости
другая/ национальная валюта (название):
Tanzanian shillings
Если это необходимо, укажите обменный курс от доллара США к местной валюте (например, 1 доллар США = 79,9 бразильского реала): 1 доллар США =:
1700,0
Укажите среднюю дневную заработную плату наемных работников:
1.12
4.3 Мероприятия, необходимые для начала реализации
| Деятельность | Время (сессия) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | once |
4.4 Вложения и затраты, необходимые для начала реализации
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Оплата труда | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Оплата труда | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | |
| Оборудование | Tools | Number | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Посадочный материал | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 235,29 | 235,29 | |
| Посадочный материал | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,65 | 117,65 | |
| Удобрения и ядохимикаты | Fertilizer | kg | 125,0 | 0,588 | 73,5 | |
| Другие | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость запуска Технологии | 651,9 | |||||
| Общие затраты на создание Технологии в долларах США | 0,38 | |||||
Пояснения:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 Поддержание/ текущее обслуживание
| Деятельность | Сроки/ повторяемость проведения | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Weekly |
4.6 Стоимость поддержания/ текущего обслуживания ( в год)
| Опишите затраты | Единица | Количество | Затраты на единицу | Общая стоимость на единицу | % затрат, оплаченных землепользователями | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Оплата труда | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,76466 | 26,47 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,53 | 52,95 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Оплата труда | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Общая стоимость поддержания Технологии | 432,36 | |||||
| Общие затраты на поддержание Технологии в долларах США | 0,25 | |||||
Пояснения:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.7 Наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат
Опишите наиболее значимые факторы, влияющие на стоимость затрат:
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. Природные и социально-экономические условия
5.1 Климат
Среднегодовое количество осадков
- < 250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1000 мм
- 1001-1500 мм
- 1501-2000 мм
- 2001-3000 мм
- 3001-4000 мм
- > 4000 мм
Пояснения/ комментарии по осадкам:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
Агроклиматическая зона
- Умеренно-влажная
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 Рельеф
Склоны (преобладающие):
- пологие (0-2%)
- покатые (3-5%)
- покато-крутые (6-10%)
- крутые (11-15%)
- очень крутые (16-30%)
- чрезвычайно крутые (31-60%)
- обрывистые (>60%)
Формы рельефа:
- плато/ равнины
- гребни хребтов/холмов
- склоны гор
- склоны холмов
- подножья
- днища долин
Зона высотной поясности:
- 0-100 м над уровнем моря
- 101-500 м н.у.м.
- 501-1000 м н.у.м.
- 1001-1500 м н.у.м.
- 1501-2000 м н.у.м.
- 2001-2500 м н.у.м.
- 2501-3000 м н.у.м.
- 3001-4000 м н.у.м.
- > 4 тыс. м н.у.м.
Комментарии и дополнительные сведения по условиям рельефа/ топографии :
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 Почвы
Средняя мощность почв:
- поверхностные (0-20 см)
- неглубокие (21-50 см)
- умеренно глубокие (51-80 см)
- глубокие (81-120 см)
- очень глубокие (> 120 см)
Гранулометрический состав (верхнего горизонта):
- грубый крупнозернистый/ лёгкий (песчаный)
- тонкодисперсный/ тяжёлый (глинистый)
Содержание органического вещества в верхнем горизонте:
- низкое (< 1%)
Если возможно, приложите полное описание почв или укажите доступную информацию, например тип почв, рH/ кислотность почв, ёмкость катионного обмена, содержание азота, содержание солей и т.д.
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 Доступность и качество воды
Уровень грунтовых вод:
на поверхности
Доступность поверхностных вод:
средняя
Качество воды (без обработки):
питьевая вода плохого качества (необходима обработка)
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по качеству и количеству воды:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 Биоразнообразие
Видовое разнообразие:
- низкое
Комментарии и дополнительная информация по биоразнообразию:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 Характеристика землепользователей, применяющих Технологию
Рыночная ориентация производства:
- смешанный (натуральный / коммерческий)
Доходы из других источников:
- < 10% всех доходов
Индивидуальное или коллективное хозяйство:
- частное/ домовладение
Пол:
- женщины
- мужчины
Укажите другие важные характеристики землепользователей:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 Средняя площадь земель, используемых землепользователями с применением Технологии
- < 0,5 га
- 0,5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1000 га
- 1000-10000 га
- > 10000 га
Считается ли это мелким, средним или крупным хозяйством (по местным масштабам)?
- мелкое
Пояснения:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 Собственность на землю, права на земле- и водопользование
Землевладелец:
- индивидуальная, не оформленная в собственность
Право землепользования:
- индивидуальное
Право водопользования:
- неограниченное (неконтролируемое)
Пояснения:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 Доступ к базовым услугам и инфраструктуре
медицинское обслуживание:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
образование:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
технические консультации:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
занятость (вне хозяйства):
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
рынки:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
транспорт и дорожная сеть:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
водоснабжение и канализация:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
финансовые услуги:
- плохой
- средний
- хорошая
6. Воздействия и заключительные положения
6.1 Влияние Технологии УЗП в пределах территории ее применения
Социально-экономическое воздействие
Продуктивность
производство сельскозяйственных культур
Количество до применения УЗП :
5.0 ton/ha
Количество после применения УЗП:
6-7.0 ton/ha
Комментарий/ пояснения:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
производство кормов
Количество до применения УЗП :
2 acres/annum
Количество после применения УЗП:
10 acre/annum
Комментарий/ пояснения:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
качество кормов
Количество до применения УЗП :
3
Количество после применения УЗП:
8
Комментарий/ пояснения:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
производство продуктов животноводства
Количество до применения УЗП :
1200litres/cow/yeer
Количество после применения УЗП:
2000litres/cow/year
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
Доходы и затраты
сельскохозяйственные издержки
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
разнообразие источников дохода
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
Социальное и культурное воздействие
продовольственная безопасность/ самообеспечение
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
местное самоуправление
Количество до применения УЗП :
weak
Количество после применения УЗП:
strong
Комментарий/ пояснения:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
знания в области УЗП/ деградации земель
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
смягчение конфликтов
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Комментарий/ пояснения:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
Экологическое воздействие
Водный цикл/ поверхностный сток
количество воды
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
поверхностный сток
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Resultant of vergetation cover
испарение
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
Почвы
почвенный покров
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Improved vegetation cover
утрата почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
образование корки на поверхности почв/ запечатывание
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
уплотнение почв
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
Биоразнообразие: растительность, животный мир
биомасса/ содержание углерода в надземной биомассе
Количество до применения УЗП :
low
Количество после применения УЗП:
high
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Controlled fire burning
Климат и снижение риска стихийных бедствий
выбросы углекислого газа и парниковых газов
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Controled bush fire
риск пожаров
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 Влияние Технологии за пределами территории ее применения
отложение наносов ниже по течению
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
загрязнение подземных/ речных вод
Количество до применения УЗП :
high
Количество после применения УЗП:
low
Комментарий/ пояснения:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 Подверженность и чувствительность Технологии УЗП к постепенным изменениям климата и экстремальным погодным явлениям/ стихийным бедствиям, связанным с изменением климата (в понимании землепользователей)
Постепенное изменение климата
Постепенное изменение климата
| Сезон | увеличение или уменьшение | Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| среднегодовые температуры | увеличилось | хорошо |
Экстремальные явления, связанные с изменением климата (стихийные бедствия)
Погодные стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| местные ливневые дожди | не известно |
| местные ураганы | не известно |
Стихийные бедствия климатического характера
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| засухи | плохо |
Гидрологические стихийные бедствия
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| регулярные наводнения (выход рек из берегов) | не известно |
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
Другие воздействия, связанные с изменением климата
| Насколько успешно Технология справляется с этим? | |
|---|---|
| сокращение вегетационного периода | плохо |
Пояснения:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 Анализ эффективности затрат
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с первоначальными вложениями (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Насколько получаемый результат сопоставим с текущими расходами по поддержанию технологии (с точки зрения землепользователей)?
Эффективность затрат в краткосрочной перспективе:
слабо позитивное
Эффективность затрат в долгосрочной перспективе:
позитивное
Пояснения:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 Внедрение Технологии
Пояснения:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности Технологии
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению землепользователей |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| Сильные стороны/ преимущества/ возможности по мнению составителя или других ключевых специалистов |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски Технологии и пути их преодоления
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению землепользователей | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| Слабые стороны/ недостатки/ риски по мнению составителя или ответственных специалистов | Возможные пути их преодоления/снижения? |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. Справочные материалы и ссылки
7.1 Методы сбора/ источники информации
- выезды на места, полевые обследования
- опросы землепользователей
Когда были собраны данные (на местах)?
03/06/2014
Ссылки и модули
Развернуть все Свернуть всеСсылки

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Танзания]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Составитель: ALLAN BUBELWA
Модули
Нет модулей