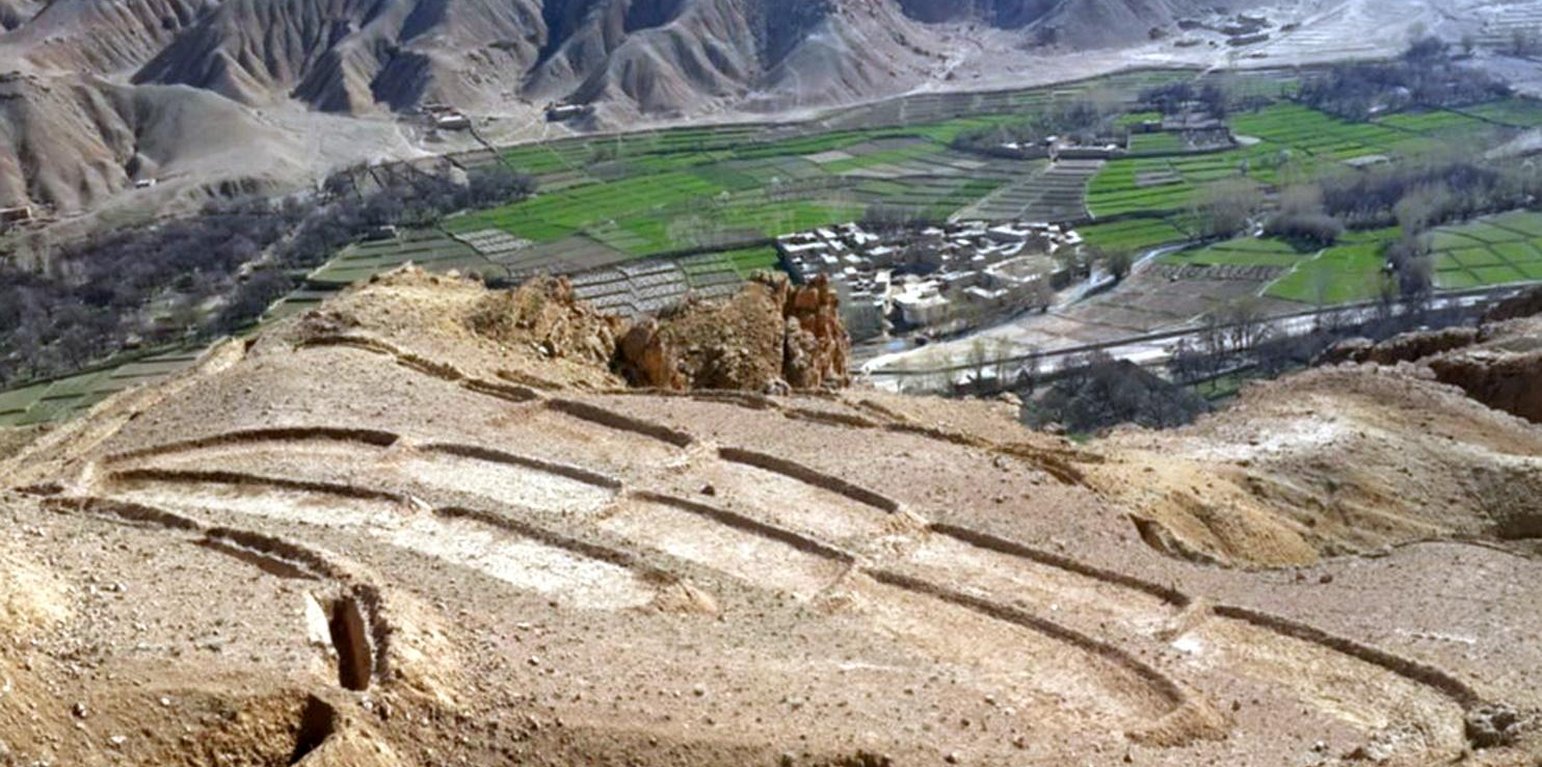




The terracing in watershed fact-sheet is documented by Sustainable Land Management Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation which is funded by Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC).
Due to the enduring conflict and to the breakdown of common-pool resources management in upper catchments areas over the past decades, most pastures in Afghanistan are degraded.
Uncontrolled grazing of animals tilling grazing land to grow cereal crops are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in the upper catchments. One of the negative consequences is repeated flash floods each year causing loss and damage of agriculture lands, gardens, road, canal, infrastructure, houses and even lives. To decrease the severity of flash floods and extend vegetation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation in Saighan district has established watershed activities.
Purpose of the Technology: Terrace construction was identified as an effective measure in degraded watershed areas to:
•control runoff and decrease flash flood;
•increase water infiltration;
•create the opportunity for income from cultivation of valuable crops in the terraces.
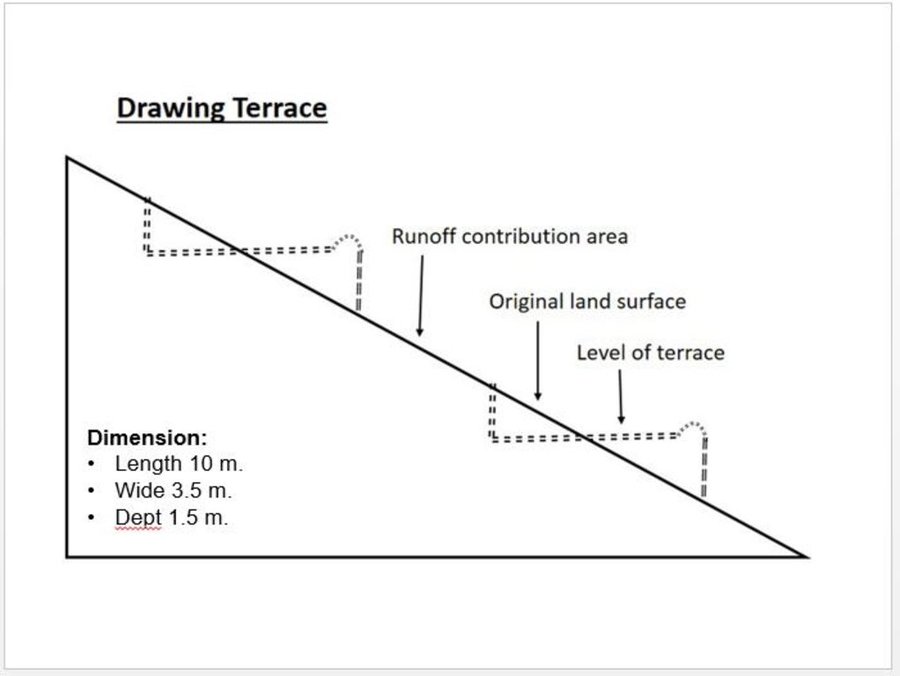
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Having selected the watersheds and established watershed committees, watershed master plans were prepared and various structural and agronomical measures identified and estimated for each unit of land. Community laborers, trained by HELVETAS technical staff, constructed the terraces under supervision of watershed committee members. 600 terraces, each measuring 10 m x 3.6 m were constructed on seven hectares of land. To ensure maintenance, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation facilitated the creation of community saving systems and invested 10% of the project budget for maintenance of each watershed. It improved the capacity of watershed members, so after ending project support the community watershed committee would be able to manage maintenance of watershed measures.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan province is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The soil texture is clay, sandy loam and clay loam with moderate type of soil fertility, naked area of upper catchments causes that most of Saighan villages face to water scarcity during May to September and can’t grow valuable crops.The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple crops (wheat) and fodder crops.Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity during May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
The average annual income from one hectare in the area of having enough irrigation water is 250000 AFN (3676 USD) and in the area which has no enough irrigation water is 67500 AFN (992 USD).
สถานที่: Saighan, Bamyan, อัฟกานิสถาน
ตำนวนการวิเคราะห์เทคโนโลยี:
การเผยแพร่ของเทคโนโลยี: กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่ (approx. 1-10 ตร.กม.)
In a permanently protected area?:
วันที่ในการดำเนินการ: น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
ประเภทของการแนะนำ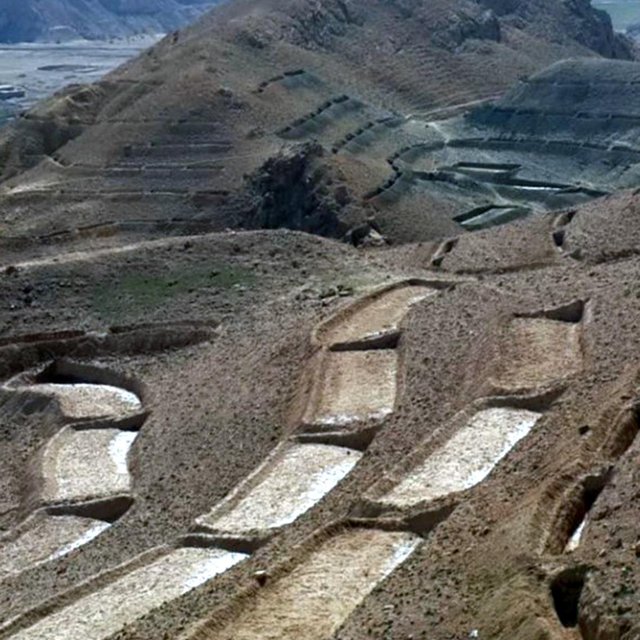




| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Labor cost for the construction of the terraces | persons/day | 1200.0 | 5.88 | 7056.0 | 10.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 7'056.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 7'056.0 | ||||
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย (USD) | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า (USD) | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
| แรงงาน | |||||
| Repairing of few terraces | persons/day | 6.0 | 5.833333 | 35.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 35.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 35.0 | ||||
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 60
หลังจาก SLM: 80
Technology reduce flood and lower lands doesnt effect by floods
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 20
หลังจาก SLM: 25
Increasing under ground water by applying technology
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 0
หลังจาก SLM: 50
Cultivation of cash crop in the terraces (farm income from uplands)
The technology has effective role on reducing flash flood and as well through cultivation of valuable crops the community get more income from watershed area
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 0
หลังจาก SLM: 100
Leveled terraces infilter the water
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 0
หลังจาก SLM: 50
Technology let the water infilteration more
จำนวนก่อน SLM: 0
หลังจาก SLM: 50
Control runoff